funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Bringing order and understanding to unstructured information located across disparate silos has been one of the more significant breakthroughs of the big data era, and today a European startup that has built a platform to help with this challenge specifically in the area of life sciences — and has, notably, been used by labs to sequence and so far identify two major COVID-19 variants — is announcing some funding to continue building out its tools to a wider set of use cases, and to expand into North America.
Seqera Labs, a Barcelona-based data orchestration and workflow platform tailored to help scientists and engineers order and gain insights from cloud-based genomic data troves, as well as to tackle other life science applications that involve harnessing complex data from multiple locations, has raised $5.5 million in seed funding.
Talis Capital and Speedinvest co-led this round, with participation also from previous backer BoxOne Ventures and a grant from the Chan Zuckerberg Initiative, Mark Zuckerberg and Dr. Priscilla Chan’s effort to back open source software projects for science applications.
Seqera — a portmanteau of “sequence” and “era”, the age of sequencing data, basically — had previously raised less than $1 million, and quietly, it is already generating revenues, with five of the world’s biggest pharmaceutical companies part of its customer base, alongside biotech and other life sciences customers.
Seqera was spun out of the Centre for Genomic Regulation, a biomedical research center based out of Barcelona, where it was built as the commercial application of Nextflow, open source workflow and data orchestration software originally created by the founders of Seqera, Evan Floden and Paolo Di Tommaso, at the CGR.
Floden, Seqera’s CEO, told TechCrunch that he and Di Tommaso were motivated to create Seqera in 2018 after seeing Nextflow gain a lot of traction in the life science community, and subsequently getting a lot of repeat requests for further customization and features. Both Nextflow and Seqera have seen a lot of usage: the Nextflow runtime has been downloaded more than 2 million times, the company said, while Seqera’s commercial cloud offering has now processed more than 5 billion tasks.
The COVID-19 pandemic is a classic example of the acute challenge that Seqera (and by association Nextflow) aims to address in the scientific community. With COVID-19 outbreaks happening globally, each time a test for COVID-19 is processed in a lab, live genetic samples of the virus get collected. Taken together, these millions of tests represent a goldmine of information about the coronavirus and how it is mutating, and when and where it is doing so. For a new virus about which so little is understood and that is still persisting, that’s invaluable data.
So the problem is not if the data exists for better insights (it does); it is that it’s nearly impossible to use more legacy tools to view that data as a holistic body. It’s in too many places, and there is just too much of it, and it’s growing every day (and changing every day), which means that traditional approaches of porting data to a centralized location to run analytics on it just wouldn’t be efficient, and would cost a fortune to execute.
That is where Segera comes in. The company’s technology treats each source of data across different clouds as a salient pipeline which can be merged and analyzed as a single body, without that data ever leaving the boundaries of the infrastructure where it already exists. Customised to focus on genomic troves, scientists can then query that information for more insights. Seqera was central to the discovery of both the Alpha and Delta variants of the virus, and work is still ongoing as COVID-19 continues to hammer the globe.
Seqera is being used in other kinds of medical applications, such as in the realm of so-called “precision medicine.” This is emerging as a very big opportunity in complex fields like oncology: cancer mutates and behaves differently depending on many factors, including genetic differences of the patients themselves, which means that treatments are less effective if they are “one size fits all.”
Increasingly, we are seeing approaches that leverage machine learning and big data analytics to better understand individual cancers and how they develop for different populations, to subsequently create more personalized treatments, and Seqera comes into play as a way to sequence that kind of data.
This also highlights something else notable about the Seqera platform: it is used directly by the people who are analyzing the data — that is, the researchers and scientists themselves, without data specialists necessarily needing to get involved. This was a practical priority for the company, Floden told me, but nonetheless, it’s an interesting detail of how the platform is inadvertently part of that bigger trend of “no-code/low-code” software, designed to make highly technical processes usable by non-technical people.
It’s both the existing opportunity and how Seqera might be applied in the future across other kinds of data that lives in the cloud that makes it an interesting company, and it seems an interesting investment, too.
“Advancements in machine learning, and the proliferation of volumes and types of data, are leading to increasingly more applications of computer science in life sciences and biology,” said Kirill Tasilov, principal at Talis Capital, in a statement. “While this is incredibly exciting from a humanity perspective, it’s also skyrocketing the cost of experiments to sometimes millions of dollars per project as they become computer-heavy and complex to run. Nextflow is already a ubiquitous solution in this space and Seqera is driving those capabilities at an enterprise level – and in doing so, is bringing the entire life sciences industry into the modern age. We’re thrilled to be a part of Seqera’s journey.”
