Asia
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Tokyo-based SODA, which runs sneaker reselling platform SNKRDUNK, has raised a $22 million Series B led by SoftBank Ventures Asia. Investors also included basepartners, Colopl Next, THE GUILD and other strategic partners. Part of the funding will be used to expand into other Asian countries. Most of SNKRDUNK’s transactions are within Japan now, but it plans to become a cross-border marketplace.
Along with SODA’s $3 million Series A last year, this brings the startup’s total funding to $25 million.
While the COVID-19 pandemic was initially expected to put a damper on the sneaker resell market, C2C marketplaces have actually seen their business increase. For example, StockX, one of the biggest sneaker resell platforms in the world (which hit a valuation of $2.8 billion after its recent Series E), said May and June 2020 were its biggest months for sales ever.
SNKRDUNK’s sales also grew last year, and in December 2020, it recorded a 3,000% year-over-year increase in monthly gross merchandise value. Chief executive officer Yuta Uchiyama told TechCrunch this was because demand for sneakers remained high, while more people also started buying things online.
Launched in 2018, SNKRDUNK now has 2.5 million monthly users, which it says makes it the largest C2C sneaker marketplace in Japan. The Series B will allow it to speed up the pace of its international expansion, add more categories and expand its authentication facilities.
Like StockX and GOAT, SNKRDUNK’s user fees cover authentication holds before sneakers are sent to buyers. The company partners with FAKE BUSTERS, an authentication service based in Japan, to check sneakers before they are sent to buyers.
In addition to its marketplace, SNKRDUNK also runs a sneaker news site and an online community.
SODA plans to work with other companies in SoftBank Venture Asia’s portfolio that develop AI-based tech to help automate its operations, including logistics, payment, customer service and counterfeit inspection.
Powered by WPeMatico
Amazon is doubling down on one of the biggest strengths of its Prime Video streaming service: aggressive pricing.
The e-commerce giant on Wednesday launched Prime Video Mobile Edition, an even more affordable tier of the on-demand video streaming service — now also bundling some mobile data.
Prime Video Mobile Edition, for which Amazon has partnered with Indian telecom network Airtel, will feature 28-day mobile-only, single-user, standard definition (SD) access to customers in India for Rs 89 ($1.22). This tier will include 6GB of mobile data that customers can consume during the subscription period. There’s also a slightly expensive plan for Prime Video Mobile Edition that will charge customers Rs 299 but will offer 1.5GB mobile data for each day of the subscription. To anyone who subscribes to Prime Video Mobile Edition, Amazon says it will pick the tab for the first month.
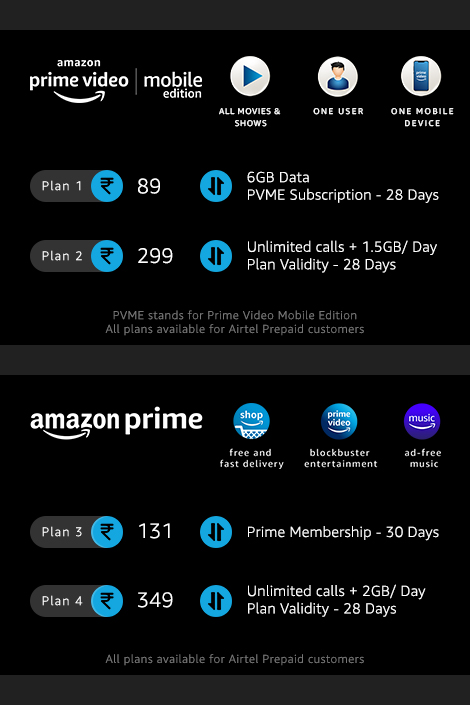
Amazon Prime subscription costs $1.7 a month in India and includes access to Prime Video and Prime Music.
The new Prime Video plan is currently only available in India. Its launch comes two years after Netflix unveiled a similar plan in India.
Affordable pricing is key for on-demand steaming services that are looking to make inroads in India, the world’s second-largest internet market. Even as more than 600 million users are online in the country today, only a fraction of them currently pay to access digital subscriptions. In a recent report to clients, analysts at Goldman Sachs estimated that gaming and video streaming market in India could clock as much as $5 billion in gross value transactions by March 2025.
