funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
One year after voice-based AI technology company ConverseNow raised a $3.3 million seed round, the company is back with a cash infusion of $15 million in Series A funding in a round led by Craft Ventures.
The Austin-based company’s AI voice ordering assistants George and Becky work inside quick-serve restaurants to take orders via phone, chat, drive-thru and self-service kiosks, freeing up staff to concentrate on food preparation and customer service.
Joining Craft in the Series A round were LiveOak Venture Partners, Tensility Venture Partners, Knoll Ventures, Bala Investments, 2048 Ventures, Bridge Investments, Moneta Ventures and angel investors Federico Castellucci and Ashish Gupta. This new investment brings ConverseNow’s total funding to $18.3 million, Vinay Shukla, co-founder and CEO of ConverseNow, told TechCrunch.
As part of the investment, Bryan Rosenblatt, partner at Craft Ventures, is joining the company’s board of directors, and said in a written statement that “post-pandemic, quick-service restaurants are primed for digital transformation, and we see a unique opportunity for ConverseNow to become a driving force in the space.”
At the time when ConverseNow raised its seed funding in 2020, it was piloting its technology in just a handful of stores. Today, it is live in over 750 stores and grew seven times in revenue and five times in headcount.
Restaurants were some of the hardest-hit industries during the pandemic, and as they reopen, Shukla said their two main problems will be labor and supply chain, and “that is where our technology intersects.”
The AI assistants are able to step in during peak times when workers are busy to help take orders so that customers are not waiting to place their orders, or calls get dropped or abandoned, something Shukla said happens often.
It can also drive more business. ConverseNow said it is shown to increase average orders by 23% and revenue by 20%, while adding up to 12 hours of extra deployable labor time per store per week.
Company co-founder Rahul Aggarwal said more people prefer to order remotely, which has led to an increase in volume. However, the more workers have to multitask, the less focus they have on any one job.
“If you step into restaurants with ConverseNow, you see them reimagined,” Aggarwal said. “You find workers focusing on the job they like to do, which is preparing food. It is also driving better work balance, while on the customer side, you don’t have to wait in the queue. Operators have more time to churn orders, and service time comes down.”
ConverseNow is one of the startups within the global restaurant management software market that is forecasted to reach $6.94 billion by 2025, according to Grand View Research. Over the past year, startups in the space attracted both investors and acquirers. For example, point-of-sale software company Lightspeed acquired Upserve in December for $430 million. Earlier this year, Sunday raised $24 million for its checkout technology.
The new funding will enable ConverseNow to continue developing its line-busting technology and invest in marketing, sales and product innovation. It will also be working on building a database from every conversation and onboarding new customers quicker, which involves inputting the initial menu.
By leveraging artificial intelligence, the company will be able to course-correct any inconsistencies, like background noise on a call, and better predict what a customer might be saying. It will also correct missing words and translate the order better. In the future, Shukla and Aggarwal also want the platform to be able to tell what is going on around the restaurant — what traffic is like, the weather and any menu promotions to drive upsell.
Powered by WPeMatico
Small and medium enterprises have become a big opportunity in the world of B2B technology in the last several years, and today a startup that’s building tools aimed at helping them manage their teams of workers is announcing some funding that underscores the state of that market.
Homebase, which provides a platform that helps SMBs manage various services related to their hourly workforces, has closed $71 million in funding, a Series C that values the company between $500 million and $600 million, according to sources close to the startup.
The round has a number of big names in it that are as much a sign of how large VCs are valuing the SMB market right now as it is of the strategic interest of the individuals who are participating. GGV Capital is leading the round, with past backers Bain Capital Ventures, Baseline Ventures, Bedrock, Cowboy Ventures and Khosla Ventures also participating. Individuals include Focus Brands President Kat Cole; Jocelyn Mangan, a board member at Papa John’s and Chownow and former COO of Snag; former CFO of payroll and benefits company Gusto, Mike Dinsdale; Guild Education founder Rachel Carlson; star athletes Jrue and Lauren Holiday; and alright alright alright actor and famous everyman and future political candidate Matthew McConaughey.
Homebase has raised $108 million to date.
The funding is coming on the heels of strong growth for Homebase (which is not to be confused with the U.K./Irish home improvement chain of the same name, nor the YC-backed Vietnamese proptech startup).
