With 17 startups participating, Berkeley SkyDeck’s Demo Day isn’t the largest cohort we’ve seen by any stretch. The collection of companies is, however, defined by a wide range of focuses, from pioneering diabetes treatments to retrofitting autonomous trucking, curated by the SkyDeck’s small team and a number of advisors.
Founded in 2012, the accelerator is focused on developing early-stage companies tied to the University of California system. Applicants must be affiliated with either one of the 10 UC schools or their national laboratories in Berkeley, Livermore and Los Alamos. Notable alumni include micromobility unicorn, Lime, and delivery robotics firm, Kiwi.
In 2020, SkyDeck — along with much of the rest of the world — went virtual.
“While flight restrictions did cause some international founders to pull crazy hours from our home countries to participate in the sessions, virtual sessions allowed additional members of our teams to participate that would otherwise not have been able to do so,” the accelerator’s organizers said in a TechCrunch post last year. “We are also hearing chatter that Demo Day will be larger than ever before because virtual events are much more scalable.”
The 17 startups presenting today were whittled down from 1,850 applicants, according to the accelerator. Being a member of the cohort involves six months of launch assistance from SkyDeck, coupled with up $105,000. “In six months, you’re going to pitch on stage at demo day, to an institutional investor in your industry,” Executive Director Caroline Winnett tells TechCrunch.
Here’s a closer look at six highlights from this Demo Day.
EndoCrine
Image Credits: EndoCrine Bio, Inc.
Building on technologies developed in the stem cell research labs of UCSF, EndoCrine is looking to commercialize a better way to discover and develop drugs. Specifically, the startup is hoping to improve diabetes treatment beyond standard insulin injections.
“EndoCrine’s proprietary human stem cell-derived islet platform revolutionizes the drug discovery and development process, saving years of time and millions of dollars usually spent by pharma companies,” CEO Gopika Nair said in a statement offered to TechCrunch. “Our innovative solution opens an exciting era of personalized medicine in diabetes.”
The company says SkyDeck helped it take the earliest steps out of the lab and into startup mode.
NuPort Robotics

Image Credits: NuPort Robotics Inc.
NuPort Robotics is among the most mature of the 17 startups included here. In fact, in mid-March, the startup signed a partnership with Canadian Tire and the Ontario government, as part of a $3 million investment in an autonomous middle-mile trucking solution.
Rather than building autonomous trucking from scratch, NuPort’s solution is designed to retrofit semis with autonomous technologies.
“This results in operational cost reduction by eliminating the need to replace their existing fleet and yields a safer, more efficient and sustainable transportation system,” CEO Raghavender Sahdev tells TechCrunch.
The Hurd Co.
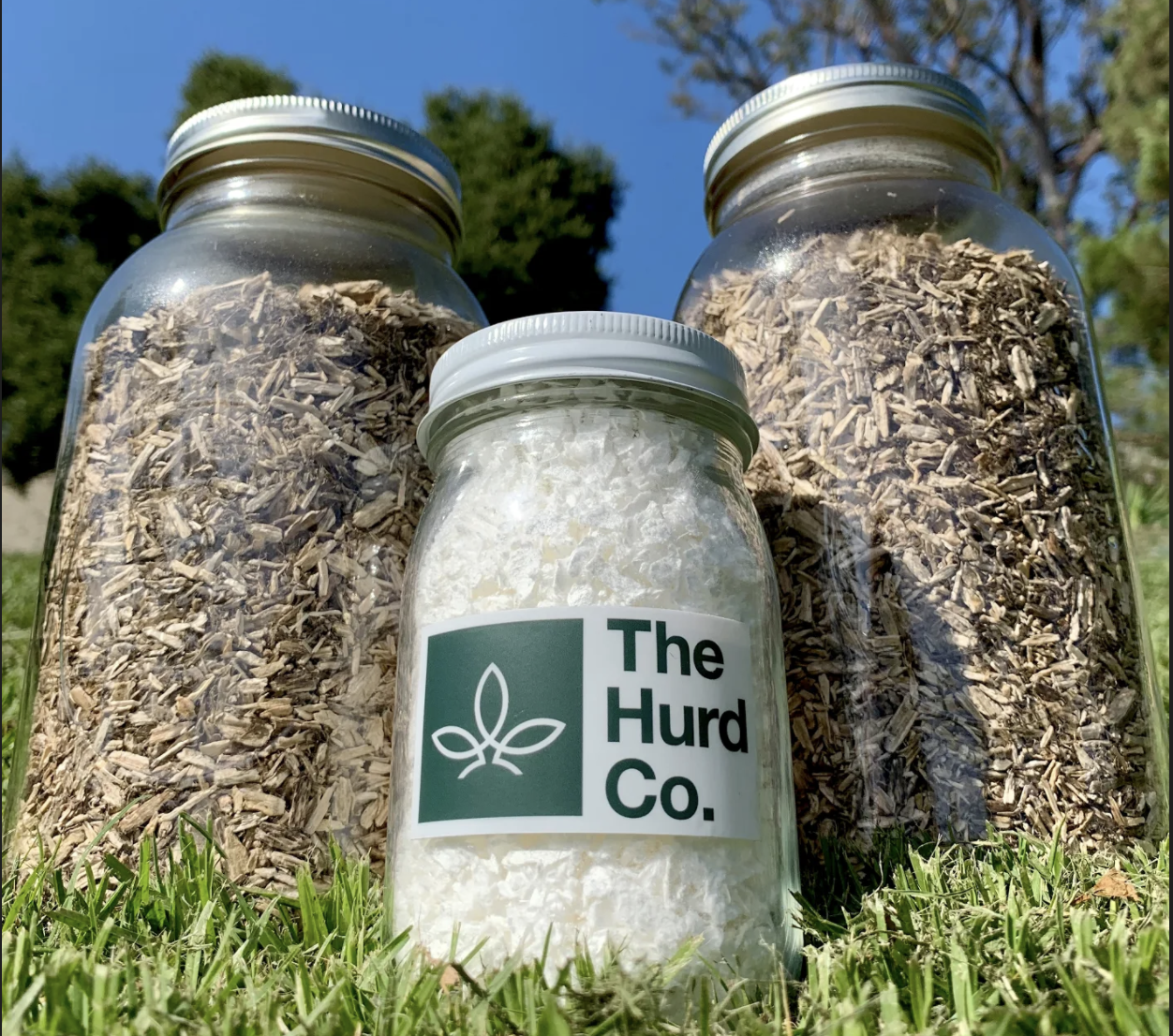