“With the explosion of biological data from cheap, commercial DNA sequencing, there is a pressing need to analyse increasingly growing and complex quantities of data,” added Arnaud Bakker, principal at Speedinvest. “Seqera’s open and cloud-first framework provides an advanced tooling kit allowing organisations to scale complex deployments of data analysis and enable data-driven life sciences solutions.”
Although medicine and life sciences are perhaps Seqera’s most obvious and timely applications today, the framework originally designed for genetics and biology can be applied to any a number of other areas: AI training, image analysis and astronomy are three early use cases, Floden said. Astronomy is perhaps very apt, since it seems that the sky is the limit.
“We think we are in the century of biology,” Floden said. “It’s the center of activity and it’s becoming data-centric, and we are here to build services around that.”
Seqera is not disclosing its valuation with this round.
Powered by WPeMatico
The pandemic has triggered more demand for contactless and staff-less operations in the hospitality sector, and now H2O Hospitality, the unmanned hotel management company, has closed a $30 million round on the back of that boost. The South Korea and Japan-based startup automates front and backend processes including accommodation reservation, room management and front desk duties, and it will be using the funds to continue expanding its business.
The Series C round (equivalent to about 34 billion won) is being led by Kakao Investment and Korea Development Bank (KDB), Gorilla Private Equity, Intervest and NICE Investment also participated. With Southeast Asia’s joint fund, Kejora-Intervest Growth Fund also joined in the round, it is a sign that H2O Hospitality will be focusing specifically on the Southeast Asian Market. H2O Hospitality has raised $7 million Series B round from Samsung Ventures, Stonebridge Ventures, IMM Investment and Shinhan Capital in February 2020.
H2O Hospitality will expand its business further by adding various types of accommodations in South Korea and Japan in 2021 and 2022 and plans to enter Singapore and Indonesia in 4Q in 2022 in line with its Southeast Asia penetration strategy, according to H2O Hospitality co-founder and CEO John Lee.
“H2O Hospitality is currently speaking with several global hotel chain companies to partner with their digital transformation and operation outside of Korea and Japan,” Lee told TechCrunch.
H2O will invest in R&D to advance its customer channel solutions and contactless check-in systems depending on customer needs of each country in Asia, Lee continued.
“We need optimal system development and customization for each accommodation and situation to lead successful hotel digital transformation even after COVID-19,” Lee said in an email interview.
H2O Hospitality was founded in South Korea 2015 by CEO John Lee, and it has been on something of an acquisition-expansion spree. It entered Japan in 2017, for example, by acquiring several Japanese hospitality management companies. In 2021, H2O acquired two South Korean companies such as the contactless hotel solution company, ImGATE, and a local creator startup, Replace, in order to enhance its technology and ESG competence.
These days, the company operates approximately 7,500 accommodations including hotels, ryokans and guest houses, in Tokyo, Osaka, Seoul, Busan, and Bangkok.
H2O Hospitality’s Information and Communications Technology (ICT)-based hotel management system, which enables hotel management to automate and digitize, includes the Channel Management System (CMS), Property Management System (PMS), Room Management System (RMS), and Facility Management System (FMS).
Its integrated hotel management system can reduce hotel management’s fixed operating costs by 50%, while increasing revenue by as much as 20%, according to its statement.
“COVID-19 hit the hospitality industry the most and most of the hotels wanted to decrease their fixed cost level, but it was impossible with their current operational flow,” Lee continued, “They had to go through digital transformation”.
When asked how the pandemic affected H2O as COVID-19 still freezes most of the tourism industry, Lee said H2O’s revenue has been increased by as much as 30% before the pandemic, but that percentage has been dropped to 5-15% post COVID-19. Revenue drivers these days are based around tools it’s built to improve the efficiency of its customers. They include its automated dynamic pricing (ADR) tool and diverse sales channels like online and offline travel agencies in domestic and overseas, he said.
Lee also pointed out that H2O has been onboarding a lot of properties and that has also contributed to H2O’s revenue growth in the last 18 months. H2O was the only company in Asia, he claims, and many property owners have started to get onboard since August 2020, he explained.
“Every single hotel that we onboarded during the pandemic turned around their profits & losses statements and started to recover their financial loss,” Lee said.
There are currently about 16.4 million hotel rooms in the world that generate $570 billion a year, according to Lee. H2O believes that it can digitize all the lodging accommodations in the world as the company’s main goal is not building a hotel brand but allowing hotel owners to operate their properties with better operation, he said.
Lee explained that the current hotel operation process looks a lot like that of “2G phones”, that was at a stage before turning to smartphones, and H2O is turning the overall hotel operation into a “smartphone”.
“This is a very natural transition for the (hospitality) industry as it was also natural for the cellphone users to transit from 2G phone to smartphone,” Lee said.
