Since the pandemic began, have you been walking more, or do you know someone who bought a new car? Perhaps you ran your first errand on a rented e-bike or scooter?
Over the last year, I’ve experimented with different mobility options to see which ones best suit my needs, as have most people I know. It can be challenging to maintain a recommended physical distance on a bus or subway. (After a decade-plus hiatus, I even briefly considered rejoining the ranks of automobile owners!)
Full Extra Crunch articles are only available to members.
Use discount code ECFriday to save 20% off a one- or two-year subscription.
It took some getting used to, but I now enjoy traveling around San Francisco on a scooter or e-bike. Pre-pandemic, I was leery of riding two-wheeled vehicles in a city with a high rate of injury collisions, but there are fewer cars on the road than there used to be.
COVID-19 has spotlighted many of the weakest points in our transportation system, but some of the rapid shifts in consumer behavior are creating opportunities for tech once considered fanciful, like sidewalk delivery robots and eVTOLs (electric vertical and takeoff vehicles).
Transportation editor Kirsten Korosec reached out to 10 investors to learn more “about the state of mobility, which trends they’re most excited about and what they’re looking for in their next investments.”
Here’s who she interviewed:
- Clara Brenner, co-founder and managing partner, Urban Innovation Fund
- Shawn Carolan, partner, Menlo Ventures
- Dave Clark, partner, Expa
- Abhijit Ganguly, senior manager, Goodyear Ventures
- Rachel Holt, co-founder and general partner, Construct Capital
- David Lawee, founder and general partner, CapitalG
- Sasha Ostojic, operating partner, Playground Global
- Sebastian Peck, managing director, InMotion Ventures
- Natalia Quintero and Rachel Haot, Transit Innovation Partnership/Transit Tech Lab
Thanks very much for reading Extra Crunch this week!
Walter Thompson
Senior Editor, TechCrunch
@yourprotagonist
A fraction of Robinhood’s users are driving its runaway growth

Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
Yesterday’s House Financial Services Committee hearing on the GameStop short squeeze saga was fairly typical: Most lawmakers used their time to grandstand and little new information was revealed.
But Alex Wilhelm found one tidbit: Much of Robinhood’s revenue is generated from payment for order flow (PFOF). Under the practice, market makers pay the trading platform for executing trades.
To get a sense of how much Robinhood’s high rollers contribute to the company’s general health, he calculated its PFOF revenues for the last three months of 2020.
“Borrowing a term from the casino trade, these whales generate the bulk of the company’s revenue stream.”
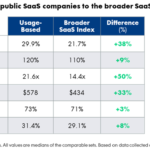
Why do SaaS companies with usage-based pricing grow faster?

Image Credits: John Lund (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
HubStop introduced usage-based pricing in 2011 to boost its retention rate, then near 70%.
When it went public three years later, its net revenue retention rate was edging close to 100%, “all without hurting the company’s ability to acquire new customers.”
Offering new users frictionless onboarding, customer support and free credits is a proven method for making them more active — and loyal.
So, why do public SaaS firms with usage-based pricing see faster growth?
“Because they’re better at landing new customers, growing with them and keeping them as customers,” says Kyle Powar, VP of growth at OpenView.
Paying $115B for Stripe or $77B for Coinbase might be quite rational

Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
In October 2018, private-market money valued Coinbase at around $8 billion. As of this week, it’s valued at $77 billion.
Similarly, Stripe is valued at $115 billion on secondary markets. In the middle of last year, that figure was closer to $36 billion.
“Would I line up to pay $77 billion for Coinbase?” asked Alex. “Probably not, but that doesn’t mean that the public markets won’t.”
Pandemic-era growth and SPACs are helping edtech startups graduate early