The company now has some 100,000 small businesses, with 1 million employees in total, on its platform. Businesses use Homebase to manage all manner of activities related to workers that are paid hourly, including (most recently) payroll, as well as shift scheduling, timeclocks and timesheets, hiring and onboarding, communication and HR compliance.
John Waldmann, Homebase’s founder and CEO, said the funding will go toward both continuing to bring on more customers as well as expanding the list of services offered to them, which could include more features geared to frontline and service workers, as well as features for small businesses who might also have some “desk” workers who might still work hourly.
The common thread, Waldmann said, is not the exact nature of those jobs, but the fact that all of them, partly because of that hourly aspect, have been largely underserved by tech up to now.
“From the beginning, our mission was to help local businesses and their teams,” he said. Part of his inspiration came from people he knew: a childhood friend who owned an independent, expanding restaurant chain, and was going through the challenges of managing his teams there, carrying out most of his work on paper; and his sister, who worked in hospitality, which didn’t look all that different from his restaurant friend’s challenges. She had to call in to see when she was working, writing her hours in a notebook to make sure she got paid accurately.
“There are a lot of tech companies focused on making work easier for folks that sit at computers or desks, but are building tools for these others,” Waldmann said. “In the world of work, the experience just looks different with technology.”
Homebase currently is focused on the North American market — there are some 5 million small businesses in the U.S. alone, and so there is a lot of opportunity there. The huge pressure that many have experienced in the last 16 months of COVID-19 living, leading some to shut down altogether, has also focused them on how to manage and carry out work much more efficiently and in a more organized way, ensuring you know where your staff is and that your staff knows what it should be doing at all times.
What will be interesting is to see what kinds of services Homebase adds to its platform over time: In a way, it’s a sign of how hourly wage workers are becoming a more sophisticated and salient aspect of the workforce, with their own unique demands. Payroll, which is now live in 27 states, also comes with pay advances, opening the door to other kinds of financial services for Homebase, for example.
“Small businesses are the lifeblood of the American economy, with more than 60% of Americans employed by one of our 30 million small businesses. In a post-pandemic world, technology has never been more important to businesses of all sizes, including SMBs,” Jeff Richards, managing partner at GGV Capital and new Homebase board member, said in a statement. “The team at Homebase has worked tirelessly for years to bring technology to SMBs in a way that helps drive increased profitability, better hiring and growth. We’re thrilled to see Homebase playing such an important role in America’s small business recovery and thrilled to be part of the mission going forward.”
It’s interesting to see McConaughey involved in this round, given that he’s most recently made a turn toward politics, with plans to run for governor of Texas in 2022.
“Hardworking people who work in and run restaurants and local businesses are important to all of us,” he said in a statement. “They play an important role in giving our cities a sense of livelihood, identity and community. This is why I’ve invested in Homebase. Homebase brings small business operations into the modern age and helps folks across the country not only continue to work harder, but work smarter.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Data may be the new oil, but it’s only valuable if you make good use of it. Today, a startup that has built a new kind of production analytics platform for developers, security engineers, and data scientists to track and better understand how data is moving around their networks is announcing a round of funding that underscores the demand for their technology.
Coralogix, which provides stateful streaming services to engineering teams, has picked up $55 million in a Series C round of funding.
The round was led by Greenfield Partners, with Red Dot Capital Partners, StageOne Ventures, Eyal Ofer’s O.G. Tech, Janvest Capital Partners, Maor Investments and 2B Angels also participating.
This Series C is coming about 10 months after the company’s Series B of $25 million, and from what we understand, Coralogix’s valuation is now in the range of $300 million to $400 million, a big jump for the startup, coming on the back of it growing 250% since this time last year, racking up some 2,000 paying customers, with some small teams paying as little as $100/year and large enterprises paying $1.5 million/year.
Previously, Coralogix — founded in Tel Aviv and with an HQ also in San Francisco — had also raised a round of $10 million.
Coralogix got its start as a platform aimed at quality assurance support for R&D and engineering teams. The focus here is on log analytics and metrics for platform engineers, and this still forms a big part of its business today. Added to that, in recent years, Coralogix’s tools are being applied to cloud security services, contributing to a company’s threat intelligence by providing a way to observe data for any inconsistencies that typically might point to a breach or another incident. (It integrates with Alien Vault and others for this purpose.)
The third area that is just picking up now and will be developed further — one of the uses of this investment, in fact — will be to develop how Coralogix is used for business intelligence. This is a particularly interesting area because it plays into how Coralogix is built, to provide analytics on data before it is indexed.
