Instagram officially tests hiding Like counts
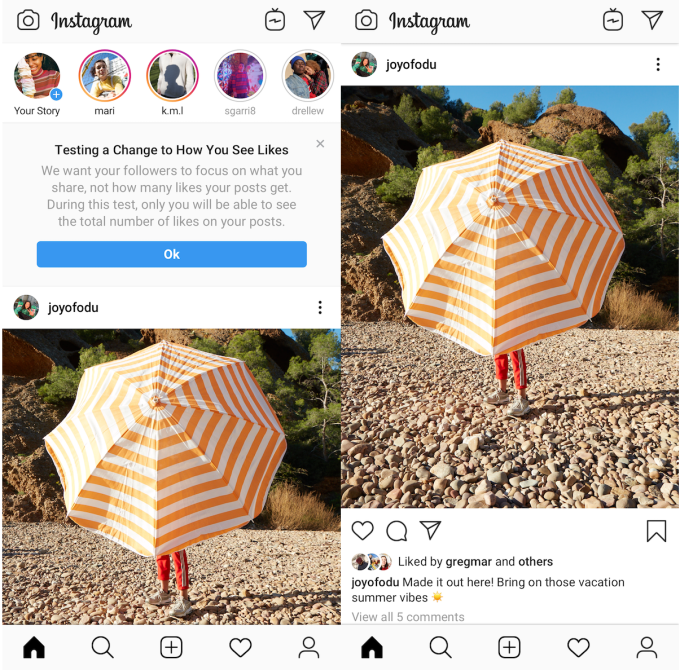
Would we feel less envious, shameful and competitive if Instagram didn’t tell us how many Likes a post received? That’s the idea behind Instagram now hiding Like counts from both a post’s viewers as part of an experiment in Canada. A post’s creator can still open the Likers window to see the names of everyone who hearted their post. Instagram has also recently redesigned the profile to make follower count much less prominent, the app’s head Adam Mosseri says.
Even though Like totals would still impact how the algorithm ranks a post in the feed, if rolled out, the change would refocus Instagram on self-expression instead of being a popularity contest. Users might be less likely to delete a photo or video because it didn’t get enough Likes, or resort to their Finsta account to post something authentic but less “perfect.” It could make us less likely to envy-spiral because we wouldn’t see friends or influencers getting more Likes than us. And people might be more willing to post what truly represents their complicated identities because they’re not battling for the biggest Like count.

“Later this week, we’re running a test in Canada that removes the total number of likes on photos and video views in Feed, Permalink pages and Profile,” an Instagram spokesperson tells TechCrunch. “We are testing this because we want your followers to focus on the photos and videos you share, not how many likes they get.” The small percentage of Canadian users in the test will see a notice atop their feed warning them of “a change to how you see Likes.” The announcement came alongside a slew of new product debuts at Facebook’s F8 conference.
One big concern, though, is that influencers often get discovered for paid promotions or have their sponsored content measured by public Like counts or a screenshot of their Liker list. “We understand that this is important for many creators, and while this test is in exploratory stages, we are thinking through ways for them to communicate value to their brand partners,” an Instagram spokesperson tells TechCrunch.
TechCrunch first reported two weeks ago that Instagram had prototyped hiding public Like counts, as spotted by Jane Manchun Wong. The company confirmed the feature had been built but not tested in the wild. The news immediately set off a wave of commentary from users. Many, while initially shocked, thought it would make Instagram usage healthier and cutback on some of the toxic anxiety produced by staring at the little numbers.
So why test in Canada? “Canadians are highly social and tech savvy, with over 24 million people connecting across our family of apps each month. We wanted to test this with a digitally savvy audience that has a thriving community on Instagram,” a company spokesperson told us.
Leading The Fight Against Bullying
On stage at F8, Mosseri announced that Instagram doesn’t just want to stop bullying, but lead the Internet’s battle against it. To that end, he announced several new tests of features Instagram hopes will make the app less toxic and hateful.
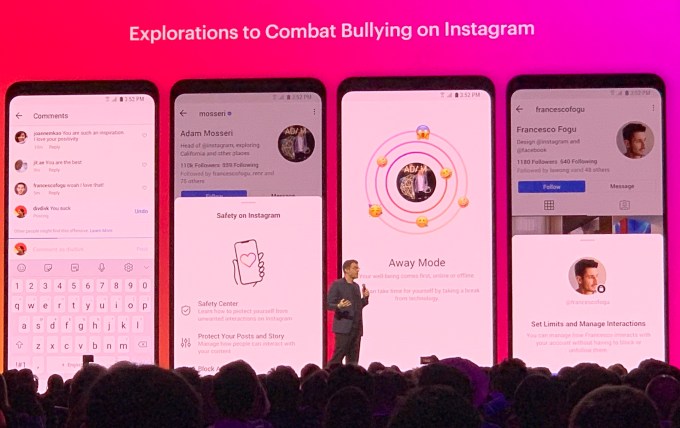
- A new “nudge” feature will warn users if they’re about to comment something hurtful. The test stops short of censorship while still addressing bullying before it happens.
- “Away Mode” will encourage users to take a break from Instagram at intense times in their life, like moving to a new school. They don’t have to delete their account, but can still get a break from constant notifications and concerns about how they look.
- “Manage Interactions” will allow users to set limits on how certain people interact with them without having to block them completely. Maybe you don’t want someone to be able to comment on your posts, but still Like them. Or you’re cool with them seeing your photos but don’t want to get DMs from them.
If these features succeed at promoting digital well-being, Instagram will likely roll them out to everyone.
It’s reassuring to see Instagram adding new well-being features after the departure of founders Kevin Systrom and Mike Krieger. Systrom in particular had been a big proponent of reducing envy and inauthenticity on social media, which was part of the impetus for launching Instagram Stories, where users could share unpolished looks at their lives. Before he left in September, Instagram rolled out its Your Activity dashboard showing the average time you spent per day on the app, plus a “You’re All Caught Up” warning that tells users they’ve seen all recent feed posts and can stop scrolling.
A 2013 study by Krasnova et al. discovered that 20 percent of envy-causing situations that experiment participants experienced happened on Facebook. They also determined that Facebook causes toxic envy, noting that “intensity of passive following is likely to reduce users’ life satisfaction in the long-run, as it triggers upward social comparison and invidious emotions.” Instagram, with its focus on imagery and manicured looks at our lives, might cause even more envy. Hiding Likes would be a strong step toward us judging ourselves less.
Click below to check out all of TechCrunch’s Facebook conference coverage from today:
Correction: Instagram originally told us a post’s creator couldn’t see its Like count either, but now tells us the count will only be hidden from viewers.