Unfortunately, the cross-border inbound tourism market has still been stopped for both Korea and Japan even though each domestic market is still pumping demand for the market, Lee mentioned.
“We believe the inbound tourism market will recover within a year as the vaccinations grow for both countries (Korea and Japan),” Lee said.
Managing Director at Kejora-Intervest Growth Fund Jun-seok Kang told TechCrunch: “We knew this new wave for hotel digital transformation trend was coming even before the pandemic; however, COVID-19 definitely expedited the transition period, and we believe H2O will thrive in the transforming hotel market.”
Powered by WPeMatico
The manufacturing industry took a hard hit from the Covid-19 pandemic, but there are signs of how it is slowly starting to come back into shape — helped in part by new efforts to make factories more responsive to the fluctuations in demand that come with the ups and downs of grappling with the shifting economy, virus outbreaks and more. Today, a businesses that is positioning itself as part of that new guard of flexible custom manufacturing — a startup called Fractory — is announcing a Series A of $9 million (€7.7 million) that underscores the trend.
The funding is being led by OTB Ventures, a leading European investor focussed on early growth, post-product, high-tech start-ups, with existing investors Trind Ventures, Superhero Capital, United Angels VC, Startup Wise Guys and Verve Ventures also participating.
Founded in Estonia but now based in Manchester, England — historically a strong hub for manufacturing in the country, and close to Fractory’s customers — Fractory has built a platform to make it easier for those that need to get custom metalwork to upload and order it, and for factories to pick up new customers and jobs based on those requests.
Fractory’s Series A will be used to continue expanding its technology, and to bring more partners into its ecosystem.
To date, the company has worked with more than 24,000 customers and hundreds of manufacturers and metal companies, and altogether it has helped crank out more than 2.5 million metal parts.
To be clear, Fractory isn’t a manufacturer itself, nor does it have no plans to get involved in that part of the process. Rather, it is in the business of enterprise software, with a marketplace for those who are able to carry out manufacturing jobs — currently in the area of metalwork — to engage with companies that need metal parts made for them, using intelligent tools to identify what needs to be made and connecting that potential job to the specialist manufacturers that can make it.
The challenge that Fractory is solving is not unlike that faced in a lot of industries that have variable supply and demand, a lot of fragmentation, and generally an inefficient way of sourcing work.
As Martin Vares, Fractory’s founder and MD, described it to me, companies who need metal parts made might have one factory they regularly work with. But if there are any circumstances that might mean that this factory cannot carry out a job, then the customer needs to shop around and find others to do it instead. This can be a time-consuming, and costly process.
“It’s a very fragmented market and there are so many ways to manufacture products, and the connection between those two is complicated,” he said. “In the past, if you wanted to outsource something, it would mean multiple emails to multiple places. But you can’t go to 30 different suppliers like that individually. We make it into a one-stop shop.”
On the other side, factories are always looking for better ways to fill out their roster of work so there is little downtime — factories want to avoid having people paid to work with no work coming in, or machinery that is not being used.
“The average uptime capacity is 50%,” Vares said of the metalwork plants on Fractory’s platform (and in the industry in general). “We have a lot more machines out there than are being used. We really want to solve the issue of leftover capacity and make the market function better and reduce waste. We want to make their factories more efficient and thus sustainable.”
The Fractory approach involves customers — today those customers are typically in construction, or other heavy machinery industries like ship building, aerospace and automotive — uploading CAD files specifying what they need made. These then get sent out to a network of manufacturers to bid for and take on as jobs — a little like a freelance marketplace, but for manufacturing jobs. About 30% of those jobs are then fully automated, while the other 70% might include some involvement from Fractory to help advise customers on their approach, including in the quoting of the work, manufacturing, delivery and more. The plan is to build in more technology to improve the proportion that can be automated, Vares said. That would include further investment in RPA, but also computer vision to better understand what a customer is looking to do, and how best to execute it.
Currently Fractory’s platform can help fill orders for laser cutting and metal folding services, including work like CNC machining, and it’s next looking at industrial additive 3D printing. It will also be looking at other materials like stonework and chip making.
Manufacturing is one of those industries that has in some ways been very slow to modernize, which in a way is not a huge surprise: equipment is heavy and expensive, and generally the maxim of “if it ain’t broke, don’t fix it” applies in this world. That’s why companies that are building more intelligent software to at least run that legacy equipment more efficiently are finding some footing. Xometry, a bigger company out of the U.S. that also has built a bridge between manufacturers and companies that need things custom made, went public earlier this year and now has a market cap of over $3 billion. Others in the same space include Hubs (which is now part of Protolabs) and Qimtek, among others.
