Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Fearing weak fundraising options in the wake of the WeWork implosion, late stage startups are tightening their belts. The latest is another Softbank-funded company, joining Zume Pizza (80% of staff laid off), Wag (80%+), Fair (40%), Getaround (25%), Rappi (6%), and Oyo (5%) that have all cut staff to slow their burn rate and reduce their funding needs. Freight forwarding startup Flexport that is laying off 3% of its global staff.
“We’re restructuring some parts of our organization to move faster and with greater clarity and purpose. With that came the difficult decision to part ways with around 50 employees” a Flexport spokesperson tells TechCrunch after we asked today if it had seen layoffs like its peers.

Flexport CEO Ryan Petersen
Flexport had raised a $1 billion Series D led by SoftBank at a $3.2 billion valuation a year ago, bringing it to $1.3 billion in funding. The company helps move shipping containers full of goods between manufacturers and retailers using digital tools unlike its old-school competitors.
“We underinvested in areas that help us serve clients efficiently, and we over-invested in scaling our existing process, when we actually needed to be agile and adaptable to best serve our clients, especially in a year of unprecedented volatility in global trade” the spokesperson explained.
Flexport still had a record year, working with 10,000 clients to finance and transport goods. The shipping industry is so huge that it’s still only the seventh largest freight forwarder on its top Trans-Pacific Eastbound leg. The massive headroom for growth plus its use of software to coordinate supply chains and optimize routing is what attracted SoftBank.
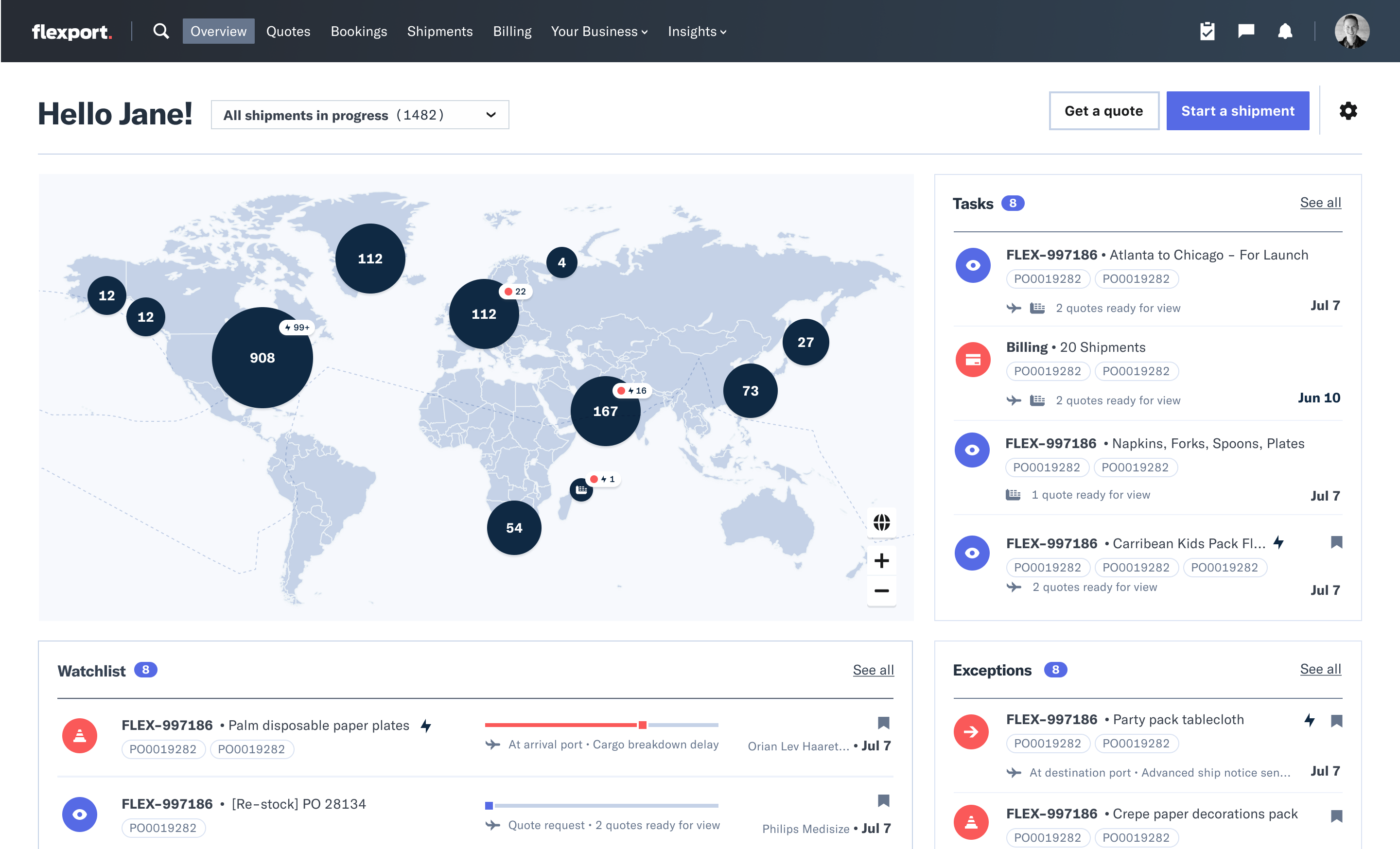
The Flexboard Platform dashboard offers maps, notifications, task lists, and chat for Flexport clients and their factory suppliers.