Powered by WPeMatico
Facebook Messenger will get desktop apps, co-watching, emoji status
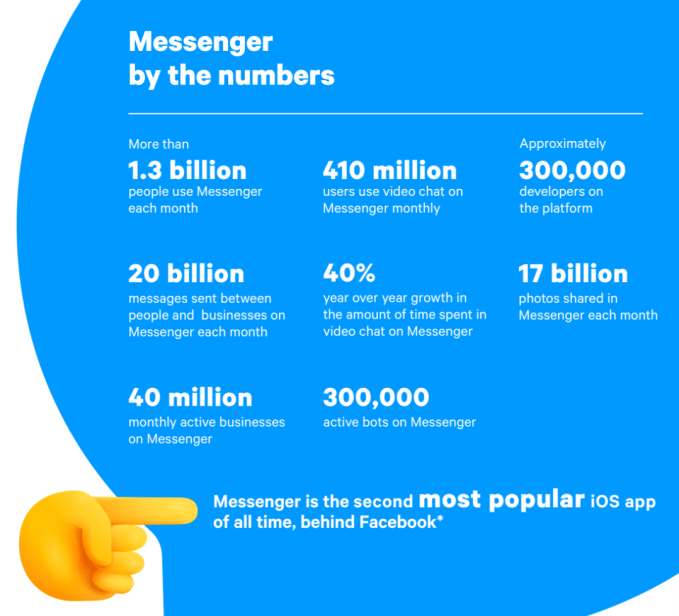
To win chat, Facebook Messenger must be as accessible as SMS, yet more entertaining than Snapchat. Today, Messenger pushes on both fronts with a series of announcements at Facebook’s F8 conference. Those include that it will launch Mac and PC desktop apps, a faster and smaller mobile app, simultaneous video co-watching and a revamped Friends tab, where friends can use an emoji to tell you what they’re up to or down for.
Facebook is also beefing up its tools for the 40 million active businesses and 300,000 businesses on Messenger, up from 200,000 businesses a year ago. Merchants will be able to let users book appointments at salons and masseuses, collect information with new lead generation chatbot templates and provide customer service to verified customers through authenticated m.me links. Facebook hopes this will boost the app beyond the 20 billion messages sent between people and businesses each month, which is up 10X from December 2017.
“We believe you can build practically any utility on top of messaging,” says Facebook’s head of Messenger Stan Chudnovsky. But he stresses that “All of the engineering behind it is has been redone” to make it more reliable, and to comply with CEO Mark Zuckerberg’s directive to unite the backends of Messenger, WhatsApp and Instagram Direct. “Of course, if we didn’t have to do all that, we’d be able to invest more in utilities. But we feel that utilities will be less functional if we don’t do that work. They need to go hand-in-hand together. Utilities will be more powerful, more functional and more desired if built on top of a system that’s interoperable and end-to-end encrypted.”
Here’s a look at the major Messenger announcements and why they’re important:
Messenger Desktop – A stripped-down version of Messenger focused on chat, audio and video calls will debut later this year. Chudnovsky says it will remove the need to juggle and resize browser tabs by giving you an always-accessible version of Messenger that can replace some of the unofficial knock-offs. Especially as Messenger focuses more on businesses, giving them a dedicated desktop interface could convince them to invest more in lead generation and customer service through Messenger.
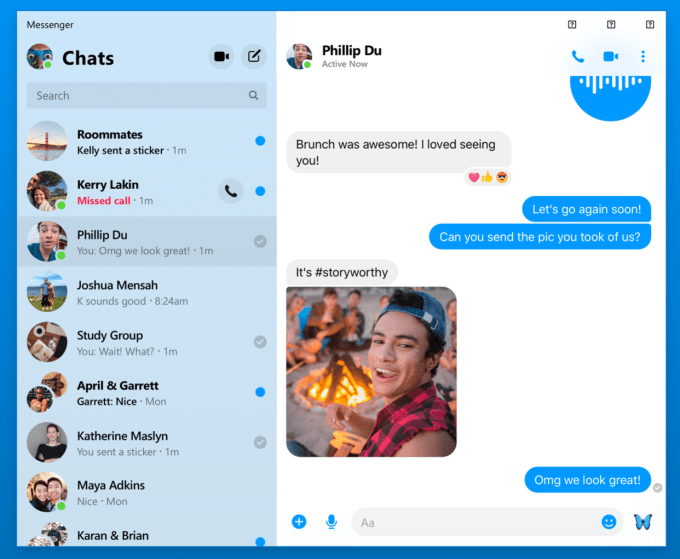
Facebook Messenger’s upcoming desktop app
Project Lightspeed – Messenger is reengineering its app to cut 70 mb off its download size so people with low-storage phones don’t have to delete as many photos to install it. In testing, the app can cold start in merely 1.3 seconds, which Chudnovsky says is just 25 percent of where Messenger and many other apps are today. While Facebook already offers Messenger Light for the developing world, making the main app faster for everyone else could help Messenger swoop in and steal users from the status quo of SMS. The Lightspeed update will roll out later this year.
Video Co-Watching – TechCrunch reported in November that Messenger was building a Facebook Watch Party-style experience that would let users pick videos to watch at the same time as a friend, with reaction cams of their faces shown below the video. Now in testing before rolling out later this year, users can pick any Facebook video, invite one or multiple friends and laugh together. Unique capabilities like this could make Messenger more entertaining between utilitarian chat threads and appeal to a younger audience Facebook is at risk of losing.
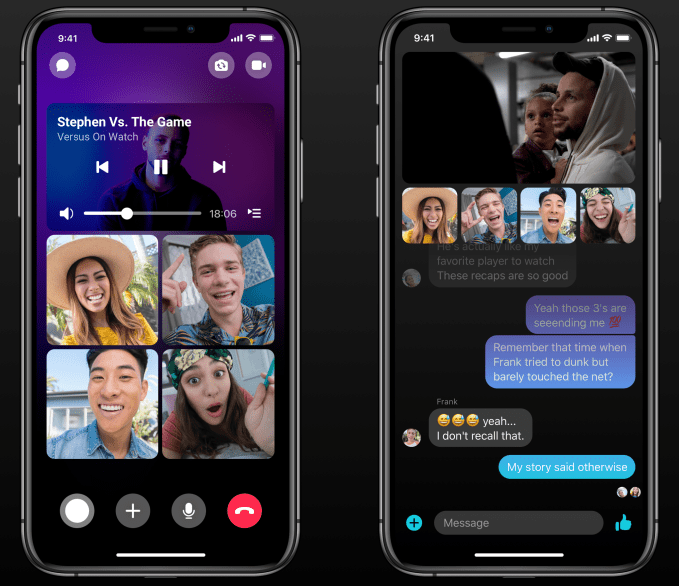
Watch Videos Together on Messenger
Business Tools – After a rough start to its chatbot program a few years ago, where bots couldn’t figure out users’ open-ended responses, Chudnovsky says the platform is now picking up steam with 300,000 developers on board. One option that’s worked especially well is lead-generation templates, which teach bots to ask people standardized questions to collect contact info or business intent, so Messenger is adding more of those templates with completion reminders and seamless hand-off to a live agent.
