Welcome back to This Week in Apps, the weekly TechCrunch series that recaps the latest in mobile OS news, mobile applications and the overall app economy.
The app industry continues to grow, with a record 218 billion downloads and $143 billion in global consumer spend in 2020. Consumers last year also spent 3.5 trillion minutes using apps on Android devices alone. And in the U.S., app usage surged ahead of the time spent watching live TV. Currently, the average American watches 3.7 hours of live TV per day, but now spends four hours per day on their mobile devices.
Apps aren’t just a way to pass idle hours — they’re also a big business. In 2019, mobile-first companies had a combined $544 billion valuation, 6.5x higher than those without a mobile focus. In 2020, investors poured $73 billion in capital into mobile companies — a figure that’s up 27% year-over-year.
This Week in Apps offers a way to keep up with this fast-moving industry in one place, with the latest from the world of apps, including news, updates, startup fundings, mergers and acquisitions, and suggestions about new apps and games to try, too.
Do you want This Week in Apps in your inbox every Saturday? Sign up here: techcrunch.com/newsletters
Top Stories
Apple to scan for CSAM imagery
Apple announced a major initiative to scan devices for CSAM imagery. The company on Thursday announced a new set of features, arriving later this year, that will detect child sexual abuse material (CSAM) in its cloud and report it to law enforcement. Companies like Dropbox, Google and Microsoft already scan for CSAM in their cloud services, but Apple had allowed users to encrypt their data before it reached iCloud. Now, Apple’s new technology, NeuralHash, will run on users’ devices, tatformso detect when a users upload known CSAM imagery — without having to first decrypt the images. It even can detect the imagery if it’s been cropped or edited in an attempt to avoid detection.
Meanwhile, on iPhone and iPad, the company will roll out protections to Messages app users that will filter images and alert children and parents if sexually explicit photos are sent to or from a child’s account. Children will not be shown the images but will instead see a grayed-out image instead. If they try to view the image anyway through the link, they’ll be shown interruptive screens that explain why the material may be harmful and are warned that their parents will be notified.
Some privacy advocates pushed back at the idea of such a system, believing it could expand to end-to-end encrypted photos, lead to false positives, or set the stage for more on-device government surveillance in the future. But many cryptology experts believe the system Apple developed provides a good balance between privacy and utility, and have offered their endorsement of the technology. In addition, Apple said reports are manually reviewed before being sent to the National Center for Missing and Exploited Children (NCMEC).
The changes may also benefit iOS developers who deal in user photos and uploads, as predators will no longer store CSAM imagery on iOS devices in the first place, given the new risk of detection.
In-App Events appear on the App Store
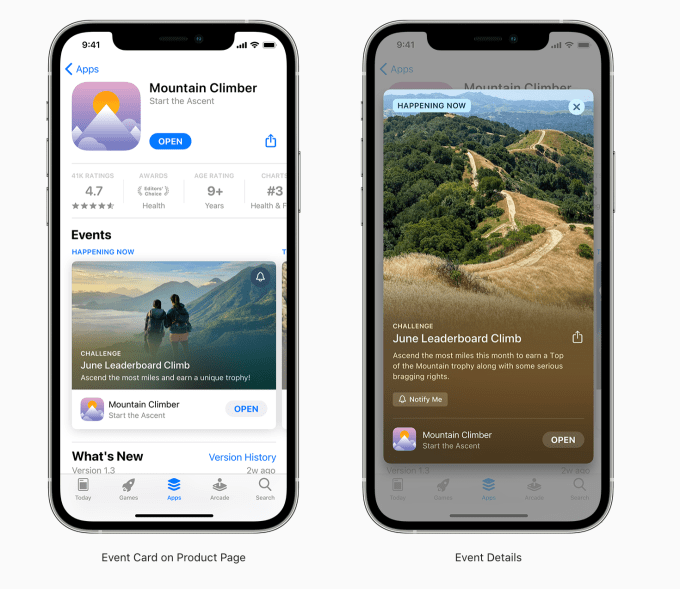
Image Credits: Apple
Though not yet publicly available to all users, those testing the new iOS 15 mobile operating system got their first glimpse of a new App Store discovery feature this week: “in-app events.” First announced at this year’s WWDC, the feature will allow developers and Apple editors alike to showcase directly on the App Store upcoming events taking place inside apps.