But many late-stage startups are worried about where they’ll get their next round after taking huge sums of cash from SoftBank at tall valuations. As of November, SoftBank had only managed to raise about $2 billion for its Vision Fund 2 despite plans for a total of $108 billion, Bloomberg reported. LPs were partially spooked by SoftBank’s reckless investment in WeWork. Further layoffs at its portfolio companies could further stoke concerns about entrusting it with more cash.
Unless growth stage startups can cobble together enough institutional investors to build big rounds, or other huge capital sources like sovereign wealth funds materialize for them, they might not be able to raise enough to keep rapidly burning. Those that can’t reach profitability or find an exit may face down-rounds that can come with onerous terms, trigger talent exodus death spirals, or just not provide enough money.
Flexport has managed to escape with just 3% layoffs for now. Being proactive about cuts to reach sustainability may be smarter than gambling that one’s business or the funding climate with suddenly improve. But while other SoftBank startups had to spend tons to edge out direct competitors or make up for weak on-demand service margins, Flexport at least has a tried and true business where incumbents have been asleep at the wheel.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to our regular morning look at private companies, public markets and the gray space in between.
Asana, a well-known workplace productivity company, announced yesterday it has filed privately to go public. The San Francisco-based company is well-funded, having raised more than $200 million; well-known, due in part to its tech-famous founding duo; and valuable, having last raised at a $1.5 billion valuation.
Each of those factors — plus the fact that Asana is going public — makes the company worth exploring, but its plans to offer a direct listing instead of a traditional initial public offering make it irresistible.
Today, we’ll rewind through Asana’s fundraising and valuation history. Then, we’ll mix in what we know about its financial performance, growth rates and capital efficiency to see how much we can tell about the company as we count down to its public S-1 filing. The Asana flotation is going to be big news, so let’s get all our facts and figures straightened out.
Powered by WPeMatico
Infor announced today that Koch Industries has bought the company in a deal sources peg at close to $13 billion.
Infor, which makes large-scale cloud ERP software, has been around since 2002 and counts Koch as both a customer and an investor, so the deal makes sense on that level. Koch was lead investor last year in a $1.5 billion investment, wherein the company indicated that it was a step before going public.
It’s not clear if that is still the goal, as sources suggested that staying private might provide the company with more capital flexibility in the future. Daniel Newman, founder and principal analyst at Futurum Research, says staying private longer could benefit Infor in the long run.
“There have been thoughts of an IPO, but remaining private should give the company flexibility without the quarterly pressure to refine its strategy, make necessary investments in the platform and achieve the growth rates that would make the company more of an exciting IPO,” he said.
Under the terms of the deal, Koch will be buying out the remaining equity stake in Golden Gate Capital, a secondary investor in last year’s investment. The company’s management team will remain in place and Infor will act as a standalone subsidiary of Koch.
Company CEO Kevin Samuelson, as you would expect, saw the deal as a positive move that allowed the company to operate with a well capitalized parent behind it. “As a subsidiary of a $110 billion+ revenue company that re-invests 90% of earnings back into its businesses, we will be in the unique position to drive digital transformation in the markets we serve,” he said in a statement.