One selling point that Fractory has been pushing is that it generally aims to keep manufacturing local to the customer to reduce the logistics component of the work to reduce carbon emissions, although as the company grows it will be interesting to see how and if it adheres to that commitment.
In the meantime, investors believe that Fractory’s approach and fast growth are strong signs that it’s here to stay and make an impact in the industry.
“Fractory has created an enterprise software platform like no other in the manufacturing setting. Its rapid customer adoption is clear demonstrable feedback of the value that Fractory brings to manufacturing supply chains with technology to automate and digitise an ecosystem poised for innovation,” said Marcin Hejka in a statement. “We have invested in a great product and a talented group of software engineers, committed to developing a product and continuing with their formidable track record of rapid international growth
Powered by WPeMatico
Quantum Machines, an Israeli startup that is building the classical hardware and software infrastructure to help run quantum machines, announced a $50 million Series B investment today.
Today’s round was led by Red Dot Capital Partners with help from Exor, Claridge Israel, Samsung NEXT, Valor Equity Partners, Atreides Management, LP, as well as TLV Partners, Battery Ventures, 2i Ventures and other existing investors. The company has now raised approximately $83 million, according to Crunchbase data.
While quantum computing in general is in its early days, Quantum Machines has developed a nice niche by building a hardware and software system, what they call The Quantum Orchestration Platform, that helps run the burgeoning quantum machines, leaving it plenty of room to grow as the industry develops.
Certainly Quantum Machines co-founder and CEO Itamar Sivan, who has been working in quantum his entire career, sees the vast potential of this technology. “Quantum computers have the promise of potentially speeding up very substantially computations that are impossible to complete in reasonable time with classical computers, and this is at the highest level the interest in the field right now. Our vision specifically at Quantum Machines is to make quantum computers ubiquitous and disruptive across all industries,” he said.
To achieve that, the company has created a system that relies on classical computers to power quantum computers as they develop. While the company has designed its own silicon for this purpose, it is important to note that it is not building quantum chips. As Sivan explains, the classical computer has a software and hardware layer, but quantum machines have three layers: “The quantum hardware, which is the heart, and on top of that you have classical hardware […] and then on top of that you have software,” he said.
“We focus on the two latter layers. So classical hardware and the software that drives it. Now at the heart of our hardware is in fact a classical processor. So this is I think one of the most interesting parts of the quantum stack,” he explained.
He says that this interaction between classical computing and quantum computing is one that is fundamental to the technology, and it’s a mix that will last well into the future, possibly forever. What Quantum Machines is building is essentially the classical cloud infrastructure required to run quantum computers.

Quantum Machines founding team: Itamar Sivan, Nissim Ofek, Yonatan Cohen. Photo Credit: Quantum Machines
So far the approach has been working quite well, as Sivan reports that governments, researchers, universities and the hyper scaler operators (which could include companies like Amazon, Netflix and Google, although the company has not said they are customers) are all interested in QM’s technology. While it isn’t discussing specific metrics, the company has customers in 15 countries at the moment and is working with some large entities that it couldn’t name.
The money from this round helps validate what the company is doing, enabling it to continue building out the solution, while also investing heavily in research and development, which is essential as the industry is still in early development and much will change over time.
They have been able to create this solution to this point with just 60 employees, and with the new funding should be able to build out the team in a substantial way in the coming years. He says that when it comes to diversity, he comes from an academic background where this is the norm and he has carried this forth to his company as he hires new people. What’s more, the pandemic has allowed him to hire from anywhere and he says that the company has taken advantage of this opportunity.
“First of all, we’re not hiring just in Israel, we’re hiring globally, and we’re not limited to hiring in specific geographies. We have people [from a number of countries],” he said. He adds, “Diversity for me personally means involving as many people as possible in hiring processes. That is the only way to ensure that there is diversity.”
Even throughout the pandemic, the hardware team has been meeting in person in the office with necessary precautions when it has been allowed, but most employees have continued to work from home, and that is an approach he will continue to take even when it’s safe to return to the office on a regular basis.
“Of course, work in a post-COVID era will include a substantial amount of remote work. […] So even in [our] headquarters, we anticipate allowing people to work remotely [if they wish].
Powered by WPeMatico
There’s an old startup adage that goes: Cash is king. I’m not sure that is true anymore.
In today’s cash rich environment, options are more valuable than cash. Founders have many guides on how to raise money, but not enough has been written about how to protect your startup’s option pool. As a founder, recruiting talent is the most important factor for success. In turn, managing your option pool may be the most effective action you can take to ensure you can recruit and retain talent.
That said, managing your option pool is no easy task. However, with some foresight and planning, it’s possible to take advantage of certain tools at your disposal and avoid common pitfalls.