“India is one of our fastest growing territories in the world with very high engagement rates. Buoyed by this response, we want to double-down by offering our much-loved entertainment content to an even larger base of Indian customers. Given high mobile broadband penetration in the country, the mobile phone has become one of the most widely used streaming devices,” said Jay Marine, vice president, Amazon Prime Video Worldwide, in a statement.
Airtel, the second-largest telecom operator in India, is the first roll-out partner for Prime Video Mobile Edition, said Sameer Batra, director, Mobile Business Development at Amazon, suggesting that the company may ink similar deals with other telecom operators in the country as it looks to expand the “reach of our service to the entire pre-paid customer base in India.”
Nearly every on-demand video streaming service in India, including Netflix and Disney+ Hotstar, maintain various partnerships with local telecom operators and satellite TV providers to reach more users in the country. Amazon did not explicitly say when or if it plans to extend Prime Video Mobile Edition outside of India.
Powered by WPeMatico
Launched in South Korea five years ago, content discovery platform Dable now serves a total of six markets in Asia. Now it plans to speed up the pace of its expansion, with six new markets in the region planned for this year, before entering European countries and the United States. Dable announced today that it has raised a $12 million Series C at a valuation of $90 million, led by South Korean venture capital firm SV Investment. Other participants included KB Investment and K2 Investment, as well as returning investor Kakao Ventures, a subsidiary of Kakao Corporation, one of South Korea’s largest internet firms.
Dable (the name is a combination of “data” and “able”) currently serves more than 2,500 media outlets in South Korea, Japan, Taiwan, Indonesia, Vietnam and Malaysia. It has subsidiaries in Taiwan, which accounts for 70% of its overseas sales, and Indonesia.
The Series C brings Dable’s total funding so far to $20.5 million. So far, the company has taken a gradual approach to international expansion, co-founder and chief executive officer Chaehyun Lee told TechCrunch, first entering one or two markets and then waiting for business there to stabilize. In 2021, however, it plans to use its Series C to speed up the pace of its expansion, launching in Hong Kong, Singapore, Thailand, mainland China, Australia and Turkey before entering markets in Europe and the United States, too.
The company’s goal is to become the “most utilized personalized recommendation platform in at last 30 countries by 2024.” Lee said it also has plans to transform into a media tech company by launching a content management system (CMS) next year.
Dable currently claims an average annual sales growth rate since founding of more than 50%, and says it reached $27.5 million in sales in 2020, up from 63% the previous year. Each month, it has a total of 540 million unique users and recommends five billion pieces of content, resulting in more than 100 million clicks. Dable also says its average annual sales growth rate since founding is more than 50%, and in that 2020, it reached $27.5 million in sales, up 63% from the previous year.
Before launching Dable, Lee and three other members of its founding team worked at RecoPick, a recommendation engine developer operated by SK Telecom subsidiary SK Planet. For media outlets, Dable offers two big data and machine learning-based products: Dable News to make personalized recommendations of content, including articles, to visitors, and Dable Native Ad, which draws on ad networks including Google, MSN and Kakao.
A third product, called karamel.ai, is an ad-targeting solution for e-commerce platforms that also makes personalized product recommendations.
Dable’s main rivals include Taboola and Outbrain, both of which are headquartered in New York (and recently called off a merger), but also do business in Asian markets, and Tokyo-based Popin, which also serves clients in Japan and Taiwan.
Lee said Dable proves the competitiveness of its products by running A/B tests to compare the performance of competitors against Dable’s recommendations and see which one results in the most clickthroughs. It also does A/B testing to compare the performance of articles picked by editors against ones that were recommended by Dable’s algorithms.
Dable also provides algorithms that allow clients more flexibility in what kind of personalized content they display, which is a selling point as media companies try to recover from the massive drop in ad spending precipitated by the COVID-19 pandemic. For example, Dable’s Related Articles algorithm is based on content that visitors have already viewed, while its Perused Article algorithm gauges how interested visitors are in certain articles based on metrics like how much time they spent reading them. It also has another algorithm that displays the most viewed articles based on gender and age groups.
Powered by WPeMatico
WhatsApp has enjoyed unrivaled reach in India for years. By mid-2019, the Facebook-owned app had amassed over 400 million users in the country. Its closest app rival at the time was YouTube, which, according to the company’s own statement and data from mobile insight firm App Annie, had about 260 million users in India then.
Things have changed dramatically since.
In the month of December, YouTube had 425 million monthly active users on Android phones and tablets in India, according to App Annie, the data of which an industry executive shared with TechCrunch. In comparison, WhatsApp had 422 million monthly active users on Android in India last month.
