Asia
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Online lending firms might be beginning to feel the heat of the coronavirus pandemic in Southeast Asia, but investors’ faith in digital insurance startups remains unflinching in the region.
Jakarta-based Qoala has raised $13.5 million in its Series A financing round, the one-year-old startup said Tuesday. Centauri Fund, a joint venture between funds from South Korea’s Kookmin Bank and Telkom Indonesia, led the round.
Sequoia India, Flourish Ventures, Kookmin Bank Investments, Mirae Asset Venture Investment, Mirae Asset Sekuritas and existing investors MassMutual Ventures Southeast Asia, MDI Ventures, SeedPlus and Bank Central Asia’s Central Capital Ventura participated in the round, which pushes the startup’s to-date raise to $15 million.
Qoala works with leading insurers including AXA Mandiri, Tokio Marine, Great Eastern to offer customers cover against phone display damage, e-commerce logistics and hotel-quality checks. The startup says it offers personalized products to customers and eases the burden while making claims by allowing them to upload pictures.
The startup maintains partnership with several e-commerce firms including Grabkios, JD.ID, Shopee and Tokopedia and hotel and travel booking firms PegiPegi and RedBus.
It uses machine learning to detect fraud claims. It’s a win-win scenario for customers, who can make claims easily and have more affordable and sachet insurance products to buy, and for insurers, who can reach more customers.
Qoala processes more than 2 million policies each month, up from 7,000 in March last year. The startup said it is working on insurance products to cover health and peer-to-peer categories. The startup, which employs about 150 people currently, plans to double its headcount in a year.
“As a relatively new entrant in the space we are delighted to partner with leading global investors whose tremendous thought leadership as well as operational experience will allow us to maintain our innovative edge. This truly demonstrates the ecosystem’s belief in what Qoala is trying to achieve — humanizing insurance and making it accessible and affordable to all,” said Harshet Lunani, founder and chief executive of Qoala, in a statement.
Kenneth Li, managing partner at Centauri Fund, said Qoala’s multi-channel approach has the potential to unlock Indonesia’s untapped insurance industry.
“Our thesis identified that Indonesia has a considerably low gross written premium (GWP) to GDP ratio in comparison to other emerging countries, coupled with the large growing middle class in need of more security in their financial planning which allows immense potential for the insurance sector to take off in Indonesia through innovative propositions,” he added.
According to one estimate (PDF), Southeast Asia’s digital insurance market is currently valued at $2 billion and is expected to grow to $8 billion by 2025. Last week, Singapore-based Igloo extended its Series A financing round to add $8.2 million to it.
Powered by WPeMatico
Oriente, a Hong Kong-based startup that develops tech infrastructure for digital credit and other online financial services, has raised $50 million for its ongoing Series B round. The funding was led by Peter Lee, co-chairman of Henderson Land, one of Hong Kong’s largest property developers, with participation from investors including website development platform Wix.com.
Launched in 2017 by Geoff Prentice (one of Skype’s co-founders), Hubert Tai and Lawrence Chu, Oriente focuses on markets that are underserved by traditional financial institutions. The new funding will be used for growth in Oriente’s existing markets, the Philippines and Indonesia, and expansion into new countries, including Vietnam.
It will also be used to continue building Oriente’s technology, which uses big data analytics to help merchants increase sales conversions and lower risk. Oriente has now raised more than $160 million in equity and debt, including a $105 million round in November 2018.
While many large tech companies, including Grab, Google, Facebook, Amazon, Uber, Apple and Samsung, are looking at digital payments and other online financial services, they need the tech infrastructure to do so, and partners that can also help them handle regulations in different markets.
Oriente doesn’t compete with payment providers. Instead, it is “innovating credit as a service,” Prentice told TechCrunch, by building technology that allows offline and online merchants to launch digital credit solutions quickly.
Oriente “is the only company that is focusing on building an end-to-end digital financial services infrastructure,” he added, with services created for consumers, online and offline merchants, and enterprise clients.