“It’s about high-volume, but low-value data,” Ariel Assaraf, Coralogix’s CEO, said in an interview. “Customers don’t want to store the data [or index it] but want to view it live and visualize it. We are starting to see a use case where business information and our analytics come together for sentiment analysis and other areas.”
There are dozens of strong companies providing tools these days to cover log analytics and data observability, underscoring the general growth and importance of DevOps these days. They include companies like DataDog, Sumo Logic and Splunk.
However, Assaraf believes that what sets his company apart is its approach: Essentially, it has devised a way of observing and analyzing data streams before they get indexed, giving engineers more flexibility to query the data in different ways and glean more insights, faster. The other issue with indexing, he said, is that it impacts latency, which also has a big impact on overall costs for an organization.
For many of Coralogix’s competitors, turning around the nature of the business to focus not first on indexing would be akin to completely rebuilding the business, hard to do at their scale (although this is what Coralogix did when it pivoted as a small company several years ago, which is when Assaraf took on the role of CEO). One company he believes might be more of a direct rival is Confluent.
“I think we will see Confluent getting into observability very soon because they have the streaming capabilities,” he said, “but not the tools we have.” Another potential competitor looming on the horizon: Salesforce, and its potential move into that area, underscores the shifting sands of what is powering enterprise IT investment decisions today.
Salesforce already has Heroku, Slack and Tableau, three major tools developers use for tracking and working with data, Assaraf pointed out, and there were strong rumors of it trying to buy DataDog, “so we definitely see where they are going. For sure, they understand the way things are changing. All the budgets when Salesforce first started were in marketing and sales. Now you sell to IT. Salesforce understands that shift to developers, and so that is where they are going.”
It makes for a very interesting landscape and future for companies like Coralogix, one that investors believe the startup will continue to shape as it has up to now.
“The dramatic shift in digital transformation is generating an explosion of data, which until now has forced enterprises to decide between cost and coverage,” said Shay Grinfeld, managing partner at Greenfield Partners. “Coralogix’s real-time streaming analytics pipeline employs proprietary algorithms to break this tradeoff and generate significant cost savings. Coralogix has built a customer roster that comprises some of the largest and most innovative companies in the world. We’re thrilled to partner with Ariel and the Coralogix team on their journey to reinvent the future of data observability.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Cairo and Dubai-based ride-sharing company Swvl plans to go public in a merger with special purpose acquisition company Queen’s Gambit Growth Capital, Swvl said Tuesday. The deal will see Swvl valued at roughly $1.5 billion.
Swvl was founded by Mostafa Kandil, Mahmoud Nouh and Ahmed Sabbah in 2017. The trio started the company as a bus-hailing service in Egypt and other ride-sharing services in emerging markets with fragmented public transportation.
Its services, mainly bus-hailing, enables users to make intra-state journeys by booking seats on buses running a fixed route. This is pocket-friendly for residents in these markets compared to single-rider options and helps reduce emissions (Swvl claims it has prevented over 240 million pounds of carbon emission since inception).
After its Egypt launch, Swvl expanded to Kenya, Pakistan, Jordan and Saudi Arabia. The company also moved its headquarters to Dubai as part of its strategy to become a global company.
Swvl offerings have expanded beyond bus-hailing services. Now, the company offers inter-city rides, car ride-sharing, and corporate services across the 10 cities it operates in across Africa and the Middle East.
Queen’s Gambit, the women-led SPAC in charge of the deal, raised $300 million in January and added $45 million via an underwriters’ overallotment option focusing on startups in clean energy, healthcare and mobility sectors.
The statement also mentions a group of investors — Agility, Luxor Capital and Zain Group — which will contribute $100 million through a private investment in public equity, or PIPE.
Per Crunchbase, Swvl has raised over $170 million. From an African perspective, Swvl features as one of the most venture-backed startups on the continent. The company has been touted to reach unicorn status in the past and will when this SPAC merger is completed.
The company will aptly trade under the ticker SWVL. The listing will make it the first Egyptian startup to go public outside Egypt and the second to go public after Fawry. It will also make the mobility company the largest African unicorn debut on any U.S.-listed exchange, beating Jumia’s debut of $1.1 billion on the NYSE. In the Middle East, Swvl joins music-streaming platform Anghami as the second startup to go public via a SPAC merger.