The events can appear on the App Store homepage, on the app’s product pages or can be discovered through personalized recommendations and search. In some cases, editors will curate events to feature on the App Store. But developers will also be provided tools to submit their own in-app events. TikTok’s “Summer Camp” for creators was one of the first in-app events to be featured, where it received a top spot on the iPadOS 15 App Store.
Weekly News
Platforms: Apple
Apple expands support for student IDs on iPhone and Apple Watch ahead of the fall semester. Tens of thousands more U.S. and Canadian colleges will now support mobile student IDs in the Apple Wallet app, including Auburn University, Northern Arizona University, University of Maine, New Mexico State University and others.
Apple was accused of promoting scam apps in the App Store’s featured section. The company’s failure to properly police its store is one thing, but to curate an editorial list that actually includes the scams is quite another. One of the games rounded up under “Slime Relaxations,” an already iffy category to say the least, was a subscription-based slime simulator that locked users into a $13 AUD per week subscription for its slime simulator. One of the apps on the curated list didn’t even function, implying that Apple’s editors hadn’t even tested the apps they recommend.
Tax changes hit the App Store. Apple announced tax and price changes for apps and IAPs in South Africa, the U.K. and all territories using the Euro currency, all of which will see decreases. Increases will occur in Georgia and Tajikistan, due to new tax changes. Proceeds on the App Store in Italy will be increased to reflect a change to the Digital Services Tax effective rate.
Game Center changes, too. Apple said that on August 4, a new certificate for server-based Game Center verification will be available via the publicKeyUrl.
Fintech
Robinhood stock jumped more than 24% to $46.80 on Tuesday after initially falling 8% on its first day of trading last week, after which it had continued to trade below its opening price of $38.
Square’s Cash app nearly doubled its gross profit to $546 million in Q2, but also reported a $45 million impairment loss on its bitcoin holdings.
Coinbase’s app now lets you buy your cryptocurrency using Apple Pay. The company previously made its Coinbase Card compatible with Apple Pay in June.
Social
An anonymous app called Sendit, which relies on Snap Kit to function, is climbing the charts of the U.S. App Store after Snap suspended similar apps, YOLO and LMK. Snap was sued by the parent of child who was bullied through those apps, which led to his suicide. Sendit also allows for anonymity, and reviews compare it to YOLO. But some reviews also complained about bullying. This isn’t the first time Snap has been involved in a lawsuit related to a young person’s death related to its app. The company was also sued for its irresponsible “speed filter” that critics said encouraged unsafe driving. Three young men died using the filter, which captured them doing 123 mph.
TikTok is testing Stories. As Twitter’s own Stories integrations, Fleets, shuts down, TikTok confirmed it’s testing its own Stories product. The TikTok Stories appear in a left-hand sidebar and allow users to post ephemeral images or video that disappear in 24 hours. Users can also comment on Stories, which are public to their mutual friends and the creator. Stories on TikTok may make more sense than they did on Twitter, as TikTok is already known as a creative platform and it gives the app a more familiar place to integrate its effects toolset and, eventually, advertisements.
Facebook has again re-arranged its privacy settings. The company continually moves around where its privacy features are located, ostensibly to make them easier to find. But users then have to re-learn where to go to find the tools they need, after they had finally memorized the location. This time, the settings have been grouped into six top-level categories, but “privacy” settings have been unbundled from one location to be scattered among the other categories.
A VICE report details ban-as-a-service operations that allow anyone to harass or censor online creators on Instagram. Assuming you can find it, one operation charged $60 per ban, the listing says.
