AMD unveils the 12-core Ryzen 9 3900X, at half the price of Intel’s competing Core i9 9920X chipset
AMD CEO Lisa Su gave the Computex keynote in Taipei today, the first time the company has been invited to do so (the event officially starts tomorrow). During the presentation, AMD unveiled news about its chips and graphics processors that will increase pressure on competitors Intel and Nvidia, both in terms of pricing and performance.
Chips
All new third-generation Ryzen CPUs, the first with 7-nanometer desktop chips, will go on sale on July 7. The showstopper of Su’s keynote was the announcement of AMD’s 12-core, 24-thread Ryzen 9 3900x chip, the flagship of its third-generation Ryzen family. It will retail starting at $499, half the price of Intel’s competing Core i9 9920X chipset, which is priced at $1,189 and up.
The 3900x has 4.6 Ghz boost speed and 70 MB of total cache and uses 105 watts of thermal design power (versus the i9 9920x’s 165 watts), making it more efficient. AMD says that in a Blender demo against Intel i9-9920x, the 3900x finished about 18 percent more quickly.
Here’s an exclusive #COMPUTEX2019 look at the newest edition to the Ryzen family, the 12 core/24 thread 3rd Gen AMD Ryzen 9 3900X processor. https://t.co/OgLHoqWv9T pic.twitter.com/75FzfpdiKx
— AMD Ryzen (@AMDRyzen) May 27, 2019
Starting prices for other chips in the family are $199 for the 6-core, 12-thread 3600; $329 for the 8-core, 16-thread Ryzen 3700x (with 4.4 Ghz boost, 36 MB of total cache and a 65 watt TDP); and $399 for the 8-core, 16-thread Ryzen 3800X (4.5 Ghz, 32MB cache, 105w).
GPUs
AMD also revealed that its first Navi graphics processor units will be the Radeon RX 5000 series. Pricing is being closely watched because it may pressure Nvidia to bring down prices on competing products. AMD announced that the GPUs will be available in July, but more details, including pricing, performance and new features, won’t be announced until E3 next month in Los Angeles.
Introducing the world’s first “Navi” gaming GPU family based on the all new RDNA gaming architecture: the AMD Radeon RX 5700 series. Learn more from #COMPUTEX2019: https://t.co/xwexmdDMin pic.twitter.com/rY2dAsq52l
— AMD (@AMD) May 27, 2019
Data processors
AMD announced that its EPYC Rome data center processors, first demoed at CES in January, will launch next quarter, one quarter earlier than previously anticipated, to compete with Intel’s Cascade Lake. AMD says that during a benchmark test, EPYC Rome performed twice as fast as Cascade Lake.
AMD CEO @LisaSu just gave the first public competitive demonstration of a 2nd Gen AMD #EPYC server platform outperforming the competition in a NAMD Apo1 v2.12 benchmark test by more than 2x. #COMPUTEX2019 https://t.co/ZHmrqBigjB pic.twitter.com/HQI5EPLmFf
— AMD EPYC (@AMDServer) May 27, 2019
Powered by WPeMatico
These ‘microbe-grown’ headphones could be the future of sustainable electronics
The culture of planned obsolescence in electronics produces a huge amount of toxic waste unlikely to go anywhere but a landfill for the next millennium or so. Nature produces some of the strongest and most versatile substances we’ve ever encountered, so why not use them instead? That’s what Finnish design house Aivan has attempted with this concept pair of headphones made from fungus, bioplastics, and other natural materials.
The idea was to replace everything they could with naturally-derived materials, of which there’s a great variety — but some can be a bit difficult to get your hands on.
As Dezeen reports, the Korvaa headset, everything you see here is natural in origin, although that doesn’t mean they just picked it up in the forest.
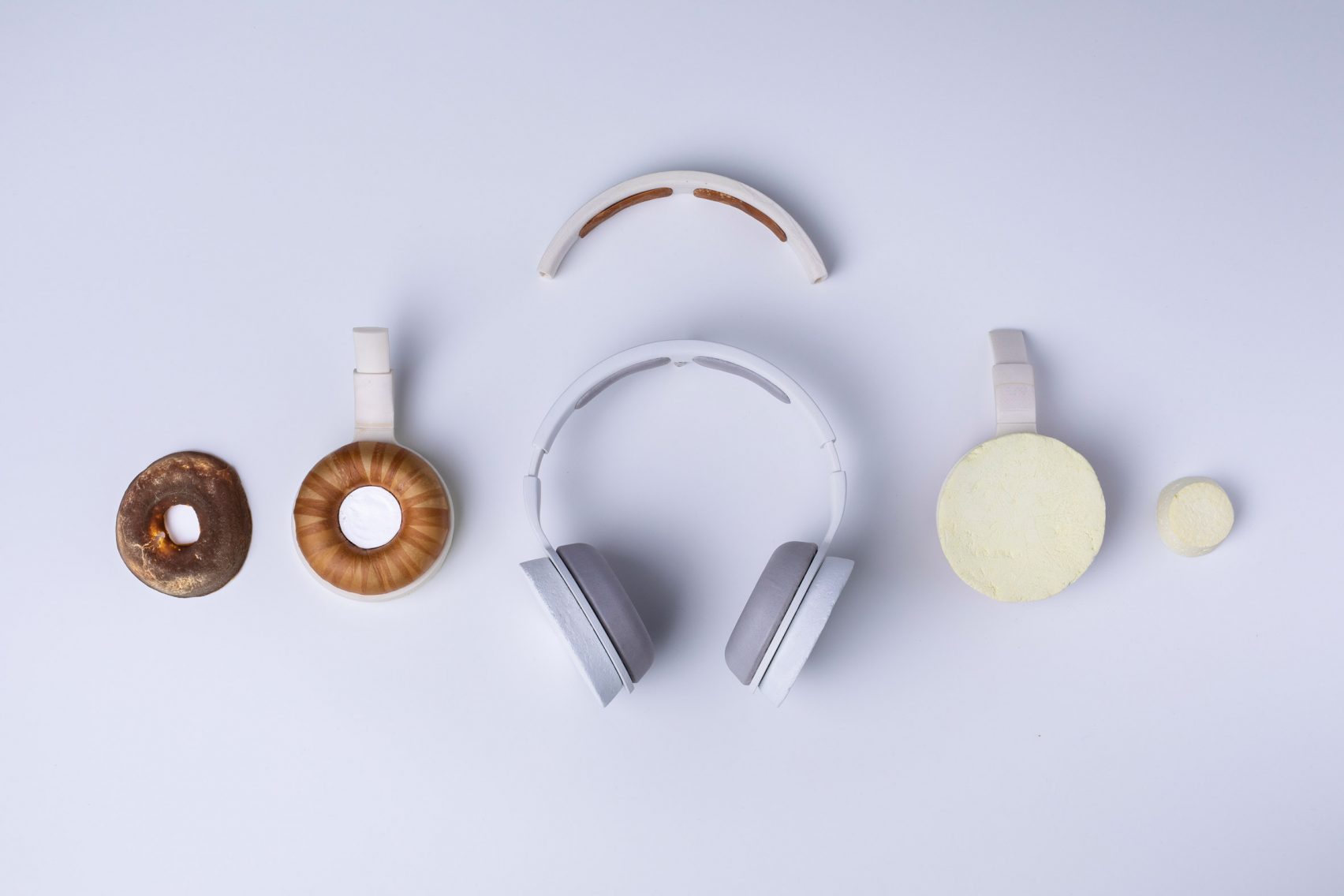 The main structure of the headphones is 3D-printed, using a bioplastic created as a byproduct of yeast processing lactic acid. The polylactic acid polymer is strong but flexible enough to be used as the crown and cup shell.