Factoring in the traction both these apps have garnered on iOS devices, WhatsApp still assumes a lead in India with 459 million active users1, but YouTube is not too far behind with 452 million users.
With China keeping its doors closed to U.S. tech giants, India emerged as the top market for Silicon Valley and Chinese companies looking to continue their growth in the last decade. India had about 50 million internet users in 2010, but it ended the decade with more than 600 million. Google and Facebook played their part to make this happen.
In the last four years, both Google and Facebook have invested in ways to bring the internet to people who are offline in India, a country of nearly 1.4 billion people. Google kickstarted a project to bring Wi-Fi to 400 railway stations in the country and planned to extend this program to other public places. Facebook launched Free Basics in India, and then — after the program was banned in the country — it launched Express Wi-Fi.
Both Google and Facebook, which identify India as their biggest market by users, have scaled down on their connectivity efforts in recent years after India’s richest man, Mukesh Ambani, took it upon himself to bring the country online. After he succeeded, both the companies bought multibillion-dollar stakes in his firm, Jio Platforms, which has amassed over 400 million subscribers.
Jio Platforms’ cut-rate mobile data tariff has allowed hundreds of millions of people in India, where much of the online user base was previously too conscious about how much data they spent on the internet, to consume, worry-free, hours of content on YouTube and other video platforms in recent years. This growth might explain why Google is doubling down on short-video apps.
The new figures shared with TechCrunch illustrate a number of other findings about the Indian market. Even as WhatsApp’s growth has slowed2 in India, it continues to enjoy an unprecedented loyalty among its users.
More than 95% of WhatsApp’s monthly active users in India use the app each day, and nearly its entire user base checks the app at least once a week. In comparison, three-fourths of YouTube’s monthly active users in India are also its daily active users.
The data also showed that Google’s eponymous app as well as Chrome — both of which, like YouTube, ship pre-installed3 on most Android smartphones — has also surpassed over 400 million monthly active users in India in recent months. Facebook’s app, in comparison, had about 325 million monthly active users in India last month.
When asked for comment, a Google spokesperson pointed TechCrunch to a report from Comscore last year, which estimated that YouTube had about 325 million monthly unique users in India in May 2020.
A separate report by research firm Media Partners Asia on Monday estimated that YouTube commanded 43% of the revenue generated in the online video market in India last year (about $1.4 billion). Disney+ Hotstar assumed 16% of the market, while Netflix had 14%.
Powered by WPeMatico
Spending on cosmetics has usually weathered economic crises, but that changed during the COVID-19 pandemic, with stay-at-home orders and masks tempering people’s desire to wear makeup. This forced retailers to accelerate their online strategies, finding new ways to capture shoppers’ attention without in-store samples. Virtual beauty try-on technology, like the ones developed by Perfect Corp., will play an important role in this shift to digital. The company announced today it has raised a Series C of $50 million led by Goldman Sachs.
Based in New Taipei City, Taiwan and led by chief executive officer Alice Chang, Perfect Corp . is probably best known to consumers for its beauty app YouCam Makeup, which lets users “try on” virtual samples from more than 300 global brands, including ones owned by beauty conglomerates Estée Lauder and L’Oréal Paris. Launched in 2014, YouCam Makeup now counts about 40 million to 50 million monthly active users and has expanded from augmented selfies to include livestreams and tutorials from beauty influencers, social features and a “Skin Score” feature.
Perfect Corp.’s technology is also used for in-store retail, e-commerce and social media tools. For example, its tech helped create a new augmented reality-powered try-on tool for Google Search that launched last month (its was previously used for YouTube’s makeup try-on features, too). It also worked with Snap to integrate beauty try-on features into Snapchat.
The new funding brings Perfect Corp.’s total raised so far to about $130 million. Its last funding announcement was a $25 million Series A in October 2017. The Series C will be used to further develop Perfect Corp.’s technology for multichannel retail and open more international offices (it currently has operations in 11 cities).
In a press statement, Xinyi Feng, a managing director in the Merchant Banking Division of Goldman Sachs, said, “The integration of technology through artificial intelligence, machine learning and augmented reality into the beauty industry will unlock significant advantages, including amplification of digital sales channels, increased personalization and deeper consumer engagement.”
Perfect Corp. will also be part of the investment firm’s Launch with GS, a $500 million investment initiative to support a diverse, international cohort of entrepreneurs.