To let users interact with appointment-based businesses through a platform they’re already familiar with, Messenger launched a beta program for barbers, dentists and more that will soon open to let any business handle appointment booking through the app. And with new authenticated m.me links, a business can take a logged-in user on their website and pass them to Messenger while still knowing their order history and other info. Getting more businesses hooked on Messenger customer service could be very lucrative down the line.
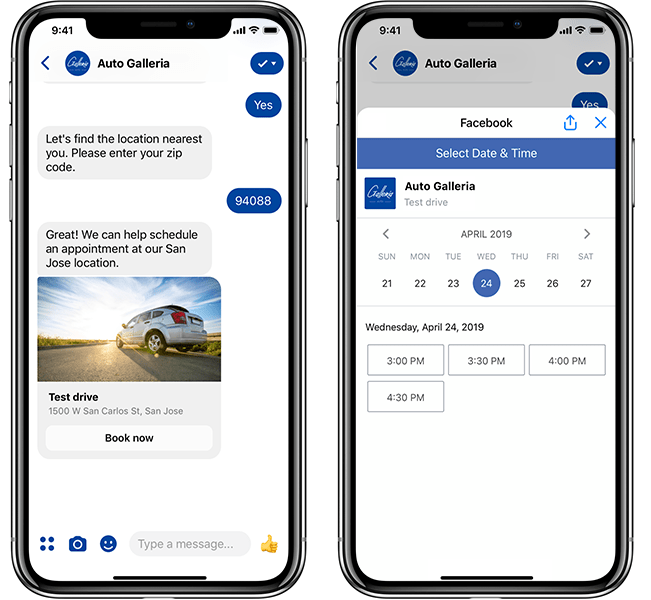
Appointment booking on Messenger
Close Friends and Emoji Status – Perhaps the most interesting update to Messenger, though, is its upcoming effort to help you make offline plans. Messenger is in the early stages of rebuilding its Friends tab into “Close Friends,” which will host big previews of friends’ Stories, photos shared in your chats, and let people overlay an emoji on their profile pic to show friends what they’re doing. We first reported this “Your Emoji” status update feature was being built a year ago, but it quietly cropped up in the video for Messenger Close Friends. This iteration lets you add an emoji like a home, barbell, low battery or beer mug, plus a short text description, to let friends know you’re back from work, at the gym, might not respond or are interested in getting a drink. These will show up atop the Close Friends tab as well as on location-sharing maps and more once this eventually rolls out.

Messenger’s upcoming Close Friends tab with Your Emoji status
Facebook Messenger is the best poised app to solve the loneliness problem. We often end up by ourselves because we’re not sure which of our friends are free to hang out, and we’re embarrassed to look desperate by constantly reaching out. But with emoji status, Messenger users could quietly signal their intentions without seeming needy. This “what are you doing offline” feature could be a whole social network of its own, as apps like Down To Lunch have tried. But with 1.3 billion users and built-in chat, Messenger has the ubiquity and utility to turn a hope into a hangout.
Click below to check out all of TechCrunch’s Facebook conference coverage from today:
Powered by WPeMatico
Energizer’s massive battery/phone proves a viral hit ≠ crowdfunding success
Oof. This isn’t the sort of thing you want to see when you’re rounding the corner of your crowdfunding campaign:

There are long shots and then there’s coming up with $15,000 of your $1.2 million goal. The Indiegogo page for the Energizer Power Max P18K Pop understandably focused on the viral sensation the ridiculously beefy phone with the 18,000mAh battery spurred at Mobile World Congress this year. There are even photos of the scrum of journalists elbowing to take a shot of the thing at the event.
Understandable that its creators took that approach. Heck, the thing may have outshined all of the foldable and 5G phones that were set to take center stage at the event. We wrote about it. Lucas rightfully called it “basically a giant battery with a smartphone built into it.”
The takeaway seems clear, though. Just because everyone’s talking about a product doesn’t mean that anyone intends to buy it. If anything, the devices seemed more a comment on the state of smartphone battery life than actual enticing product.
And honestly, there’s been a shift in recent years among many smartphone manufacturers to provide power saving options and larger capacity batteries, so this has become less of a problem (though 5G’s approach could aversely impact that). Also, there are eight million power banks, and you can get them pretty cheap these days, making the P18K Pop any even sillier proposition. Not to mention all the things that can go wrong when you buy a phone based on a single feature.
Even so, the product’s creators closed the campaign out on a hopeful note, writing, “Although it didn’t reach its goal, we will work on further improvement on the P18K (design, thickness, etc.) as we do believe there is a rising interest for smartphones with incredible battery life, which can also be used as power banks.”
Certainly features from companies like Samsung and Huawei have proven that power sharing is a compelling feature. It just probably won’t come with Energizer’s name attached.
Powered by WPeMatico
After account hacks, Twitch streamers take security into their own hands
Twitch has an account hacking problem.
After the breach of popular browser game Town of Salem in January, some 7.8 million stolen passwords quickly became the weakest link not only for the game but gamers’ other accounts. The passwords were stored using a long-deprecated scrambling algorithm, making them easily cracked.
It didn’t take long for security researcher and gamer Matthew Jakubowski to see the aftermath.
In the weeks following, the main subreddit for Amazon-owned game streaming site Twitch — of which Jakubowski is a moderator — was flooded with complaints about account hijacks. One after the other, users said their accounts had been hacked. Many of the hijacked accounts had used their Town of Salem password for their Twitch account.
Jakubowski blamed the attacks on automated account takeovers — bots that cycle through password lists stolen from breached sites, including Town of Salem.
“Twitch knows it’s a problem — but this has been going on for months and there’s no end in sight,” Jakubowski told TechCrunch.
Credential stuffing is a security problem that requires participation from both tech companies and their users. Hackers take lists of usernames and passwords from other breached sites and brute-force their way into other accounts. Customers of DoorDash and Chipotle have in recent months complained of account breaches, but have denied their systems have been hacked, offered little help to their users or shown any effort to bolster their security, and instead washed their hands of any responsibility.
Jakubowski, working with fellow security researcher Johnny Xmas, said Twitch no longer accepting email addresses to log in and incentivizing users to set up two-factor authentication would all but eliminate the problem.
The Russia connection
In new research out Tuesday, Jakubowski and Xmas said Russian hackers are a likely culprit.
The researchers found attackers would run massive lists of stolen credentials against Twitch’s login systems using widely available automation tools. With no discernible system to prevent automated logins, the attackers can hack into Twitch accounts at speed. Once logged in, the attackers then change the password to gain persistent access to the account. Even if they’re caught, some users are claiming a turnaround time of four weeks for Twitch support to get their accounts back.