The main structure of the headphones is 3D-printed, using a bioplastic created as a byproduct of yeast processing lactic acid. The polylactic acid polymer is strong but flexible enough to be used as the crown and cup shell.
The padded earpieces are made from a protein known as hydrophobin that, like artificial foam, is made up of many tiny bubbles — but these are produced by a fungus and reinforced with plant cellulose. They’re covered with mycelium, another fungus-derived material that’s leathery and flexible.
And on top of those would be a mesh created by spinning out synthetic spider silk — something Bolt Threads is trying to do at scale for ordinary garments.
To be clear, these headphones don’t work — they’re just a prototype or concept product right now. But the point wasn’t to create a fully functioning replacement for your existing headphones. Rather the idea is to show that those headphones don’t need to be made, as they are now, entirely of non-biodegradable materials.
“This was certainly only a surface scratch into where biology-engineered materials are going, and what we can do with them in the future,” one of the group’s designers, Thomas Tallqvist, told Dezeen.
The headphones will be on display at a couple design shows in Finland — here’s hoping someone from Audio Technica or Sennheiser drops by and gets inspired.
Powered by WPeMatico
As the term ‘unicorn’ goes broke from overuse, what’s actually rare?
Contributor
On Wednesday a few unicorns were born. You’ve already forgotten their names if you learned them at all (Tip: It was Marqeta and Ivalua.)
Don’t worry, I’m not cross with you. It’s merely that there are so many unicorns in the market today — they stampede by the hundred in 2019 — that they are impossible to keep tabs on.
In fact, so many firms now make the cut that we’ve gotten into the habit of torturing the word “unicorn” to mean more than what it was originally tasked to describe. As we wrote recently, there are undercorns now, and decacorns. Toss in minotaurs and horses and the inevitable centacorns and see, we’re all bored.
Paraphrasing Asimov, successive shocks lead to decreasing impact. So has the phrase unicorn lost all meaning. As I joked the other day, it now mostly means “middle-aged startup.” Even our redefinition of the word “startup” allowed for firms to be worth several billion and still claim the title, though that might have been an error.
In today’s world of super- and hypergiant rounds, it’s not impossible to put together a unicorn. And people sure are doing it.
So, now what
“Unicorn” is now only useful as a valuation-descriptor. It no longer implies something rare.
So, what we need is either a redefinition of a unicorn to make it rarer… or, we need an entirely new concept. Regardless of if we change up what “unicorn” itself means, or invent a new word, it has become clear what we need to add to the mix to really tease out the exceptional companies from the merely very good.
Profits.
Zoom, before its IPO, was profitable and growing like hell. TransferWise, we recently learned, is profitable and growing as well. Can you name another company worth $1 billion or more that is growing and profitable? I can’t. That means they are rare.
TechCrunch’s Kate Clark and I chatted about this on Equity, and this was our general point of agreement (her tweet here). Profit is what really makes you rare. Not just a high valuation. There’s enough money flying around to print the latter by the dozen. Earning the former? Now’s that’s legendary and hard to find.
Just like a unicorn.
Powered by WPeMatico
The savage genius of SoftBank funding competitors
Venture capitalists aren’t supposed to make their portfolio companies battle to the death. There’s a long-standing but unofficial rule that investors shouldn’t fund multiple competitors in the same space. Conflicts of interest could arise, information about one startup’s strategy could be improperly shared with the other, and the companies could become suspicious of advice provided by their investors. That leads to problems down the line for VCs, as founders may avoid them if they fear the firm might fund their rival down the line.
SoftBank shatters that norm with its juggernaut $100 billion Vision Fund plus its Innovation Fund. The investor hasn’t been shy about funding multiple sides of the same fight.
The problem is that SoftBank’s power distorts the market dynamics. Startups might take exploitative deals from the firm under the threat that they’ll be outspent whoever is willing to take the term sheet. That can hurt employees, especially ones joining later, who might have a reduced chance for a meaningful exit. SoftBank could advocate for mergers, acquisitions, or product differentiation that boost its odds of reaping a fortune at the expense of the startups’ potential.
Powered by WPeMatico
This is one smart device that every urban home could use
Living in a dense urban environment brings many startup-fuelled conveniences, be it near instant delivery of food — or pretty much whatever else you fancy — to a whole range of wheels that can be hopped on (or into) to whisk you around at the tap of an app.
But the biggest problem afflicting city dwellers is not some minor inconvenience. It’s bad, poor, terrible, horrible, unhealthy air. And there’s no app to fix that.
Nor can hardware solve this problem. But smart hardware can at least help.
For about a month I’ve been road-testing a wi-fi connected air purifier made by Swedish company, Blueair. It uses an Hepa filtration system combined with integrated air quality sensors to provide real-time in-app feedback which can be reassuring or alert you to unseen problems.
Flip to the bottom of this article for a speed take or continue reading for the full review of the Blueair Classic 480i with dual filters to reduce dust, smoke and pollen
Review
If you’re even vaguely environmentally aware it’s fascinating and not a little horrifying to see how variable the air quality is inside your home. Everyday stuff like cooking, cleaning and changing the sheets can cause drastic swings in PM 2.5 and tVOC levels. Aka very small particles such as fine dust, smoke, odours and mite feces; and total volatile organic compounds, which refers to hundreds of different gases emitted by certain solids and liquids — including stuff humans breathe out by also harmful VOCs like formaldehyde.
What you learn from smart hardware can be not just informative but instructive. For instance I’ve switched to a less dusty cat litter after seeing how quickly the machine’s fan stepped up a gear after clearing the litter tray. I also have a new depth of understanding of quite how much pollution finds its way into my apartment when the upstairs neighbour is having a rooftop BBQ. Which makes it doubly offensive I wasn’t invited.
Though, I must admit, I’ve yet to figure out a diplomatic way to convince him to rethink his regular cook-out sessions. Again, some problems can’t be fixed by apps. Meanwhile city life means we’re all, to a greater or lesser degree, adding to the collectively polluted atmosphere. Changing that requires new politics.
You cannot hermetically seal your home against outdoor air pollution. It wouldn’t make for a healthy environment either. Indoor spaces must be properly ventilated. Adequate ventilation is also of course necessary to control moisture levels to prevent other nasty issues like mould. And using this device I’ve watched as opening a window almost instantly reduced tVOC levels.
Pretty much every city resident is affected by air pollution, to some degree. And it’s a heck of a lot harder to switch your home than change your brand of cat litter. But even on that far less fixable front, having an air quality sensor indoors can be really useful — to help you figure out the best (and worst) times to air out the house. I certainly won’t be opening the balcony doors on a busy Saturday afternoon any time soon, for example.
Blueair sells a range of air purifiers. The model I’ve been testing, the Blueair Classic 480i, is large enough to filter a room of up to 40m2. It includes filters capable of filtering both particulate matter and traffic fumes (aka its “SmokeStop” filter). The latter was important for me, given I live near a pretty busy road. But the model can be bought with just a particle filter if you prefer. The dual filtration model I’m testing is priced at €725 for EU buyers.
Point number one is that if you’re serious about improving indoor air quality the size of an air purifier really does matter. You need a device with a fan that’s powerful enough to cycle all the air in the room in a reasonable timeframe. (Blueair promises five air changes per hour for this model, per the correct room size).
So while smaller air filter devices might look cute, if a desktop is all the space you can stretch to you’d probably be better off getting a few pot plants.
Blueair’s hardware also has software in the mix too, of course. The companion Blueair Friend app serves up the real-time feedback on both indoor air quality and out. The latter via a third party service whose provider can vary depending on your location. Where I live in Europe it’s powered by BreezoMeter.
This is a handy addition for getting the bigger picture. If you find you have stubbornly bad air quality levels indoors and really can’t figure out why, most often a quick tab switch will confirm local pollution levels are indeed awful right now. It’s likely not just you but the whole neighbourhood suffering.
