funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Cent was founded in 2017 as an ad-free creator network that allows users to offer each other crypto rewards for good posts and comments — it’s like gifting awards on Reddit, but with Ethereum. But in late 2020, Cent’s small, San Francisco-based team created Valuables, an NFT market for tweets, and by March, the small blockchain startup was thrown a serendipitous curveball.
“We just wrapped up for the day, and I was about to go eat dinner, and all these people started texting me,” remembers CEO Cameron Hejazi. Then, he realized that Twitter CEO Jack Dorsey had minted Twitter’s first-ever Tweet through Cent’s Valuables application. “I was basically like, mildly shivering for the rest of the night. The whole team, we were like, ‘Okay, battle stations, prepare to get hacked!’ ”
Dorsey ended up selling his NFT for $2.9 million, and he donated the proceeds to Give Directly’s Africa Response fund for COVID-19 relief. But for Cent, it was as if the small company had just been handed a free marketing campaign. Now, about five months later, Cent is announcing a $3 million round of seed funding with investors like Galaxy Interactive, former Disney chairman Jeffrey Katzenberg, will.i.am and Zynga founder Mark Pincus.
On Valuables, anyone on the internet can place an offer on any tweet, which then makes it possible for someone else to make a counter-offer. If the author of the tweet accepts an offer (logging into Valuables requires you to validate your Twitter account), then Cent will mint the tweet on the blockchain and create a 1-of-1 NFT.
The NFT itself contains the text of the tweet, the username of the creator, the time it was minted and the creator’s digital signature. The NFT also includes a link to the tweet, though the linked content lives outside the blockchain.

Image Credits: Cent (opens in a new window)
There’s nothing proprietary about minting tweets as NFTs — another company could do the same thing that Cent is doing. Even Twitter itself has recently dabbled in giving away free NFT art, though it hasn’t tried to sell actual tweets as NFTs like Cent. Still, Hejazi sees Dorsey’s use of Cent like an endorsement — he thinks it would be difficult for Twitter to shut them down, since Dorsey made $2.9 million on the platform himself. After all, Dorsey chose Cent instead of taking a screenshot of his first tweet, minting the .JPG as an NFT and posting it on a larger NFT platform, like OpenSea.
“We’ve spoken with people at Twitter. I’m positive that we have a healthy relationship going,” Hejazi said (Twitter declined to comment on or confirm whether that’s true). “We thought about applying this approach to other social platforms, like Instagram and TikTok, but we hypothesized that this is particularly suited for Twitter, because it’s a conversation platform, and it’s where all of the crypto people are actually living.”
With Cent’s seed funding Hejazi hopes to continue building the platform. The company’s goal is to enable anyone creative to make an income through the use of NFTs — that means developing tools to make it simpler for its users to mint NFTs, but also, building out its existing creator-focused social network. The content people post on Cent is usually creative work, like art and writing, rather than short posts — it’s closer to DeviantArt than it is to Reddit. These are lofty goals for a $3 million seed funding round, but there are aspects of Cent’s Beta platform that make it promising.
“There’s already value in what we post on social media. It’s just being proxied through ad dollars, and it doesn’t have to be the case that there’s so much wealth concentration in a single entity. We can work toward a system that decentralizes that wealth,” said Hejazi. “These networks as they exist have monopolies on distribution — you can’t take your Twitter audience, download it as a .CSV and send them all an email.”
A screenshot of Cent’s social platform.
In addition to independent distribution lists, Hejazi wants to move away from the ad-supported internet. He references Substack as an example of a company where the creator has control of their list, and at the same time, the platform can remain ad-free, since the money that propels it comes from the users who pay to subscribe to newsletters (and also, venture capital helps).
But Cent does something different by allowing users to essentially invest in creators who they think have the potential to take off on their platform.
Users can “seed” a post, which is how you subscribe to a creator participating on the creatives side of Cent’s platform. As the seeder, you pay a set fee of at least one dollar per month. There’s an incentive to support up-and-coming creators on the platform, because seeders get a portion of the creators’ future profit — it’s like making a bet on them that they will continue to make great content in the future. Five percent of profits go toward Cent, but the remaining 95% is split 50/50 between the creator and all of their past seeders. Participating on this platform would allow creators to network and show support for one another, but doesn’t prevent them from more directly monetizing their work on other creator platforms, like Patreon.