On the accounts with a stored payment card — or an associated Amazon Prime membership — the attackers follow streaming channels they run or pay a small fee to access, of which Twitch takes a cut. Twitch also has its own virtual currency — bits — to help streamers solicit donations, which can be abused by the attackers to funnel funds into their coffers.
When the attacker’s streaming account hits the payout limit, the attacker cashes out.
The researchers said the attackers stream prerecorded gameplay footage on their own Twitch channels, often using Russian words and names.
“You’ll see these Russian accounts that will stream what appears to be old video game footage — you’ll never see a face or hear anybody talking but you’ll get tons of people subscribing and following in the channel,” said Xmas. “You’ll get people donating bits when nothing is going on in there — even when the channel isn’t streaming,” he said.
This activity helps cloak the attackers’ account takeover and pay-to-follow activity, said Xmas, but the attackers would keep the subscriber counts low enough to garner payouts from Twitch but not draw attention.
“If it’s something easy enough for [Jakubowski] to stumble across, it should be easy for Twitch to handle,” said Xmas. “But Twitch is staying silent and users are constantly being defrauded.”
Two-factor all the things
Twitch, unlike other sites and services with a credential stuffing problem, already lets its 15 million daily users set up two-factor authentication on their accounts, putting much of the onus to stay secure on the users themselves.
Twitch partners, like Jakubowski, and affiliates are required to set up two-factor on their accounts.
But the researchers say Twitch should do more to incentivize ordinary users — the primary target for account hijackers and fraudsters — to secure their accounts.
“I think [Twitch] doesn’t want that extra step between a valid user trying to pay for something and adding friction to that process,” said Jakubowski.
“The hackers have no idea how valuable an account is until they log in. They’re just going to try everyone — and take a shotgun approach.”
Matthew Jakubowski, security researcher and Twitch partner
“Two-factor is important — everyone knows it’s important but users still aren’t using it because it’s inconvenient,” said Xmas. “That’s the bottom line: Twitch doesn’t want to inconvenience people because that loses Twitch money,” he said.
Recognizing there was still a lack of awareness around password security and with no help from Twitch, Jakubowski and Xmas took matters into their own hands. The pair teamed up to write a comprehensive Twitch user security guide to explain why seemingly unremarkable accounts are a target for hackers, and hosted a Reddit “ask me anything” to let users to ask questions and get instant feedback.
Even during Jakubowski’s streaming sessions, he doesn’t waste a chance to warn his viewers about the security problem — often fielding other security-related questions from his fans.
“Every 10 minutes or so, I’ll remind people watching to set-up two factor,” he said.
“The hackers have no idea how valuable an account is until they log in,” said Jakubowski. “They’re just going to try everyone — and take a shotgun approach,” he said.
Xmas said users “don’t realize” how vulnerable they are. “They don’t understand why their account — which they don’t even use to stream — is desirable to hackers,” he said. “If you have a payment card associated with your account, that’s what they want.”
Carrot and the stick
Jakubowski said that convincing the users is the big challenge.
Twitch could encourage users with free perks — like badges or emotes — costing the company nothing, the researchers said. Twitch lets users collect badges to flair their accounts. World of Warcraft maker Blizzard offers perks for setting up two-factor, and Epic Games offers similar incentives to their gamers.
“Rewarding users for implementing two-factor would go a huge way,” said Xmas. “It’s incredible to see how effective that is.”
The two said the company could also integrate third-party leaked credential monitoring services, like Have I Been Pwned, to warn users if their passwords have been leaked or exposed. And, among other fixes, the researchers say removing two-factor by text message would reduce SIM swapping attacks. Xmas, who serves as director of field engineering at anti-bot startup Kasada — which TechCrunch profiled earlier this year — said Twitch could invest in systems that detect bot activity to prevent automated logins.
Twitch, when reached prior to publication, did not comment.
Jakubowski said until Twitch acts, streamers can do their part by encouraging their viewers to switch on the security feature. “Streamers are influencers — more users are likely to switch on two-factor if they hear it from a streamer,” he said.
“Getting more streamers to get on board with security will hopefully go a much longer way,” he said.
Read more:
- A leaky database of SMS text messages exposed password resets and two-factor codes
- Chipotle customers are saying their accounts have been hacked
- We found a massive spam operation — and sunk its server
- Dow Jones’ watchlist of 2.4 million high-risk individuals has leaked
- Stop saying, ‘We take your privacy and security seriously’
- Robocaller firm Stratics Networks exposed millions of call recordings
- Massive mortgage and loan data leak gets worse as original documents also exposed
Powered by WPeMatico
Alphabet cites ‘headwinds’ in smartphone sales, teases I/O hardware announcement
Alphabet’s Q1 earnings were a disappointment for Wall Street, courtesy primarily of ad revenue shortcomings. The hardware team met with some difficulties, as well, owing in part to a stagnating global smartphone market that has impacted virtually all players.
CEO Sundar Pichai cited “year over year headwinds” when referring to the company’s smartphone line, following the release of the Pixel 3 and Pixel 3 XL last fall. The executive rightly referenced the company’s relatively recent entry as a standalone hardware developer and painted a hopeful picture of the industry’s innovations going forward.
“I do continue to be excited to see 5G coming and the early foldable phones, which Android plays a big part in driving,” Pichai said on the call. Google has notably taken an important role developing an Android UI designed for the foldable form factor, along with working closely beside Samsung on its recently delayed foldable.
CFO Ruth Porat echoed Pichai’s comments, while hinting at what’s to come from the company. “While the first quarter results reflect pressure in the premium smartphone industry,” the exec explained, “we are pleased with the ongoing momentum of Assistant-enabled Home devices, particularly the Home Hub and Mini devices and look forward to our May 7 announcement at I/O from our hardware team.”
The reference to “premium smartphone[s]” looks to be a roundabout confirmation of the rumored Pixel 3a. The mid-tier take on the Pixel line is rumored to be a rare I/O hardware debut, coming next month. The arrival of such a device could go a ways toward helping jumpstart slowing sales for the line.
Pichai referenced the company’s newly opened “campus and engineering hub.” A result of the company’s massive deal with struggling handset maker, HTC, the Taipei R&D center will be primarily focused on Google’s smartphone offerings. He also referenced the company’s Amazon-competing Home line as a bright spot for its hardware offerings, particularly the Mini and Hub.