For consumers, the startup currently offers two apps, Cashalo in the Philippines and Finmas in Indonesia, which it says has a combined 5 million users and more than 1,000 merchants. Services include cash loans, online credit and working capital for small to medium-sized enterprises.
Oriente says that in 2019, it saw a 700% year-over-year growth in transactions and served more than 4 million new users, while merchant partners had a more than 20% increase in sales volume.
Over the next few months, Oriente plans to expand its Pay Later digital credit feature and launch new growth capital solutions for small businesses that need financing. Oriente also has several partnerships in the works to expand its enterprise solutions for larger businesses and corporations.
In Vietnam, Oriente is currently beta testing a consumer platform similar to Cashalo and Finmas. It will offer online credit and financing, as well as other services in partnership with local companies.
Oriente has also started focusing on how to serve businesses during the COVID-19 pandemic, since many merchants are coping with revenue declines, loss of users and cash flow issues.
“Over the past few weeks, we’ve reprioritized our corporate strategy to focus on the top opportunities within each market. We have also taken various steps to rebuild our organizations for optimized operational and financial efficiency in line with current and forecasted market conditions and our more focused strategy,” Prentice said.
“Our aim is not only to mitigate anticipated headwinds on liquidity but to demonstrate that our business has the potential to overcome and outperform the market in a recession—unlocking value for all stakeholders for years to come.”
Powered by WPeMatico
India has emerged as one of the fastest growing smartphone markets in the last decade, reporting growth each quarter even as handset shipments slowed or declined elsewhere globally. But the world’s second largest smartphone is beginning to feel the coronavirus heat, too.
The Indian smartphone market grew by a modest 4% year-over-year in the quarter that ended on March 31, research firm Counterpoint said Friday evening. The shipment grew annually in January and February, when several firms launched their smartphones and unveiled aggressive promotional plans.
But in March the shipment saw a 19% year-over-year dip, the firm said. Counterpoint estimated that the smartphone shipments in India will decline by 10% this year, compared to a 8.9% growth in 2019 and 10% growth in 2018.
The research firm also cautioned that India’s lockdown, ordered last month, has severely slowed down the local smartphone industry and it may take seven to eight months to get back on track. Currently, only select items such as grocery products are permitted to be sold in India.
Prachir Singh, Senior Research Analyst at Counterpoint Research, said the COVID-19 impact on India was relatively mild until mid-March. “However, economic activities declined as people save money in expectation of an extended period of uncertainty and an almost complete lockdown. Almost all smartphone manufacturing has been suspended. Further, with the social distancing norms, factories will be running at lower capacities even after the lockdown is lifted,” he said.
Overall, 31 million smartphone units shipped in India in Q1 2020. Chinese smartphone maker Xiaomi, which has held the tentpole position in what has become its biggest market globally for more than two years, widened its lead to command 30% of the market.
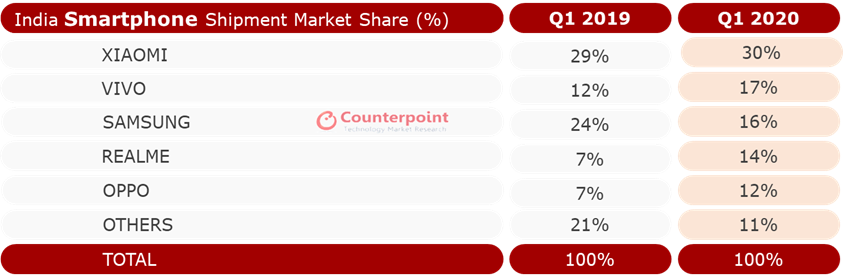
Vivo’s share grew to 17%, up from 12% during the same period last year. Samsung, which once led the Indian market, now sits at the third spot with 16% market share, down from 24% in Q1 2019. Apple maintained its recent momentum and grew by a strong 78% year-over-year in Q1 this year. It now commands 55% of the premium smartphone segment (handsets priced at $600 or above.).