Swvl had annual gross revenue of $26 million in 2020, according to the statement, and the company expects its annual gross revenue to increase to $79 million this year and $1 billion by 2025 after expanding to 20 countries across five continents.
On why Queen’s Gambit picked Swvl for this deal, Victoria Grace, founder and CEO, said in a statement that the company fit the profile of what she was looking for: “a disruptive platform that solves complex challenges and empowers underserved populations.”
“Having established a leadership position in key emerging markets, we believe Swvl is ready to capitalize on a truly global market opportunity,” she added.
In May, TechCrunch wrote that SPACs didn’t target African startups for several reasons, including a lack of global appeal and private capital and market satisfaction. Judging by Grace’s comments, Swvl has that global appeal and is ready to venture into the public market despite being in operation for just four years.
Powered by WPeMatico
When co-founders Songe LaRon and Dave Salvant first began barbershop tech platform Squire in 2016, they leaned in: The duo bought a barbershop in New York City’s Chelsea neighborhood to see firsthand how the business worked. For one year, the co-founders religiously worked at the shop, now owned by a larger barbershop chain, handling every bit of the business (except cutting hair).
Five years later, the co-founders view that experience as a key moment in the history of Squire, now a 175-person company with a tech platform used by over 2,000 shops across three continents. After last raising a Series C in December and tripling its valuation, Squire announced today that it has raised a $60 million round led by Tiger Global.
And, it tripled its valuation, again. Off of 300% year-over-year revenue growth, the New York startup is now valued at $750 million. It’s a massive uptick: A little over a year ago, Squire was valued at $75 million.
Like many startups these days, Squire wasn’t searching for capital when Tiger Global, which participated in its Series B and C rounds, offered to lead its next financing. The startup has only spent 10% of its previous round, a $45 million equity round, and now has tens of millions more in the bank. Ultimately, its decision to bring on more capital is so it can expand in the U.K. and Canada more aggressively — even in the wake of early-stage competitors like Boulevard. Squire’s dry powder also puts the co-founders in a position to acquire companies, a strategy that Salvant is into and plans to be “aggressive about.”
Squire also announced today the official launch of a product that has been in the roadmap since inception: Squire Capital, a money management platform with tools tailored to the needs of barbershop operations, such as instant payments. Squire’s core business has been more around appointments, loyalty programs and the installment of contactless payment. Now, a fintech layer aims to offer a more niche service than current financial services heavyweights like Square or Paypal.
Fintech is a “natural next frontier” for Squire, Salvant said, because the startup already has deep insights into how its businesses operate and how they process sales; now, it wants to add another service so it can offer a more holistic experience to them.
Squire Capital was built with Bond, a venture-backed fintech infrastructure startup that aims to help enterprise operations launch their own banking products. After experimenting with a $15 million debt financing arm around the time of its Series C, Squire isn’t offering loans at this time, hoping to find a better way to scale offerings in the future.
Squire is en route to becoming a historical and unfortunately still rare Black-led unicorn. Salvant talked about the significance of that feat, noting that this was “the optimal outcome” when founding the company. He hopes that VCs and investors will start to invest more in Black founders with Squire as a data point of a success story.
“Let’s face it, we’re not typical founders, we don’t look the same and we don’t act the same,” Salvant said. “I just want to serve as a lighthouse and this is validation for myself, my co-founder, but more importantly, what’s coming after us.”
Powered by WPeMatico
When it comes to software to help IT manage workers’ devices wherever they happen to be, enterprises have long been spoiled for choice — a situation that has come in especially handy in the last 18 months, when many offices globally have gone remote and people have logged into their systems from home. But the same can’t really be said for small and medium enterprises: As with so many other aspects of tech, they’ve long been overlooked when it comes to building modern IT management solutions tailored to their size and needs.
But there are signs of that changing. Today, a startup called Atera that has been building remote, and low-cost, predictive IT management solutions specifically for organizations with less than 1,000 employees, is announcing a funding round of $77 million — a sign of the demand in the market, and Atera’s own success in addressing it. The investment values Atera at $500 million, the company confirmed.
The Tel Aviv-based startup has amassed some 7,000 customers to date, managing millions of endpoints — computers and other devices connected to them — across some 90 countries, providing real-time diagnostics across the data points generated by those devices to predict problems with hardware, software and network, or with security issues.
