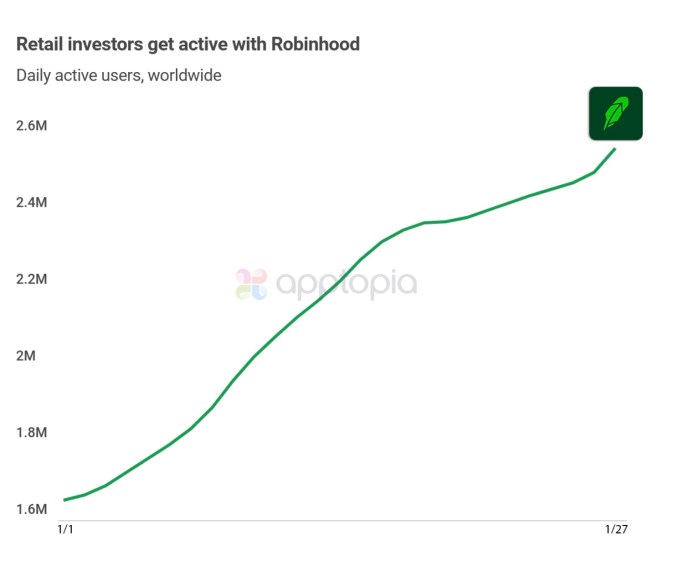
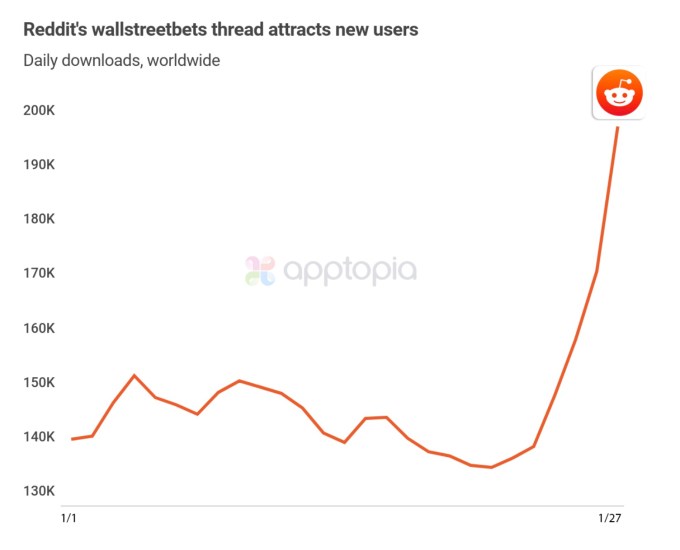
Edtech is so widespread, we already need more consumer-friendly nomenclature to describe the products, services and tools it encompasses.
I know someone who reads stories to their grandchildren on two continents via Zoom each weekend. Is that “edtech?”
Similarly, many Netflix subscribers sought out online chess instructors after watching “The Queen’s Gambit,” but I doubt if they all ran searches for “remote learning” first.
Edtech needs to reach beyond underfunded public school systems to become more sustainable, which is why more investors and founders are focusing on lifelong learning.
Besides serving traditional students with field trips and art classes, a maturing sector is now branching out to offer software tutors, cooking classes and singing lessons.
For our latest investor survey, Natasha Mascarenhas polled 13 edtech VCs to learn more about how “employer-led up-skilling and a renewed interest in self-improvement” is expanding the sector’s TAM.
Here’s who she spoke to:
- Deborah Quazzo, managing partner, GSV Ventures
- Ashley Bittner, founding partner, Firework Ventures (a future of work fund with portfolio companies LearnIn and TransfrVR)
- Jomayra Herrera, principal, Cowboy Ventures (a generalist fund with portfolio companies Hone and Guild Education)
- John Danner, managing partner, Dunce Capital (an edtech and future of work fund with portfolio companies Lambda School and Outschool)
- Mercedes Bent and Bradley Twohig, partners, Lightspeed Venture Partners (a multistage generalist fund with investments including Forage, Clever and Outschool)
- Ian Chiu, managing director, Owl Ventures (a large edtech-focused fund backing highly valued companies including Byju’s, Newsela and Masterclass)
- Jan Lynn-Matern, founder and partner, Emerge Education (a leading edtech seed fund in Europe with portfolio companies like Aula, Unibuddy and BibliU)
- Benoit Wirz, partner, Brighteye Ventures (an active edtech-focused venture capital fund in Europe that backs YouSchool, Lightneer and Aula)
- Charles Birnbaum, partner, Bessemer Venture Partners (a generalist fund with portfolio companies including Guild Education and Brightwheel)
- Daniel Pianko, co-founder and managing director, University Ventures (a higher ed and future of work fund that is backing Imbellus and Admithub)
- Rebecca Kaden, managing partner, Union Square Ventures (a generalist fund with portfolio companies including TopHat, Quizlet, Duolingo)
- Andreata Muforo, partner, TLCom Capital (a generalist fund backing uLesson)
Full Extra Crunch articles are only available to members
Use discount code ECFriday to save 20% off a one- or two-year subscription
In other news: Extra Crunch Live, a series of interviews with leading investors and entrepreneurs, returns next month with a full slate of guests. This year, we’re adding a new feature: Our guests will analyze pitch decks submitted by members of the audience to identify their strengths and weaknesses.
If you’d like an expert eye on your deck, please sign up for Extra Crunch and join the conversation.
Thanks very much for reading! I hope you have a fantastic weekend — we’ve all earned it.
Walter Thompson
Senior Editor, TechCrunch
@yourprotagonist
13 investors say lifelong learning is taking edtech mainstream