TikTok merged personal accounts with creator accounts. The change means now all non-business accounts on TikTok will have access to the creator tools under Settings, including Analytics, Creator Portal, Promote and Q&A. TikTok shared the news directly with subscribers of its TikTok Creators newsletter in August, and all users will get a push notification alerting them to the change, the company told us.
Discord now lets users customize their profile on its apps. The company added new features to its iOS and Android apps that let you add a description, links and emojis and select a profile color. Paid subscribers can also choose an image or GIF as their banner.
Twitter Spaces added a co-hosting option that allows up to two co-hosts to be added to the live audio chat rooms. Now Spaces can have one main host, two co-hosts and up to 10 speakers. Co-hosts have all the moderation abilities as hosts, but can’t add or remove others as co-hosts.
Messaging
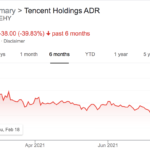
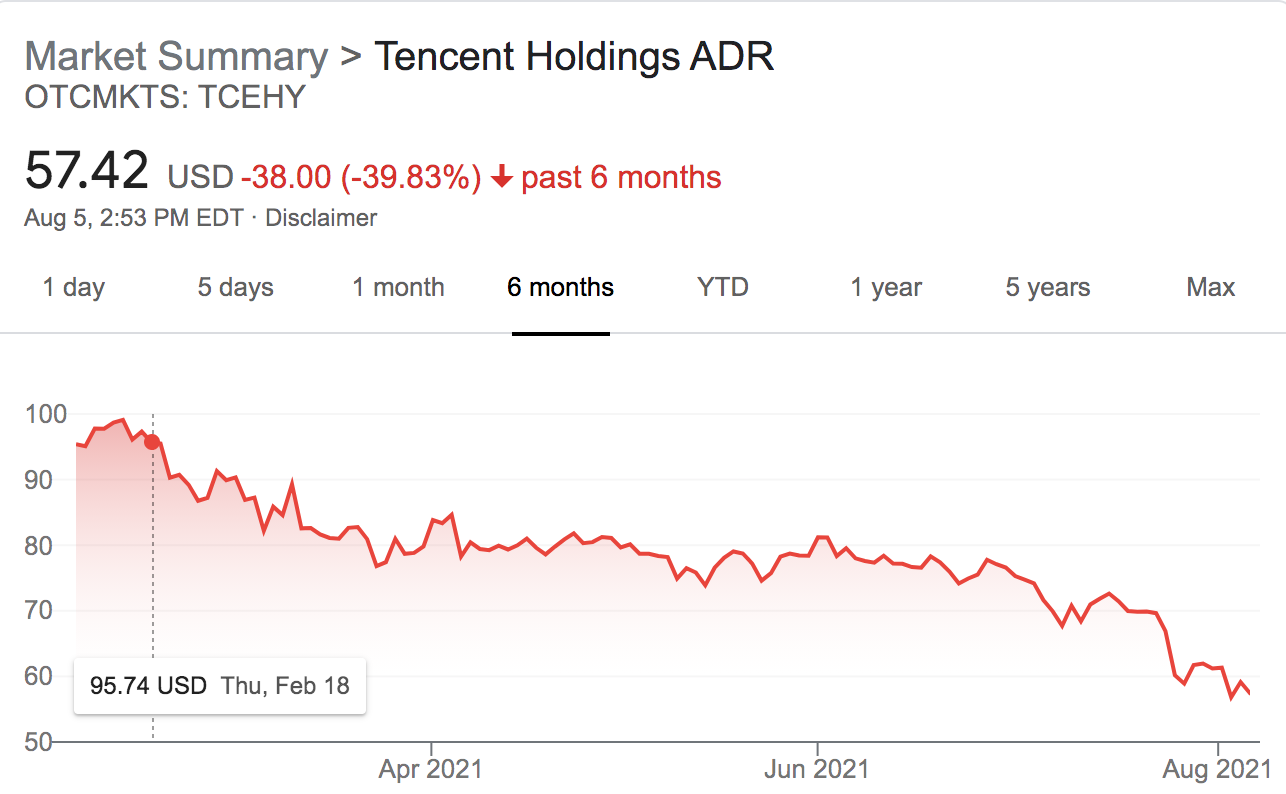
Tencent reopened new user sign-ups for its WeChat messaging app, after having suspended registrations last week for unspecified “technical upgrades.” The company, like many other Chinese tech giants, had to address new regulations from Beijing impacting the tech industry. New rules address how companies handle user data collection and storage, antitrust behavior and other checks on capitalist “excess.” The gaming industry is now worried it’s next to be impacted, with regulations that would restrict gaming for minors to fight addiction.