The company uses facial landmark tracking technology, which creates a “3D mesh” around users’ faces so beauty try-ons look more realistic. In terms of privacy, chief strategy officer Louis Chen told TechCrunch that no user data, including photos or biometrics, is saved, and all computing is done within the user’s phone.
The vast majority, or about 90%, of Perfect Corp.’s clients are cosmetic or skincare brands, while the rest sell haircare, hair coloring or accessories. Chen said the goal of Perfect Corp.’s technology is to replicate as closely as possible the experience of trying on makeup in a store. When a user virtually applies lipstick, for example, they don’t just see the color on their lips, but also the texture, like matte, glossy, shimmer or metallic (the company currently offers seven lipstick textures, which Chen said is the most in the industry).
While sales of makeup have dropped during the pandemic, interest in skincare has grown. A September 2020 report from the NPD Group found that American women are buying more types of products than they were last year, and using them more frequently. To help brands capitalize on that, Perfect Corp. recently launched a tool called AI Skin Diagnostic solution, which it says is verified by dermatologists and grades facial skin on eight metrics, including moisture, wrinkles and dark circles. The tool can be used on skincare brand websites to recommend products to shoppers.
Before COVID-19, YouCam Makeup and the company’s augmented reality try-on tools appealed to Gen Z shoppers who are comfortable with selfies and filters. But the pandemic is forcing makeup and skincare brands to speed up their adaption of technology for all shoppers. As a McKinsey report about the impact of COVID-19 on the beauty industry put it, “the use of artificial intelligence for testing, discovery and customization will need to accelerate as concerns about safety and hygiene fundamentally disrupt product testing and in-person consultations.”
“Depending on the geography of the brand, in the past probably only 10%, no more than 20%, of their business was direct to consumer, while 80% was going through retail distribution and distribution partnerships, the network they already built over the year,” said Chen. But beauty companies are investing more heavily in e-commerce now, and Perfect Corp. capitalizes on that by offering its technology as a SaaS.
Another way Perfect Corp. has adapted its offerings during the pandemic is offering remote consultation tools, which means beauty and skincare consultants who usually work in salons or a store like Ulta can demonstrate makeup looks on clients through video calls instead.
“Every single thing we are building now is not a siloed technology,” said Chang. “It’s now always combined with video-streaming.” In addition to one-on-one chats, this also means live-cast shopping, which is extremely popular in China and gradually taking off in other countries, and the kind of AR technology that was integrated into YouTube and Snapchat.
Powered by WPeMatico
ShareChat, an Indian social network that added Twitter as an investor in 2019, may soon receive the backing of two more American firms.
The Bangalore-based startup is in advanced stages of talks to raise money from Google and Snap, as well as several existing investors, including Twitter, three sources familiar with the matter told TechCrunch.
The new financing round — a Series E — is slated to be larger than $200 million, with Google alone financing more than $100 million of it, four sources said, requesting anonymity as the talks are private. The round values ShareChat at more than $1 billion, two of the sources said.
ShareChat, Google and Snap did not immediately respond to a request for comment. ShareChat has raised about $264 million to date and was valued at nearly $700 million last year.
The terms of the deal could change and the talks may not materialize into an investment, the sources cautioned. Local TV channel ET Now reported last year that Google was in talks to acquire ShareChat.
ShareChat’s marquee and eponymous app caters to users in 15 Indian languages and has a large following in small Indian cities and towns. Twitter and Snap, on the other hand, are struggling to gain users beyond urban cities in the world’s second-largest internet market. Both Twitter and Snapchat have about 50 million monthly active users in India, according to a popular mobile insight firm.
In an interview with TechCrunch last year, Ankush Sachdeva, co-founder and chief executive of ShareChat, said the app was growing “exponentially” and that users were spending, on average, more than 30 minutes on the app each day.
If the deal goes through, it would be the first investment from Snapchat’s parent company into an Indian startup. Google, on the other hand, has been on a spree of late. The Android-maker last month invested in DailyHunt and InMobi’s Glance, both of which operate short-video apps.
Like the two, ShareChat also operates a short-video app. Its app, called Moj, had amassed more than 80 million monthly active users as of September last year, the startup said at the time. Several of these short videos apps, as well as Times Internet’s MX TakaTak (operated by MX Player), have witnessed an accelerated growth in recent quarters thanks in part to New Delhi banning ByteDance’s TikTok and hundreds of other Chinese apps mid-last year.