“If you take products like Google Home and Assistant products, we’ve been doing really well,” said Pichai. “We see strong momentum. We’re market leaders in the category, especially when you look at it on a global basis.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Canonical’s Mark Shuttleworth on dueling open-source foundations
At the Open Infrastructure Summit, which was previously known as the OpenStack Summit, Canonical founder Mark Shuttleworth used his keynote to talk about the state of open-source foundations — and what often feels like the increasing competition between them. “I know for a fact that nobody asked to replace dueling vendors with dueling foundations,” he said. “Nobody asked for that.”
He then put a point on this, saying, “what’s the difference between a vendor that only promotes the ideas that are in its own interest and a foundation that does the same thing. Or worse, a foundation that will only represent projects that it’s paid to represent.”
Somewhat uncharacteristically, Shuttleworth didn’t say which foundations he was talking about, but since there are really only two foundations that fit the bill here, it’s pretty clear that he was talking about the OpenStack Foundation and the Linux Foundation — and maybe more precisely the Cloud Native Computing Foundation, the home of the incredibly popular Kubernetes project.
It turns out, that’s only part of his misgivings about the current state of open-source foundations, though. I sat down with Shuttleworth after his keynote to discuss his comments, as well as Canonical’s announcements around open infrastructure.
One thing that’s worth noting at the outset is that the OpenStack Foundation is using this event to highlight that fact that it has now brought in more new open infrastructure projects outside of the core OpenStack software, with two of them graduating from their pilot phase. Shuttleworth, who has made big bets on OpenStack in the past and is seeing a lot of interest from customers, is not a fan. Canonical, it’s worth noting, is also a major sponsor of the OpenStack Foundation. He, however, believes, the foundation should focus on the core OpenStack project.
“We’re busy deploying 27 OpenStack clouds — that’s more than double the run rate last year,” he said. “OpenStack is important. It’s very complicated and hard. And a lot of our focus has been on making it simpler and cleaner, despite the efforts of those around us in this community. But I believe in it. I think that if you need large-scale, multi-tenant virtualization infrastructure, it’s the best game in town. But it has problems. It needs focus. I’m super committed to that. And I worry about people losing their focus because something newer and shinier has shown up.”
To clarify that, I asked him if he essentially believes that the OpenStack Foundation is making a mistake by trying to be all things infrastructure. “Yes, absolutely,” he said. “At the end of the day, I think there are some projects that this community is famous for. They need focus, they need attention, right? It’s very hard to argue that they will get focus and attention when you’re launching a ton of other things that nobody’s ever heard of, right? Why are you launching those things? Who is behind those decisions? Is it a money question as well? Those are all fair questions to ask.”
He doesn’t believe all of the blame should fall on the Foundation leadership, though. “I think these guys are trying really hard. I think the common characterization that it was hapless isn’t helpful and isn’t accurate. We’re trying to figure stuff out.” Shuttleworth indeed doesn’t believe the leadership is hapless, something he stressed, but he clearly isn’t all that happy with the current path the OpenStack Foundation is on either.
The Foundation, of course, doesn’t agree. As OpenStack Foundation COO Mark Collier told me, the organization remains as committed to OpenStack as ever. “The Foundation, the board, the community, the staff — we’ve never been more committed to OpenStack,” he said. “If you look at the state of OpenStack, it’s one of the top-three most active open-source projects in the world right now […] There’s no wavering in our commitment to OpenStack.” He also noted that the other projects that are now part of the foundation are the kind of software that is helpful to OpenStack users. “These are efforts which are good for OpenStack,” he said. In addition, he stressed that the process of opening up the Foundation has been going on for more than two years, with the vast majority of the community (roughly 97 percent) voting in favor.
OpenStack board member Allison Randal echoed this. “Over the past few years, and a long series of strategic conversations, we realized that OpenStack doesn’t exist in a vacuum. OpenStack’s success depends on the success of a whole network of other open-source projects, including Linux distributions and dependencies like Python and hypervisors, but also on the success of other open infrastructure projects which our users are deploying together. The OpenStack community has learned a few things about successful open collaboration over the years, and we hope that sharing those lessons and offering a little support can help other open infrastructure projects succeed too. The rising tide of open source lifts all boats.”
As far as open-source foundations in general, he surely also doesn’t believe that it’s a good thing to have numerous foundations compete over projects. He argues that we’re still trying to figure out the role of open-source foundations and that we’re currently in a slightly awkward position because we’re still trying to determine how to best organize these foundations. “Open source in society is really interesting. And how we organize that in society is really interesting,” he said. “How we lead that, how we organize that is really interesting and there will be steps forward and steps backward. Foundations tweeting angrily at each other is not very presidential.”
He also challenged the notion that if you just put a project into a foundation, “everything gets better.” That’s too simplistic, he argues, because so much depends on the leadership of the foundation and how they define being open. “When you see foundations as nonprofit entities effectively arguing over who controls the more important toys, I don’t think that’s serving users.”
When I asked him whether he thinks some foundations are doing a better job than others, he essentially declined to comment. But he did say that he thinks the Linux Foundation is doing a good job with Linux, in large parts because it employs Linus Torvalds . “I think the technical leadership of a complex project that serves the needs of many organizations is best served that way and something that the OpenStack Foundation could learn from the Linux Foundation. I’d be much happier with my membership fees actually paying for thoughtful, independent leadership of the complexity of OpenStack rather than the sort of bizarre bun fights and stuffed ballots that we see today. For all the kumbaya, it flatly doesn’t work.” He believes that projects should have independent leaders who can make long-term plans. “Linus’ finger is a damn useful tool and it’s hard when everybody tries to get reelected. It’s easy to get outraged at Linus, but he’s doing a fucking good job, right?”
OpenStack, he believes, often lacks that kind of decisiveness because it tries to please everybody and attract more sponsors. “That’s perhaps the root cause,” he said, and it leads to too much “behind-the-scenes puppet mastering.”
In addition to our talk about foundations, Shuttleworth also noted that he believes the company is still on the path to an IPO. He’s obviously not committing to a time frame, but after a year of resetting in 2018, he argues that Canonical’s business is looking up. “We want to be north of $200 million in revenue and a decent growth rate and the right set of stories around the data center, around public cloud and IoT.” First, though, Canonical will do a growth equity round.
Powered by WPeMatico
What we want to know in the We Company (WeWork) S-1
With news that the We Company (formerly known as WeWork) has officially filed to go public confidentially with the SEC today, there’s a big question on everyone’s mind: Is this the next massive startup win or a house of cards waiting to be toppled by the glare of the public markets?
No company I follow has as much polarized opinion as the We Company. And while the company will have to reveal at least some of its hand in its official S-1, my guess is that the polarization around the company will not be alleviated until well after it goes public, if ever.
The challenge with understanding its business is how much the details of each of its leases, real estate markets and tenants matter to its bottom line. We already know the top line numbers: the company had revenue of $1.8 billion in 2018, and a net loss of $1.9 billion that year. That led to the received opinion that the company has an extraordinarily weak business. As Crunchbase News editor Alex Wilhelm put it:
Powered by WPeMatico
ManyChat raises $18M to help businesses tap into messaging
Mobile marketing company ManyChat has raised $18 million in Series A funding.