Image Credits: Witthaya Prasongsin (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Natasha Mascarenhas reports that some edtech startups are hitching rides with special purpose acquisition vehicles so they can speed up their journey to the public markets.
To learn more, she interviewed Susan Wolford, chairperson of $200 million SPAC Edify Acquisition, and Nerdy CEO Chuck Cohn. Nerdy, parent company of Varsity Tutors, is going through a reverse merger with TPG Pace Tech Opportunities.
“It’s less about going into the public markets and more about that this transaction allows us to take an offensive position and lean into the big opportunities,” Cohn said.
Dear Sophie: Tips for filing for a green card for my soon-to-be spouse
Image Credits: Bryce Durbin/TechCrunch
Dear Sophie:
My fiancé is in the U.S. on an H-1B visa, which is set to expire in about a year and a half.
We were originally planning to marry last year, but both he and I want to have a ceremony and party with our families and friends, so we decided to hold off until the pandemic ends. I’m a U.S. citizen and plan to sponsor my fiancé for a green card.
How long does it typically take to get a green card for a spouse? Any tips you can share?
— Sweetheart in San Francisco
Inside Rover and MoneyLion’s SPAC-led public debuts
Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
When I saw that Alex Wilhelm wrote on Tuesday about two more startups that were taking the SPAC route to public markets, I briefly wondered if we’ve been covering special purpose acquisition companies too frequently.
After I read his first sentence, I realized Alex made exactly the right call because the trend that emerged in 2020 may be turning into a actual wave: This week, pet e-commerce company Rover and fintech startup MoneyLion both announced that they’re planning SPAC-led debuts.
On Monday, Alex covered the news that Lerer Hippeau Acquisition Corp. and Khosla Ventures Acquisition Co. I, II and III. filed S-1 filings last week.
“You have to wonder if every VC worth a damn in the future will have their own raft of SPAC offerings,” says Alex.
Wrote Lerer Hippeau Acquisition Corp.:
With our portfolio now maturing to the stage at which many are considering the public markets, we view SPACs as a natural next step in the evolution of our platform.
“If we are not careful, every entry of this column could consist of SPAC news,” writes Alex.
From dorm rooms to board rooms: How universities are promoting entrepreneurship

Image Credits: CasarsaGuru (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Fifteen U.S.-based institutions of higher learning have joined forces to create the University Technology Licensing Program LLC (UTLP).
The program makes it easier for entrepreneurs and investors to find IP that can drive their companies forward, but it’s also an attempt to repair what one participant calls “the somewhat broken interface between universities and very large companies in the tech space.”
4 strategies for deep tech companies recruiting top growth marketers

Image Credits: Mallika Wiriyathitipirm/EyeEm (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Here’s some real talk for technical founders: if you find it frustrating to work with growth experts and marketing professionals, the feeling’s probably mutual.
“Incredible growth people are independent and creative and are drawn to environments that explicitly value these traits,” says Jessica Li, a content/growth professional who was previously a VC.
To land top talent, “demonstrate that you have a team structure in place where a growth marketer could fit in and thrive.”
9 investors discuss hurdles, opportunities and the impact of cloud vendors in enterprise data lakes

Image Credits: Donald Iain Smith (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Before my first cup of coffee this morning, I’d already interacted with four different devices that transmitted details about my behavior to a data lake.
Hopefully, the response I sent to an automated text while waiting for the kettle to boil will generate a discount offer in my inbox later today. (And hopefully, the raw data I’m transmitting has been properly secured and cataloged.)
Enterprise reporter Ron Miller interviewed nine investors to learn more about their approach to the lucrative data lake market:
- Caryn Marooney, general partner, Coatue Management
- Dharmesh Thakker, general partner, Battery Ventures
- Casey Aylward, principal, Costanoa Ventures
- Derek Zanutto, general partner, CapitalG
- Navin Chaddha, managing director, Mayfield
- Jon Lehr, co-founder and general partner, Work-Bench
- Peter Wagner, founding partner, Wing Ventures
- Nicole Priel, managing director, Ibex Ventures
- Ilya Sukah, partner, Matrix Partners
Felicis’ Aydin Senkut and Guideline’s Kevin Busque on the value of simple pitch decks

Image Credits: Felicis Ventures / Guideline
When it comes to building a durable relationship between a founder and an investor, “the trust starts in the pitch deck,” says Guideline CEO Kevin Busque.
Busque joined Extra Crunch Live last week with Felicis Ventures’ Aydin Senku to discuss the seed round Senku declined to join — and the Series B he led a short while later.
In keeping with our new format, the pair also offered feedback on pitch decks submitted by members of the audience. Read highlights, or watch a video with the full conversation.
Powered by WPeMatico



 , Chris is back! He’s working on the next iteration of the show, something that you will be able to see starting Very Soon. Get hyped!
, Chris is back! He’s working on the next iteration of the show, something that you will be able to see starting Very Soon. Get hyped!