In addition to seeding posts, users can also “spot” other people’s posts — Cent’s version of a “like” button. Each “spot” is the equivalent of one cent from the user’s crypto wallet. Cent’s argument is that getting 1,000 likes on a post on other platforms yields nothing but a vague sensation of social clout. But on Cent, if a user gets 1,000 “spots,” that’s $10. Still, a project like this can only work if enough people use the platform.
“When we started Cent, we chose cryptocurrencies because we loved the idea of someone being able to earn money with nothing more than their creativity and a crypto address,” Hejazi said. “Over time, we’ve found it to be limiting as a payment type — very few people actually own it and have it ready to spend. We’re working on ways to make payments to creators using Cent easier, and are exploring both crypto-native and non-crypto options.”
This mindset echoes other NFT startups like Yat, which allows payments via credit card as part of its “progressive decentralization” model. So much of these companies’ success depends on public buy-in toward an eventual decentralized, blockchain-based internet. But until then, companies like Cent will continue to experiment in reimagining how creatives can get paid online.
Powered by WPeMatico
During the pandemic, especially when we were in lockdown, just about every retailer had to build its online presence and do it quickly. As people move to shop online in larger numbers, being able to personalize that experience has become more crucial. That made the pandemic a pivotal moment for Bluecore, an e-commerce personalization platform, and today the company announced a $125 million Series E on a $1 billion valuation.
Existing investor Georgian led the round, with participation from other existing investors FirstMark and Norwest, along with new investor Silver Lake Waterman. Today’s investment brings the total raised to $225 million, according to the company.
Until fairly recently, Bluecore CEO and co-founder Fayez Mohamood says that retail outreach was mostly about driving traffic to brick and mortar stores or to the company website, but as more business gets conducted online, it has changed how brands have to interact with their customers.
“We believe in that shift, and Bluecore is a retail-specific, multichannel personalization platform, and we combine basically three types of data. First is customer identity. Second is shopper behavior. And then thirdly and most importantly, the product catalog of a retailer, and using that we drive personalized experiences on various channels,” Mohamood explained.
The company was founded in 2013, and has been able to evolve the notion of personalization since then in a significant way. Mohamood says the pandemic really pushed things into the digital realm where his company’s strength lies, and that’s one of the primary reasons they are taking on this funding.
“Personalization has always been important, but I think the value retailers can derive from it has dramatically accelerated as digital became a bigger and bigger portion of everybody’s revenue stream. And over the last year, that became even more critical,” he said.
As the company’s growth has accelerated, so has the hiring. In May 2020, Bluecore had 236 employees; today it has more than 300, and it’s shooting to be over 400 by the end of the year. He says that as he grows the company, diversity and inclusion is a crucial component to have the employee base reflect the diversity of the customers they serve.
“It starts with the executive team, so I’m extremely proud of the fact that on our executive team close to half our team is female. We have a committee that is represented by the core employees that is a diversity, equity and inclusion committee where we have thoughts and ideas and most most importantly actions on how we can build a better diverse, inclusive workplace. And that translates it into OKRs,” he said.
As a Series E company with a billion-dollar valuation, Mohamood can see becoming a public company at some point, but it is not an immediate goal, as he pursues growth over profitability. “The way we think about it is we have this brand that’s going to help us invest in our product capabilities, our leadership capabilities and our go-to-market capabilities to build something that has the ability to [be a public company some day]. Having said that, we’re pursuing growth, and if that’s the goal, we find that staying private helps us do that,” he said. And with $125 million of runway, the company has plenty of freedom to take its time.
Powered by WPeMatico
As more people dust off their luggage and passports after stowing them away during the global pandemic, Elude aims to show travelers a new way to take spontaneous trips.
The Los Angeles-based startup launched its travel discovery mobile app Thursday, a budget-first search engine that shows people how far their money will take them. The platform’s personalized onboarding experience customizes trip packages and offers future travel suggestions based on those preferences.
The idea for the company came three years ago from Alex Simon, CEO, and Frankie Scerbo, CMO, who met in college and bonded over their love of traveling and would do so together any time they had a long weekend. One New Year’s they tried planning a trip, but everything was too expensive. Not being able to find something on their budget, they came up with the idea for Elude.
Rather than searching by destination, Elude gathers information like budget, time frame and trip preferences (think beach versus mountains), then presents users with flight and hotel results for destinations they may never have thought existed or could be traveled to on their budgets.
The company taps into the same flight and hotel databases that all online travel companies use that store hundreds of thousands of flights and hotels and only suggests hotels with 3.5 stars and above.