In this piece, I’ll cover:
Let’s run through a quick case study that sets the stage before we dive deeper. In this example, there are three equal co-founders who decide to quit their jobs to become startup founders.
Since they know they need to hire talent, the trio gets going with a 10% option pool at inception. They then cobble together enough money across angel, pre-seed and seed rounds (with 25% cumulative dilution across those rounds) to achieve product-market fit (PMF). With PMF in the bag, they raise a Series A, which results in a further 25% dilution.
The easiest way to ensure you don’t run out of options too quickly is simply to start with a bigger pool.
After hiring a few C-suite executives, they are now running low on options. So at the Series B, the company does a 5% option pool top-up pre-money — in addition to giving up 20% in equity related to the new cash injection. When the Series C and D rounds come by with dilutions of 15% and 10%, the company has hit its stride and has an imminent IPO in the works. Success!
For simplicity, I will assume a few things that don’t normally happen but will make illustrating the math here a bit easier:
Obviously, every situation is unique and your mileage may vary. But this is a close enough proxy to what happens to a lot of startups in practice. Here is what the available option pool will look like over time across rounds:
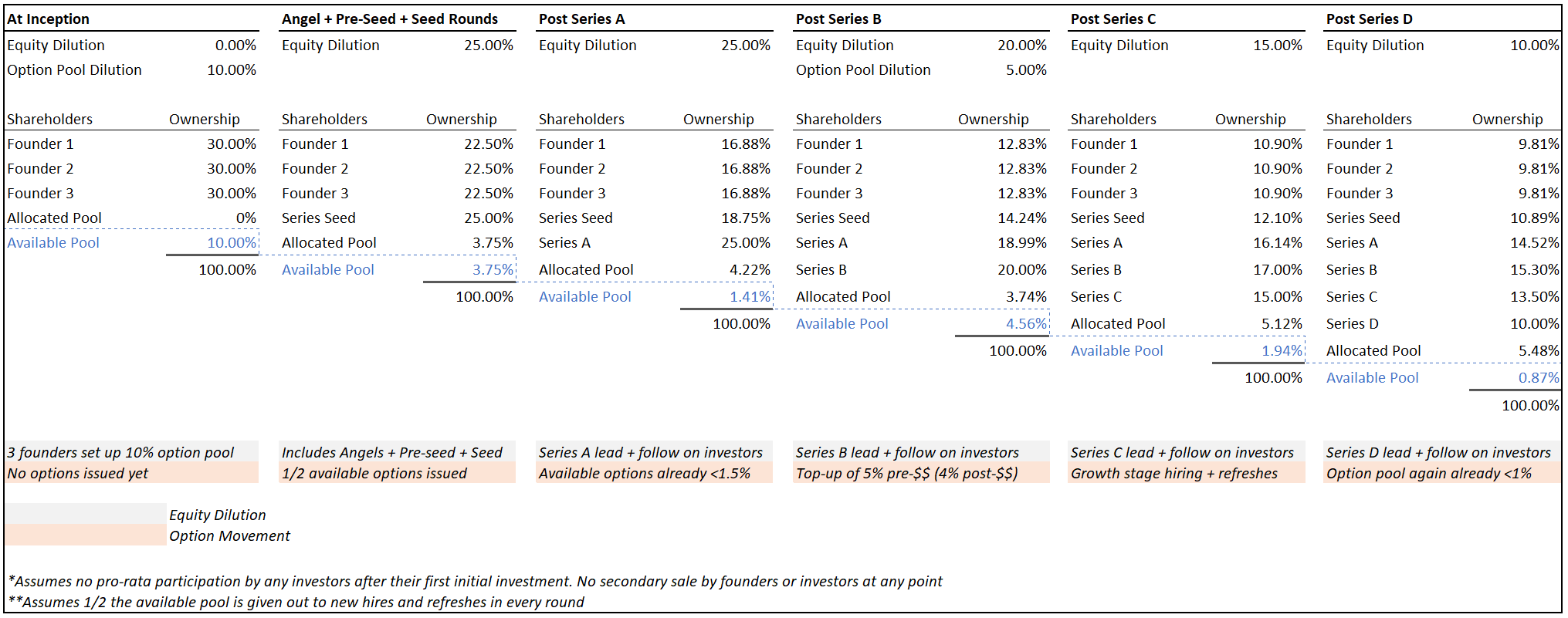
Image Credits: Allen Miller
Note how quickly the pool thins out — especially early on. In the beginning, 10% sounds like a lot, but it’s hard to make the first few hires when you have nothing to show the world and no cash to pay salaries. In addition, early rounds don’t just dilute your equity as a founder, they dilute everyone’s — including your option pool (both allocated and unallocated). By the time the company raises its Series B, the available pool is already less than 1.5%.