Last year, Google announced that it plans to invest $10 billion in India over the course of five to seven years. Days later, the company invested $4.5 billion in Indian telecom giant Jio Platforms. Google and Facebook, which invested $5.7 billion in Jio Platforms last year, reach more than 400 million users in the country.
Google, Facebook, ShareChat, DailyHunt and Glance generate most of their revenue through ads. About 85% of the ad market in India is currently commanded by Facebook and Google, analysts at Bank of America wrote in a report to clients last year. “We estimate this market to be $10 billion by 2024 and see room for Facebook to increase its market-share by 4 percentage points in 4 years led by partnership with Jio. We estimate Facebook may have $4.7 billion revenues by 2024,” they wrote in the equity research report, obtained by TechCrunch.
Powered by WPeMatico
Bangalore-based CRED is kickstarting the new year on a high note.
The two-year-old startup, led by high-profile entrepreneur Kunal Shah, said on Monday it has raised $81 million in a new financing round and bought shares worth $1.2 million (about 90 million Indian rupees) from employees.
The Series C financing round, as first reported by TechCrunch in late November, was led by DST Global. Existing investors Sequoia Capital, Ribbit Capital, Tiger Global and General Catalyst also participated in the round, and so did a few new names, including Satyan Gajwani of Indian conglomerate Times Internet, Sofina and Coatue.
The round gave CRED — which operates an eponymous app to reward customers for paying their credit card bill on time and offers deals from interesting online brands — a post-money valuation of $806 million.
In an interview with TechCrunch, Shah said that about 10% of CRED’s cap table is currently allocated to employees, and those who held vested stocks were eligible to sell up to 50% of their shares back to the startup in its first ESOP liquidity program. “We believe that startups should think about creating wealth for every shareholder, including employees.”
CRED has nearly doubled its customer base to about 5.9 million in the past year, or about 20% of the credit card holder base in India. The startup said that the median credit score of its customer was about 830, and about 30% of its customer base today holds a premium credit card. (On a side note, more than 50% of CRED customers pay their bills using UPI.)
CRED is one of the most talked-about startups in India, in part because of the scale at which its valuation has soared and the amount of capital it has been able to raise in such a short period.
One of the biggest questions surrounding CRED is just how it makes money, given how most fintech startups in the country — and there are many of them — are struggling to find a business model.
Shah said CRED makes money by cross-selling financing products — for which it has a revenue-sharing arrangement with banks and other financial institutions — and levies a similar cut from merchants who are on the platform today. More than 1,300 brands — including big names Starbucks, TAGG, Eat.Fit, Nykaa and emerging premium direct-to-consumer brands such as The Man Company, Sleepy Cat and Crossbeats –have joined the platform in recent years.
Direct-to-consumer market in India is still in its nascent stage, though some estimates say it could be worth $100 billion by 2025.
“I don’t think we were very deliberate to make D2C happen. It just so happened that in the early days when we offered rewards for D2C brands, they started to see huge traction,” he said, adding that CRED drove more than 30% sales for some brands.
“We realized that we were able to solve the discovery problem for customers. We are approaching this with themes — work-from-home and coffee — and it’s working out well. We are now playing matchmaking role between customers and brands that otherwise had to spend a lot of money in marketing.”
One of the biggest propositions of CRED is that it has been able to court some of the most sought-after customers in India. Unlike many other startups and giants such as Google and Facebook, CRED is not going after the next billion users.
“About 20 million customers account for 90% of all online consumption in India. These are the customers we are focusing on,” said Shah, who previously ran financial services firm Freecharge and delivered one of the rare successful exits in the country. The core challenge in chasing customers in smaller cities and towns in India is that very few people have the financial capacity to buy things, Shah said.
For that model to work, the GDP of India — where the average annual income of an individual is about $2,000 — needs to grow. And for that, we need more participation from females, said Shah. Less than 10% of the female population in India are currently part of the workforce, compared to over 90% in China.
An interesting use case for CRED today is that it could potentially license to venture firms data about the traction D2C brands are seeing on its platform, which could use it as a signal to inform their investment decisions.
Shah cautioned that the startup is “extraordinarily sensitive about data” but said the team is thinking about ways to help venture firms discover these firms. “We are planning to create a newsletter to showcase many of these brands to the investor world,” he said.
And finally, will CRED launch a credit card or other banking products? “Can we partner with banks to cross-sell every product that they today offer? The answer is yes,” said Shah, though he cautioned that the startup is in no hurry to supercharge its offerings.