Jim Hannan, executive vice president and CEO of enterprises for Koch Industries, saw it similarly, with Koch’s deep pockets helping to propel Infor in the future. “As a global organization spanning multiple industries across 60 countries, Koch has the resources, knowledge and relationships to help Infor continue to expand its transformative capabilities,” he said in a statement.
Holger Mueller, an analyst at Constellation Research, says it’s a strange deal on its face, but if Koch leaves Infor alone, it might work out. “When you think you have seen it all, something new comes along: A regular enterprise buys a top-five ERP vendor. Now [we’ll have to see] if Koch can ensure Infor keeps building market leading software, using Koch as showcase, or becomes the Koch software affiliate.
“The latter would be an unfortunate outcome. On the positive side, enterprise software built from real user validation, that can also serve as a reference, can be very powerful,” Mueller told TechCrunch. He said it could work out great, but also has the potential to go very wrong, depending on how Koch manages a software asset.
Infor is a huge company. As we reported last year at the time of its investment:
Infor may be the largest company you never heard of, with more than 17,000 employees and 68,000 customers in more than 100 countries worldwide. All of those customers generated $3 billion in revenue in 2018. That’s a significant presence.
Powered by WPeMatico
HPE announced today that it has acquired Scytale, a cloud native security startup that is built on the open-source Secure Production Identity Framework for Everyone (SPIFFE) protocol. The companies did not share the acquisition price.
Specifically, Scytale looks at application-to-application identity and access management, something that is increasingly important as more transactions take place between applications without any human intervention. It’s imperative that the application knows it’s OK to share information with the other application.
This is an area that HPE wants to expand into, Dave Husak, HPE fellow and GM of cloudless initiative wrote in a blog post announcing the acquisition. “As HPE progresses into this next chapter, delivering on our differentiated, edge to cloud platform as-a-service strategy, security will continue to play a fundamental role. We recognize that every organization that operates in a hybrid, multi-cloud environment requires 100% secure, zero trust systems, that can dynamically identify and authenticate data and applications in real-time,” Husak wrote.
He also was careful to stress that HPE would continue to be good stewards of the SPIFFE and SPIRE (the SPIFFE Runtime Environment) projects, both of which are under the auspices of the Cloud Native Computing Foundation.
Scytale co-founder Sunil James, writing in a blog post about the deal, indicated that this was important to the founders that HPE respect the startup’s open-source roots. “Scytale’s DNA is security, distributed systems, and open-source. Under HPE, Scytale will continue to help steward SPIFFE. Our ever-growing and vocal community will lead us. We’ll toil to maintain this transparent and vendor-neutral project, which will be fundamental in HPE’s plans to deliver a dynamic, open, and secure edge-to-cloud platform,” he wrote.
Scytale was founded in 2017 and had raised $8 million, according to PitchBook data. The bulk of that was in a $5 million Series A last March led by Bessemer. The deal closed today.
Powered by WPeMatico
Shares of One Medical are worth $19.50 this morning after the venture-backed unicorn priced its IPO at $14 per share last night. The company opened at $18 before rising further, according to Yahoo Finance data. At its current price, One Medical is worth about 40% more than its IPO price, a strong debut for the company.
The result is a boon for One Medical, which raised $532.1 million during its time as a private company. At $14 per share, the company was worth $1.71 billion. At 19.50, One Medical is worth $2.38 billion, a winning result for a company said to be worth around $1.5 billion as a private company.
For investors The Carlyle Group, J.P. Morgan, Redmile Group, GV and Benchmark (among others), the debut is a success, pricing their stakes in the company higher once again. For other unicorns, the news is even better. One Medical, a company with gross margins under the 50% mark, deeply minority recurring revenue and 30% revenue growth in 2019 at best is now worth about 8.5x its trailing revenues.
That is about as good a signal as one could imagine for venture-backed companies that aren’t in as good shape as Slack or Zoom were letting them know that now is the time to go public.
It’s possible to read One Medical’s new revenue multiple in a few ways. You can be positive, saying that its valuation and resulting metrics are signs of investor optimism for the medical service company. Or you could go negative and assume that its pricing looks like a case of the market being more excited about a brand than a set of accounting results.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast, where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
It was yet another jam-packed week full of big news, IPO happenings and venture activity. As always, we’ve done our best to deliver the gist on what’s been going on. We had Alex Wilhelm and Danny Crichton on hand to handle it all, which went medium-good. In other Equity news, we’re back with guests over the next few weeks, so if you miss us having a venture capitalist along for the ride, fear not, their return is just around the corner.
