I took a long walk on Saturday. It’s become a routine during the pandemic, a chance to unwind after too many hours indoors, while seeing parts of the city that would otherwise be lost to subway rides in normal years. Saturday was more purpose-driven, heading to a newly opened Trader Joe’s before Henri unleashed itself on the Eastern Seaboard.
Taking respite from the early rain, I found a food court in Long Island City, ordered a shawarma and pulled the Galaxy Z Flip from my pocket. I unfolded the phone, popped the new Galaxy Buds in my ears and watched a baseball game on the MLB.TV app. The Flip really made sense in that moment, open in landscape mode at a 135-degree angle to keep the 6.7-inch screen upright. When the game ended (spoiler, it didn’t end well), I snapped the phone shut, stuck it in my pocket and went on my way.
It doesn’t always come with a piece of new technology, but sometimes you get lucky and have an experience where it just clicks. There were plenty of jokes about the long-ago death of the clamshell when the first Flip arrived. Those won’t be going away anytime soon, of course, but the phone also offered the first sense for many that maybe Samsung was heading in the right direction with its foldable ambitions.

Image Credits: Brian Heater
Setting aside the early flaws with the first Galaxy Fold (we’ve covered them ad nauseum elsewhere), the device is also unwieldy. While it’s true the foldable screen affords you the ability to carry around a screen that might otherwise be impossible, it’s a large device when folded, and the opportunities to unfold don’t readily present themselves. The Flip splits the difference nicely between screen size and portability. In terms of display size, it’s effectively a Galaxy Note that snaps in two and fits nicely in your pocket.
Most of the talk of Samsung mainstreaming foldables has centered on the Galaxy Z Fold — mostly from the company itself. Samsung has made a big to-do about positioning the Fold as its latest flagship — augmenting or, perhaps replacing, the Note in its lineup. The Fold 3 certainly blurs the lines with the addition of S Pen functionality, but the Flip is the much clearer bridge between Samsung’s existing flagships and the foldable future it envisions.
Mainstreaming foldables was always going to be a tricky proposition. Right out of the gate, they were hit with negative coverage over production issues and prices; $2,000 is a lot to pay for a product you essentially have to handle with kid gloves. You shouldn’t have to worry about accidentally damaging your daily driver through normal use. The Flip benefits from the mistakes of earlier fold generations, getting a more robust design and water resistance as a result.