More than 100 smartphone plants in India assemble or produce about 700,000 to 800,000 handsets a day, some of which are exported outside of the country. But the lockdown has halted the production and could cost the industry more than $3 billion to $4 billion in direct loss this year.
“We often draw parallels between India and China. But in China, their factories have adopted automation at various levels, something that is not the case in India,” said Tarun Pathak, a senior analyst at Counterpoint, earlier this week.
China, where smartphone sales declined by 38% annually in February this year, has already started to see recovery. Xiaomi said last month that its phone factories were already operating at more than 80% of their capacity. Globally, smartphone shipment declined by 14% in February, according to Counterpoint.
Powered by WPeMatico
While some U.S. investors might have taken comfort from China’s rebound, we still find ourselves in the early innings of this period of uncertainty.
Some epidemiologists have estimated that COVID-19 cases will peak in April, but PitchBook reports that dealmaking was down -26% in March, compared to February’s weekly average. The decline is likely to continue in coming weeks — many of the deals that closed last month were initiated before the pandemic, and there is a lag between when deals are made and when they are announced.
However, there’s still hope. A recent report concluded that because valuations are lower and there’s less competition for deals, “the best-performing vintages tend to be those that invest at the nadir of a downturn and into the early stage of recovery.” There are countless examples from the 2008 recession, including many highly valued VC-backed businesses such as WhatsApp, Venmo, Groupon, Uber, Slack and Square. Other early-stage VCs seem to have arrived at a similar conclusion.
Also, early-stage investing seems more resilient. During the last recession, angel and seed activity increased 34% as interest in the stage boomed during a period of prolonged growth.
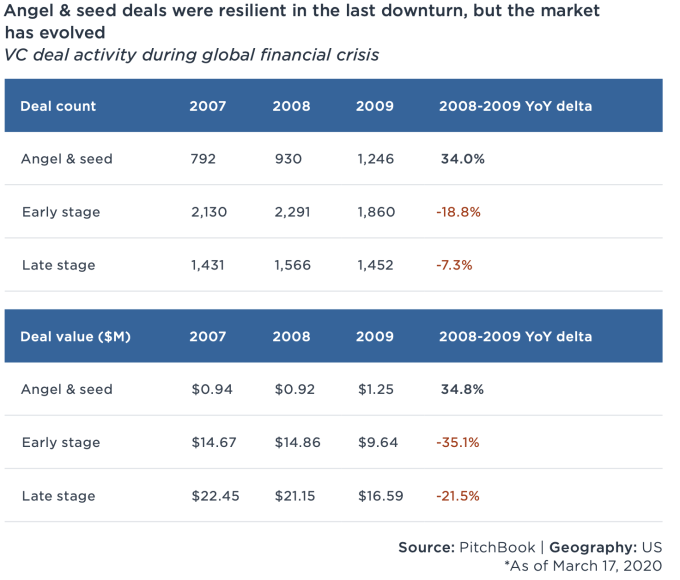
Image Credits: PitchBook (opens in a new window)
Furthermore, there is still capital to be deployed in categories that interested investors before the pandemic, which may set the new order in a post-COVID-19 world. According to data provider Preqin Ltd., VC dry powder rose for a seventh consecutive year to roughly $276 billion in 2019, and another $21 billion were raised last quarter. And looking at the deals on the early-stage side that were made year to date, especially in March, the vertical categories that garnered the most funding were enterprise SaaS, fintech, life sciences, healthcare IT, edtech and cybersecurity.