Elude app
The co-founders have now raised $2.1 million in seed funding led by a group of investors including Mucker Capital, Unicorn Ventures, Upfront Scout Fund, StartupO, Grayson Capital and Flight VC.
When Erik Rannala, co-founder and managing partner at Mucker Capital, initially invested in Elude, it was before the global pandemic. However, he sees travel getting back to normal, though with flights now more expensive than before, more people are looking for travel deals, something that wasn’t being addressed until Elude came along.
Travel is “a massive category,” with most people in either “look mode” or “book mode,” with the money only being made in book mode, Rannala said. By taking a budget-first approach, Elude is bridging people from look mode to book mode more quickly.
“The way they have done it is to help people discover something new based on their budget that is available to book right now,” he added. “It’s a unique way to solve the problem and to give people a good deal.”
With millenials spending over $200 billion annually on travel, Elude’s goal is to reduce the hours of scrolling in search of a trip and more time actively booking vacations. Whereas competitors may show flights only or hotels only, Elude produces flight and hotel packages.
“In just a few clicks, we can show you, for example, that you could go to Barcelona for the same price as Miami,” Scerbo told TechCrunch. “If you knew that kind of information, you would take a better trip. This opens doors to taking a trip every few months instead of the one or two trips a year most people take.”
Prior to today, Elude was in private beta mode where the company had amassed some 40,000 people on the waitlist. Simon said.
Elude plans to use the funding to advance technology, marketing function, operations and customer support.
Powered by WPeMatico
Statsig is taking the A/B testing applications that drive Facebook’s growth and putting similar functionalities into the hands of any product team so that they, too, can make faster, data-informed decisions on building products customers want.
The Seattle-based company on Thursday announced $10.4 million in Series A funding, led by Sequoia Capital, with participation from Madrona Venture Group and a group of individual investors, including Robinhood CPO Aparna Chennapragada, Segment co-founder Calvin French-Owen, Figma CEO Dylan Field, Instacart CEO Fidji Simo, DoorDash exec Gokul Rajaram, Code.org CEO Hadi Partovi and a16z general partner Sriram Krishnan.
Founder and CEO Vijaye Raji started the company with seven other former Facebook colleagues in February, but the idea for the company started more than a year ago.
He told TechCrunch that while working at Facebook, A/B testing applications, like Gatekeeper, Quick Experiments and Deltoid, were successfully built internally. The Statsig team saw an opportunity to rebuild these features from scratch outside of Facebook so that other companies that have products to build — but no time to build their own quick testing capabilities — can be just as successful.
Statsig’s platform enables product developers to run quick product experiments and analyze how users respond to new features and functionalities. Tools like Pulse, Experiments+ and AutoTune allow for hundreds of experiments every week, while business metrics guide product teams to build and ship the right products to their customers.
Raji intends to use the new funding to hire folks in the area of design, product, data science, sales and marketing. The team is already up to 14 since February.
“We already have a set of customers asking for features, and that is a good problem, but now we want to scale and build them out,” he added.
Statsig has no subscription or upfront fees and is already serving millions of end-users every month for customers like Clutter, Common Room and Take App. The company will always offer a free tier so customers can try out features, but also offers a Pro tier for 5 cents per thousand events so that when the customer grows, so does Statsig.
Raji sees adoption of Statsig coming from a few different places: developers and engineers that are downloading it and using it to serve a few million people a month, and then through referrals. In fact, the adoption the company is getting is “bottom up,” which is what Statsig wants, he said. Now the company is talking to bigger customers.
There are plenty of competitors for this product, including incumbents in the market, according to Raji, but they mostly focus on features, while Statsig provides insights and ties metrics back to features. In addition, the company has automated analysis where other products require manual set up and analysis.
Sequoia partner Mike Vernal worked at Facebook prior to joining the venture capital firm and had worked with Raji, calling him “a top 1% engineer” that he was happy to work with.
Having sat on many company boards, he has found that many companies spend a long time talking about sales and marketing, but very little on product because there is not an easy way to get precise numbers for planning purposes, just a discussion about what they did and plan to do.
What Vernal said he likes about Statsig is that the company is bringing that measurement aspect to the table so that companies don’t have to hack together a poorer version.
“What Statsig can do, uniquely, is not only set up an experiment and tell if someone likes green or blue buttons, but to answer questions like what the impact this is of the experiment on new user growth, retention and monitorization,” he added. “That they can also answer holistic questions and understand the impact on any single feature on every metric is really novel and not possible before the maturation of the data stack.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Though 2021 is far from over, it’s already witnessed a record level of venture capital activity in the technology sector. With larger round sizes announced daily, founders may have their pick of term sheets — but they need to think critically and strategically about which firms to add to their cap table.