Perhaps even more importantly, however, is pricing. The Galaxy Z Flip is Samsung’s first foldable under $1,000. Now, granted, it’s literally one penny under that threshold — a price point that puts it in line with expensive premium phones from the likes of Samsung and Apple. But in the world of foldables, that’s a really big win. The first couple of generations could — to some degree — survive on novelty alone.
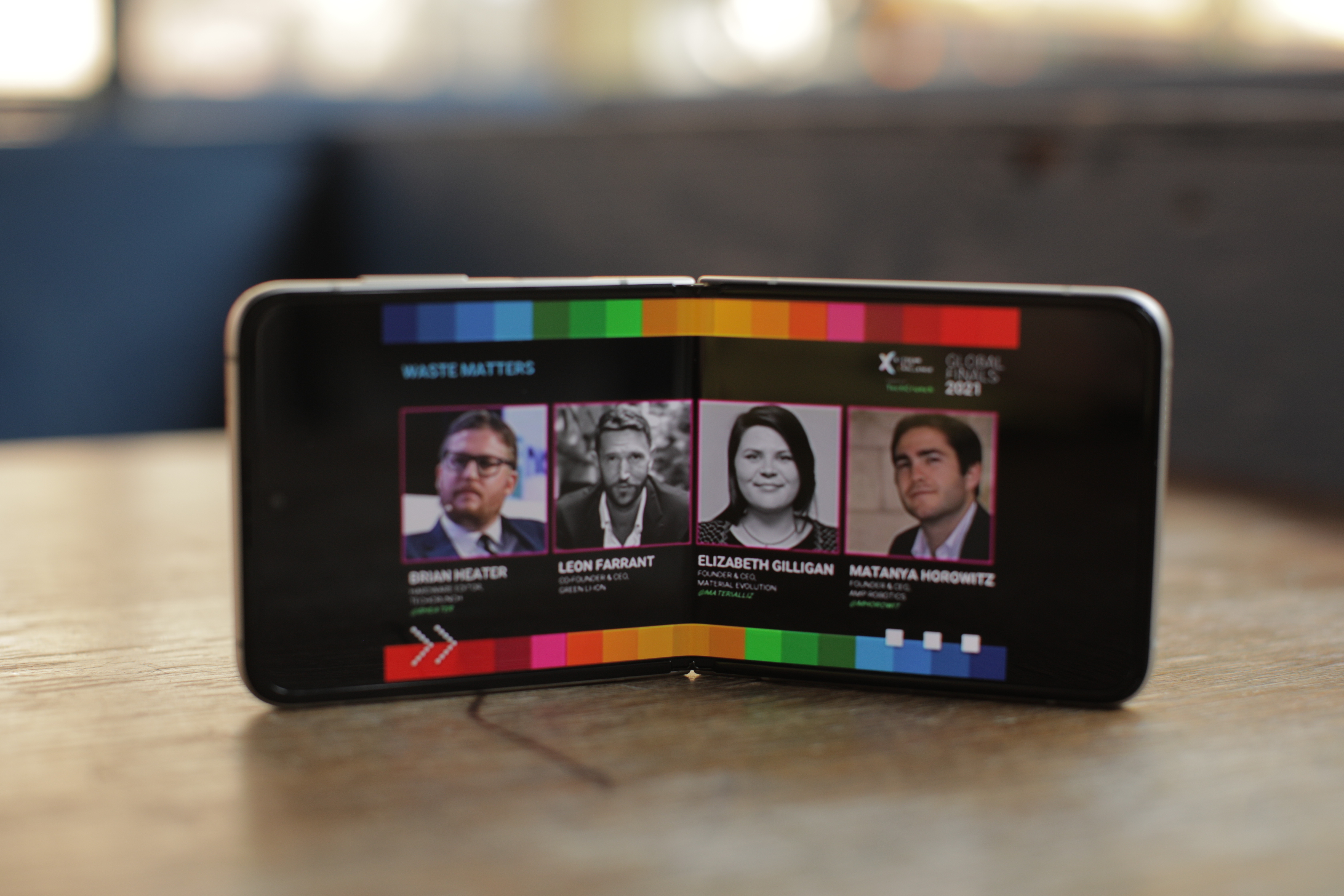

Image Credits: Brian Heater
As more of these devices make their way into the world, utility supersedes novelty. But growing popularity also means scale — and, as a result, price drops. For the first time, buying a Samsung foldable is not the financial equivalent of buying two phones. That’s a much more significant threshold than the Galaxy Fold dropping $200 over its previous generation.
The company noted this week, that “in just 10 days since announcement pre-orders for the Galaxy Z Fold3 and Galaxy Z Flip3 have already surpassed total global Samsung foldables sales in all of 2021, also making it the strongest pre-order for Samsung foldables ever.” There are a lot of factors here, including a lower price, more robust design, the absence of a new Note and an aggressive push to get consumers to preorder. But it’s safe to say the line is, at the very least, trending the right way.
Expectedly, the company’s numbers don’t break down sales in terms of Fold versus Flip. Admittedly, the Fold is more fully featured, and 7.6 inches of screen is better than 6.7 inches of screen, when it comes, to, say, watching a full movie. But for most people in most instances, the Galaxy Flip is a better choice. I can say with no hesitation: The Samsung Galaxy Z Flip is the most mainstream foldable on the market.
If you’re not sold on the importance of foldables, such a statement understandably doesn’t mean much. But for a vast majority of people looking to make the leap to what is increasingly looking like a key part of the mobile future, the Flip is an obvious choice. And while it’s easy to make fun of the clamshell design as a relic of a bygone era, there’s a reason phones went that way in the first place. One assumes a big part of the reason they largely went away is that — until now — smartphones weren’t foldable.