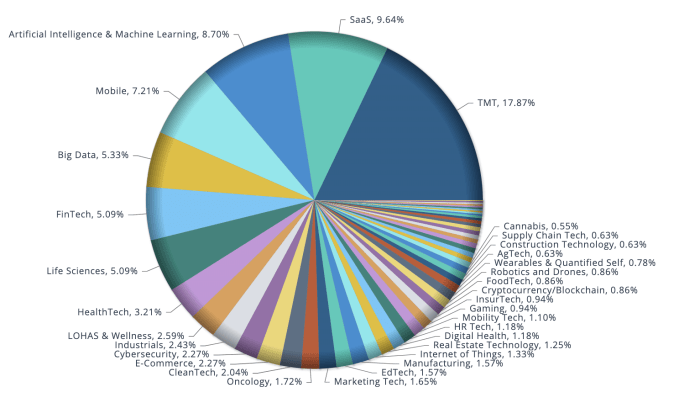
Image Credits: PitchBook
That said, if VCs have the capital to deploy and are able to overcome the obstacle of “having never met in person,” here are six investment trends that could emerge when the pandemic is over.
Powered by WPeMatico
On-demand mobility, when done successfully, strikes a balance between demand and supply while providing reliable service and making a profit. It’s a sweet spot that can be difficult, if not impossible, to find.
Autofleet, a startup that develops fleet optimization software to redirect underused vehicles into ride-hailing and delivery services, wants to solve that mission impossible. Now, the company founded by former Avis and Gett employees, has raised $7.5 million in seed and Series A funding to expand into international markets and grow its research and development team.
The Series A was led by MizMaa Ventures with participation from Maniv Mobility, Next Gear Ventures and Liil Ventures. Its seed financing was led by Maniv Mobility.
Autofleet developed a fleet management platform that can be used by rental car companies, car sharing operators and automakers to launch or better manage mobility services. The platform includes a booking app and integrations to delivery services, demand prediction, pooling and optimization algorithms as well as a driver app, and control center. The company also has developed a simulator tool that lets operators plan how a fleet will be deployed before a single vehicle hits the road.
For example, a rental company with abundant inventory and little demand for traditional multi-day contracts could use the platform to launch and then manage a car-sharing service. Autofleet already has partnerships with Avis Budget Group, Zipcar, Keolis and Suzuki .
That focus on managing supply side constraints is what attracted Maniv Mobility to invest in the seeding and Series A rounds, according the firm’s general partner Olaf Sakkers.
Autofleet’s biggest markets today are in Europe and the U.S., CEO Kobi Eisenberg told TechCrunch . The company is seeing early traction and fast growth in Latin America and Asia-Pacific. Eisenberg said they plan to double down on these markets. The company also expects to announce a partnership in Asia to accelerate growth in that region.
Autofleet is also looking for new opportunities for how vehicle fleets can be used, including ways to help micromobility companies improve their unit economics, according to Eisenberg.
In this age of COVID-19 — when asset-heavy businesses like rental car companies have seen their businesses upended — Autofleet has already discovered new uses for its platform. The platform is being used to help companies shift fleets to meet today’s demand for logistics and medical transportation. Autofleet is also selling its platform to companies looking to leverage their vehicle assets for their delivery services.
“We’re hearing from fleet partners around the globe who are experiencing dramatic drops in demand, and therefore significant portions of their fleet and drivers are un-utilized,” Eisenberg said. “At the same time, we have seen a sharp increase in demand for delivery services from businesses across all verticals: retail and supermarkets, restaurants.”
Powered by WPeMatico
More than six dozen startup founders, venture capitalists and lobby groups in India have requested the government to grant them a “robust relief package” to help combat severe disruptions their businesses face due to the coronavirus outbreak.
In a joint letter to India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi, startups requested the government to bankroll 50% of their workforce’s salaries for six months, provide interest-free loans from banks, waive rent for three months and offer tax benefits among other things.
“Unfortunately, our startup companies across the nation are inherently young, less resilient and most vulnerable. Many of them face likely devastation during this extraordinary economic downturn. At this dire moment, Indian startups need a robust relief package from the government, lest all our collective efforts of the past few years are in vain,” they wrote.