So far this year, we’ve seen $292.4 billion in venture financing across the globe, of which $138.9 billion was raised in the United States. Specific to tech companies, the capital is only accelerating: In Q2, founders raised 157% more capital compared to the same period last year, according to the latest data from CB Insights.
It’s not just that more companies are raising money — they are doing so at a higher valuation. Median seed and Series A stage valuations today stand at $12 million and $42 million, respectively, up 20% to 30% from 2020. This can be partly attributed to growing exits/M&A activity in the technology sector, a record number of IPOs and a general bullishness around technology, as well as low interest rates and liquidity in the market.
Good VCs who are aligned with a startup’s vision create more value than the dollars they bring to the table.
At a time when we are witnessing record VC activity, founders would be well served to go back to the basics and focus on the principles of fundraising when determining who sits on their cap table. Here are a few pointers for founders in that direction:
Good VCs who are aligned with a startup’s vision create more value than the dollars they bring to the table. Typically, such value is created across a few distinct functions — product, sales, domain expertise, business development and recruiting, to name a few — based on the background of the partners of the fund and the composition of their limited partners (investors in the venture fund).
Further, the right VC can serve as an authentic, objective sounding board for CEOs, which can be an asset to have as a startup navigates uncertainty and the typical challenges that come with scaling a young company. As founders assess multiple term sheets, it’s worth thinking through whether they should optimize for VCs who offer the highest valuation, or for ones who bring the most value to the table.
Running an efficient fundraising process, in part, entails holding VCs accountable to their own diligence requests. While it is unfortunately common for VCs to request a lot of data upfront, startups should share information after assessing intent and appetite on the investors’ part.
For every additional data request, founders are well within their rights (and should) check with their potential investors on where the process stands and get indicative timelines for moving forward with next steps. Mark Suster said it best: “Data rooms are where fundraising processes go to die.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Less than six months after raising $55 million in a Series C round of funding, SMB 401(k) provider Human Interest today announced it has raised $200 million in a round that propels it to unicorn status.
The Rise Fund, TPG’s global impact investing platform, led the round and was joined by SoftBank Vision Fund 2. The financing included participation from new investor Crosslink Capital and existing backers NewView Capital, Glynn Capital, U.S. Venture Partners, Wing Venture Capital, Uncork Capital, Slow Capital, Susa Ventures and others.
Over the past year, the San Francisco-based company has raised $305 million. With the latest financing, it has now raised a total of $336.7 million since its 2015 inception.
The company admittedly has an IPO in its sights, as evidenced by the appointment of former Yodlee CFO Mike Armsby to the role of CFO at Human Interest. It’s targeting a traditional IPO sometime in 2023, with execs saying the target is to have “$200 million+ in run-rate revenue before going public.” Currently, it’s at “tens of millions of run-rate revenue” now, and adding millions of new revenue each month.
Human Interest’s digital retirement benefits platform allows users “to launch a retirement plan in minutes and put it on autopilot,” according to the company. It also touts that it has eliminated all 401(k) transaction fees.
Demand for 401(k)s by SMBs appears to be at an all-time high, with Human Interest reporting that its sales tripled over the last year. The company has also more than doubled its headcount over the last 12 months to 350 employees.
The startup said it is seeing strong adoption in verticals that have not previously had retirement benefits, including construction, retail, manufacturing, restaurants, nonprofits and hospitality. For example, over the past three quarters, Human Interest has seen 4.5x customer growth in the restaurant sector. Since the start of the pandemic, Human Interest has experienced 2x higher enrollment growth among hourly workers than salaried workers, and hourly worker assets have tripled.
“Promoting financial health is a core investment pillar for The Rise Fund. Human Interest delivers one of the most compelling solutions to the persistent problem that roughly half of Americans will not have enough savings when they reach retirement age,” said Maya Chorengel, co-managing partner at The Rise Fund, in a written statement. “Despite recent legislation, primarily at the state level, legacy programs have not, to date, produced the same participant outcomes as Human Interest.”
The company said it will be using its new capital to expand its network of integrations and partnerships with financial advisers, benefits brokers and payroll companies. It also expects to, naturally, do some hiring –– another 200 employees by year’s end, primarily in its product, engineering and revenue teams.