Powered by WPeMatico
TheCut, a technology platform designed to handle back-end operations for barbers, raised $4.5 million in new funding.
Nextgen Venture Partners led the round and was joined by Elevate Ventures, Singh Capital and Leadout Capital. The latest funding gives theCut $5.35 million in total funding since the company was founded in 2016, founder Obi Omile Jr. told TechCrunch.
Omile and Kush Patel created the mobile app that provides information and reviews on barbers for potential customers while also managing appointments, mobile payments and pricing on the back end for barbers.
“Kush and I both had terrible experiences with haircuts, and decided to build an app to help find good barbers,” Omile said. “We found there were great barbers, but no way to discover them. You can do a Google search, but it doesn’t list the individual barber. With theCut, you can discover an individual barber and discover if they are a great fit for you and won’t screw up your hair.”
The app also enables barbers, perhaps for the first time, to have a list of clients and keep notes and photos of hair styles, as well as track visits and spending. By providing payments, barbers can also leverage digital trends to provide additional services and extras to bring in more revenue. On the customer side, there is a search function with barber profile, photos of their work, ratings and reviews, a list of service offerings and pricing.
Omile said there are 400,000 to 600,000 barbers in the U.S., and it is one of the fastest-growth markets. As a result, the new funding will be used to hire additional talent, marketing and to grow the business across the country.
“We’ve gotten to a place where we are hitting our stride and seeing business catapulting, so we are in hiring mode,” he added.
Indeed, the company generated more than $500 million in revenue for barbers since its launch and is adding over 100,000 users each month. In addition, the app averages 1.5 million appointment bookings each month.
Next up, Omile wants to build out some new features like a digital store and the ability to process more physical payments by rolling out a card reader for in-person payments. TheCut will also focus on enabling barbers to have more personal relationships with their customers.
“We are building software to empower people to be the best version of themselves, in this case barbers,” he added. “The relationship with customers is an opportunity for the barber to make specific recommendations on products and create a grooming experience.”
As part of the investment, Leadout founder and managing partner Ali Rosenthal joined the company’s board of directors. She said Omile and Patel are the kind of founders that venture capitalists look for — experts in their markets and data-driven technologists.
“They had done so much with so little by the time we met them,” Rosenthal added. “They are creating a passionate community and set of modern, tech-driven features that are tailored to the needs of their customers.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Explosion, a company that has combined an open source machine learning library with a set of commercial developer tools, announced a $6 million Series A today on a $120 million valuation. The round was led by SignalFire, and the company reported that today’s investment represents 5% of its value.
Oana Olteanu from SignalFire will be joining the board under the terms of the deal, which includes warrants of $12 million in additional investment at the same price.
“Fundamentally, Explosion is a software company and we build developer tools for AI and machine learning and natural language processing. So our goal is to make developers more productive and more focused on their natural language processing, so basically understanding large volumes of text, and training machine learning models to help with that and automate some processes,” company co-founder and CEO Ines Montani told me.
The company started in 2016 when Montani met her co-founder, Matthew Honnibal in Berlin where he was working on the spaCy open source machine learning library. Since then, that open source project has been downloaded over 40 million times.
In 2017, they added Prodigy, a commercial product for generating data for the machine learning model. “Machine learning is code plus data, so to really get the most out of the technologies you almost always want to train your models and build custom systems because what’s really most valuable are problems that are super specific to you and your business and what you’re trying to find out, and so we saw that the area of creating training data, training these machine learning models, was something that people didn’t pay very much attention to at all,” she said.
The next step is a product called Prodigy Teams, which is a big reason the company is taking on this investment. “Prodigy Teams is [a hosted service that] adds user management and collaboration features to Prodigy, and you can run it in the cloud without compromising on what people love most about Prodigy, which is the data privacy, so no data ever needs to get seen by our servers,” she said. They do this by letting the data sit on the customer’s private cluster in a private cloud, and then use Prodigy Team’s management features in the public cloud service.
Today, they have 500 companies using Prodigy including Microsoft and Bayer in addition to the huge community of millions of open source users. They’ve built all this with just six early employees, a number that has grown to 17 recently (they hope to reach 20 by year’s end).
She believes if you’re thinking too much about diversity in your hiring process, you probably have a problem already. “If you go into hiring and you’re thinking like, oh, how can I make sure that the way I’m hiring is diverse, I think that already shows that there’s maybe a problem,” she said.
“If you have a company, and it’s 50 dudes in their 20s, it’s not surprising that you might have problems attracting people who are not white dudes in their 20s. But in our case, our strategy is to hire good people and good people are often very diverse people, and again if you play by the [startup] playbook, you could be limited in a lot of other ways.”
