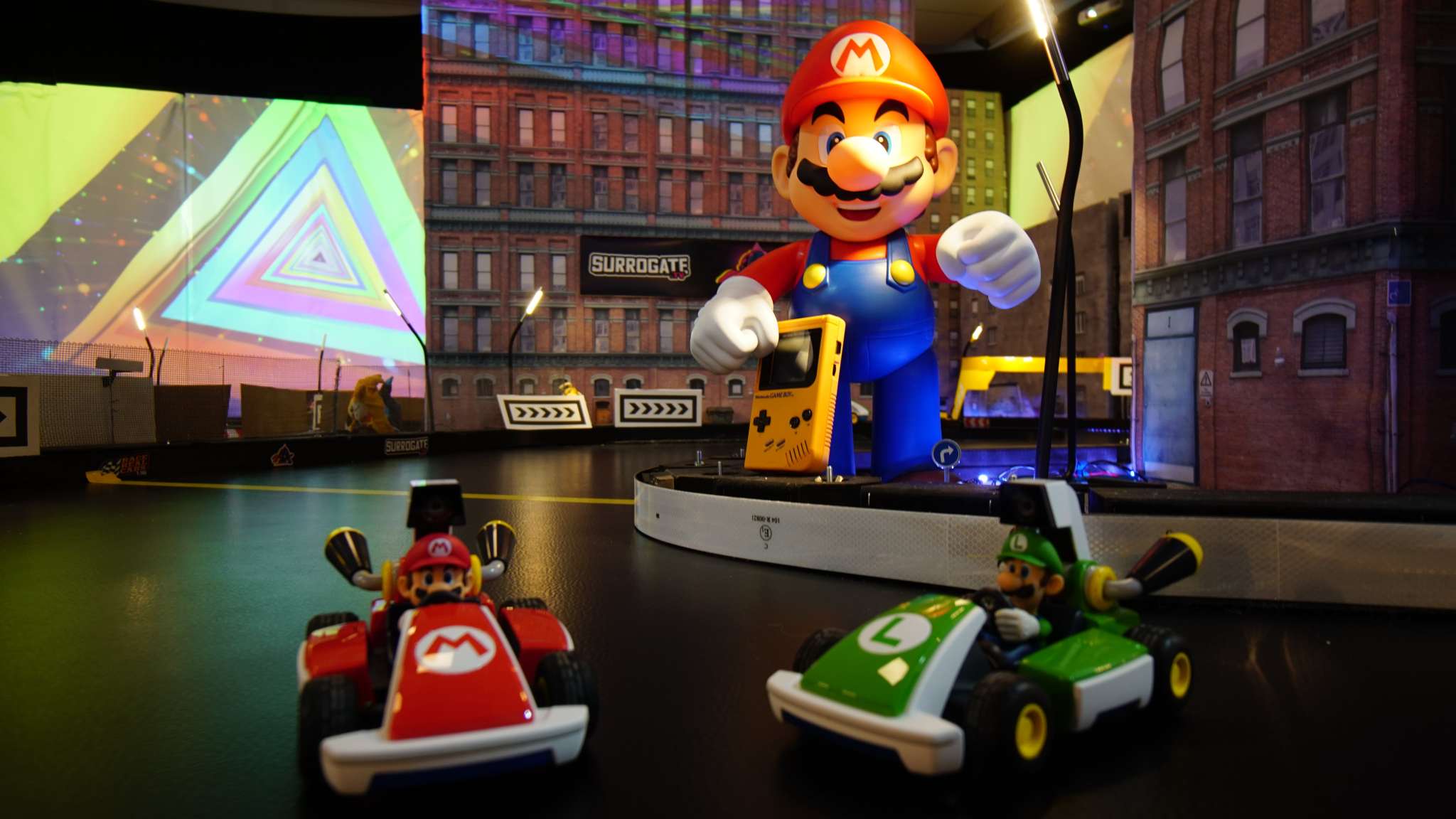
The global software as a service (SaaS) industry is sustaining its steep growth trajectory, but developing and pricing professional services is oftentimes a difficult proposition for SaaS companies.
Gartner recently forecast that SaaS revenue worldwide could surpass $140 billion by 2022, which would represent a 40% increase over 2019’s roughly $100 billion. These are heady figures for an industry that gained its footing only 20 years ago.
As someone who has led many investments in SaaS companies, there is clear consensus within boardrooms, assuming compelling sales efficiency metrics: The more ARR the better. It is also clear that looking across the SaaS industry, there is strong consistency in overall software gross margins, generally landing in the 60% to 80% range.
There is clear consensus within boardrooms, assuming compelling sales efficiency metrics: The more ARR the better.
What is much less obvious is how to charge customers for professional services, whether for implementations, consulting work or training.
While historically, in the perpetual software days, such offerings were billed on a time and materials basis or for a fixed fee with a targeted gross margin of say 10%-30%, fast-forward to the recurring revenue model today and these services can be equally profitable but also result in big losses given wide differences in how companies charge for these services.
Looking at SaaS companies, one can see 50-point margin swings, or more, on services revenue, from -30% to 20%. Why do we see such differences in margins for professional services, and what are the implications of these differing approaches for a SaaS company’s strategy?
Are professional services a profit center or a loss leader?
We can start by asking why a company would accept a single-digit or even negative margins on its professional services. For some, it’s a strategy to accelerate its ARR by covering part of that expense by foregoing, say, an implementation fee for a higher annual subscription amount. The view here is to remove some friction out of the sales process by reducing any services fees. This will accelerate new logo velocity, resulting in higher ARR, and thus stronger growth, which should translate into higher stock price appreciation.
To execute this strategy, a SaaS company may increase its subscription price, although not by much. While this allows the provider to offer such services without detailing its cost in a separate line item, is this really the right answer? As with so many questions, the answer depends on many variables, such as: Does it expedite the sales cycle? Would charging for such services make clients more responsive and result in quicker implementations? How much costs do you need to cover such services? What is the impact of doing so on the cash position, profitability and financing needs of the business?
Two professional services pricing strategies
Let’s compare the three-year impact of two professional services pricing strategies, and the resulting impact on the financing needs:
- Company A: Provides professional services with an annual value of $10 million with a -20% gross margin, resulting in a $2 million annual loss. Total losses over the three-year period are $6 million.
Powered by WPeMatico