The 401(k) for SMB space is heating up as of late. In June, competitor Guideline also raised $200 million in a round led by General Atlantic.
Additional details around the IPO and revenue were added post-publication.
Powered by WPeMatico
Reserve Trust, a Denver-based financial services provider, has raised $30.5 million in a Series A round led by QED Investors.
FinTech Collective, Ardent Venture Partners, Flywire CEO Mike Massaro and Quovo founder and CEO Lowell Putnam also participated in the financing, which included $17.9 million in secondary shares. It brings the startup’s total raised since its 2016 inception to $35.5 million.
Reserve Trust describes itself as “the first fintech trust company with a Federal Reserve master account.” What does that mean exactly? Basically, a federal reserve master account allows Reserve Trust to move dollars on behalf of its customers directly, via wire and ACH payment rails, without an intermediate or partner bank.
Historically, only banks were able to access these payment rails directly, which left both domestic and international fintechs “with limited partner options, poor technology and slow implementations when it came to embedding high-value B2B payments,” says COO Dave Cahill. Reserve Trust touts that its technology and services give companies all over the world the ability to “seamlessly move money via the first cloud-based payment system connected directly to the Federal Reserve” since it is not limited by legacy banking systems.

Image Credits: CEO Dave Wright and COO Dave Cahill / Reserve Trust
In conjunction with the fundraise, Reserve Trust is also announcing that Dave Wright has been named CEO and Cahill joined as COO. The pair worked together previously at SolidFire, a flash storage startup that Wright founded and sold to NetApp for $870 million in 2016.
Reserve Trust works with businesses that seek to embed domestic and cross-border B2B payment by offering them the ability to store funds in custody accounts that are backed by its Federal Reserve master account.
The history of the company relates back to the global financial crisis. After the crisis, banks in the U.S. went through a process called derisking, which meant they shed businesses that on a risk return basis weren’t as strong as other businesses. One of those included the handling of U.S. dollar payments, particularly in emerging countries.
“One of the consequences of this is that it became significantly more difficult and expensive for businesses and smaller economies to trade and move U.S. dollars around the world,” Wright told TechCrunch. “And the founders of Reserve Trust saw this opportunity to build a new type of financial institution that was focused on helping to provide U.S. dollar payment services, especially to emerging fintechs in markets around the world, and helping to reconnect those economies to global trade.”
But rather than start a bank, the founders (Dennis Gingold, Justin Guilder) navigated a previously unexplored part of regulatory waters to create a state-chartered trust company with a Federal Reserve master account.
“That’s something that had never really been done before,” Wright added. “Pretty much every other trust company has to work through banks for all their payment services. Reserve Trust is the first that has actually managed to get a Federal Reserve master account and can process payments directly with the Federal Reserve.”
The complex process took about three years, and in 2018, the company got a Federal Reserve master account and started providing U.S. dollar custody and payment services for fintechs all over the world. Reserve Trust began to see strong demand from payment and fintech companies that were struggling to develop strong partner bank relationships, even though fundamentally there wasn’t any reason the banks couldn’t work with them.
“They found working with banks to be a slow process, one that didn’t involve a lot of technology expertise on the side of the banks, and it was really inhibiting their ability to develop their technology,” Wright said. And that was even here in the U.S. Today, more than half of its business is from domestic fintechs, although Reserve Trust still has a strong international presence as well.
The new funds will mainly go toward helping the company scale to handle what Wright describes as “a fairly overwhelming amount of demand” and toward building out the team, the technology and the services it needs to address the payment needs of larger, faster growing fintechs around the world.
“Most of our customers today are small and midsize fintechs, but now we’re seeing demand for much larger fintechs that have much higher payment volumes and are involved in embedded banking and B2B payments,” Wright said. “They are looking for a stronger banking partner than what they’ve been able to find among the role of traditional banks.” Customers include Unlimint and VertoFX, among others.
QED Investors partner Amias Gerety and FinTech Collective principal Matt Levinson are bullish both on Reserve Trust’s history and its potential.
The pair point to payments giant Stripe as an example of how far Reserve Trust can go.
“Stripe has significant market share doing merchant acquiring and processing e-commerce payments for the consumer,” Levinson said. “B2B payments is significantly bigger in terms of volume, so we’re talking about well over $20 trillion of addressable payment flow. But there’s no real technology company that’s brought the modern payments platform to market without being beholden to legacy banks. And that’s why we’re so excited about this business.”
Reserve Trust, he added, is giving businesses a way to facilitate B2B payments that “are smarter, faster and cheaper.”