Powered by WPeMatico
TMYTEK recently raised a Series A+ round of about $10 million for products that make it easier to test 5G millimeter wave equipment. So far, the company’s clients include KDDI, NTT DoCoMo and research institutions. But the Taiwanese startup has aspirations to sell its own base stations, too, competing with well-established players like Nokia, Ericsson, Samsung and Huawei. TMYTEK plans to use its expertise, gleaned from helping other researchers develop 5G infrastructure, to create what its chief executive officer describes as a “complete 5G industrial chain.”
Its latest funding round was led by TMYTEK’s manufacturing partner Inventec, one of the largest OEMs in Taiwan, and brings the startup’s total funding so far to $13.3 million. Other investors included Taisic Materials, ITEQ, Tamagawa Electronics and Taiwan’s National Development Fund. TMYTEK also recently took part in SparkLabs Taipei’s accelerator program.
Co-founder and chief executive officer Su-Wei Chang told TechCrunch that it plans to raise a Series B next to develop and commercialize its base stations. To get ready for its base station business, TMYTEK recently joined the O-RAN Alliance, founded by some of the world’s biggest telecoms to create more interoperable mobile networks, in a bid to encourage the development of new technology and faster deployment.
Chang said TMYTEK’s base in Taiwan gives it a strategic advantage. 5G manufacturing is an important part of Taiwan’s economy, with exports reaching record highs during the second half of 2020, thanks in part to demand for 5G-related equipment and technology for smartphones, autonomous vehicles and smart devices.
Chang studied at University of Massachusetts Amherst and when TMYTEK was founded six years ago, he was often asked why he didn’t stay in the United States, where it would have been easier to secure startup funding. But being in Taiwan puts the company closer to many important markets, including Japan, where 30% of its current business comes from, and gives TMYTEK a good foundation to expand into the U.S. and European market, he said.
It has also given the company a supply chain advantage. TMYTEK has manufacturing partners across Asia, including Inventec in Taiwan, and factories in Vietnam and Thailand, in addition to China. Chang said this means TMYTEK was not limited by the COVID-19 pandemic or the U.S.-China trade war.
Before launching TMYTEK in 2014, Chang and co-founder Ethan Lin both worked at Academia Sinica, one of the top research institutions in Taiwan, where they focused on millimeter waves even though at the time most researchers were more interested in the mid-band spectrum.
But as more devices and applications began to crowd the 4G spectrum, mmWave became less niche. With Qualcomm’s launch of next-generation 5G mmWave hardware and chips, and more carriers launching mmWave coverage, mmWave is poised to become mainstream.
Millimeter waves offer powerful signals with wide bandwidth and low latency, but drawbacks include difficulty traveling through obstacles like buildings. It also has a limited range, which is why millimeter waves need more base stations. Beamforming, which directs signals toward a specific device, and antenna array, or multiple antennas that work like a single antenna, are used to extend its coverage.
One of the main challenges for the millimeter wave market, however, is the lack of R&D tools to speed up their development and time to market, resulting in higher costs and slower deployment.
To keep up with market opportunities, TMYTEK transitioned from design and manufacturing projects for clients to offering 5G-focused solutions like the BBox, which stands for “beamforming box.” The BBox was created after a professor at National Taiwan University told Chang that his team was working on antenna design, but didn’t have the resources to work on beamforming technology, too. It lets researchers create 16 beams and control the signal’s amplitude and phase with software, so they can test how it works with antennas and other hardware more quickly. TMYTEK claims the BBox can save researchers and engineers up to 80% in time and cost.
Chang said TMYTEK realized that if researchers at NTU, one of Taiwan’s largest research universities, needed a solution, then other labs did, too. So far, it has delivered 30 sets to companies including KDDI, NTT DoCoMo, Fujitsu, several Fortune 500 companies and research institutions.
While the BBox was created for antenna designers, the company also began exploring solutions to help other designers, including algorithm developers who want to test beam tracking, communicate with base stations and collect data.

TMYTEK vice president Ethan Lin holds the antenna-in-package for its XBeam millimeter wave testing solution (Image Credits: TMYTEK)
For that scenario, TMYTEK created the XBeam, which it describes as a “total solution,” and is meant for the mass production phase, testing modules, smartphones and base stations before they are shipped. Traditional solutions to test modules rely on mechanical rotators, but Chang said this is more suited to the research and development process. The XBeam, which is based on the BBox, electronically scans beams instead. The company claims the XBeam is up to 20 times faster than other testing solutions.