She said that they have never seen themselves as a traditional startup following some conventional playbook. “We didn’t raise any investment money [until now]. We grew the team organically, and we focused on being profitable and independent [before we got outside investment],” she said.
But more than the money, Montani says that they needed to find an investor that would understand and support the open source side of the business, even while they got capital to expand all parts of the company. “Open source is a community of users, customers and employees. They are real people, and [they are not] pawns in [some] startup game, and it’s not a game. It’s real, and these are real people,” she said.
“They deserve more than just my eyeballs and grand promises. […] And so it’s very important that even if we’re selling a small stake in our company for some capital [to build our next] product [that open source remains at] the core of our company and that’s something we don’t want to compromise on,” Montani said.
Powered by WPeMatico
YouTravel.Me is the latest startup to grab some venture capital dollars as the travel industry gets back on its feet amid the global pandemic.
Over the past month, we’ve seen companies like Thatch raise $3 million for its platform aimed at travel creators, travel tech company Hopper bring in $175 million, Wheel the World grab $2 million for its disability-friendly vacation planner, Elude raise $2.1 million to bring spontaneous travel back to a hard-hit industry and Wanderlog bag $1.5 million for its free travel itinerary platform.
Today YouTravel.Me joins them after raising $1 million to continue developing its online platform designed for matching like-minded travelers to small-group adventures organized by travel experts. Starta VC led the round and was joined by Liqvest.com, Mission Gate and a group of individual investors like Bas Godska, general partner at Acrobator Ventures.
Olga Bortnikova, her husband Ivan Bortnikov and Ivan Mikheev founded the company in Europe three years ago. The idea for the company came to Bortnikova and Bortnikov when a trip to China went awry after a tour operator sold them a package where excursions turned out to be trips to souvenir shops. One delayed flight and other mishaps along the way, and the pair went looking for better travel experiences and a way to share them with others. When they couldn’t find what they were looking for, they decided to create it themselves.
“It’s hard for adults to make friends, but when you are on a two-week trip with just 15 people in a group, you form a deep connection, share the same language and experiences,” Bortnikova told TechCrunch. “That’s our secret sauce — we want to make a connection.”
Much like a dating app, the YouTravel.Me’s algorithms connect travelers to trips and getaways based on their interests, values and past experiences. Matched individuals can connect with each via chat or voice, work with a travel expert and complete their reservations. They also have a BeGuide offering for travel experts to do research and create itineraries.
Since 2018, CEO Bortnikova said that YouTravel.Me has become the top travel marketplace in Eastern Europe, amassing over 15,900 tours in 130 countries and attracting over 10,000 travelers and 4,200 travel experts to the platform. It was starting to branch out to international sales in 2020 when the global pandemic hit.
“Sales and tourism crashed down, and we didn’t know what to do,” she said. “We found that we have more than 4,000 travel experts on our site and they feel lonely because the pandemic was a test of the industry. We understood that and built a community and educational product for them on how to build and scale their business.”
After a McKinsey study showed that adventure travel was recovering faster than other sectors of the industry, the founders decided to go after that market, becoming part of 500 Startups at the end of 2020. As a result, YouTravel.Me doubled its revenue while still a bootstrapped company, but wanted to enter the North American market.
The new funding will be deployed into marketing in the U.S., hiring and attracting more travel experts, technology and product development and increasing gross merchandise value to $2.7 million per month by the end of 2021, Bortnikov said. The goal is to grow the number of trips to 20,000 and its travel experts to 6,000 by the beginning of next year.
Godska, also an angel investor, learned about YouTravel.Me from a mutual friend. It happened that it was the same time that he was vacationing in Sri Lanka where he was one of very few tourists. Godska was previously involved in online travel before as part of Orbitz in Europe and in Russia selling tour packages before setting up a venture capital fund.
“I was sitting there in the jungle with a bad internet connection, and it sparked my interest,” he said. “When I spoke with them, I felt the innovation and this bright vibe of how they are doing this. It instantly attracted me to help support them. The whole curated thing is a very interesting move. Independent travelers that want to travel in groups are not touched much by the traditional sector.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Pixalate raised $18.1 million in growth capital for its fraud protection, privacy and compliance analytics platform that monitors connected television and mobile advertising.
Western Technology Investment and Javelin Venture Partners led the latest funding round, which brings Pixalate’s total funding to $22.7 million to date. This includes a $4.6 million Series A round raised back in 2014, Jalal Nasir, founder and CEO of Pixalate, told TechCrunch.