Up top this week was Jon Shieber’s report that Kleiner Perkins has rapidly deployed its most recent fund, a $600 million vehicle. While the news felt surprising, digging back through our archives we were reminded that the firm had indicated it might put its capital to work quickly. Still, as Danny pointed out, it’s rare that venture capitalists have to go out raising from LPs on an annual basis.
After that, we turned to some funding rounds that held our attention, including the Free Agency round that is working to bring talent management to the technology industry similar to the sports and entertainment worlds.
The concept makes some sense, as compensation packages for top talent in the industry can extend into the seven-figures (Free Agency takes a 5-10% cut of an employee’s income using the increasingly popular income-share agreements). Also, this round felt a bit like a reminder that the labor market is tight at the moment.
We then moved on to Josh Constine’s story about “Ring for enterprise” startup Verkada, which raised a massive $80 million round at a $1.6 billion valuation. That’s eye-popping, since the extremely small dilution implied with those numbers (5%) is very rare in the venture world.
After that we turned to a few rounds that Alex has had his eye on, namely the somewhat-recent Insurify round, the pretty-recent Gabi round and the most-recent Policygenius. All told, they sum to $150 million, which made us ask the question, why are venture capitalists so into insurance marketplace startups?
Finally, we touched on the latest from the intra-SoftBank delivery war between DoorDash and Uber Eats, including who is impacted, and what it means for future consolidation in the on-demand world. Or more precisely, why hasn’t there been more?
Finally, don’t forget that IPO season is upon us. Are you caught up?
Equity drops every Friday at 6:00 am PT, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast, Spotify and all the casts.
Powered by WPeMatico
Insticator, a startup helping publishers add to their content elements like polls, quizzes and suggested story widgets, has made its first acquisition — a commenting platform called Squawk-It.
Insticator CEO Zack Dugow said his platform benefits online publishers by keeping audiences engaged and bringing in new ad revenue (which is split between Insticator and the publisher). And he sees commenting as a natural next step toward his goal to become “the main monetization and community engagement solution for publishers.”
While “don’t read the comments” remains one of the most reliable pieces of advice you’ll get online, Dugow said Squawk-It (it was formerly known as Solid Opinion) stands out from other commenting platforms because of its reliance on “100 percent human moderation,” with moderators working in three shifts to monitor partner sites 24 hours each day.
“Anybody can game an algorithm,” he said.
And when I brought up the concern that so much of the discussion has moved out of the comments section and onto social media, Dugow responded that “merging social commenting” so that it feels like everything is part of the same conversation is “in our roadmap.”
Like other Insticator products, Squawk-It comments (which you can see below the article here) are monetized through advertising. But Dugow noted that the ads run above the comments, rather than interrupting or distracting from the comments themselves.
The financial terms of the acquisition were not disclosed. Dugow said the entire 13-person Squawk-It team (headquartered in New York but with an engineering team in Kiev) has joined Insticator, and that the product has already been rebranded as Insticator Comments.
Powered by WPeMatico
The Bouqs plans to take a slice of Japan’s $6 billion flower market this year with a $30 million strategic growth round from Japanese enterprise business investor Yamasa. While The Bouqs still must compete with bigger contenders like 1-800-Flowers and FTD in the U.S., it will now have to take on incumbents like Ayoma Flower Market and FloraJapan, both of which also offer same-day delivery throughout the land of the rising sun.
So why Japan? According to The Bouqs founder and CEO John Tabis, his company had been looking to expand internationally for awhile and Japan seemed to fit well within that plan.

The Bouqs CEO and founder John Tabis
But as far as bigger competition in any country, Tabis is undeterred, telling TechCrunch there’s plenty of opportunities in the flower delivery business if you know where to look. “There’ve been four or five other startups that tried something similar — some of them no longer exist,” Tabis said. “But the thing that’s worked for us, the first is the way that we’ve sourced is unique and it’s really the foundation of our brand.”
The Bouqs sprung up in a wave of Silicon Valley funded flower delivery startups like BloomThat, Farm Girl and Urban Stems, all promising Pinterest -worthy bouquets at the click of a button. But what set it apart was its farm-direct supply chain, cutting out costs from middlemen and delivering flowers that last longer.