Dirty cities
From Asia to America the burning of fossil fuels has consequences for air quality and health that are usually especially pronounced in dense urban environments where humans increasingly live. More than half the world’s population now lives in urban areas — with the UN predicting this will grow to around 70% by 2050.
In Europe, this is already true for more than 70% of the population which makes air pollution a major concern in many regional cities.
Growing awareness of the problem is beginning to lead to policy interventions — such as London’s ultra low emission charging zone and car free Sundays one day a month in Paris’ city center. But EU citizens are still, all too often, stuck sucking in unhealthy air.
London’s toxic air is an invisible killer.
We launched the world’s first Ultra Low Emission Zone to cut air pollution. Since then, there have been on average 9400 fewer polluting vehicles on our streets every day. #LetLondonBreathe #ULEZ pic.twitter.com/0mYcIGi1xP
— Mayor of London (@MayorofLondon) May 23, 2019
Last year six EU nations, including the UK, France and Germany, were referred to the highest court in Europe for failing to tackle air pollution — including illegally high levels of nitrogen dioxide produced by diesel-powered vehicles.
Around one in eight EU citizens who live in an urban area is exposed to air pollutant levels that exceed one or more of the region’s air quality standards, according to a briefing note published by the European Environment Agency (EEA) last year.
It also said up to 96% of EU urban citizens are exposed to levels of one or more air pollutants deemed damaging to health when measured against the World Health Organization’s more stringent guidelines.
There are multiple and sometimes interlinked factors impacting air quality in urban environments. Traffic fumes is a very big one. But changes in meteorological conditions due to climate change are also expected to increase certain concentrations of air pollutants. While emissions from wildfires is another problem exacerbated by drought conditions which are linked to climate change that can also degrade air quality in nearby cities.
Action to tackle climate change continues to lag far behind what’s needed to put a check on global warming. Even as far too little is still being done in most urban regions to reduce vehicular emissions at a local level.
In short, this problem isn’t going away anytime soon — and all too often air quality is still getting worse.
At the same time health risks from air pollution are omnipresent and can be especially dangerous for children. A landmark global study of the impact of traffic fumes on childhood asthma, published recently in the Lancet, estimates that four million children develop the condition every year primarily as a result of nitrogen dioxide air pollution emitted by vehicles.
The majority (64%) of these new cases were found to occur in urban centres — increasing to 90% when factoring in surrounding suburban areas.
The study also found that damage caused by air pollution is not limited to the most highly polluted cities in China and India. “Many high-income countries have high NO2 exposures, especially those in North America, western Europe, and Asia Pacific,” it notes.
The long and short of all this is that cities the world over are going to need to get radically great at managing air quality — especially traffic emissions — and fast. But, in the meanwhile, city dwellers who can’t or don’t want to quit the bright lights are stuck breathing dirty air. So it’s easy to imagine consumer demand growing for in-home devices that can sense and filter pollutants as urbanities try to find ways to balance living in a city with reducing their exposure to the bad stuff.
Cleaner air
That’s not to say that any commercial air purifier will be able to provide a complete fix. The overarching problem of air pollution is far too big and bad for that. A true fix would demand radical policy interventions, such as removing all polluting vehicles from urban living spaces. (And there’s precious little sign of anything so radical on the horizon.)
But at least at an individual home level, a large air purifier with decent filtration technology should reduce your exposure to pollution in the place you likely spend the most time.
If, as the Blueair Classic 480i model does, the filtration device also includes embedded sensors to give real-time feedback on air quality it can further help you manage pollution risk — by providing data so you can better understand the risks in and around your home and make better decisions about, for instance, when to open a window.
“Air quality does always change,” admits Blueair’s chief product officer, Jonas Holst, when we chat. “We cannot promise to our consumers that you will always have super, super, clean air. But we can promise to consumers that you will always have a lot cleaner air by having our product — because it depends on what happens around you. In the outdoor, by your neighbours, if you’re cooking, what your cat does or something. All of those things impact air quality.
“But by having high speeds, thanks to the HepaSilent technology that we use, we can make sure that we always constantly fight that bombardment of pollutants.”
On the technology front, Blueair is using established filtration technology — Hepa and active carbon filters to remove particular matter and gaseous pollutants — but with an ionizing twist (which it brands ‘HepaSilent’).
This involves applying mechanical and electrostatic filtration in combination to enhance performance of the air purifier without boosting noise levels or requiring large amounts of energy to run. Holst dubs it one of the “core strengths” of the Blueair product line.
“Mechanical filtration just means a filter [plus a fan to draw the air through it]. We have a filter but by using the ionization chamber we have inside the product we can boost the performance of the filter without making it very, very dense. And by doing that we can let more air through the product and simply then clean more air faster,” he explains.
“It’s also something that is constantly being developed,” he adds of the firm’s Hepa + ionizing technology, which it’s been developing in its products for some 20 years. “We have had many developments of this technology since but the base technical structure is there in the combination between a mechanical and electrostatical filtration. That is what allows us to have less noise and less energy because the fan doesn’t work as hard.”
On top of that, in the model I’m testing, Blueair has embedded air quality sensors — which connect via wi-fi to the companion app where the curious user can see real-time plots of things like PM 2.5 and tVOC levels, and start to join the dots between what’s going on in their home and what the machine is sniffing out.
The sensors mean the unit can step up and down the fan speed and filtration level automatically in response to pollution spikes (you can choose it to trigger on particulate matter only, or PM 2.5 and tVOC gaseous compounds, or turn automation off altogether). So if you’re really not at all curious that’s okay too. You can just plug it in, hook it to the wi-fi and let it work.
Sound, energy and sensing smarts in a big package
To give a ballpark of energy consumption for this model, Holst says the Blueair Classic 480i consumes “approximately” the same amount of energy as running a lightbulb — assuming it’s running mostly on lower fan speeds.
As and when the fan steps up in response to a spike in levels of potential pollutants he admits it will consume “a little bit more” energy.
The official specs list the model’s energy consumption at between 15-90 watts.
On the noise front it’s extremely quiet when on the lowest fan setting. To the point of being barely noticeable. You can sleep in the same room and certainly won’t be kept awake.
You will notice when the fan switches up to the second or, especially, the third (max) speed — where it can hit 52 dB(A)). The latter’s rushing air sounds are discernible from a distance, even in another room. But you hopefully won’t be stuck listening to level 3 fan noise for too long, unless you live in a really polluted place. Or, well, unless you run into an algorithmic malfunction (more on that below).
As noted earlier, the unit’s smart sensing capabilities mean fan speed can be set to automatically adjust in response to changing pollution levels — which is obviously the most useful mode to use since you won’t need to keep checking in to see whether or not the air is clean.
You can manually override the automation and fix/switch the fan at a speed of your choice via the app. And as I found there are scenarios where an override is essential. Which we’ll get to shortly.
The unit I was testing, a model that’s around two years old, arrived with instructions to let it run for a week without unplugging so that the machine learning algorithms could configure to local conditions and offer a more accurate read on gases and particles. Holst told us that the U.S. version of the 480i is “slightly updated” — and, as such, this learning process has been eliminated. So you should be able to just plug it in and get the most accurate reads right away.
The company recommends changing the filters every six months to “ensure performance”, or more if you live in a very polluted area. The companion app tracks days (estimated) remaining running time in the form of a days left countdown.
Looks wise, there’s no getting around the Blueair Classic 480i is a big device. Think ‘bedside table’ big.
You’re not going to miss it in your room and it does need a bigger footprint of free space around it so as not to block the air intake and outlet. Something in the region of ~80x60cm. Its lozenge shape helps by ensuring no awkward corners and with finding somewhere it can be parked parallel but not too close to a wall.