Image Credits: Brian Heater
Samsung gets the design language right here. The Flip 3 is easily the company’s best-looking foldable to date. The dual-color shell is striking. The company sent along a cream color, which I’m not particularly fond of, but the green, lavender and even plain black or white are quite striking. It pairs well with the strip of black that houses the exterior display, which has been bumped from 1.1 to 1.9 inches. It doesn’t sound like a lot, sure, but that’s a healthy increase on a screen this size.
Of course, you’re losing the full exterior screen functionality you get on the Fold. The Flip’s display is effectively a quick-glance secondary screen for notifications. Pull it out, and it shows you the time, date and how much battery you’ve got left. Swipe right and you’ll see your notifications.
Swipe left and you get an alarm or timer, with the option of adding more widgets to the screen, including weather, media playback (effectively audio play/pause) and Samsung Health Metrics. It’s a small list, but one that will no doubt increase if more people pick up the Flip. Swipe down for some quick settings and Swipe up for Samsung Pause.
In a time when many of us are trying to make a concerted effort to minimize our phone use, I appreciate the dichotomy between the two screens. It’s a much clearer line in the sand than the one separating the Fold’s 6.2- and 7.6-inch screens. Phone closed = checking my notifications. Phone open = engagement. When the time comes to open the phone, the Flip is a much easier proposition than the phones. I haven’t quite mastered the art of the one-handed open just yet, but it’s much easier to execute on the fly than the Fold, which is effectively like opening a book. The biggest downside to the form factor in terms of speed is there’s no quick way to fire off a photo.
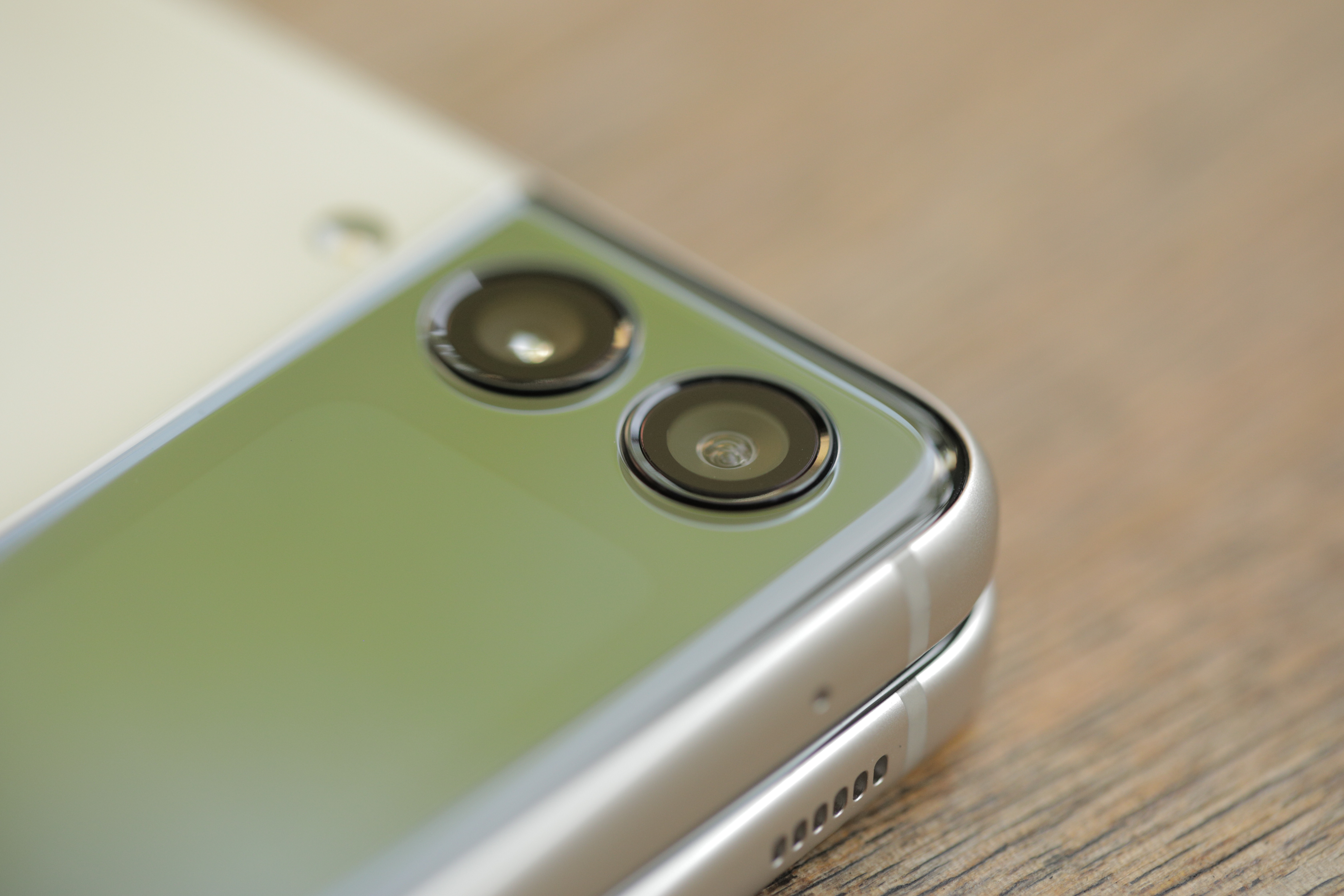

Image Credits: Brian Heater
Taking photos is far more deliberate, requiring one to open the phone to see the internal view finder. You can, however, snap off some selfies by double-pressing the power button, with the small front-facing screen doubling as a small viewfinder. Swiping to the left toggles between still, while swiping up and down changes the level of zoom. It’s a bit awkward and clunky, but the pair of 12-megapixel cameras (wide and ultra-wide) will get you a much better selfie than most pinhole cameras (including the Flip’s 10 megapixel lens).