Image Credits: Bryce Durbin
Rising African venture investment powers fintech, clean tech bets in 2020

Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
After falling into yesterday’s wild news cycle, Alex Wilhelm returned to The Exchange this morning with a close look at venture capital activity across Africa in 2020.
“Comparing aggregate 2020 figures to 2019 results, it appears that last year was a somewhat robust year for African startups, albeit one with fewer large rounds,” he found.
For more context, he interviewed Dario Giuliani, the director of research firm Briter Bridges, which focuses on emerging markets in Africa, Asia and Latin America.
Talent and capital are shifting cybersecurity investors’ focus away from Silicon Valley

Image Credits: MCCAIG (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
New cybersecurity ecosystems are popping up in different parts of the world.
Some of of that growth has been fueled by an exodus from the Bay Area, but many early-stage security startups already have deep roots in East Coast cities like Boston and New York.
In the United Kingdom and Europe, government innovation programs have helped entrepreneurs close higher numbers of Series A and B rounds.
Investor interest and expertise is migrating out of Silicon Valley: This post will help you understand where it’s going.
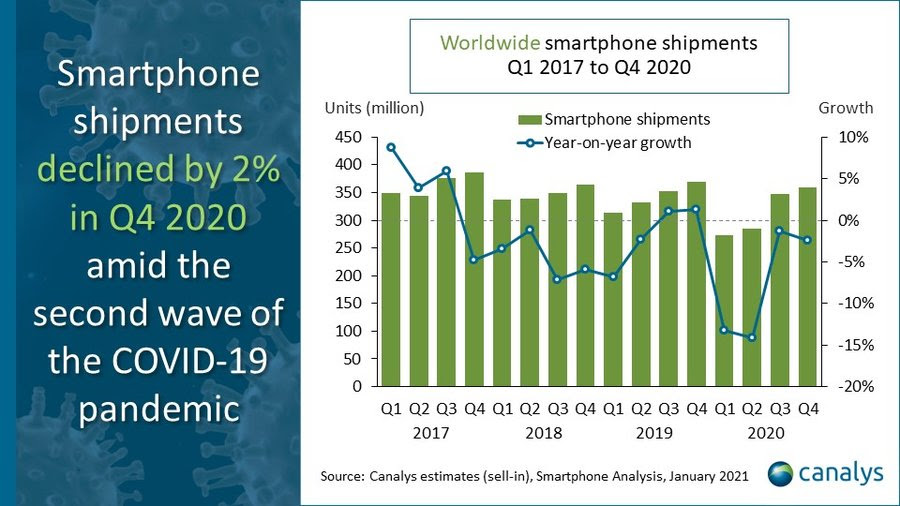
Will Apple’s spectacular iPhone 12 sales figures boost the smartphone industry in 2021?

Image Credits: NurPhoto (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Today’s smartphones are unfathomably feature-rich and durable, so it’s logical that sales have slowed.
A phone purchased 18 months ago is probably “good enough” for many consumers, especially in times of economic uncertainty.
Then again, of the record $111.4 billion in revenue Apple earned last quarter, $65.68 billion came from phone sales, largely driven by the release of the iPhone 12.
Even though “Apple’s success this quarter was kind of a perfect storm,” writes Hardware Editor Brian Heater, “it’s safe to project a rebound for the industry at large in 2021.”
The 5 biggest mistakes I made as a first-time startup founder