There’s not much more to say about the design of this particular model except that it’s thoughtful. The unit has a minimalist look which avoids coming across too much like a piece of ugly office furniture. While its white and gun metal grey hues plus curved flanks help it blend into the background. I haven’t found it to be an eyesore.
A neat flip up lid hides a set of basic physical controls. But once you’ve done the wi-fi set-up and linked it to the companion app you may never need to use these buttons as everything can be controlled in the app.
Real-time pollution levels at your fingertips
Warning: This app can be addictive! For weeks after installing the unit it was almost impossible to resist constantly checking the pollution levels. Mostly because it was fascinating to watch how domestic activity could send one or other level spiking or falling.
As well as PM 2.5 and tVOC pollutants this model tracks temperature and humidity levels. It offers day, week and monthly plots for everything it tracks.
The day view is definitely the most addictive — as it’s where you see instant changes and can try to understand what’s triggering what. So you can literally join the dots between, for example, hearing a street sweeper below your window and watching a rise in PM 2.5 levels in the app right after. Erk!
Though don’t expect a more detailed breakdown of the two pollutant categories; it’s an aggregated mix in both cases. (And some of the gases that make up the tVOC mix aren’t harmful.)
The month tab gives a longer overview which can be handy to spot regular pollution patterns (though the view is a little cramped on less phablet-y smartphone screens).
While week view offers a more recent snapshot if you’re trying to get a sense of your average pollution exposure over a shorter time frame.
That was one feature I thought the app could have calculated for you. But, equally, more granular quantification might risk over-egging the pudding. It would also risk being mislead if the sensor accuracy fails on you. The overarching problem with pollution exposure is that, sadly, there’s only so much an individual can do to reduce it. So it probably makes sense not to calculate your pollution exposure score.
The app could certainly provide more detail than it does but Holst told us the aim is to offer enough info to people who are interested without it being overwhelming. He also said many customers just want to plug it in and let it work, not be checking out daily charts. (Though if you’re geeky you will of course want the data.)
It’s clear there is lots of simplification going, as you’d expect with this being a consumer device, not a scientific instrument. I found the Blueair app satisfied my surface curiosity while seeing ways its utility could be extended with more features. But in the end I get that it’s designed to be an air-suck, not a time-suck, so I do think they’ve got the balance there pretty much right.
There are enough real-time signals to be able to link specific activities/events with changes in air quality. So you can literally watch as the tVOC level drops when you open a window. (Or rises if your neighbor is BBQing… ). And I very quickly learnt that opening a window will (usually) lower tVOC but send PM 2.5 rising — at least where I live in a dusty, polluted city. So, again, cleaner air is all you should expect.
Using the app you can try and figure out, for instance, optimal ventilation timings. I also found having the real-time info gave me a new appreciation for heavy rain — which seemed to be really great for clearing dust out of the air, frequently translating into “excellent” levels of PM 2.5 in the app for a while after.
Here are a few examples of how the sensors reacted to different events — and what the reaction suggests…
Cleaning products can temporarily spike tVOC levels:
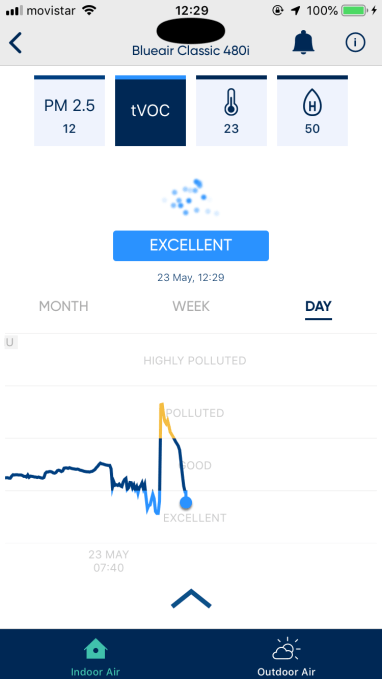
Changing bed sheets can also look pretty disturbing…
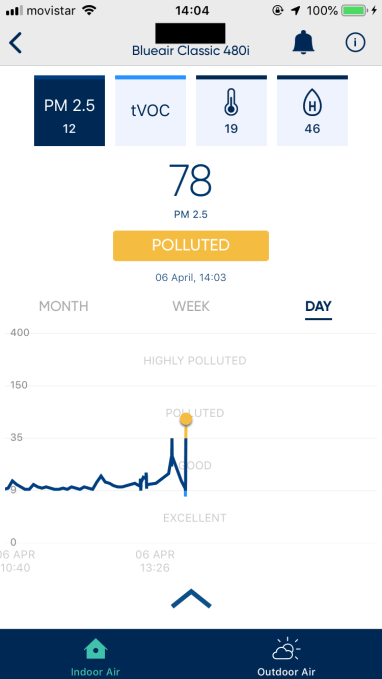
An evening BBQ on a nearby roof terrace appears much, much worse though:
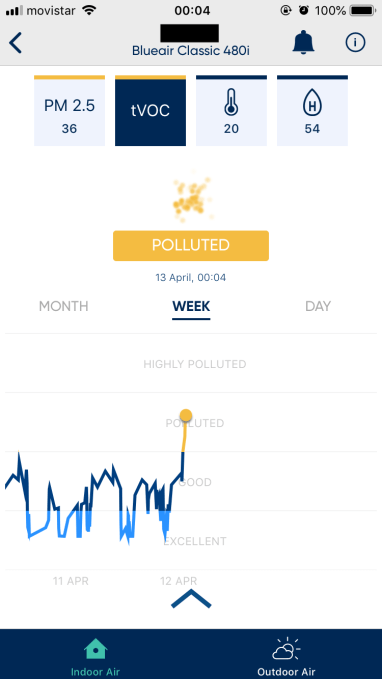
And opening the balcony door to the street on a busy Saturday afternoon is just… insane…
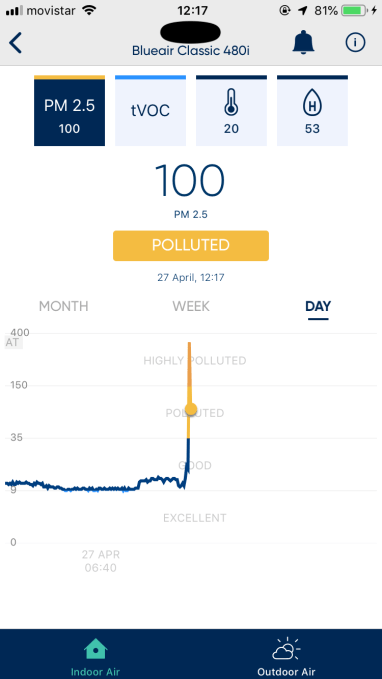
Uh-oh, algorithm malfunction…
After a few minutes of leaving the balcony door open one fateful Saturday afternoon, which almost instantly sent the unit into max fan speed overdrive, I was surprised to find the fan still blasting away an hour later, and then three hours later, and at bedtime, and in the morning. By which point I thought something really didn’t seem right.
The read from the app showed the pollution level had dropped down from the very high spike but it was still being rated as ‘polluted’ — a level which keeps the fan at the top speed. So I started to suspect something had misfired.
This is where being able to switch to manual is essential — meaning I could override the algorithm’s conviction that the air was really bad and dial the fan down to a lower setting.