Atera’s aim is to use the funding both to continue building out that customer footprint, and to expand its product — specifically adding more functionality to the AI that it currently uses (and for which Atera has been granted patents) to run predictive analytics, one of the technologies that today are part and parcel of solutions targeting larger enterprises but typically are absent from much of the software out there aimed at SMBs.
“We are in essence democratizing capabilities that exist for enterprises but not for the other half of the economy, SMBs,” said Gil Pekelman, Atera’s CEO, in an interview.
The funding is being led by General Atlantic, and it is notable for being only the second time that Atera has ever raised money — the first was earlier this year, a $25 million round from K1 Investment Management, which is also in this latest round. Before this year, Atera, which was founded in 2016, turned profitable in 2017 and then intentionally went out of profit in 2019 as it used cash from its balance sheet to grow. Through all of that, it was bootstrapped. (And it still has cash from that initial round earlier this year.)
As Pekelman — who co-founded the company with Oshri Moyal (CTO) — describes it, Atera’s approach to remote monitoring and management, as the space is typically called, starts first with software clients installed at the endpoints that connect into a network, which give IT managers the ability to monitor a network, regardless of the actual physical range, as if it’s located in a single office. Around that architecture, Atera essentially monitors and collects “data points” covering activity from those devices — currently taking in some 40,000 data points per second.
To be clear, these data points are not related to what a person is working on, or any content at all, but how the devices behave, and the diagnostics that Atera amasses and focuses on cover three main areas: hardware performance, networking and software performance and security. Through this, Atera’s system can predict when something might be about to go wrong with a machine, or why a network connection might not be working as it should, or if there is some suspicious behavior that might need a security-oriented response. It supplements its work in the third area with integrations with third-party security software — Bitdefender and Acronis among them — and by issuing updated security patches for devices on the network.
The whole system is built to be run in a self-service way. You buy Atera’s products online, and there are no salespeople involved — in fact most of its marketing today is done through Facebook and Google, Pekelman said, which is one area where it will continue to invest. This is one reason why it’s not really targeting larger enterprises (the others are the level of customization that would be needed; as well as more sophisticated service level agreements). But it is also the reason why Atera is so cheap: it costs $89 per month per IT technician, regardless of the number of endpoints that are being managed.
“Our constituencies are up to 1,000 employees, which is a world that was in essence quite neglected up to now,” Pekelman said. “The market we are targeting and that we care about are these smaller guys and they just don’t have tools like these today.” Since its model is $89 dollars per month per technician using the software, it means that a company with 500 people with four technicians is paying $356 per month to manage their networks, peanuts in the greater scheme of IT services, and one reason why Atera has caught on as more and more employees have gone remote and are looking like they will stay that way.
The fact that this model is thriving is also one of the reason and investors are interested.
“Atera has developed a compelling all-in-one platform that provides immense value for its customer base, and we are thrilled to be supporting the company in this important moment of its growth trajectory,” said Alex Crisses, MD, global head of New Investment Sourcing and co-head of Emerging Growth at General Atlantic, in a statement. “We are excited to work with a category-defining Israeli company, extending General Atlantic’s presence in the country’s cutting-edge technology sector and marking our fifth investment in the region. We look forward to partnering with Gil, Oshri and the Atera team to help the company realize its vision.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Gupshup, a business messaging platform that began its journey in India 15 years ago, surprised many when it raised $100 million in April this year, roughly 10 years after its last financing round, and attained the coveted unicorn status. Now just three months later, the San Francisco-headquartered startup has secured even more capital from high-profile investors.
On Wednesday, Gupshup said it had raised an additional $240 million as part of the same Series F financing round. The new investment was led by Fidelity Management, Tiger Global, Think Investments, Malabar Investments, Harbor Spring Capital, certain accounts managed by Neuberger Berman Investment Advisers and White Oak.
Neeraj Arora, formerly a high-profile executive at WhatsApp who played an instrumental role in helping the messaging platform sell to Facebook, also wrote a significant check to Gupshup in the new tranche of investment, which continues to value the startup at $1.4 billion as in April.
In an interview with TechCrunch earlier this week, Beerud Sheth, co-founder and chief executive of Gupshup, said he extended the financing round after receiving too many inbound requests from investors. The new investors will provide the startup with crucial insight and expertise, he said. The round is now closed, he continued.
The startup, which operates a conversational messaging platform that is used by over 100,000 businesses and developers today to build their own messaging and conversational experiences to serve their users and customers, is beginning to consider exploring the public markets by next year, said Sheth, though he cautioned a final decision is yet to be made.