Among those who have signed the letter include Mohit Bhatnagar, a managing director at Sequoia Capital, which is in advanced stages to close a fresh $1.3 billion fund for India and Southeast Asia, Gaurav Agarwal of online medicine store 1mg, Debjani Ghosh of industry body Nasscom, Karthik Reddy of Blume Ventures, Anand Lunia of India Quotient, Deepinder Goyal of Zomato, and Sriharsha Majety of Swiggy.
Some prominent startup founders and VCs including Vijay Shekhar Sharma of Paytm, and Ritesh Agarwal of Oyo, have also held a meeting with Piyush Goyal, the commerce minister in India, for a similar relief.
“We seek your urgent intervention to help ensure India’s startup ecosystem survives this crisis to emerge as a pillar of growth, employment and innovation to help drive India’s recovery. We need the startup ecosystem to survive in order to help the economy bounce back. We have enclosed herewith our submission for your kind consideration and we look forward to your support in this regard,” the joint letter reads.
The request for bailout comes amid a national lockdown in India that has disrupted countless businesses. New Delhi ordered a 21-day lockdown last month in a bid to curtail the spread of Covid-19.
Earlier this month, ten prominent VC and PE funds in India cautioned startups to brace for the “worst” months ahead.
“Assumptions from bull market financings or even from a few weeks ago do not apply. Many investors will move away from thinking about ‘growth at all costs’ to ‘reasonable growth with a path to profitability.’ Adjust your business plan and messaging accordingly,” they said.
As India, where the economy growth has been slowing for several quarters, scrambles to provide for its 1.3 billion citizens, the letter has drawn some criticism from industry figures.
Disappointed to see many startup leaders & investors that I admire add their names to this shameful letter to the govt asking for bailouts – surely at this time the govt has more important things to worry about than pay “50% of salary bills & contract wage bills paid by startups”
— Sumanth Raghavendra (@sumanthr) April 10, 2020
“I can’t fathom how such a list gets made in a country of more than a billion people who are facing a crisis unlike any they’ve seen before. A significant majority of them daily wage earners who have no financial cushion or any idea where their next meal is going to come from. Let’s not even stray into health and the need for medical emergencies; just putting three square meals on the table a day is proving to be impossible for so many,” wrote Ashish K. Mishra in a column on The Morning Context.
“At this very moment, it is they who need the government’s support. Not fat cats with bloated, middling business models and venture capital funds whose begging bowls are now seemingly larger than their risk appetite,” he added.
Companies asking for a bailout is not limited to India. Oil giants have sought similar help from the U.S. President Donald Trump — and VCs and startups are beginning to explore their option. Brent Hoberman, chairman and co-founder of Founders Factory and Firstminute Capital, urged the UK government to provide some relief to startups last month. But the government has yet to do much about it, just ask Deliveroo, Graphcore and other big UK startups.
Powered by WPeMatico
Sony said on Thursday that it is investing $400 million to secure a 4.98% stake in Chinese entertainment giant Bilibili.
10-year old Bilibili started as an animation site, but has expanded to other categories including e-sports, user-generated music videos, documentaries, and games. The service, which has amassed over 130 million users, has attracted several big investors over the years, including Chinese giants Tencent and Alibaba.
The announcement pushed Bilibili’s share up by 7.6% in pre-market trading. Sony has made the investment through its wholly-owned subsidiary Sony Corporation of America.
In a statement, Sony said the company believes China is a key strategic region in the entertainment business. BiliBili says it targets China’s Gen-Z. The vast majority of its users — about 80% — were born between 1990 and 2009.
The two companies have also agreed to pursue collaboration opportunities in the entertainment field in China, including animation and mobile game apps, they said.
You can read more about Bilibili’s business and dominance in China in my colleague Rita Liao’s piece here.