That override provided a temporary ‘fix’ but the unnaturally elevated ‘pollution’ read continued for the best part of a week. This made it look like the whole sensing capacity had broken. And without the ability to automatically adapt to changing pollution levels the smart air purifier was now suddenly dumb…
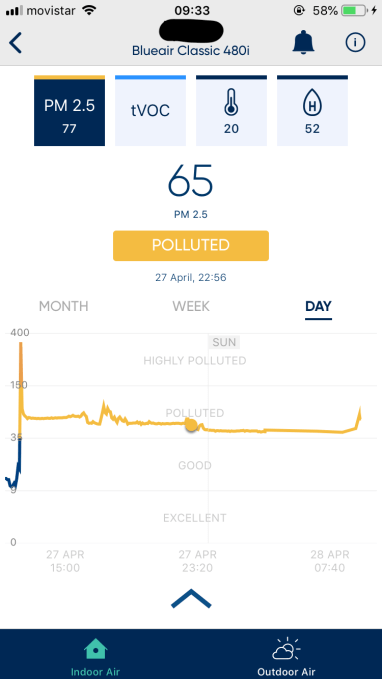
It turned out Blueair has a fix for this sort of algorithmic malfunction. Though it’s not quick.
After explaining the issue to the company, laying out my suspicion that the sensors weren’t reading correctly, it told me the algorithms are programmed to respond to this type of situation by reseting around seven days after the event, assuming the read accuracy hasn’t already corrected itself by then.
Sure enough, almost a week later that’s exactly what happened. Though I couldn’t find anything to explain this might happen in the user manual, so it would be helpful if they include it in a troubleshooting section.
Here’s the month view showing the crazy PM 2.5 spike; the elevated extended (false) reading; then the correction; followed finally by (relatively) normal service…
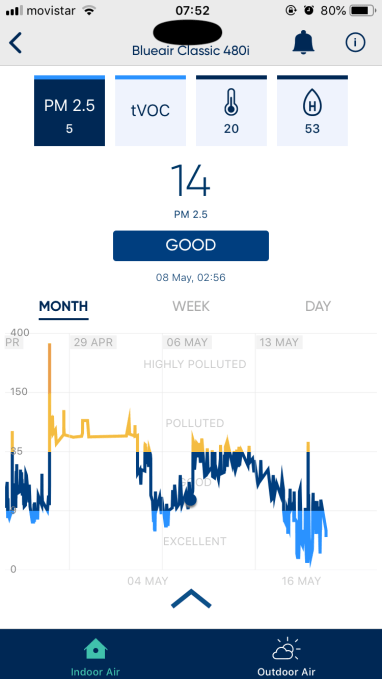
For a while after this incident the algorithms also seemed overly sensitive — and I had to step in again several times to override the top gear setting as its read on pollution levels was back into the yellow without an obvious reason why.
When the level reads ‘polluted’ it automatically triggers the highest fan speed. Paradoxically, this sometimes seems to have the self-defeating effect of appearing to draw dust up into the air — thereby keeping the PM 2.5 level elevated. So at times manually lowering the fan when it’s only slightly polluted can reduce pollution levels quicker than just letting it blast away. Which is one product niggle.
When viewed in the app the sustained elevated pollution level did look pretty obviously wrong — to the human brain at least. So, like every ‘smart’ device, this one also benefits from having human logic involved to complete the loop.
Concluding thoughts after a month’s use
A few weeks on from the first algorithm malfunction the unit’s sensing capacity at first appeared to have stabilized — in that it was back to the not-so-hair-trigger-sensitivity that had been the case prior to balcony-door-gate.
For a while it seemed less prone to have a sustained freak out over relatively minor domestic activities like lifting clean sheets out of the cupboard, as if it had clicked into a smoother operating grove. Though I remained wary of trying the full bore Saturday balcony door.
I thought this period of relative tranquility might signal improved measurement accuracy, the learning algos having been through not just an initial training cycle but a major malfunction plus correction. Though of course there was no way to be sure.
It’s possible there had also been a genuine improvement in indoor air quality — i.e. as a consequence of, for example, better ventilation habits and avoiding key pollution triggers because I now have real-time air quality feedback to act on so can be smarter about when to open windows, where to shake sheets, which type of cat litter to buy and so on.
It’s a reassuring idea. Though one that requires putting your faith in algorithms that are demonstrably far from perfect. Even when they’re functioning they’re a simplification and approximation of what’s really going on. And when they fail, well, they are clearly getting it totally wrong.
Almost bang on the month mark of testing there was suddenly another crazy high PM 2.5 spike.
One rainy afternoon the read surged from ‘good’ to ‘highly polluted’ without any real explanation. I had opened a patio on the other side of the apartment but it does not open onto a street. This time the reading stuck at 400 even with the fan going full blast. So it looked like an even more major algorithm crash…
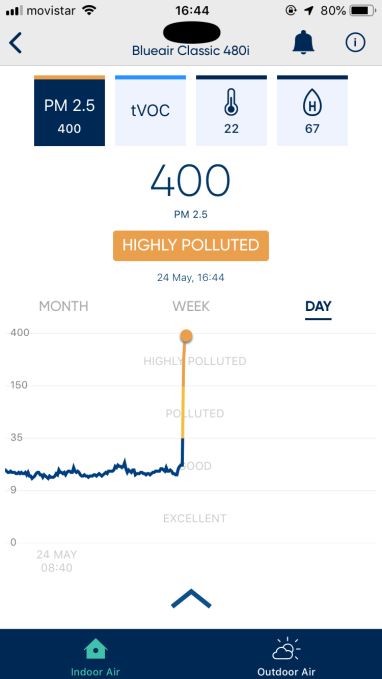
Really clean air is impossible to mistake. Take a walk in the mountains far from civilization and your lungs will thank you. But cleaner air is harder for humans to quantify. Yet, increasingly, we do need to know how clean or otherwise the stuff we’re breathing is, as more of us are packed into cities exposed to each others’ fumes — and because the harmful health impacts of pollution are increasingly clear.
Without radical policy interventions we’re fast accelerating towards a place where we could be forced to trust sensing algorithms to tell us whether what we’re breathing is harmful or not.
Machines whose algorithms are fallible and might be making rough guestimates, and/or prone to sensing malfunctions. And machines that also won’t be able to promise to make the air entirely safe to breathe. Frankly it’s pretty scary to contemplate.
So while I can’t now imagine doing without some form of in-home air purifier to help manage my urban pollution risk — I’d definitely prefer that this kind of smart hardware wasn’t necessary at all.
In Blueair’s case, the company clearly still has work to do to improve the robustness of its sensing algorithms. Operating conditions for this sort of product will obviously vary widely, so there’s loads of parameters for its algorithms to balance.
With all that stuff to juggle it just seems a bit too easy for the sensing function to spin out of control.
10-second take
The good
Easy to set up, thoughtful product design, including relatively clear in-app controls and content which lets you understand pollution triggers to manage risk. Embedded air quality sensors greatly extend the product’s utility by enabling autonomous response to changes in pollution levels. Quiet operation during regular conditions. Choice of automated or manual fan speed settings. Filtration is powerful and since using the device indoor air quality does seem cleaner.
The bad
Sensing accuracy is not always reliable. The algorithms appear prone to being confused by air pressure changes indoors, such as a large window being opened which can trigger unbelievably high pollution readings that lead to an extended period of inaccurate readings when you can’t rely on the automation to work at all. I also found the feedback in the app can sometimes lag. App content/features are on the minimalist side so you may want more detail. When the pollution level is marginal an elevated fan speed can sometimes appear to challenge the efficacy of the filtration as if it’s holding pollution levels in place rather than reducing them.
Bottom line
If you’re looking for a smart air purifier the Blueair Classic 480i does have a lot to recommend it. Quiet operation, ease of use and a tangible improvement in air quality, thanks to powerful filtration. However the accuracy of the sensing algorithms does pose a dilemma. For me this problem has recurred twice in a month. That’s clearly not ideal when it takes a full week to reset. If it were not for this reliability issue I would not hesitate to recommend the product, as — when not going crazy — the real-time feedback it provides really helps you manage a variety of pollution risks in and around your home. Hopefully the company will work on improving the stability of the algorithms. Or at least offer an option in the app so you can manually reset it if/when it does go wrong.