Image Credits: The Hurd Co.
The Hurd Co.’s goal is simple: reduce the environmental impact of clothing companies by helping to remove trees from the process. Specifically, the company creates cellulosic fiber pulp from agricultural byproducts. This is designed to bypass tree-based agrilose, which is used in the production of a wide variety of fabrics, including rayon.
“Apparel brands are scrambling for new, low-impact fabric that will allow them to meet their ambitious sustainability goals,” CEO Taylor Heisley-Cook tells TechCrunch. “We completely eliminate trees from the supply chain with a hyper-efficient process that dramatically reduces brands’ impact on the environment.”
The company says its process uses half the water and significantly less energy than standard processes. The technology was developed by Hurd’s CTO, Charles Cai.
Humm

Image Credits: Humm
I won’t lie, this is the one in the batch I have the most questions about, having seen a number of companies claim their wearables can increase memory.
Here’s what CEO Iain McIntyre has to say: “It’s ideal for activities that depend on memory, like reading, problem solving or multi-tasking. The Humm patch uses tACS (transcranial alternating stimulation) and in clinical research studies, the Humm patch saw a measurable (+~20%) improvement against placebo.”
It’s an interesting underlying technology, and the advisors — which include a number of university professors in the sciences — certainly see commercial potential. There are some lingering questions around tACS.
Quoting Scientific American from January: “The potential therapeutic effects of tACS on memory, food craving and other neural processes have been tested in dozens of studies in the past. Questions have been raised about whether this method actually exerts any meaningful changes in the brain, however.”
Definitely interested in seeing more about this one and perhaps taking it for a spin when the product ships, later this year.
As far as elevator pitches go, Publica may have the best one of the show. “Publica is Shopify for Digital Content.” Essentially, the company wants to be a direct conduit between content creators and consumers.
“Publica is a service that enables authors and content creators to have their own custom storefront to share, market and sell e-books, audiobooks and any other types of digital content with no intermediaries,” CEO Pablo Laurino tells TechCrunch. “In the era of D2C and marketplaces, Publica helps authors and content to achieve that on their own storefront, offering authors complete control over their brand and ownership of the relationships.”
The system helps creators make their own own digital storefront to sell a wide variety of products, including audiobooks and e-books. The site is already up and running, with more than 1,200 stores created by 250 clients.
Serinus Labs

Image Credits: Serinus Labs
Serinus is developing a warning system for detecting failure in lithium-ion batteries.
Per CEO, Hossain Fahad, “Battery safety is the biggest challenge in the EV industry today. Serinus Labs’ proprietary LiCANS technology provides early warning signals to prevent catastrophic battery failure in electric vehicles.”
The tech uses gas sensing to detect early traces of vented gases that occur prior to battery failure.
Powered by WPeMatico