Gerety agrees.
“Despite all the excitement around digital payments and infrastructure, there is still no fintech that can offer direct integration with the U.S. payment system,” he said. “With Reserve Trust, we are creating foundational infrastructure to hold and move payments globally and at scale.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Fresh off a strategic partnership with Toyota Industries Corporation to build an autonomous forklift, Third Wave Automation has snagged another $40 million from investors.
The California-based startup, which was founded in 2018, has raised $40 million in a Series B round led by Norwest Venture Partners, including participation from prior investors Innovation Endeavors and Eclipse, along with Toyota Ventures, according to a Form D filed with regulators. Matt Howard, general partner at Norwest Venture Partners, will join Third Wave’s board of directors.
The injection of capital came after Howard learned of Third Wave’s partnership with Toyota Industries Corporation, which builds a third of the world’s forklifts, Third Wave CEO Arshan Poursohi told TechCrunch. Under that deal, which was announced in May, Third Wave and Toyota Industries (TICO) will develop an autonomous forklift together. The machine will be manufactured at a TICO factory and be equipped with Third Wave’s sensors and compute stack. Third Wave will support the software side.
Third Wave’s three co-founders — including Mac Mason, who is chief roboticist, and James Davidson, who is no longer with the company — have long backgrounds in robotics, oftentimes working together at places like Google’s robotics program and Google Research and Toyota Research Institute.
“We’ve covered just about every kind of robot there is,” Poursohi said. “But all of these robots that we built ended up, you know, sitting in a closet somewhere because ultimately, Google or, in my case, Sun Microsystems, would decide it’s not worth scaling it out because it’s not the core business, or some other reason.”
The co-founders struck out to form their own company to focus on robots that would be used and would meet an immediate need.
“When we looked at forklifts, it’s this beautiful manipulation problem, so it’s a robot that actually touches the world on purpose,” Poursohi said. “And it’s a thing that we can actually build and ship on a time horizon that is not measured in decades.”
The forklifts they have developed operate under what is called shared autonomy. This means the forklift, which can lift pallets and move them around, will operate on its own 90% of the time. However, every robot can also be controlled remotely if the need arises. The robots are easy to operate, meaning the customer, not Third Wave, can have on-site employees to provide assistance remotely if the robot encounters something that prevents it from operating.
“There’s a big impact we can make on logistics and supply chain, just by moving pallets around, and that’s where we’ve been concentrated. The key to our technology is that it’s very fast to set up and it works in brownfield [environments],” Poursohi said.
Third Wave is still at an early stage in its development, but it’s making progress. The momentum from the funding and the recent completion of technical trials will allow the company to speed up its hiring effort and focus on commercialization, Poursohi said. He noted that Third Wave is in active conversations with 20 third-party logistics operators and retailers in the industry.
“We’ve tackled and have solid answers on all the technical fronts,” Poursohi said. “The next year and a half to two years is about is scaling out our operations team. And the market demand for this right now is massive.”
The target is to have 100 units in the field — meaning warehouses and other indoor locations — by the end of 2022 and scaling to 350 to 400 by the end of 2023.
Powered by WPeMatico
Zeni, a Palo Alto fintech company providing real-time financial services data to venture-backed startups, raised $34 million in Series B funding led by Elevation Capital.
The new investment comes just five months after Zeni announced $13.5 million in a combined seed and Series A round. The company has now raised $47.5 million in total since it was co-founded in 2019 by twin brothers Swapnil Shinde and Snehal Shinde.
Elevation was joined in the new round by new investors Think Investments and Neeraj Arora, as well as existing investors Saama Capital, Amit Singhal, Sierra Ventures, Twin Ventures, Dragon Capital and Liquid 2 Ventures. As part of the investment, Ravi Adusumalli, founder and managing partner at Elevation Capital, will join Zeni’s board.
The Shinde siblings started the company after selling their last company, Mezi, a travel concierge, to American Express in 2018. Zeni’s AI-powered finance concierge platform offers bookkeeping, accounting, tax and CFO services, managing these for a flat monthly fee starting at $299 per month. Founders have real-time access to financial insights via the Zeni Dashboard, including cash in and out, operating expenses, yearly taxes and financial projections. They can also download the financial data in the “slice” that they want.
At the time of its seed/Series A round, the company was managing more than $200 million in funds each month, and that has ballooned to more than $500 million, CEO Swapnil Shinde told TechCrunch. Its customers range from pre-revenue startups to businesses generating more than $100 million in annual revenue.