The startup, co-founded by CEO Mikael Yang, is currently focused on Facebook Messenger. It offers tools for creating a bot on Messenger while also supporting live human chatting (ManyChat says its approach is a “smart blend of automation and personal outreach”), and additional options like advertising to get more users to engage with your messaging channels.
ManyChat is just one of several startups hoping to build a business around Facebook Messenger bots, but this sounds like a product that businesses are actually using. The company says more than 1 million accounts have been created on the platform, with customers coming from e-commerce, traditional retail, gyms, beauty salons restaurants and more.
Those customers have collectively enlisted 350 million Messenger subscribers, and there are 7 billion messages sent on the platform each month. Plus, with an average open rate of 80 percent, these messages are actually being read.
The funding was led by Bessemer Venture Capital, with participation from Flint Capital. Bessemer’s Ethan Kurzweil is joining the board of directors, while the firm’s Alex Ferrara also becomes a board observer.
“ManyChat is at the forefront of a major shift in how businesses market to customers,” Kurzweil said in the funding announcement. “It’s not a matter of ‘if’ but ‘when’ email lists and static forms get replaced with a more personalized and conversational approach to customer engagement.”
He added that the company’s work with Messenger is “only the beginning”: “With Instagram, WhatsApp, RCS, and others on the horizon, there’s endless potential to scale.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Getting a piece of Uber
Menlo Ventures was founded in 1976 but it took 35 years for the venture capital firm to hit the jackpot.
Since the dot-com boom, Menlo Ventures has teetered between good and great. A prolific Silicon Valley investor, it’s never quite reached the heights of Accel or Andreessen Horowitz (a16z), or established the level of name recognition as Benchmark or Sequoia, firms that struck gold with bets on Facebook, Instagram and Snap.
But where others missed the boat entirely on one of the most valuable tech startups of all time, Menlo Ventures gnawed its way into an early deal at the last possible moment.
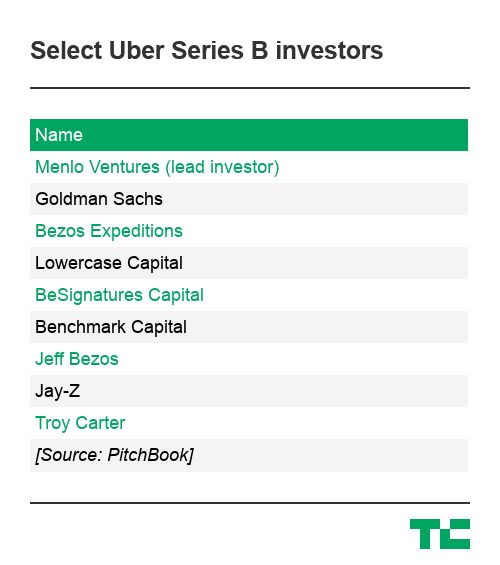
In 2011, the firm led a $32 million Series B funding in a fledgling on-demand car service called Uber, agreeing to value the startup at a colossal $322 million after the company’s first-choice investor, a16z, failed to accept Uber’s sky-high terms. Menlo would go on to invest a total of $66.5 million in the company on expected total returns of up to $3.1 billion.
“I wouldn’t have dared to dream quite this big,” Menlo Ventures partner Shawn Carolan told TechCrunch. Carolan and embattled investor Shervin Pishevar, the former Menlo Ventures partner and founder of Sherpa Capital accused of sexual misconduct, secured Menlo a spot on Uber’s cap table years ago when several firms were vying for a stake.
The pair, according to discussions with insiders, are polar opposites, representatives of the diverging approaches to deal-making in Silicon Valley. While Pishevar, described to TechCrunch as “overpowering” and “self-promotional,” developed a lasting relationship with Uber co-founder and former chief executive officer Travis Kalanick crucial to the deal, Carolan, a reserved Midwesterner, crunched the numbers and worked to convince his firm that Uber, a young startup with a hot-headed leader, was worth their time and money.
Now, as Uber preps for an imminent initial public offering, the firm wants to shine a light on Carolan, an under-the-radar investor known more for his humility than his portfolio.

Menlo Ventures partner Shawn Carolan’s last-ditch effort to convince his firm to invest in Uber in late 2011.
A historic IPO
As Uber approaches its IPO, a slew of investors that were in the right place at the right time await a payday of unforeseen scale.
Uber dropped its IPO prospectus in early April. Next week, it’s expected to debut on the New York Stock Exchange at a valuation between $80 billion and $100 billion, up from its most recent private valuation of $72 billion. The IPO will be amidst the largest liquidity events for a U.S. VC-backed technology company in history, on par with Facebook’s 2012 public offering that valued the social media empire at $104 billion.
In addition to Menlo Ventures, the Japanese telecom giant SoftBank, Benchmark, Uber co-founders Travis Kalanick and Garrett Camp, Saudi Arabia’s Public Investment Fund and GV, the investment arm of Alphabet, own stakes in Uber worth billions.
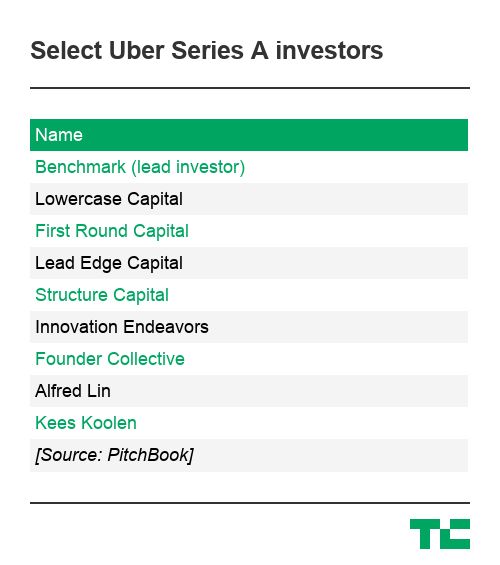
Seed backers like Chris Sacca of Lowercase Capital and Rob Hayes of First Round Capital, who invested in “UberCab” before it had anything to show for itself, will also earn tremendous payouts.