“Conversation is becoming a bigger part of doing business and it has partly been driven by the pandemic,” he said over a phone call. “Second, we have always been the leader in this space, but the product innovation we have focused on in the last two to three years has worked in our favor.”
The new investment, which includes some secondary buyback (some early investors and employees are selling their stakes), will be deployed into broadening the product offerings of Gupshup, he said. The startup is also eyeing some M&A opportunities and may close some deals this year, he added.

Some of the notable customers of Gupshup, which leads the business messaging market. Image Credits: Gupshup
Before Gupshup became so popular with businesses, it existed in a different avatar. For the first six years of its existence, Gupshup was best known for enabling users in India to send group messages to friends. (These cheap texts and other clever techniques enabled tens of millions of Indians to stay in touch with one another on phones a decade ago.)
That model eventually became unfeasible to continue, Sheth told TechCrunch in an earlier interview.
“For that service to work, Gupshup was subsidizing the messages. We were paying the cost to the mobile operators. The idea was that once we scale up, we will put advertisements in those messages. Long story short, we thought as the volume of messages increases, operators will lower their prices, but they didn’t. And also the regulator said we can’t put ads in the messages,” he said earlier this year.
That’s when Gupshup decided to pivot. “We were neither able to subsidize the messages, nor monetize our user base. But we had all of this advanced technology for high-performance messaging. So we switched from a consumer model to an enterprise model. So we started to serve banks, e-commerce firms and airlines that need to send high-level messages and can afford to pay for it,” said Sheth, who also co-founded freelance workplace Elance in 1998.
Over the years, Gupshup has expanded to newer messaging channels, including conversational bots and it also helps businesses set up and run their WhatsApp channels to engage with customers.
Sheth said scores of major firms worldwide in banking, e-commerce, travel and hospitality and other sectors are among the clients of Gupshup. These firms are using Gupshup to send their customers transaction information and authentication codes, among other use cases. “These are not advertising or promotional messages. These are core service information,” he said.
“We have followed Gupshup’s progress for a long while and believe that they are the most evolved customer communications platform In India and increasingly in other emerging markets, with a leadership position in the most attractive and fastest growing subsegments of the market,” said Sumeet Nagar, managing director of Malabar Investments, in a statement.
“We believe that Beerud and team have the unique opportunity to expand the addressable market on the back of new offerings and scale the business up significantly, which is a perfect recipe for massive value creation. I have known Beerud for over three decades, and all of us at Malabar are delighted to partner with Gupshup in the next stage of their journey.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Among Silicon Valley circles, a fun parlor game is to ask to what extent world GDP levels are held back by a lack of computer science and technical training. How many startups could be built if hundreds of thousands or even millions more people could code and bring their entrepreneurial ideas to fruition? How many bureaucratic processes could be eliminated if developers were more latent in every business?
The answer, of course, is on the order of “a lot,” but the barriers to reaching this world remain formidable. Computer science is a challenging field, and despite proactive attempts by legislatures to add more coding skills into school curriculums, the reality is that the demand for software engineering vastly outstrips the supply available in the market.
Coding is not a bubble, and Bubble wants to empower the democratization of software development and the creation of new startups. Through its platform, Bubble enables anyone — coder or not — to begin building modern web applications using a click-and-drag interface that can connect data sources and other software together in one fluid interface.
It’s a bold bet — and it’s just received a bold bet as well. Bubble announced today that Ryan Hinkle of Insight Partners has led a $100 million Series A round into the company. Hinkle, a longtime managing director at the firm, specializes in growth buyout deals as well as growth SaaS companies.
If that round size seems huge, it’s because Bubble has had a long history as a bootstrapped company before reaching its current scale. Co-founders Emmanuel Straschnov and Josh Haas spent seven years bootstrapping and tinkering with the product before securing a $6.5 million seed round in June 2019 led by SignalFire. Interestingly, according to Straschnov, Insight was the first venture firm to reach out to Bubble all the way back in 2014. Seven years on, the two have now signed and closed a deal.
Since the seed round, Bubble has been expanding its functionality. As a no-code tool, any missing feature could potentially block an application from being built. “In our business, it’s a features game,” Straschnov said. “[Our users] are not technical, but they have high standards.” He noted that the company introduced a plugins system that allows the Bubble community to build their own additions to the platform.