In addition to the cash in and cash out analysis, the company also created a search function for transactions and spend and income trends on every customer and vendor, Snehal Shinde, chief product officer, said.
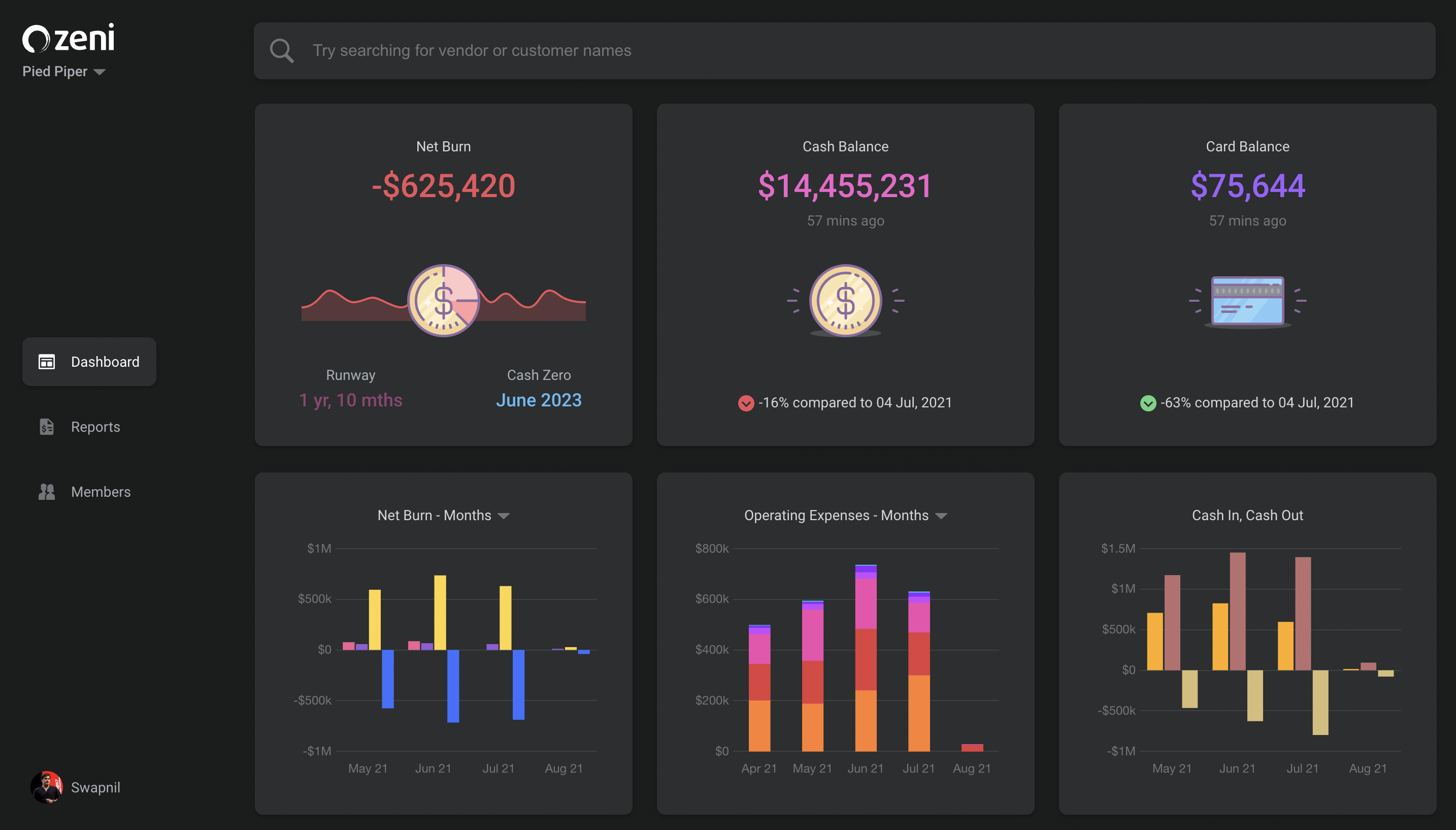
Zeni’s dashboard
Zeni experienced 550% revenue growth year-over-year, while the company’s customer base grew 375%, driven by referrals and organic growth, Swapnil Shinde said.
Despite the growth, the Series B came as a surprise to the siblings. The company was already “very well capitalized,” with a majority of the previous round still around, Swapnil Shinde said.