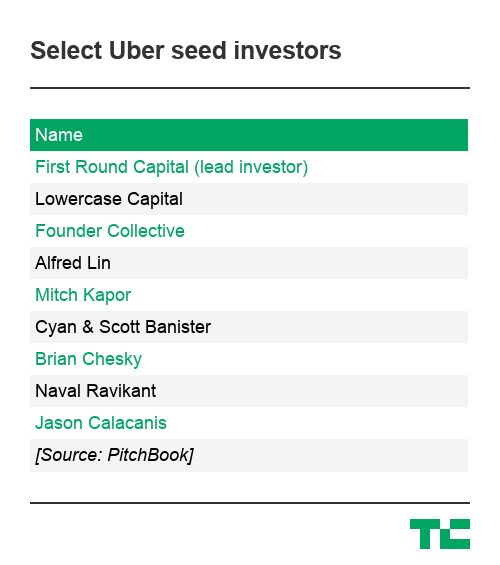
Menlo has already raked in hundreds of millions in profits from its Uber investment, as have several other investors that sold their shares on the secondary market. In 2018, Menlo earned $973 million when a group of investors led by SoftBank purchased nearly half of its Uber stock. The deal represented a 93x return on shares the firm had paid $10.5 million for years prior, according to the firm’s calculations.
Since that transaction, Menlo has expanded its Uber stake through the sale of its portfolio company Jump Bikes to Uber in 2018. The firm had invested $7.5 million in Jump, a provider of a dockless bicycle system, only months before it was acquired by Uber for $200 million. Menlo, as a result, banked another $50 million in Uber stock.
Today, it owns a 2.3 percent stake in Uber worth between $1.85 billion and $2.1 billion, depending on how Uber prices its IPO.
Beers and a term sheet

Uber founding CEO Travis Kalanick.
The story of Menlo Ventures’ investment in Uber dates back to 2005 when Carolan first met Travis Kalanick, Uber’s founder and former chief executive. The notorious entrepreneur was fundraising for an earlier company, a peer-to-peer file-sharing startup called Red Swoosh. Menlo didn’t invest, but Kalanick left a lasting impression.
Years later, Benchmark general partner Matt Cohler called Pishevar on his cell phone to let him know Uber had begun raising its Series B. Pishevar didn’t know Kalanick yet but had been introduced to his fast-growing car-sharing business by AngelList founder and Uber backer Naval Ravikant in 2010.
Pishevar was a garish type who would two years later leave Menlo to launch his own firm Sherpa Capital, a backer of Slack, Airbnb, Robinhood, Hyperloop One and more. Carolan was restrained, focused more on metrics than relationships. Together, the pair worked their way onto Uber’s cap table with Pishever serving as the lead investor externally and internally, both men receiving credit as leads.
Venture capitalists often brag about the skill required to land the best deals, but most of the time, it comes down to luck and timing. Menlo, in this case, got really lucky.
A recent feature on Andreessen Horowitz in Forbes detailed the firm’s biggest misstep: losing Uber. Hours before they were set to sign a term sheet, the firm shifted, offering Uber a lower valuation than what had been promised. Kalanick, known already at that point for his disdain for investors, walked. Little did the Menlo team know they were being used as a “stalking horse for leverage,” according to Forbes’ reporting. So when a16z tried to cheapen the deal, Uber turned immediately to its second-choice, Menlo Ventures.
A16z declined to provide additional details for this story.
“Whenever you have a company of this caliber that has that kind of growth rate, there’s a lot of people that are vying for the opportunity to invest,” Carolan said. “Frankly, there’s never been a company like Uber.”
With a sense of urgency, Pishevar hopped on a plane to Dublin, Ireland at Kalanick’s request. The CEO was speaking at a technology conference called Web Summit. It was there that the term sheets were signed over pints at the Shelbourne Hotel, and a close friendship between Pishevar and Kalanick would begin to blossom. Pishevar, according to The New York Times, later introduced the ride-hail chief to the club scene and Los Angeles celebrity culture. Until Kalanick’s final days as CEO, Pishevar would fiercely defend the founder’s dog-eat-dog style of management. To this day, the two are close friends.
Meanwhile, Carolan was heads down, benchmarking Uber against other tech companies, completing a thorough unit economics analysis and hoping his colleagues wouldn’t be disappointed by the Uber investment, a point of contention among certain Menlo staffers who viewed Uber as a limo dispatch company with an app, not the next billion-dollar business.
“There were a lot of things you had to believe back then and at that moment in time, Uber didn’t paint that picture, [Carolan] was the one who painted that picture,” Mark Siegel, a managing director at Menlo since 1996, told TechCrunch. “And he pounded the table pretty hard.”
After all, Uber was only active in four markets at the time of Menlo’s initial investment: San Francisco, Seattle, Chicago and New York City. Rider bookings were growing fast but were just $1 million per month, with close to zero net revenue after paying drivers. Carolan himself was unconvinced of the business’s longevity until his first ride in an Uber turned him.
Uber declined to confirm early booking figures.
“We had a lot of heartburn over the valuation,” Carolan said. “But it’s the ones you don’t chase, like YouTube, which I kind of dismissed as a lousy business and didn’t chase it. When you see something like Uber that has that type of repeated retention and essentially zero customer acquisition, it’s kind of like, okay, this is just a magical experience that’s going to sell itself.”
Carolan’s commitment was recognized internally but while Uber gained momentum, so did Pishevar. His involvement in Uber brought him notoriety, while Carolan’s role slipped through the cracks. Even when accusations of sexual misconduct against Pishevar surfaced in 2017, his name was often preceded by “early Uber investor.”
Pishevar was accused of sexually harassing multiple women, including Uber’s very own former head of global expansion, Austin Geidt. The Bloomberg expose highlighting allegations against him came just one month after a report he had been arrested in London for rape. Charges for the reported London incident were later dropped and Pishevar, through his lawyer, has said the other claims were part of a “smear campaign” against him.
Menlo Ventures sought to distance itself from the scandal, naturally, claiming in a series of tweets they had no knowledge of inappropriate behavior during his tenure at the firm.
A self-effacing venture capitalist
A Chicago native, Shawn Carolan joined Menlo Ventures in 2002 as a 28-year-old fresh out of Stanford’s business school. His wife and high school sweetheart, Jennifer Carolan, would make a career as a venture capitalist, too, co-founding Reach Capital, an edtech-focused VC fund coincidentally located next door to Menlo’s San Francisco outpost.

Menlo Ventures partner Shawn Carolan.
In 2009, the Menlo team realized they had overcompensated on enterprise and made the call to pioneer a reinvigorated consumer tech strategy spearheaded largely by Carolan.
In 2011, to bolster the new effort, Carolan hired Pishevar, a rookie VC they hoped would bring a fresh perspective to a firm of engineering geeks. Immediately, Pishevar sourced Square, Jack Dorsey’s hot new payments startup. The team rallied behind him but ultimately, Square went with Kleiner Perkins’s Mary Meeker instead. Later, Pishevar would bring in Pinterest and Snap, mere months after the ephemeral messaging app had launched but the Menlo team passed, according to a source with knowledge of the deals.
In Pishevar’s first six months at Menlo, he invested in Tumblr, Warby Parker, Machine Zone and Uber.