Powered by WPeMatico
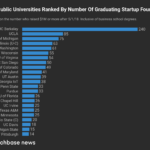
Which public US universities graduate the most funded founders?
Contributor
A lot of students attend public universities to lessen the financial burden of higher education. At last tally, tuition and fees at American public colleges and universities averaged around $6,800 a year, per the federal government. That’s far below the $32,600 mean price tag for private, nonprofit institutions.
Yet when it comes to public universities, the old adage “you get what you pay for” clearly does not apply. Leading public research universities in particular have a track record of turning out enviably knowledgeable and successful graduates. That includes a whole lot of funded startup founders.
And that leads us to our latest ranking. At Crunchbase News, we’ve been tracking the intersection of alumni affiliation and startup funding for the past few years. In a story published earlier this week, we looked at which U.S. universities graduated the most founders of startups that raised $1 million or more in roughly the past year.
For today’s follow-up, we’re focusing exclusively on public universities. Starting with a list of top-ranking research universities, we looked to see which have graduated the highest number of funded founders.
For the most part, we used the same criteria as the public-and-private list, focusing on startups that raised $1 million or more after May, 2018. The public list, however, does not separate out business school grads.
Without further ado, here’s the list:
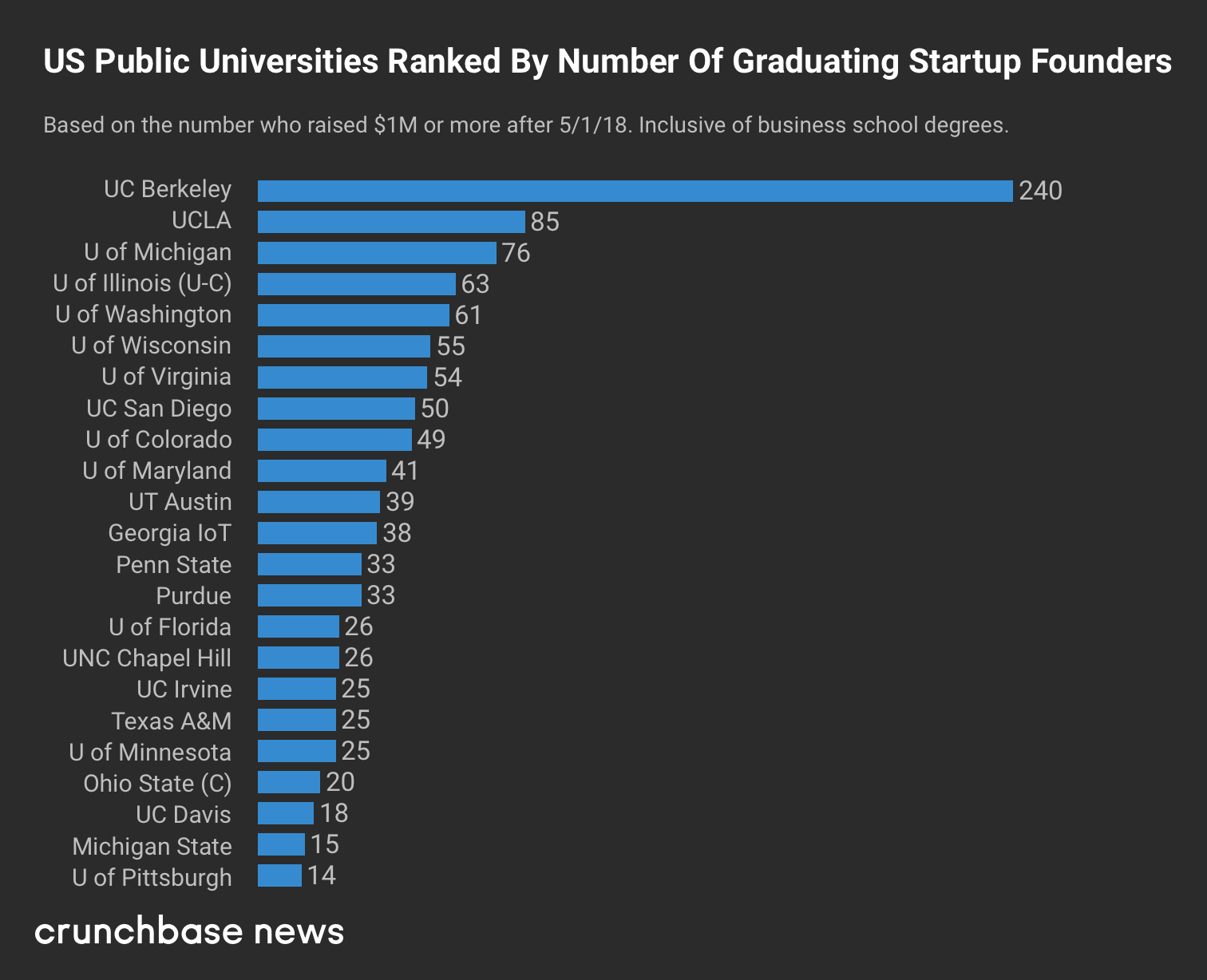
Key findings
Looking at the list above, a few things stand out. First, our top ranker, University of California at Berkeley, is multiples above the rest of the field when it comes to graduating funded founders.
Berkeley is a school that’s generally hard to get into, prominent in STEM and located in the VC-rich San Francisco Bay Area. So seeing it top the list isn’t necessarily surprising. However, the magnitude of its lead — with nearly three times the funded founders of runner-up UCLA — does warrant attention.
Big Midwestern schools also did well, with University of Michigan and University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign nabbing the third and fourth spots.
More broadly, the list includes schools from all U.S. regions, including the East Coast, West Coast, South, Midwest and Southwest. So no particular region has a lock on graduating funded entrepreneurs. That’s also not surprising. But it’s good to have some more numbers to back up that notion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Startups Weekly: VCs are drunk on beverage startups
Hello and welcome back to Startups Weekly, a newsletter published every Saturday that dives into the week’s most noteworthy venture deals, fundraises, M&A transactions and trends. Let’s take a quick moment to catch up. Last week, I wrote about an alternative to venture capital called revenue-based financing and before that, I jotted down some notes on one of VCs’ favorite spaces: cannabis tech. Remember, you can send me tips, suggestions and feedback to kate.clark@techcrunch.com or on Twitter @KateClarkTweets.

This week, I want to share some thoughts — questions, rather — on beverages. Just as my inbox has been full of cannabis-related pitches, it’s also been packed with descriptions of new…drinks. Perhaps the most noted so far is Liquid Death, canned water for the punk rock crowd, because why not? Liquid Death has attracted nearly $2 million in funding from angel investors like Away co-founder Jen Rubio and Twitter co-founder Biz Stone. Before I tell you about a few other up-and-coming beverage makers, I must beg the question: Does the beverage industry need disrupting?
Founders say yes. Why? For one, because millennials, according to various studies, are consuming less alcohol than previous generations and are therefore seeking non-alcoholic beverage alternatives. Enter Seedlip, a non-alcoholic spirits company, for example. Or Haus, launching this summer, an all-natural apéritif distilled from grapes that has a lower alcohol content than most hard liquors. Haus, like any good consumer startup in 2019, is shipped directly to your door.
Beverages are being disrupted, there’s no stopping it. pic.twitter.com/DMEg88t4iO
— Kate Clark (@KateClarkTweets) May 21, 2019
Bev, a canned wine business that recently raised $7 million in seed funding from Founders Fund, thinks marketing in the alcohol industry is the problem. Founder Alix Peabody designed a line of female-focused canned rosé. If you’re wondering why alcohol needs to be gendered in such a way, you’re not alone. Peabody explained most alcohol brands cater to men, and that’s a problem.