Powered by WPeMatico
Mergers and acquisitions largely grinded to a halt at the end of March, in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic spreading around the world, but today comes news of a deal out of Europe that underscores where pockets of activity are still happening. Avira, a cybersecurity company based out of Germany that provides antivirus, identity management and other tools both to consumers and as a white-label offering from a number of big tech brands, has been snapped up by Investcorp Technology Partners, the PE division of Investcorp Bank. Investcorp’s plan is to help Avira make acquisitions in a wider security consolidation play.
The financial terms of the acquisition are not being disclosed in the companies’ joint announcement, but the CEO of Avira, Travis Witteveen, and ITP’s MD, Gilbert Kamieniecky, both said it gives Avira a total valuation of $180 million. The deal will involve ITP taking a majority ownership in the company, with Avira founder Tjark Auerbach retaining a “significant” stake of the company in the deal, Kamieniecky added.
Avira is not a tech startup in the typical sense. It was founded in 1986 and has been bootstrapped (in that it seems never to have taken any outside investment as it has grown). Witteveen said that it has “tens of millions” of users today of its own-branded products — its anti-virus software has been resold by the likes of Facebook (as part of its now-dormant antivirus marketplace) — and many more via the white-label deals it makes with big names. Strategic partners today include NTT, Deutsche Telekom, IBM, Canonical and more.
He said that the company has had many strategic approaches for acquisition from the ranks of tech companies, and also from more typical investors, but these were not routes that it has wanted to follow, since it wanted to grow as its own business, and needed more of a financial injection to do that than what it could get from more standard VC deals.
“We wanted a partnership where someone could step in and support our organic growth, and the inorganic [acquisition] opportunity,” he said.
The plan will be to make more acquisitions to expand Avira’s footprint, both in terms of products and especially to grow its geographic footprint: today the company is active in Asia, Europe and to a lesser extent in the US, while Investcorp has a business that also extends deep into the Middle East.
Cybersecurity, meanwhile, may never go out of style as an investment and growth opportunity in tech. Not only have cyber threats become more sophisticated and ubiquitous and targeted at individual consumers and businesses over the last several years, but our increasing reliance on technology and internet-connected systems will increase the demand and need to keep these safe from malicious attacks.
That has become no more apparent than in recent weeks, when much of the world’s population has been confined to shelter in place. People have in turn spent unprecedented amounts of time online using their phones, computers and other devices to read news, communicate with their families and friends, entertain themselves, and do critical work that they may have in part done in the past offline.
“In the current market, you can imagine a lot are concerned about the uncertainties of the technology landscape, but this is one that continues to thrive,” said Kamieniecky. “In security, we have seen companies develop quite rapidly and quickly, and here we have an opportunity to do that.”
Avira has been somewhat of a consolidator up to now, buying companies like SocialShield (which provided online security specifically for younger and social media users), while ITP, with Investcorp having some $34 billion under management, has made many acquisitions (and divestments) over the years, with some of the tech deals including Ubisense, Zeta Interactive and Dialogic.
Powered by WPeMatico
We finally know just about how many subscribers Hotstar has amassed over the years in India. “Approximately 8 million.”
Disney said on Wednesday that its eponymous streaming service now has over 50 million subscribers, nearly 8 million of whom are in India, where it launched its service atop Hotstar less than a week ago.
Five-year-old Hotstar is the most popular on-demand streaming service in India with more than 300 million users. The service and its operator, Indian network Star India, were picked up by Disney as part of its $71 billion deal with Fox last year.
For years, people in the industry have been curious about Hotstar’s premium subscriber base — to no luck. Most estimates have suggested it had about 1.5 million to 2 million subscribers. Executives at rival firms have expected that figure to be lower.
In fact, a months-long analysis conducted by one streaming firm in India concluded recently that there were 2 million paying subscribers for music and video services. So 8 million is a huge milestone.
But ARPU that Disney will clock from these 8 million subscriber is going to be far lower. Disney+ Hotstar is available in India at a yearly subscription cost of about $20. (That’s the revised subscription cost. Prior to Disney+’s launch in India, Hotstar charged about $13.) The service also offers a lower-cost tier that costs under $5.5 a year.