Like the Fold, the rear cameras (which are also the front-facing cameras, depending on how you look at it) are largely unchanged since the Flip 2. A dual-camera system can feel almost antiquated in 2021, but for most intents and purposes, they do the trick, coupled with Samsung’s many years of camera software experience. The 22:9 aspect ratio means more than a quarter of the screen is occupied by the controls out of necessity.
The aspect ratio in general merits comment. It’s, like, really, really tall when open. It’s a nice amount of real estate to have when, say, scrolling through Gmail or Twitter. But when watching video, you’ll often encounter pillarboxing — letterboxing on the sides of the screen. The video world simply isn’t ready for 22:9, and quite frankly, it probably won’t ever be.
And then, of course, there’s the seam. It’s right there in the center of the lovely 2640 x 1080, 425 ppi screen. And barring some unforeseen breakthrough in foldable tech, I frankly don’t see it disappearing any time soon. I understand why that might be a deal breaker, though I’ve largely gotten used to it after spending time with these devices.
Like the Fold, the Flip runs on the Snapdragon 888 processor. Predictably, the lower cost comes with less in the way of RAM and storage, at 8 and 128GB on the Flip, to the Fold’s 12 and 256GB. Another $150 will upgrade the storage 256GB here. While Samsung mostly hasn’t skimped much on the internals, the 3,300 mAh battery does fall short.
Battery life is an issue with the Fold and an even bigger problem on the Flip — in fact, it’s the biggest complaint here. Moderate to heavy use is going to require getting near a charging cable before the day is over. Maybe not a huge deal in these pandemic days, but something to consider as we re-enter the world. Certainly long, unplugged plane rides are out of the question.

Image Credits: Brian Heater
Again, I can totally sympathize with that being a deal breaker. You pay $1,000 for a phone, you want a battery that’s going to get you through a day of use, worry-free. And certainly it’s something for Samsung to focus on in gen four.
As it stands, the Galaxy Z Flip 3 has the benefit of previous generations, with a stronger aluminum frame, improved screen protector and IPX8 water resistance (no dust resistance rating, for reasons outlined in the Fold review). It’s not a perfect phone, but it’s a strong sign of how far Samsung’s foldables have come in three generations, coupled with a sub-$1,000 price point.
The device is likely to be second fiddle as the company continues to push the Fold as its flagship foldable. But for most people looking to enter the world of foldable phones, the Flip is the easy choice.
Powered by WPeMatico