Image Credits: Randy Faris (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Finmark co-founder and CEO Rami Essaid wrote a post for Extra Crunch that candidly describes the traps he laid for himself that made him a less-effective entrepreneur.
As someone who’s worked closely with founders at several startups, each of the points he raised resonated deeply with me.
In my experience, many founders have a hard time delegating, which can quickly create cultural and operational problems. Rami’s experience bears this out:
“I became a human GPS: People could follow my directions, but they struggled to find the way themselves. Independent thinking suffered.”
Dear Sophie: How can I sponsor my mom and stepdad for green cards?
Image Credits: Bryce Durbin/TechCrunch
Dear Sophie:
I just got my U.S. citizenship! My husband and I want to bring my mom and her husband to the U.S. to help us take care of our preschooler and toddler.
My biological dad passed away several years ago when I was an adult and my mom has since remarried.
— Appreciative in Aptos
Check out the amazing speakers joining us on Extra Crunch Live in February
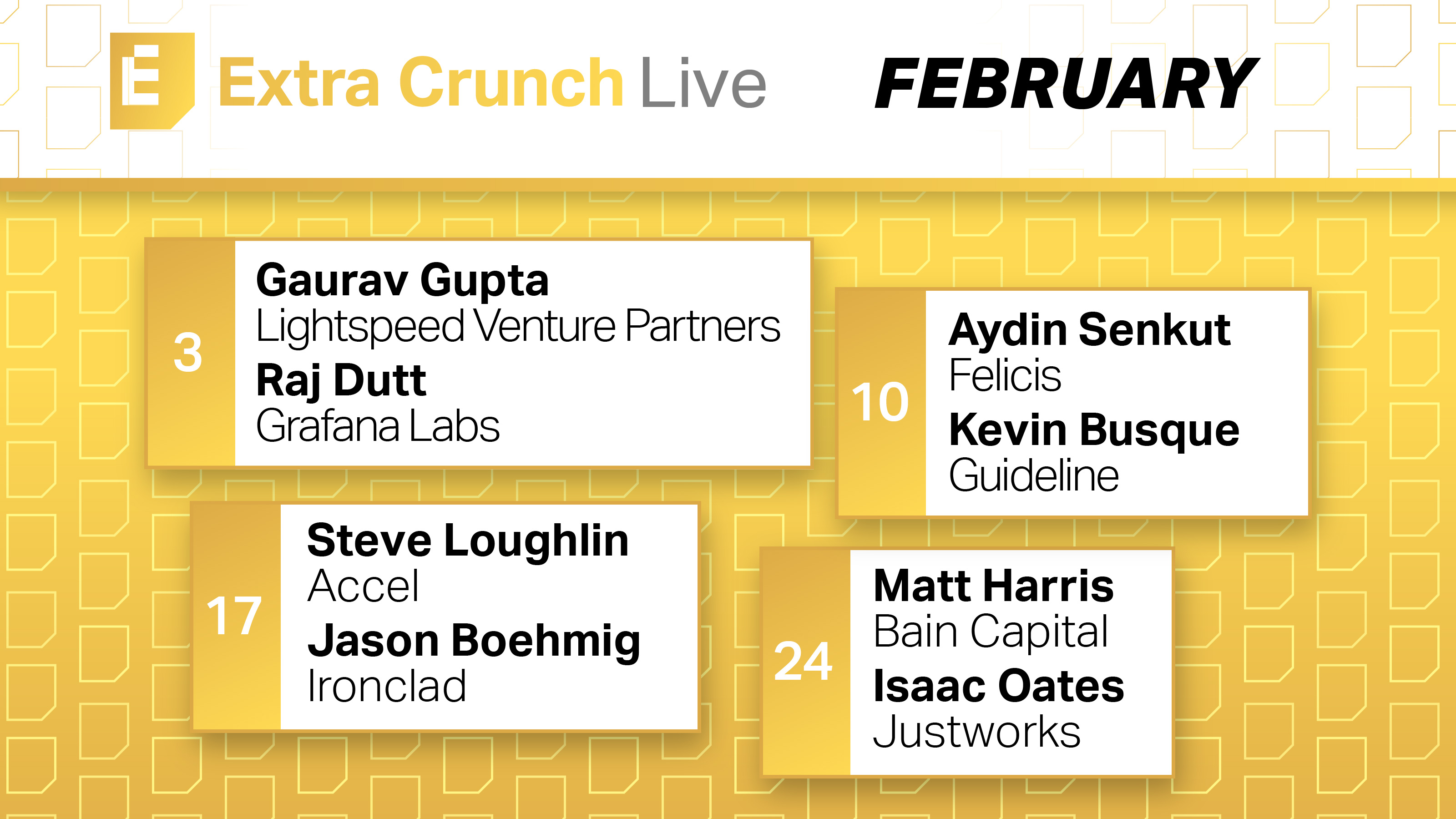
Next month, Extra Crunch Live returns with a lineup of guests who are extremely well-qualified to discuss early-stage startups.
Each Wednesday at noon PPST/3 p.m. EST, join a conversation with founders and the investors who backed their companies:
February 3:
Gaurav Gupta (Lightspeed Venture Partners) + Raj Dutt (Grafana Labs)
February 10:
Aydin Senkut (Felicis Ventures) + Kevin Busque (Guideline)
February 17:
Steve Loughlin (Accel) + Jason Boehmig (Ironclad)
February 24:
Matt Harris (Bain Capital) + Isaac Oates (Justworks)
Also, we’re adding a new feature to Extra Crunch Live — our guests will offer advice and feedback on pitch decks submitted by Extra Crunch members in the audience!
10 VCs say interactivity, regulation and independent creators will reshape digital media in 2021