“The joke I like to make is there’s a go-to type of alcohol for every type of bro and we just don’t have that for women,” Peabody told TechCrunch earlier this year.
Finally, the wellness movement is taking over, driving VCs toward some odd upstarts. From wellness chat and journaling apps to therapy substitutes to fitness companies, stick wellness in a pitch and investors will take a second look. More Labs, for example, is backed with $8 million in VC funding. The company is readying the launch of Liquid Focus, a biohacking-beverage that claims to “solve modern-day stressors without the negative side effects.” Finally, Elements, “an elevated functional wellness beverage formulated with clinical levels of adaptogens to give your body exactly what it needs in four categories (focus, vitality, calm, and rest) for specific cognitive functions” (damn, what copy), recently launched. It doesn’t appear to be funded yet, but let’s just give it a few months.
There’s more where that came from, but I’m done for now. On to other news.

I almost skipped IPO corner this week because no big-name companies dropped or amended their S-1s or completed a highly anticipated IPO, as has been the case basically every week of 2019. But I decided I better give a quick update on Luckin Coffee’s tough second week on the stock market. Luckin Coffee, if you aren’t familiar, is Starbucks’ Chinese rival. The company raised more than $550 million after pricing at $17 per share a little over a week ago. Immediately the stock skyrocketed 20 percent to a roughly $5 billion market cap; then came concerns of the company’s lofty valuation, major cash burn and uncertain path to profitability. Luckin has dropped around 25 percent since closing its debut trading day. It closed Friday down 3 percent.
Y Combinator, the popular accelerator program and investment firm announced this week that it has promoted longtime partner Geoff Ralston to president. This comes two months after former president Sam Altman stepped down to focus his efforts full-time on OpenAI. The promotion of Ralston is an unsurprising choice for YC, an organization that employs roughly 60 people, many of whom have been affiliated with it in one way or another for years.
Automattic acquires subscription payment company Prospress
Shopify quietly acquires Handshake, an e-commerce platform for B2B wholesale purchasing
Streem buys Selerio in an effort to boost its AR conferencing tech
As Amex scoops up Resy, a look at its acquisition history
The Los Angeles ecosystem is $76 million stronger this week as Fika Ventures, a seed-stage venture capital firm, announced its sophomore investment fund. Fika invests roughly half of its capital exclusively in startups headquartered in LA, with a particular fondness for B2B, enterprise and fintech companies. The firm was launched in 2017 by general partners Eva Ho and TX Zhuo, formerly of Susa Ventures and Karlin Ventures, respectively. The pair raised $41 million for the debut effort, opting to nearly double that number the second time around as a means to participate in more follow-on fundings.
DoorDash raises $600M at a $12.7B valuation
TransferWise completes $292M secondary round at a $3.5B valuation
Auth0 raises $103M, pushes its valuation over $1B
Canva gets $70M at a $2.5B valuation
Payment card startup Marqeta confirms $260M round at close to $2B valuation
Modsy scores $37M to virtually design your home
Sun Basket whips up $30M Series E
Zero raises $20M from NEA for a credit card that works like debit
Nigeria’s Gokada raises $5.3M for its motorcycle ride-hail biz
Our premium subscription service had another great week of interesting deep dives. This week, TechCrunch’s Lucas Matney went deep on Getaround’s acquisition of Drivy for his latest installment of The Exit, a new series at TechCrunch where we chat with VCs who were in the right place at the right time and made the right call on an investment that paid off. Here are some of the other Extra Crunch pieces that stood out this week:
- 10 immigration tips for luck-struck tech workers
- When will customers start buying all those AI chips?
- Takeaways from KubeCon; the latest on Kubernetes and cloud-native development
- Why startups need to be careful about export licenses and the Huawei ban
If you enjoy this newsletter, be sure to check out TechCrunch’s venture-focused podcast, Equity. In this week’s episode, available here, Crunchbase News editor-in-chief Alex Wilhelm and I discuss how startups are avoiding IPOs and VC’s insatiable interest in food delivery startups.
Powered by WPeMatico
The US Senate is coming after ‘loot boxes’
Gamers feel passionately about loot boxes; turns out some elected officials do, too.
A new Senate bill was formally introduced today with bipartisan support, and it could categorically shift how today’s top platforms and distribution platforms monetize the titles they sell. The bill’s introduction was first reported by The Verge.
The bill asserts that “pay-to-win” transactions that give users a nominal advantage for a fee or loot boxes that allow users to essentially play a slot machine for gaining rare or important items are bad for minors and need to be banned. If the bill passes, offending studios could be fined.
It’s hard to reiterate what a major impact this legislation could have; the games industry has reorganized itself around micro-transactions in the past decade. Much of the growth of the industry’s greatest success stories has been tied to the idea that free-to-download games can quickly nurture massive growth with network effects and then gradually monetize those users via small payments for items that can give them a unique look or edge.
This obviously wouldn’t fully sink in-game transactions by any means, but loot boxes have been one of the most lucrative models, and by placing a ceiling on acceptable behavior for these transactions, game companies might have to find new ways to monetize their content.
The death of loot boxes probably isn’t going to be mourned by many outside of game publishers’ accounting departments. There was something kind of fun about them for adults that knew exactly what they were doing, but it was still mostly in an infuriating way.
Missouri Republican Senator Josh Hawley, who introduced the bill, told Kotaku earlier this week that loot boxes were “basically adding casinos to children’s games,” which generally feels like a fair assertion.
As with almost all major pieces of legislation that aim to address new trends in technology, there’s potential that broadness in language can leave room for this to be very damaging to the industry, but the broadness here seems to be that this minor-oriented provision is going to end up being universal. Gizmodo notes some more issues with the grayness surrounding what exactly is “pay-to-win.”
What is a “minor-oriented” game? Is that simply any game with an ESRB rating below “M for Mature”? Nope; the bill outlines that game publishers need to focus on titles if they have “constructive knowledge that any users are under 18.” So, that’s just about every single game.
This was addressed, sort of, in a FAQs list released by Hawley’s camp:
While it is true that a large proportion of game players are adults, even games with predominantly adult player bases – including games marketed primarily to adults – tend to have enormous appeal to children. The onus should be on developers to deter child consumption of products that foster gambling and similarly compulsive purchasing behavior, just as is true in other industries that restrict access to certain kinds of products and forms of entertainment to adult consumers.
The legislation has some important problems it’s aiming to put in check, and clearly the gaming industry hasn’t been as active as it should in ensuring minors aren’t being taken advantage of in the midst of a micro-transaction land grab, so I’m not going to cry over them, but there’s a lot at play here, so hopefully nothing rushes through without proper considerations.
You can read the full text of the legislation here.
Powered by WPeMatico
Online bank Simple makes things harder by removing bill pay
With a growing number of challenger banks taking on the U.S. market, one of the original startup banks, Simple — now owned by BBVA — has taken the unusual step of removing a core banking feature: bill pay. The company claimed the feature was under-utilized and usage was trending downwards, which is why it decided to sunset the option to pay bills through its app. That decision, not surprisingly, has angered a number of customers who are taking to social media and online forums like Reddit, threatening to switch banks as a result.
It’s likely true that fewer people today use bill pay than in the past.
The feature is something of a holdover from an earlier era before electronic payment options and auto pay became as ubiquitous as they are now. And many customers may still have bill pay set up even though another electronic option has since become available. Or they may not want to take the time to reconfigure things, when what they have works.