Carolan, for his part, has returned more capital in a single year than any partner in its history, the firm said. In a 12-month period between 2017 to 2018, Roku’s IPO and the Uber stock sale brought in some $2 billion in returns for Menlo, capital that was used to fuel its latest fund, a $500 million vehicle focused on Series B and C-stage startups.
In addition to accumulating a 35.3 percent pre-IPO stake in the digital streaming business Roku, which the firm celebrated with boxes of popcorn implanted with several thousand dollars in cash bonuses for the administrative team, Carolan was the first institutional investor in Siri, the personal assistant application Apple paid a little more than $200 million for in 2010. More recently, he invested in Chime, a mobile banking platform valued at $1.5 billion in March.
Pishevar, since leaving Menlo, has continued to ink deals with high-flying unicorns, including Uber, in which Sherpa invested an additional $200 million. However, since resigning from Sherpa Capital following the sexual misconduct scandal in 2017, he’s kept a much lower profile. Most recently, he signed on as an investor and board member at Bolt Mobility, an electric scooter business in Florida. A 2018 Florida business filing listed him as the company’s sole officer, though the Bolt team recently told BuzzFeed Pishevar was strictly an investor. The Sherpa Capital team, for their part, have relaunched as ACME Capital.
Bolt has not responded to a request for comment.
An implosion
Menlo remained one of the largest institutional backers in Uber for years, a position that, while lucrative, proved tricky when Uber began to unravel internally.
When Pishevar left Menlo Ventures to build Sherpa Capital in 2013, Carolan assumed the Menlo board observer seat for the next 21 months. Pishevar, now a close friend to Kalanick, stayed on the board as an observer until 2015.
Eventually, Carolan would take a step back from Menlo to focus on his productivity startup, Handle. But when Handle failed to become the rocket ship Carolan had dreamed of, he returned to investing at Menlo full-time with a newfound empathy for founders.
Little did he know he would play a role in the high-profile ouster of one of the most notable tech founders of all time.
In July 2016, talks of Kalanick’s resignation led by Benchmark general partner and Uber board member Bill Gurley began. Menlo had given up its board observer seat by then, but was part of a consortium of four key early Uber investors (Benchmark, First Round Capital and Lowercase Capital) that controlled the preferred share vote, which was needed to make impactful decisions; for example, approving new board seats or remove a founding CEO.
In 2017, it became abundantly clear that Uber would never achieve profitability nor complete its highly anticipated IPO with Kalanick at the helm. Susan Fowler had published her infamous blog post, executives were quitting, remarks on Uber’s toxic culture could be found just about anywhere and the #DeleteUber campaign had turned social media against the ride-hail company.

Shervin Pishevar (right) looks on as he gives a press conference during the Web Summit at Parque das Nacoes, in Lisbon on November 10, 2016. (PATRICIA DE MELO MOREIRA/AFP/Getty Images)
Uber was going to implode if the board didn’t act. Benchmark’s Gurley took center stage, calling on Kalanick to resign. Pishevar remained a Kalanick confidant and later when Benchmark sued Kalanick, he published a bizarre open letter in an eleventh-hour attempt to sway the public to rally behind the ousted CEO. Carolan, reluctant to be perceived as anything other than founder friendly, turned against the founder and advocated alongside Gurley for Kalanick’s removal.
“I imagine he wouldn’t be particularly happy with me for having done that but you gotta do what you gotta do sometimes,” Carolan said. “Ultimately, our job is to help that company achieve its mission. It’s not an allegiance to any one person at the company.”
Finally, Kalanick gave up the Uber C-suite in June 2017 and former Expedia Group CEO Dara Khosrowshahi stepped in as his replacement. Sixteen months later, Uber would file confidentially for a 2019 IPO.
A lasting impact
Menlo Ventures leaped into cutting-edge consumer investing at a time when its reputation in The Valley was unremarkable. For years, decades even, the firm shielded itself from PR and declined to take the spotlight as the Andreessen Horowitzes of the world touted their successes.
Today, the firm is more accepting of attention, leveraging its Uber position to attract entrepreneurs and foster new unicorns, like the more recent portfolio additions Chime and Carta.
“It has clearly benefited us in terms of the overall perception of the firm and credibility,” Siegel said, admitting he was one of the Menlo partners dubious of its 2011 Uber investment. “There’s no doubt it has been a huge positive.”
In the years since Uber came along, Menlo has made key additions to its team, marking the beginning of a new era for the timeworn investor. In 2015, it hired Steve Sloane, who became the firm’s youngest partner to date when he was promoted earlier this year. Naomi Ionita, the firm’s only female partner, joined in early 2018. And Grace Ge, a fresh recruit from RRE Ventures in New York, started this week as a senior associate on the venture team. Another yet-to-be-announced hire will begin in June.
Uber, despite narrowly avoiding a complete implosion in 2017, has changed the game for many investors. The returns it will generate in the next several months will refresh the coffers of many venture capital funds. Money tied to Uber will flow toward the next generation of founders for years to come, and the investors responsible for its landmark success will boast about it for the remainder of their careers.
Even if Uber doesn’t turn out to be the Wall Street darling its investors hope — Lyft has struggled to accumulate value on the public markets — the company has indisputably transformed the Silicon Valley playbook for hypergrowth and execution in the gig-economy ecosystem.
Powered by WPeMatico
Diving into TED2019, the state of social media and internet behavior
Extra Crunch offers members the opportunity to tune into conference calls led and moderated by the TechCrunch writers you read every day. Last week, TechCrunch’s Anthony Ha gave us his recap of the TED2019 conference and offered key takeaways from the most interesting talks and provocative ideas shared at the event.
Under the theme, “Bigger Than Us,” the conference featured talks, Q&As and presentations from a wide array of high-profile speakers, including an appearance from Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey, which was the talk of the week. Anthony dives deeper into the questions raised in his onstage interview that kept popping up: How has social media warped our democracy? How can the big online platforms fight back against abuse and misinformation? And what is the internet good for, anyway?
“…So I would suggest that probably five years ago, the way that we wrote about a lot of these tech companies was too positive and they weren’t as good as we made them sound. Now the pendulum has swung all the way in the other direction, where they’re probably not as bad we make them sound…
…At TED, you’d see the more traditional TED talks about, “Let’s talk about the magic of finding community in the internet.” There were several versions of that talk this year. Some of them very good, but now you have to have that conversation with the acknowledgement that there’s much that is terrible on the internet.”

Image via Ryan Lash / TED
Anthony also digs into what really differentiates the TED conference from other tech events, what types of people did and should attend the event, and even how he managed to get kicked out of the theater for typing too loud.
For access to the full transcription and the call audio, and for the opportunity to participate in future conference calls, become a member of Extra Crunch. Learn more and try it for free.
Powered by WPeMatico