Spotify today is expanding its investment in personalization features with the launch of a dedicated in-app experience called Only You, which focuses on your favorite music and how you listen. The experience is similar to Spotify’s popular annual review, Spotify Wrapped, as it highlights the artists, songs, genres and other aspects of your music listening experience that are important to you, which can then be shared across social media, just as Wrapped is. The company is also today debuting Blend, a new way to create a personalized playlist with a friend.
The Only You hub will live alongside the existing Made for You hub on the Search page inside the Spotify app. In Made for You, you’ll find your other personalized playlists like Discover Weekly, Release Radar, Daily Mixes and others, like Your Time Capsule or Summer Rewind, for example, as well as the more recently added trio of playlist sets, Spotify Mixes.
From now through the end of the month, Only You will be a separate hub in the Spotify app, but it will ultimately be relocated to live inside the Made for You hub.
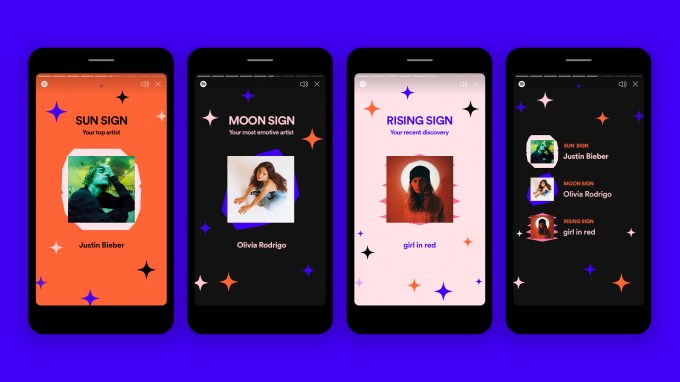
Image Credits: Spotify
The new Only You experience, meanwhile, will help you discover new trends beyond what you might see in your personalized playlists. This includes “Your Audio Birth Chart,” where the sun is the top artist you listened to over the last six months, rising is your most recent discovery and the moon is an artist you listen to that shows your emotional side; “Your Dream Dinner Party,” where you pick three favorite artists for a custom, frequently updated Spotify Mix featuring favorite songs and fresh picks; and “Your Artist Pairs,” which features unique pairings you’ve listened to recently, like those spanning genres.
It also will contain other personalized insights like the different time periods of music you’ve enjoyed, the music or podcasts you listen to at what time of day and your favorite music genres and podcast topics.
For example, your “Song Year” will show how you’ve traveled through different periods of time, based on the tracks you listened to throughout the year. The first year that will pop up here is the year you’ve streamed the most, while the second year that appears will represent the earlier release year that you’ve listened to. The third year is the most recent song year that’s been streamed.
To gather all this data, Only You looks at your Spotify in-app listening experience over the last six months (December 2020 – May 2021). Users must have streamed 30 tracks across five different artists over the past six months in order to be eligible for the new experience. Spotify says the data isn’t being used for ad targeting purposes. (And despite astrology’s connection to birth months and years, the “Your Audio Birth Chart” isn’t asking for users’ birth year to create this experience.)
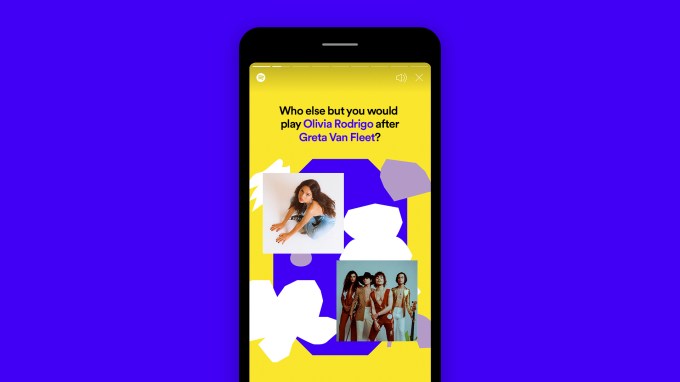
Image Credits: Spotify
Another key part of the Only You campaign is the launch of Blend, currently in beta.
This feature will sit on the “Made for Two” shelf within the Only You hub, allowing you to invite any other Spotify user to create a playlist with you. Using similar mixing technology that powers Spotify’s Family Mix and Duo Mix in their respective plans, Blend lets you invite any other Spotify user (free user or paid subscriber) to merge their musical tastes with yours to create a curated playlist featuring songs you both like.
This playlist is updated daily and will grow with users over time as their listening habits change, Spotify says.
Because it works with free accounts, Blend could encourage more users to try Spotify so they can create a playlist with a significant other, best friend, family member or others, even if they’re not on a shared plan.
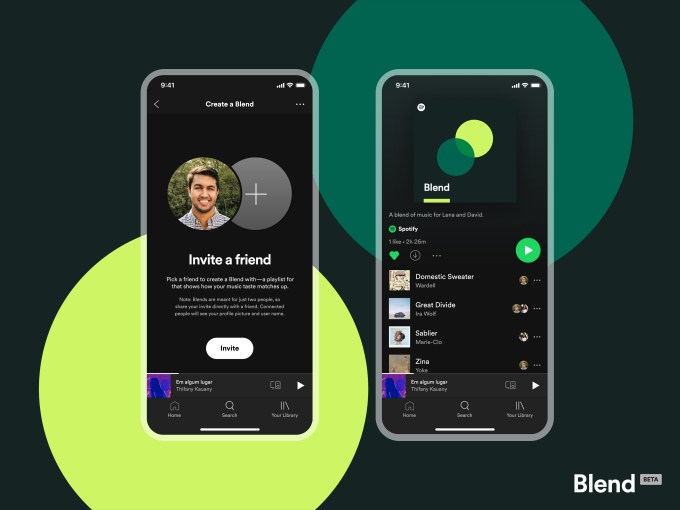
Image Credits: Spotify
Both the Only You experience and Blend build on technology Spotify had already developed to power other features, like Wrapped and various multi-user blended mixes, rather than creating something entirely new. But the bigger message Spotify wants to convey here is that it’s far ahead of competitors when it comes to personalization features. Even if rivals are duping its playlists, it wants to be the forerunner when it comes to personalized music.
Of course, that’s not always the case. The newer Spotify Mixes, for instance, were a lot like a feature Pandora had launched years prior, which created custom playlists across a number of attributes, including genre and mood. But where Spotify succeeds is its continual release of new personalization features, as it works to make its app customized to the end user. By doing so, the switching costs increase — that is, users will find it harder to jump to rival services due to how many custom playlists they may have on hand.
Spotify will begin heavily marketing the launch of Only You with a number of top artists by creating sets of stats for various fandoms, including those for Harry Styles, Selena Gomez, Lil Nas X, Doja Cat, Justin Bieber, SZA and others. The campaign will run through June 30.
Powered by WPeMatico