WhatsApp is adding a new feature that will allow users to send photos and videos that disappear after a single viewing. The Snapchat-inspired feature, however, doesn’t alert you if the other person takes a screenshot — as Snap’s app does. So it may not be ideal for sharing your most sensitive content.
Telegram’s update expands group video calls to support up to 1,000 viewers. It also announced video messages can be recorded in higher quality and can be expanded, regular videos can be watched at 0.5 or 2x speed, screen sharing with sound is available for all video calls, including 1-on-1 calls, and more.
Streaming & Entertainment
American Airlines added free access to TikTok aboard its Viasat-equipped aircraft. Passengers will be able to watch the app’s videos for up to 30 minutes for free and can even download the app if it’s not already installed. After the free time, they can opt to pay for Wi-Fi to keep watching. Considering how easy it is to fall into multi-hour TikTok viewing sessions without knowing it, the addition of the addictive app could make long plane rides feel shorter. Or at least less painful.
Chinese TikTok rival Kuaishou saw stocks fall by more than 15% in Hong Kong, the most since its February IPO. The company is another victim of an ongoing market selloff triggered by increasing investor uncertainty related to China’s recent crackdown on tech companies. Beijing’s campaign to rein in tech has also impacted Tencent, Alibaba, Jack Ma’s Ant Group, food delivery company Meituan and ride-hailing company Didi. Also related, Kuaishou shut down its controversial app Zynn, which had been paying users to watch its short-form videos, including those stolen from other apps.
Twitch overtook YouTube in consumer spending per user in April 2021, and now sees $6.20 per download as of June compared with YouTube’s $5.60, Sensor Tower found.
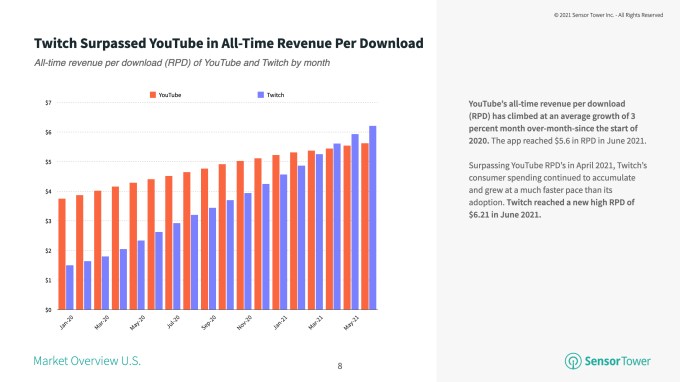
Image Credits: Sensor Tower
Spotify confirmed tests of a new ad-supported tier called Spotify Plus, which is only $0.99 per month and offers unlimited skips (like free users get on the desktop) and the ability to play the songs you want, instead of only being forced to use shuffle mode.
The company also noted in a forum posting that it’s no longer working on AirPlay2 support, due to “audio driver compatibility” issues.
Mark Cuban-backed audio app Fireside asked its users to invest in the company via an email sent to creators which didn’t share deal terms. The app has yet to launch.
YouTube kicks off its $100 million Shorts Fund aimed at taking on TikTok by providing creators with cash incentives for top videos. Creators will get bonuses of $100 to $10,000 based on their videos’ performance.