But despite bill pay’s waning usage, it’s odd to shut down such a commonplace banking feature. It’s rare to find a bank that doesn’t offer bill pay services, in fact, outside of a handful of smaller up-and-comers that aren’t full-service banks.
Even most of the newer U.S. fintech players like Chime, Qapital, SoFi Money, Varo, Aspiration and others offer bill pay services where they mail a check for you. And it’s common among more traditional online banks like Ally, as well.
Removing bill pay also greatly impacts those who pay their rent by way of a mailed check, as many landlords are not set up for electronic payments. This is a recurring complaint among the customers who are lambasting Simple for its decision.
Instead, these customers will now have to purchase Simple’s newly available paper checks (sold in packs of 25 for $5 — oh, what a timely launch!).
They’ll then need to buy stamps, address envelopes, fill out checks and actually mail them.
Postal mail, of course, is not preferred by today’s younger generation — many of whom never had to write letters, having grown up in the internet age. Millennials have even complained that the very act of having to mail things gives them anxiety, due to all the steps involved and their overall unfamiliarity with the process.
I use bill pay to support a family member.
You’re saying “paper checks will put me in control” but really what that means is that I now have something that previously was automatically handled and no I have to manually do it.
I was in control prior, you’re just taking it away
— Jonah Moses (@jonahmoses) May 19, 2019
Considering that banks like Simple are targeting the millennial customer, forcing them back to checks they have to mail themselves is not the smartest move — at least from a public relations perspective.
On top of all this, Simple’s announcement about the discontinuation of bill pay was not well-communicated. As it touted the arrival of paper checks, an email footer also quietly noted that bill bay would also shut down after July 9, 2019. Customers dinged Simple for its lack of transparency.
In the spirit of transparency, @simple should also let its users know that Bill Pay is going away. Proof here (from an email from them) pic.twitter.com/LuDmnHJIA2
— BC (@bcurielv) May 7, 2019
The company claimed it was sending emails about bill pay to customers — but many didn’t receive any message before learning of the change on Twitter. And they were angry.
Since the decision was announced, Simple has been dutifully responding to customers’ complaints on Twitter, sometimes with smiley emojis and cheerful customer service-ese, like: “We hear ya. Mailing payments for bills can be nerve wracking.”
The company even wished one customer well on their journey to find another bank.
No…..you aren’t hearing us….that’s the problem.
— Rebecca Ford (@rebannford) May 9, 2019
We do now offer paper checks for folks who want them, and many of our customers set up automatic withdrawals from the biller’s websites for their bill payments. But if you decide to look for a new bank partner, we wish you the best.
-DG
— Simple (@simple) May 23, 2019
In addition to declining usage, the company said its newer Expenses feature was not working well with Bill Pay, which was another factor in its decision.
Good question – both are true. We knew that our existing bill pay process wasn’t working well with our expenses feature, so combined with the low usage rates we decided to end it. Hope that helps to clarify! ^BC
— Simple (@simple) May 19, 2019
Predictably, the volume of customer complaints has led to the creation of a Change.org petition.
Things are now going so badly that Simple just sent customers another email in response to all the backlash. In it, the company acknowledges how unhappy customers are about its decision and its handling of the news.
“To be completely transparent, a really small percentage of our customers use Bill Pay,” the email reads. “With this service’s usage declining, we made the decision to sunset it. This allows us to use those resources to build new features that benefit a broader number of customers. We know that some of you aren’t happy about this decision or how we broke the news, and for that, we’re sorry.”
The decision, however, still stands.
Simple was one of the original innovators in online banking. But after its acquisition, the pace of innovation has decreased and customer growth has stagnated. Over the years, the company has been maligned for not allowing non-U.S. citizens to sign up and for shutting down customers’ accounts with little notice, due to transition issues.
Now it’s angering customers again just as a number of new, millennial-focused online banks are hitting the market — and as challenger banks from Europe, like N26 and Revolut, are preparing to make the jump to the U.S. That may not be the best time to send a core group of users in search of alternatives.
The full email sent to customers is below:
You probably heard this already but if you haven’t: Simple’s “Pay a bill” and “Mail a check” features (also known as “Bill Pay”) are going away on or after July 9. If you have a payment scheduled on or after that date, it will not be paid or sent.
To be completely transparent, a really small percentage of our customers use Bill Pay. With this service’s usage declining, we made the decision to sunset it. This allows us to use those resources to build new features that benefit a broader number of customers.
We know that some of you aren’t happy about this decision or how we broke the news, and for that, we’re sorry.
We’ll continue to be in touch over the coming weeks. In the meantime, if you have any questions, we’re reachable via a support message or at (888) 248-0632.
Thanks,
— The Team at Simple
Simple has been offered the opportunity to comment.
Powered by WPeMatico
How to see another company’s growth tactics and try them yourself
Every company’s online acquisition strategy is out in the open. If you know where to look.
This post shows you exactly where to look, and how to reverse engineer their growth tactics.
Why is this important? Competitive analysis de-risks your own growth experiments: You find the best growth ideas to adopt and the worst ones to avoid.
First, a warning: Your goal is not to repurpose another company’s hard work. That makes you a thief. Your goal is to identify other companies who face the same growth challenges as you, then to study their approaches for solutions to draw from.
As I walk through uncovering a competitor’s tactics, keep in mind which competitors are worth looking at: For instance, you should rarely over-analyze early-stage companies. They’re unlikely to be methodical at growth.
Meaning, if you blindly copy their site and their ads, it’s possible you’ll be copying tactics that are not actually responsible for their growth. Their success may instead be from network effects or other hidden factors.
Instead, it’s safest to get inspiration from companies who’ve sustained high growth rates for a long time, and who face the same growth challenges as you. They’re likely to have sophisticated growth operations worth studying deeply. Examples include:
- Airbnb
- Amazon
- Uber
If these aren’t your direct competitors, don’t worry. You don’t need to audit a direct competitor’s tactics to get incredibly valuable insights.
You can look past direct competitors.
You’ll gain useful insights from auditing the user acquisition funnel of any company who has a similar audience and business model.
Examples of audiences:
- Wealthy consumers
- Enterprise businesses
- Middle-class adults who use Chrome
- Dog owners
- And so on
Audiences matter because their behaviors and needs differ wildly. Each requires its own growth strategy. You want to audit a company whose audiences is similar to yours.
You also want to ensure the company shares your business model. Examples include:
- A high-touch sales process with multiple phone calls
- A consumer ecommerce site with easy checkout
- A self-serve SaaS signup with a freemium plan
- A pay-to-play mobile game
- And so on
Each model may necessitate different ads, landing pages, automated emails, and sales collateral.
The process
Never implement another company’s tactics blindly.
There’s an effective process for growth analysis, and it looks like this:
- Source potential growth ideas.
- Prioritize them.
- A/B test them.
- Measure if an A/B variant significantly outperformed its baseline and whether the cost of implementing the winner would be worthwhile.
- Only then should you implement it.
An example
Here’s a brief example before we dive into tactics.
Let’s pretend we’re a SaaS company offering consumer banking tools, and that we’re struggling to get users to onboard our app. Our hypothesis is that visitors are bouncing because they don’t trust us with their sensitive information.
Our first step is to define both our audience and our business model:
- Audience: Tech-savvy, adult consumers.
Business model: SaaS freemium funnel.
Our next step is to look for companies who share those two aspects. (We can find them on Crunchbase.)
Once we have a few in hand, we look for how they handle customers’ sensitive information throughout their funnel. Specifically, we audit their:
- Ads
- Content marketing / SEO
- Landing pages
- A/B tests
- Signup flow
- Automated (“drip”) emails
It’s time to learn how we audit all that. I’ll share how our marketer training program teaches marketers to do this on the job.
Tactic #1: How to see a company’s A/B tests
Powered by WPeMatico