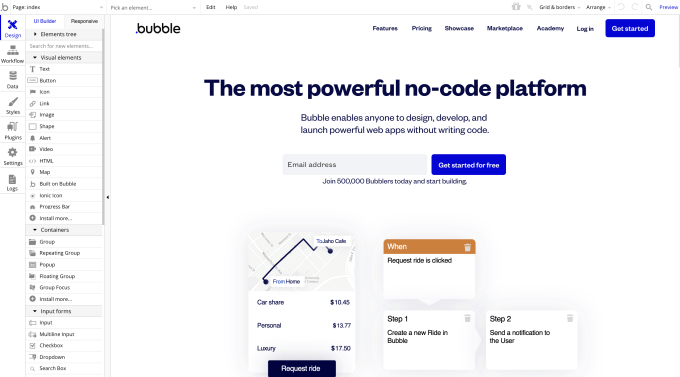
Image Credits: Bubble. Its editor offers a clickable interface for designing dynamic web applications.
As the platform matured, it happened to nail the timing of the COVID-19 pandemic last year, which saw people scrambling for new skills and improving their prospects amid a gloomy job market. Straschnov says that Bubble saw an immediate bump in usage in March and April 2020, and the company has tripled revenue over the past 12 months.
Bubble’s focus for the past eight years has been on helping people turn their ideas into startups. The company’s proposition is that a large number of even venture-backed companies could be built using Bubble without the expense of a large engineering team writing code from scratch.
Unlike other no-code tools, which focus on building internal corporate apps, Straschnov says that the company remains as focused today on these new companies as it has always been. “[We’re] not trying to move upmarket just yet — we are trying to do the same thing that AWS and Stripe did five years ago,” he said. Instead of trying to dominate the enterprise, Bubble wants to grow with its nascent customers as they expand in scale.
The company today charges a range of prices depending on the performance and scale requirements of an application. There’s a free tier, and then professional pricing starts at $25/month all the way to $475/month for its top-listed offering. Enterprise pricing is also available, as is special pricing for students.
On the latter point, Bubble is looking to invest heavily in education using its newly raised capital. While the platform is easy to use, the reality is that any design of a web application can be intimidating for a new user, particularly one who isn’t technical. So the company wants to create more videos and documentation while also heavily investing in partnerships with universities to get more students using the platform.
While the no-code space has seen prodigious investment, Straschnov said that “I don’t look at all the no-code players as competition … the true competition we have is code.” He noted that while the no-code label has been assumed by more and more startups, very few companies are focused on his company’s specific niche, and he believes he offers a compelling value proposition in that category.
The company has doubled headcount since the beginning of the pandemic, growing from around 21 employees to about 45 today. They are lightly concentrated in New York City, but the company operates remotely and has folks in 15 states as well as in France. Straschnov says that the company is looking to aggressively hire technical talent to build out the product using its new funds.
Powered by WPeMatico
Site reliability engineering platform Blameless announced Tuesday it raised $30 million in a Series B funding round, led by Third Point Ventures with participation from Accel, Decibel and Lightspeed Venture Partners, to bring total funding to over $50 million.
Site reliability engineering (SRE) is an extension of DevOps designed for more complex environments.
Blameless, based in San Mateo, California, emerged from stealth in 2019 after raising both a seed and Series A round, totaling $20 million. Since then, it has turned its business into a blossoming software platform.
Blameless’ platform provides the context, guardrails and automated workflows so engineering teams are unified in the way they communicate and interact, especially to resolve issues quicker as they build their software systems.
It originally worked with tech-forward teams at large companies, like Home Depot, that were “dipping [their toes] into the space and now [want] to double down,” co-founder and CEO Lyon Wong told TechCrunch.
The company still works with those tech-forward teams, but in the past two years, more companies sought out resident SRE architect Kurt Anderson to advise them, causing Blameless to change up its business approach, Wong said.
Other companies are also seeing a trend of customers asking for support — for example, in March, Google Cloud unveiled its Mission Critical Services support option for SRE to serve in a similar role as a consultant as companies move toward readiness with their systems. And in February, Nobl9 raised a $21 million Series B to provide enterprises with the tools they need to build service-level-objective-centric operations, which is part of a company’s SRE efforts.
Blameless now has interest from more mainstream companies in the areas of enterprise, logistics and healthcare. These companies aren’t necessarily focused on technology, but see a need for SRE.