Dating
Match Group announced during its Q2 earnings it plans to add to several of the company’s brands over the next 12 to 24 months audio and video chat, including group live video, and other livestreaming technologies. The developments will be powered by innovations from Hyperconnect, the social networking company that this year became Match’s biggest acquisition to date when it bought the Korean app maker for a sizable $1.73 billion. Since then, Match was spotted testing group live video on Tinder, but says that particular product is not launching in the near-term. At least two brands will see Hyperconnect-powered integrations in 2021.
Photos
The Photo & Video category on U.S. app stores saw strong growth in the first half of the year, a Sensor Tower report found. Consumer spend among the top 100 apps grew 34% YoY to $457 million in Q2 2021, with the majority of the revenue (83%) taking place on iOS.
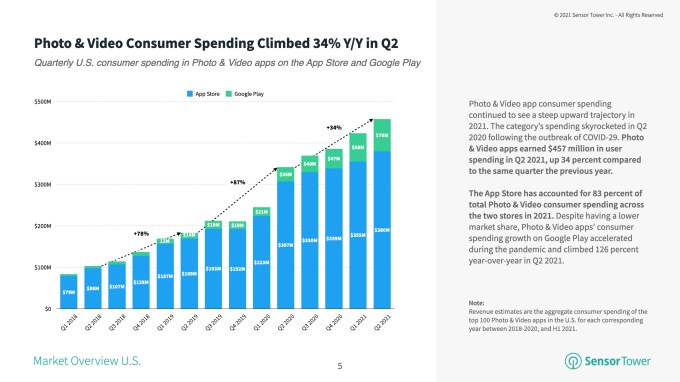
Image Credits: Sensor Tower
Gaming
Epic Games revealed the host of its in-app Rift Tour event is Ariana Grande, in the event that runs August 6-8.
Pokémon GO influencers threatened to boycott the game after Niantic removed the COVID safety measures that had allowed people to more easily play while social distancing. Niantic’s move seemed ill-timed, given the Delta variant is causing a new wave of COVID cases globally.
Health & Fitness
Apple kicked out an app called Unjected from the App Store. The new social app billed itself as a community for the unvaccinated, allowing like-minded users to connect for dating and friendships. Apple said the app violated its policies for COVID-19 content.
Google Pay expanded support for vaccine cards. In Australia, Google’s payments app now allows users to add their COVID-19 digital certification to their device for easy access. The option is available through Google’s newly updated Passes API which lets government agencies distribute digital versions of vaccine cards.
COVID Tech Connect, a U.S. nonprofit initially dedicated to collecting devices like phones and tablets for COVID ICU patients, has now launched its own app. The app, TeleHome, is a device-agnostic, HIPAA-compliant way for patients to place a video call for free at a time when the Delta variant is again filling ICU wards, this time with the unvaccinated — a condition that sometimes overlaps with being low-income. Some among the working poor have been hesitant to get the shot because they can’t miss a day of work, and are worried about side effects. Which is why the Biden administration offered a tax credit to SMBs who offered paid time off to staff to get vaccinated and recover.
Popular journaling app Day One, which was recently acquired by WordPress.com owner Automattic, rolled out a new “Concealed Journals” feature that lets users hide content from others’ viewing. By tapping the eye icon, the content can be easily concealed on a journal by journal basis, which can be useful for those who write to their journal in public, like coffee shops or public transportation.
Edtech
Recently IPO’d language learning app Duolingo is developing a math app for kids. The company says it’s still “very early” in the development process, but will announce more details at its annual conference, Duocon, later this month.
Educational publisher Pearson launched an app that offers U.S. students access to its 1,500 titles for a monthly subscription of $14.99. the Pearson+ mobile app (ack, another +), also offers the option of paying $9.99 per month for access to a single textbook for a minimum of four months.
News & Reading
Quora jumps into the subscription economy. Still not profitable from ads alone, Quora announced two new products that allow its expert creators to monetize their content on its service. With Quora+ ($5/mo or $50/yr), subscribers can pay for any content that a creator paywalls. Creators can choose to enable a adaptive paywall that will use an algorithm to determine when to show the paywall. Another product, Spaces, lets creators write paywalled publications on Quora, similar to Substack. But only a 5% cut goes to Quora, instead of 10% on Substack.