And for that $20 a year, subscribers of Disney+ Hotstar get access to a wide-range of catalog that includes access to Disney Originals in English as well as several local languages, live sporting events, dozens of TV channels, and thousands of movies and shows, including some sourced from HBO, Showtime, ABC and Fox that maintain syndication partnerships with the Indian streaming service.
“I think everyone is still trying to sort out the right pricing. It’s true the average Indian consumer is used to far lower prices and can’t afford more. However, we need to focus on the consumers likely to buy this, who have the requisite broadband access and income, etc,” Matthew Ball, former head of strategic planning for Amazon Studios, told TechCrunch in a recent conversation.
Disney+ competes with more than three dozen international and local players in India, including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Times Internet’s MX Player (which has over 175 million monthly active users), Zee5, Apple TV+ and Alt Balaji, which has over 27 million subscribers.
Most of these services monetize their viewers through ads, and have kept their monthly subscription price below $3.
Powered by WPeMatico
DeHaat, an online platform that offers full-stack agricultural services to farmers, has raised $12 million as it looks to scale its network across India.
The Series A financial round for the eight-year-old Patna and Gurgaon-based startup was led by Sequoia Capital India. Dutch entrepreneurial development bank FMO, and existing investors Omnivore and AgFunder, also participated in the round. The startup, which began to seek funding from external investors last year, has raised $16 million to date and $3 million in venture debt.
DeHaat (which means village in Hindi) eases the burden on farmers by bringing together brands, institutional financers and buyers on one platform, explained Shashank Kumar, co-founder and chief executive of the startup, in an interview with TechCrunch.
The platform helps farmers secure thousands of agri-input products, including seeds and fertilizers, and receive tailored advisory on the crop they should sow in a season. “We have built a comprehensive database of crop tests to offer advice to farmers,” he said.
DeHaat, which employs 242 people, also helps them connect with 200 institutional partners to provide farmers with working capital, and when the season is over, helps them sell their yields to bulk buyers such as Reliance Fresh, food delivery startup Zomato and business-to-business e-commerce giant Udaan.
DeHaat today operates in 20 regional hubs in the eastern part of India — states such as Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and Jharkhand — and serves more than 210,000 farmers, said Kumar.

Shashank Kumar, Amrendra Singh, Adarsh Srivastav and Shyam Sundar Singh co-founded DeHaat in 2012
The startup has developed a network of hundreds of micro-entrepreneurs in rural areas that distribute agri-input goods to farmers from their regional hubs and then bring back the output to the same hub.
“We have an app in local languages and a helpline desk that farmers, many of whom don’t own a smartphone, use to reach out to us and explain their pain points and needs,” he said.
DeHaat does not charge any fee for its advisory, but takes a cut whenever farmers use its platform to buy agri-inputs or sell their crop yields.
The startup will use the fresh capital to extend its network to 2,000 rural retail centres, on-board more micro-entrepreneurs for last-mile delivery and reach 1 million farmers by June of next year, said Kumar. DeHaat is also working on automating its supply chain and developing more sophisticated data analytics, he said.
At stake is India’s agriculture market that is worth $350 billion and serves nearly 100 million small and independent farmers, said Abhishek Mohan, VP at Sequoia Capital India, the VC fund that writes more checks than anyone else in the country.
“This industry is on the brink of a massive transformation thanks to ease of regulation, farmers getting organized and increasing penetration of smartphones. DeHaat is leveraging these trends to build the next-gen product in agricultural supply chain,” said Mohan in a statement.
“The tipping point that led to Sequoia India’s decision to partner with them was the field visit, where the farmers expressed how proud they were to be associated with a platform they felt truly worked in their favour. This impact and deep brand loyalty stems from the leadership team’s razor-sharp focus, deep empathy and fine execution,” he added.
Powered by WPeMatico