“Companies recognize the shortfall in reliability, and then the question they come to us with is how do they get from where they are to where they want to be,” Anderson said. “Often companies that don’t have a process respond with ‘all hands on deck’ all the time, but instead need to shift to the right people responding.”
Lyon plans to use the new funding to fill key leadership roles, the company’s go-to-market strategy and product development to enable the company to go after larger enterprises.
Blameless doubled its revenue in the last year and will expand to service all customer segments, adding small and emerging businesses to its roster of midmarket and large companies. The company also expects to double headcount in the next three quarters.
As part of the funding announcement, Third Point Ventures partner Dan Moskowitz will join Blameless’ board of directors with Wong, Accel partner Vas Natarajan and Lightspeed partner Ravi Mhatre.
“Freeing up engineering to focus on shipping code is exactly what Blameless achieves,” said Moskowitz in a written statement. “The Blameless market opportunity is big as we see teams struggle and resort to creating homegrown playbooks and point solutions that are incomplete and costly.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Many have tried to do away with it, but email refuses to die … although in the process it might be (figuratively speaking) killing some of us with the workload it brings on to triage and use it. A startup called Sedna has built a system to help with that — specifically for enterprise and other business customers — by “reading” the text of emails and chats, and automatically actioning items within them so that you don’t have to. Today, it’s announcing funding of $34 million to expand its work.
The funding, a Series B, is being led by Insight Partners, with Stride.VC, Chalfen Ventures and the SAP.iO fund (part of SAP) also participating. The funding will be used to continue building out more data science around Sedna’s core functionality, with the aim of moving into a wider set of verticals over time. Currently its main business is in the area of supply chain players, with Glencore, Norden and Bunge among its customers. Other customers in areas like finance include the neobank Starling. London-based Sedna is not disclosing valuation.
Bill Dobie, Sedna’s CEO and founder originally from Vancouver but now in London, said the idea for the company was hatched out of his own experience.
“I spent years building software to help users be more productive, but no matter what we built we never really reduced people’s workload,” he said. The reason: The millstone that is called email, with its endless, unsolicited, inbound messages, some of which (just enough not to ignore) might be important. “What really struck me was how long it spent to move items out of and into email,” he said of the “to-do’s” that arose out of there.
Out of that, Sedna was built to “read” emails and give them more context and direction. Its system removes duplicates of action items and essentially increases the strike rate when it comes people’s inboxes: What’s in there is more likely to be what you really need to see. And it does so at a very quick speed.
“Our main value is the sheer scale at which we operate,” Dobie said. “We read millions or even billions of messages in subsecond response times.” Indeed, while many of us are not getting “millions” of emails, there is a world of messaging out there that needs reading beyond that. Think, for example, of the volume of data that will be coming down the pike from IoT-based diagnostics.
“Smart” inboxes have definitely become a thing for consumers — although arguably none work as well as you wish they did. What’s notable about Sedna has been how it’s tuned its particular algorithms to specific verticals, letting them get smarter around the kind of content and work practices in particular organizations.
Right now the work is driven by an API framework, with elements of “low code” formatting to let people shape their own Sedna experiences. The aim will be to make that even easier over time. An API-driven framework right now, some low code we’re heading into, but mostly its SAP or shipping or a trading system that understands the transaction underway, then Sedna uses a decision tree to categorize.
Another area where Sedna might grow is in how it handles the information that it ingests. Currently, the company’s tech can be interconnected by a customer to then hand off certain work to RPA systems, as well as to specific humans. There is an obvious route to developing some of the second stage of software there — or alternatively, it’s a sign of how something like Sedna might get snapped up or copied by one of the big RPA players.
“Bill started reimagining email where it was most broken and therefore hardest to fix — large teams managing huge volumes and complicated processes,” said Rebecca Liu-Doyle, principal at Insight Partners, in a statement. “Today, Sedna’s power is in its ability to introduce immense speed, simplicity and delight to any inbox experience, regardless of scale or complexity. We are excited to partner with the Sedna team as they continue to make digital communication more intelligent for teams in global supply chain and beyond.” Liu-Doyle is joining the board with this round.
SAP is a strategic investor in this round, as Sedna potentially helps its customers be more productive while using SAP systems. “SAP continues to partner with SEDNA to deliver value to SAP customers. The ability to turn complex information into simpler intelligent collaboration has been a growing priority for many SAP customers,” said Stefan Sauer, global transport solutions lead at SAP, in a statement.
Powered by WPeMatico