Utilities
Google Maps on iOS added a new live location-sharing feature for iMessage users, allowing them to more easily show your ETA with friends and even how much battery life you have left. The feature competes with iMessage’s built-in location-sharing feature, and offers location sharing of 1 hour up to 3 days. The app also gained a dark mode.
Security & Privacy
Controversial crime app Citizen launched a $20 per month “Protect” service that includes live agent support (who can refer calls to 911 if need be). The agents can gather your precise location, alert your designated emergency contacts, help you navigate to a safe location and monitor the situation until you feel safe. The system of live agent support is similar to in-car or in-home security and safety systems, like those from ADT or OnStar, but works with users out in the real world. The controversial part, however, is the company behind the product: Citizen has been making headlines for launching private security fleets outside law enforcement, and recently offered a reward in a manhunt for an innocent person based on unsubstantiated tips.
Funding and M&A
 Square announced its acquisition of the “buy now, pay later” giant AfterPay in a $29 billion deal that values the Australian firm at more than 30% higher than the stock’s last closing price of AUS$96.66. AfterPay has served over 16 million customers and nearly 100,000 merchants globally, to date, and comes at a time when the BNPL space is heating up. Apple has also gotten into the market recently with an Affirm partnership in Canada.
Square announced its acquisition of the “buy now, pay later” giant AfterPay in a $29 billion deal that values the Australian firm at more than 30% higher than the stock’s last closing price of AUS$96.66. AfterPay has served over 16 million customers and nearly 100,000 merchants globally, to date, and comes at a time when the BNPL space is heating up. Apple has also gotten into the market recently with an Affirm partnership in Canada.
 Gaming giant Zynga acquired Chinese game developer StarLark, the team behind the mobile golf game Golf Rival, from Betta Games for $525 million in both cash and stock. Golf Rival is the second-largest mobile golf game behind Playdemic’s Golf Clash, and EA is in the process of buying that studio for $1.4 billion.
Gaming giant Zynga acquired Chinese game developer StarLark, the team behind the mobile golf game Golf Rival, from Betta Games for $525 million in both cash and stock. Golf Rival is the second-largest mobile golf game behind Playdemic’s Golf Clash, and EA is in the process of buying that studio for $1.4 billion.
 U.K.-based Humanity raised an additional $2.5 million for its app that claims to help slow down aging, bringing the total raise to date to $5 million. Backers include Calm’s co-founders, MyFitness Pal’s co-founder and others in the health space. The app works by benchmarking health advice against real-world data, to help users put better health practices into action.
U.K.-based Humanity raised an additional $2.5 million for its app that claims to help slow down aging, bringing the total raise to date to $5 million. Backers include Calm’s co-founders, MyFitness Pal’s co-founder and others in the health space. The app works by benchmarking health advice against real-world data, to help users put better health practices into action.
 YELA, a Cameo-like app for the Middle East and South Asia, raised $2 million led by U.S. investors that include Tinder co-founder Justin Mateen and Sean Rad, general partner of RAD Fund. The app is focusing on signing celebrities in the regions it serves, where smartphone penetration is high and over 6% of the population is under 35.
YELA, a Cameo-like app for the Middle East and South Asia, raised $2 million led by U.S. investors that include Tinder co-founder Justin Mateen and Sean Rad, general partner of RAD Fund. The app is focusing on signing celebrities in the regions it serves, where smartphone penetration is high and over 6% of the population is under 35.
 London-based health and wellness app maker Palta raised a $100 million Series B led by VNV Global. The company’s products include Flo.Health, Simple Fasting, Zing Fitness Coach and others, which reach a combined 2.4 million active, paid subscribers. The funds will be used to create more mobile subscription products.
London-based health and wellness app maker Palta raised a $100 million Series B led by VNV Global. The company’s products include Flo.Health, Simple Fasting, Zing Fitness Coach and others, which reach a combined 2.4 million active, paid subscribers. The funds will be used to create more mobile subscription products.