Image Credits: Aleksandar Nakic (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Since the pandemic disrupted the social rhythms of work and school, many of us have compensated by changing our relationship to digital media.
For instance, I purchased a new sofa and thicker living room curtains several months ago when I realized we have no idea when movie theaters will reopen.
Last year, podcast sponsors spent almost $800 million to reach listeners, but ad revenue is estimated to surpass $1 billion this year. Clearly, I’m not the only person who used a discount code to buy a new product in 2020.
At this point, I can scarcely keep track of the multiple streaming platforms I’m subscribed to, but a new voice-activated remote control that comes with my basic cable plan makes it easier to browse my options.
Media reporter Anthony Ha spoke to10 VCs who invest in media startups to learn more about where they see digital media heading in the months ahead. For starters, how much longer can we expect traditional advertising models to persist?
And in a world with hundreds of channels, how are creators supposed to compete for our attention? What sort of discovery tools can we expect to help us navigate between a police procedural set in a Scandinavian village and a 90s sitcom reboot?
Here’s who Anthony interviewed:
- Daniel Gulati, founding partner, Forecast Fund
- Alex Gurevich, managing director, Javelin Venture Partners
- Matthew Hartman, partner, Betaworks Ventures
- Jerry Lu, senior associate, Maveron
- Jana Messerschmidt, partner, Lightspeed Venture Partners
- Michael Palank, general partner, MaC Venture Capital (with additional commentary from MaC’s Marlon Nichols)
- Pär-Jörgen Pärson, general partner, Northzone
- M.G. Siegler, general partner, GV
- Laurel Touby, managing director, Supernode Ventures
- Hans Tung, managing partner, GGV Capital
Normally, we list each investor’s responses separately, but for this survey, we grouped their responses by question. Some readers say they use our surveys to study up on an individual VC before pitching them, so let us know which format you prefer.
Does a $27 billion or $29 billion valuation make sense for Databricks?
Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
Data analytics platform Databricks is reportedly raising new capital that could value the company between $27 billion and $29 billion.
By the end of Q3 2020, Databricks had surpassed a $350 million run rate — a $150 million YoY increase, reports Alex Wilhelm.
At the time, he described the company as “an obvious IPO candidate” with “broad private-market options.”
Which begs the question: “Can we come up with a set of numbers that help make sense of Databricks at $27 billion?”
End-to-end operators are the next generation of consumer business

Image Credits: Natalia Timchenko (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
Rapid shifts in the way we buy goods and services disrupted old-school marketplaces like local newspapers and the Yellow Pages.
Today, I can use my phone to summon a plumber, a week’s worth of groceries or a ride to a doctor’s office.
End-to-end operators like Netflix, Peloton and Lemonade take a lot of time and energy to reach scale, but “the additional capital required is often outweighed by the value captured from owning the entire experience.”
Unpacking Chamath Palihapitiya’s SPAC deals for Latch and Sunlight Financial
Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
On January 25, Social Capital CEO Chamath Palihapitiya tweeted that he was making two blank-check deals.
Enterprise SaaS company Latch makes keyless entry systems; Sunlight Financial helps consumers finance residential solar power installations.
“There are nearly 300 SPACs in the market today looking for deals,” noted Alex Wilhelm, who unpacked both transactions.
“There’s no escaping SPACs for a bit, so if you are tired of watching blind pools rip private companies into the public markets, you are not going to have a very good next few months.”
Fintechs could see $100 billion of liquidity in 2021

Image Credits: dan tarradellas (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
On Monday, we published the Matrix Fintech Index, a three-part study that weighs liquidity, public markets and e-commerce trends to create a snapshot of an industry in perpetual flux.
For four years running, the S&P 500 and incumbent financial services companies have been outperformed by companies like Afterpay, Square and Bill.com.
In light of steady VC investment, increasing consumer adoption and a crowded IPO pipeline, “fintech represents one of the most exciting major innovation cycles of this decade.”
Drupal’s journey from dorm-room project to billion-dollar exit

Image Credits: Acquia
On January 15, 2001, then-college student Dries Buytaert released Drupal 1.0.0, an open-source content-management platform. At the time, about 7% of the world’s population was online.
After raising more than $180 million, Buytaert exited to Vista Equity Partners for $1 billion in 2019.
Enterprise reporter Ron Miller interviewed Buytaert to learn more about his 18-year journey.
“His story is compelling, but it also offers lessons for startup founders who also want to build something big,” says Ron.
Powered by WPeMatico