The company, with offices in Palo Alto and London, analyzes over 5 million apps across five app stores and more 2 billion IP addresses across 300 million connected television devices to detect and report fraudulent advertising activity for its customers. In fact, there are over 40 types of invalid traffic, Nasir said.
Nasir grew up going to livestock shows with his grandfather and learned how to spot defects in animals, and he has carried that kind of insight to Pixalate, which can detect the difference between real and fake users of content and if fraudulent ads are being stacked or hidden behind real advertising that zaps smartphone batteries or siphons internet usage and even ad revenue.
Digital advertising is big business. Nasir cited Association of National Advertisers research that estimated $200 billion will be spent globally in digital advertising this year. This is up from $10 billion a year prior to 2010. Meanwhile, estimated ad fraud will cost the industry $35 billion, he added.
“Advertisers are paying a premium to be in front of the right audience, based on consumption data,” Nasir said. “Unfortunately, that data may not be authorized by the user or it is being transmitted without their consent.”
While many of Pixalate’s competitors focus on first-party risks, the company is taking a third-party approach, mainly due to people spending so much time on their devices. Some of the insights the company has found include that 16% of Apple’s apps don’t have privacy policies in place, while that number is 22% in Google’s app store. More crime and more government regulations around privacy mean that advertisers are demanding more answers, he said.
The new funding will go toward adding more privacy and data features to its product, doubling the sales and customer teams and expanding its office in London, while also opening a new office in Singapore.
The company grew 1,200% in revenue since 2014 and is gathering over 2 terabytes of data per month. In addition to the five app stores Pixalate is already monitoring, Nasir intends to add some of the China-based stores like Tencent and Baidu.
Noah Doyle, managing director at Javelin Venture Partners, is also monitoring the digital advertising ecosystem and said with networks growing, every linkage point exposes a place in an app where bad actors can come in, which was inaccessible in the past, and advertisers need a way to protect that.
“Jalal and Amin (Bandeali) have insight from where the fraud could take place and created a unique way to solve this large problem,” Doyle added. “We were impressed by their insight and vision to create an analytical approach to capturing every data point in a series of transactions — more data than other players in the industry — for comprehensive visibility to help advertisers and marketers maintain quality in their advertising.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Forum Brands, an e-commerce acquisition platform, announced today that it has secured $100 million in debt funding from TriplePoint Capital.
The financing comes just over two months after the startup raised $27 million in an equity funding round led by Norwest Venture Partners.
Brenton Howland, Ruben Amar and Alex Kopco founded New York-based Forum Brands in the summer of 2020, during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’re buying what we think are A+ high-growth e-commerce businesses that sell predominantly on Amazon and are looking to build a portfolio of standalone businesses that are category leaders, on and off Amazon,” Howland told me at the time of the company’s last raise. “A source of inspiration for us is that we saw how consumer goods and services changed fundamentally for what we think is going to be for decades and decades to come, accelerating the shift toward digital.”
Since we covered the company in June, Forum Brands says it has acquired several new brands, including Bonza, a seller of pet products, and Simka Rose, a baby-focused brand specializing in eco-friendly products. Simka sells in the U.S. and the EU and is an example of how Forum is expanding globally, Amar said.
Howland and Amar emphasize that the Forum team continues to focus on quality over quantity when evaluating potential acquisitions. Although they meet with 15-20 founders a week, they are selective in which companies they choose to acquire.
“We continue to be a quality-first buyer, and not quantity-driven,” Amar said, noting that the company will still help a company build its brand even if it does not yet meet Forum’s quality threshold or if the founders are just not ready to sell.
The new funds will be used to, naturally, acquire more e-commerce companies. As part of the debt financing, Sajal Srivastava, co-CEO and co-founder of TriplePoint Capital, will be joining Forum’s board of directors.
“We are impressed not only by Forum’s long-term strategy and ability to leverage technology and deep collective e-commerce and M&A experience but also by how Forum cultivates relationships with their sellers both before and after partnering with them,” he said in a written statement.
At the time of its June raise, Forum had about 20 employees. As of today, it has about 40.
Forum’s technology employs “advanced” algorithms and over 100 million data points to populate brand information into a central platform in real time, instantly scoring brands and generating accurate financial metrics.
On August 31, we covered the news that on the heels of Heroes announcing a $200 million raise to double down on buying and scaling third-party Amazon Marketplace sellers, another startup out of London aiming to do the same announced some significant funding of its own. Olsam, a roll-up play that is buying up both consumer and B2B merchants selling on Amazon by way of Amazon’s FBA fulfillment program, closed on $165 million — a combination of equity and debt that it will be using to fuel its M&A strategy, as well as continue building out its tech platform and to hire more talent.
Powered by WPeMatico