 Emoji database and Wikipedia-like site Emojipedia was acquired by Zedge, the makers of a phone personalization app offering wallpapers, ringtones and more to 35 million MAUs. Deal terms weren’t disclosed. Emojipedia says the deal provides it with more stability and the opportunity for future growth. For Zedge, the deal provides
Emoji database and Wikipedia-like site Emojipedia was acquired by Zedge, the makers of a phone personalization app offering wallpapers, ringtones and more to 35 million MAUs. Deal terms weren’t disclosed. Emojipedia says the deal provides it with more stability and the opportunity for future growth. For Zedge, the deal provides ….um, a popular web resource it thinks it can better monetize, we suspect.
….um, a popular web resource it thinks it can better monetize, we suspect.
 Mental health app Revery raised $2 million led by Sequoia Capital India’s Surge program for its app that combines cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia with mobile gaming concepts. The company will focus on other mental health issues in the future.
Mental health app Revery raised $2 million led by Sequoia Capital India’s Surge program for its app that combines cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia with mobile gaming concepts. The company will focus on other mental health issues in the future.
 London-based Nigerian-operating fintech startup Kuda raised a $55 million Series B, valuing its mobile-first challenger bank at $500 million. The inside round was co-led by Valar Ventures and Target Global.
London-based Nigerian-operating fintech startup Kuda raised a $55 million Series B, valuing its mobile-first challenger bank at $500 million. The inside round was co-led by Valar Ventures and Target Global.
 Vietnamese payments provider VNLife raised $250 million in a round led by U.S.-based General Atlantic and Dragoneer Investment Group. PayPal Ventures and others also participated. The round values the business at over $1 billion.
Vietnamese payments provider VNLife raised $250 million in a round led by U.S.-based General Atlantic and Dragoneer Investment Group. PayPal Ventures and others also participated. The round values the business at over $1 billion.
Downloads
Mastodon for iPhone
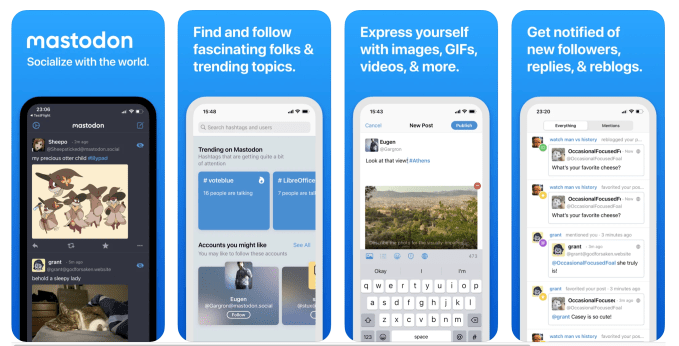
Fans of decentralized social media efforts now have a new app. The nonprofit behind the open source decentralized social network Mastodon released an official iPhone app, aimed at making the network more accessible to newcomers. The app allows you to find and follow people and topics; post text, images, GIFs, polls, and videos; and get notified of new replies and reblogs, much like Twitter.
Xingtu
TikTok users are teaching each other how to switch over to the Chinese App Store in order to get ahold of the Xingtu app for iOS. (An Android version is also available.) The app offers advanced editing tools that let users edit their face and body, like FaceTune, apply makeup, add filters and more. While image-editing apps can be controversial for how they can impact body acceptance, Xingtu offers a variety of artistic filters which is what’s primarily driving the demand. It’s interesting to see the lengths people will go to just to get a few new filters for their photos — perhaps making a case for Instagram to finally update its Post filters instead of pretending no one cares about their static photos anymore.
Tweets
Facebook still dominating top charts, but not the No. 1 spot:
Not cool, Apple:
This user acquisition strategy:
Maybe Stories don’t work everywhere:

Powered by WPeMatico





 Square
Square  U.K.-based Humanity
U.K.-based Humanity  ….um, a popular web resource it thinks it can better monetize, we suspect.
….um, a popular web resource it thinks it can better monetize, we suspect.