TMYTEK created the XBeam’s prototype in 2019 and launched the commercialized version in November 2020.
The BBox and XBeam will help TMYTEK build its own base station business in two ways, Chang said. First, having its own solutions will allow TMYTEK to test base stations and bring them to market faster. Second, the startup hopes building a reputation on effective research and development tools will help it market its base stations to private and public networks. This is especially important to TMYTEK’s ambitions since their base stations will be up against products from major players like Nokia, Ericsson, Samsung and Huawei.
“Our advantage at TMYTEK is that we’re doing the design and we have good partners for manufacturing. Inventec, our investor, is a top five manufacturer in Taiwan,” he said. “And TMYTEK also builds our own testing solution, so our value is that we can provide a total solution to our customers.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Sony said on Friday that it will launch the PlayStation 5 in India on February 2, suggesting improvements in the supply chain network that was severely impacted last year because of the coronavirus pandemic.
The Japanese firm said it will begin taking pre-order requests for the new gaming console in India, the world’s second largest internet market, on January 12. The console will be available for pre-order from a number of retailers including Amazon India, Flipkart, Croma, Reliance Digital, Games the Shop, Sony Center, and Vijay Sales, the company said.
The PlayStation 5 is priced at Indian rupees 49,990 ($685), while the digital edition of the console will sell at Indian rupees 39,990 ($550). Xbox Series X, in comparison, is priced at $685 in India, and Xbox Series S sells at $480. Both the consoles launched in India in November.
However, much like elsewhere in the world, Microsoft has been struggling to meet the demand for the new Xbox consoles in India. The Xbox Series X is facing so much shortage in the country that it’s not even easy to locate its page on Amazon India.
The announcement today should allay concerns of loyal PlayStation fans, some of whom — including, of course, yours truly — secured a unit from the gray market at a premium in recent months after India was not included in the first wave of nations for the PS5. Fans have also been frustrated at Sony and its affiliated partners for not offering clarification or providing conflicting accounts about the probable launch of the new gaming console in recent months.
In November, Sony suggested that it had delayed the launch of the PS5 in India due to local import regulations. Game news site The Mako Reactor reported earlier this week that Sony is unlikely to offer warranty and after-sales support for PlayStation 5 accessories in India — as has been the case for several previous generations.
India is not yet a big market for full-fledged gaming consoles yet. According to industry estimates, Sony and Microsoft sold only a few hundred thousand units of their previous generation consoles in the country. Thanks to the proliferation of affordable Android smartphones and world’s cheapest mobile data tariffs, tens of millions of Indians have embraced mobile gaming in recent years.
Powered by WPeMatico
The rivalry between China’s top online learning apps has become even more intense this year because of the COVID-19 pandemic. The latest company to score a significant funding round is Zuoyebang, which announced today (link in Chinese) that it has raised a $1.6 billion Series E+ from investors including Alibaba Group. Other participants included returning investors Tiger Global Management, SoftBank Vision Fund, Sequoia Capital China and FountainVest Partners.
Zuoyebang’s latest announcement comes just six months after it announced a $750 million Series E led by Tiger Global and FountainVest. The latest financing brings Zuoyebang’s total raised so far to $2.93 billion. The company did not disclose its latest worth, but Reuters reported in September that it was raising at a $10 billion valuation.
One of Zuoyebang’s main competitors is Yuanfudao, which announced in October that it had reached a $15.5 billion valuation after closing a $2.2 billion round led by Tencent. This pushed Yuanfudao ahead of Byju as the world’s most valuable edtech company. Another popular online learning app in China is Yiqizuoye, which is backed by Singapore’s Temasek.
Zuoyebang offers online courses, live lessons and homework help for kindergarten to 12th grade students, and claims about 170 million monthly active users, about 50 million of whom use the service each day. In comparison, there were about 200 million K-12 students in 2019 in China, according to the Ministry of Education (link in Chinese).
In fall 2020, the total number of students in Zuoyebang’s paid livestream classes reached more than 10 million, setting an industry record, the company claims. While a lot of the growth was driven by the pandemic, Zuoyebang founder Hou Jianbin said in the company’s funding announcement that it expects online education to continue growing in the longer term, and will invest in K-12 classes and expand its product categories.
Powered by WPeMatico