However, Zeni began receiving so many inbound inquiries that he said it was too exciting to pass on. Especially with the addition of Elevation Capital as an investor. Shinde said that was appealing because the firm was an investor in Paytm, and “knows how to partner and build unicorns.”
The new funding will be used to continue scaling and building the bookkeeping and accounting functions and to accelerate hiring, particularly in the engineering, sales and finance team verticals. Shinde expects to double or triple the finance team in the next year.
“As our customers scale through to their Series B, the more you can use our solution in real time to see what is happening with your finances, especially with startups and businesses having more of a remote workforce,” Swapnil Shinde added. “Zeni fits with that.”
Ash Lilani, managing partner at Saama Capital, one of Zeni’s earliest and largest investors, said he knew how big the total addressable market was — $200 billion — and how much these kinds of financial services were a giant pain point for startup companies.
“To know where you stand financially in real time is hard to do, usually, you get that information at month-end,” Lilani said. “I believe we have the opportunity to build a large company. Though Zeni is going after startups today, the small and medium markets can be leveraged. As they grow, Zeni will become their controller on the back end, while companies can just hire a CFO for the strategic decisions.”
Powered by WPeMatico
One year after raising $16 million, construction technology company Buildots is back to claim another $30 million, this time in Series B funding.
Lightspeed Venture Partners led the round, with participation from previous investors TLV Partners, Future Energy Ventures, Tidhar Construction Group and Maor Investments. This gives the company $46 million in total funding, Roy Danon, co-founder and CEO of Buildots, told TechCrunch.
The three-year-old company, with headquarters in Tel Aviv and London, is leveraging artificial intelligence computer vision technology to address construction inefficiencies. Danon said though construction accounts for 13% of the world’s GDP and employs hundreds of millions of people, construction productivity continues to lag, only growing 1% in the past two decades.
Danon spent six months on construction sites talking to workers to understand what was happening and learned that control was one of the areas where efficiency was breaking down. While construction processes would seem similar to manufacturing processes, building to the design or specs didn’t happen often due to different rules and reliance on numerous entities to get their jobs done first, he said.
Buildots’ technology is addressing this gap using AI algorithms to automatically validate images captured by hardhat-mounted 360-degree cameras, detecting immediately any gaps between the original design, scheduling and what is actually happening on the construction site. Project managers can then make better decisions to speed up construction.
“It even finds events where contractors are installing out of place and streamline payments so that information is transparent and clear,” Danon said. “Buildots also creates a collaborative environment and trust by having a single source telling everyone what is going on. There is no more blaming or cutting corners because the system validates that and also makes construction a healthier industry to work in.”
Buildots went after new funding once it was able to show product market fit and was expanding into other countries. The platform is being utilized on major building projects in countries like the U.S., U.K., Germany, Switzerland, Scandinavia and China. To meet demand, Buildots will use the new funding to continue that expansion; double the size of its global team with a focus on sales, marketing and R&D; and grow on the business side. Danon’s aim is “to get to the point where we are the standard for every construction site.” The company is also looking at areas outside construction where its technology would be applicable.
Tal Morgenstern, partner at Lightspeed Venture Partners, said he keeps an eye on graduates of the Israel Defense Forces, where the three Buildots founders came from. However, in the case of this company, Lightspeed actually passed on both the seed and Series A.
Morgenstern admits the decision was a mistake, but at the time, he thought the technology Buildots was trying to build “first, impossible and second, I knew construction was difficult to sell into.” He felt that Buildots, with such a premium product, would have a challenge selling to a low-margin industry that was late to adopt technology in general.
By the time the Series B came round, he said Buildots had solved both of those issues, proving that it works, but also that customers were adopting the technology without much sales and marketing. In addition, other solutions in construction tech were still relying on lasers or people to manually input or tap photos.
“Buildots is seamlessly capturing images and providing a level of insights that is so high, and that is why the company is able to command the price structure they have and are receiving interesting commercial results,” Morgenstern said.
Walking around today’s construction site, Danon said the adoption of technology is enabling Buildots to move quickly to build processes for the industry.
As such, the company saw more than 50% growth quarter over quarter over the past year in three of the countries in which it operates. It is now working with four of the top 10 construction companies in Europe and around the world.
“We did a good job selling remotely, but now we need local offices,” Danon added. “We are also sitting on piles of data from construction sites. We learn from one project to another and want to look for the challenges where data will help make a financial impact. It’s a natural next step for the company.”
Powered by WPeMatico