This particular round now puts The Bouqs up top as far as total funding raised among its flower delivery startup peers, bringing in $74 million in total funding to date, with competitor Urban Stems in second place with $27 million in funding, according to Crunchbase.
Tabis also tells TechCrunch the new funds will further the company’s development into brick-and-mortar stores and that it’s jumping into the wedding biz. As anyone who’s ever planned a wedding will tell you, it’s an industry ripe for disruption — with brides and grooms spending about 8% of the budget on the flowers alone.
One other renewed focus for the company will be its subscription business, keeping customers set up with a fresh bunch of flowers once the old bouquet is ready for tossing. “It’s sort of the linchpin of our business that’s grown very nicely…expanding both our revenue and profitability,” Tabis told TechCrunch.
The SVP of Yamasa, Norikazu Sano, also mentioned further expansion into Asia for the company in a company press release, so we could see The Bouqs in more international areas over time, if all goes right in Japan.
“This financing will enable us to fully realize our vision to create a global network of top-quality farms paired with a category-defining local floral brand enabled by proprietary supply chain technology and vertically integrated sourcing capabilities. We’re so excited for this next phase of the business, and all of the opportunities that lie ahead,” Tabis said.
Powered by WPeMatico
SoftBank wants its competing portfolio companies to stop losing so much money and, in some cases, to merge.
That’s the news out from Financial Times today, which reported that Uber and DoorDash discussed merging last year. The talks didn’t wind up in a deal.
The two companies, each heavily backed by SoftBank and its formerly active Vision Fund, compete in the food delivery space at great expense. Uber’s Eats business turned $392 million in adjusted net revenue in Q3 2019 into $316 million adjusted loss. That ocean of red ink actually makes DoorDash’s reported, projected $450 million 2019 operating loss look modest.
Perhaps by bringing the two companies together they would lose less money, and thus be in a better place to either return to their original IPO valuation or defend their existing private valuation.
Uber has famously struggled to retain value after its IPO, shedding worth during its public offering and since its debut. DoorDash, relatedly, was said to be in the market recently, but unable to close a new, large funding round. And as the two companies compete, a combination makes sense. Even more so when you consider their shared shareholder.
Uber and DoorDash aren’t the only examples of SoftBank-backed companies beating each other up with bricks of Vision Fund cash.
According to a report today in The Wall Street Journal, a fight in Latin America between several SoftBank-backed companies is raging:
Uber is under siege in Latin America amid a bruising price war where its ostensible rivals are Rappi and China’s Didi Chuxing Technology Co. But here’s the twist. All the combatants have as their biggest owner the same tech investor, Japan’s SoftBank Group Corp., which has injected a total of $20 billion into the three.
In the pre-unicorn era, you’ll recall the old venture maxim that no single group should invest in competing players. After all, why pay for one portfolio company to beat on another startup that you already helped finance? SoftBank, with its own investments and the Vision Fund, ignored that rule, and now it’s financing a fustercluck across the various American continents. (Though, there are some examples of other firms doing this, like Sequoia putting money into Uber and Didi.)
Which is why it might want DoorDash and Uber to link up. It might lessen one headache. Then SoftBank could work on figuring out how to keep Uber and Didi from beating each other up on rides in other markets, while disentangling Uber Eats and Rappi from a delivery scrap in yet more.
Perhaps SoftBank wants all the players to merge into a single, mega-delivery and ride corp. That would never pass regulatory oversight, of course, but at least it would centralize the losses and cash burn into a single income statement.
Think of the time it would save!
Powered by WPeMatico
Fifty iPads were stolen from Verkada co-founder Hans Robertson’s old company. Only when they checked the security system did they realize the video cameras hadn’t been working for months. He was pissed. “The market lagged behind the progress seen in the consumer space, where someone could buy high-end cameras with cloud-based software to protect their home,” Verkada’s CEO and co-founder Filip Kaliszan tells me of his own attempt to buy enterprise-grade security hardware.
Usually, startups ascend on the backs of fresh technologies and developer platforms. But Kaliszan and Robertson realized that commercial security was so backward that just implementing the established principles of machine vision and the cloud could create a huge company. The plan was to keep data secure yet accessible and train its cameras to take clearer photos when AI detects suspicious situations instead of just grainy video.
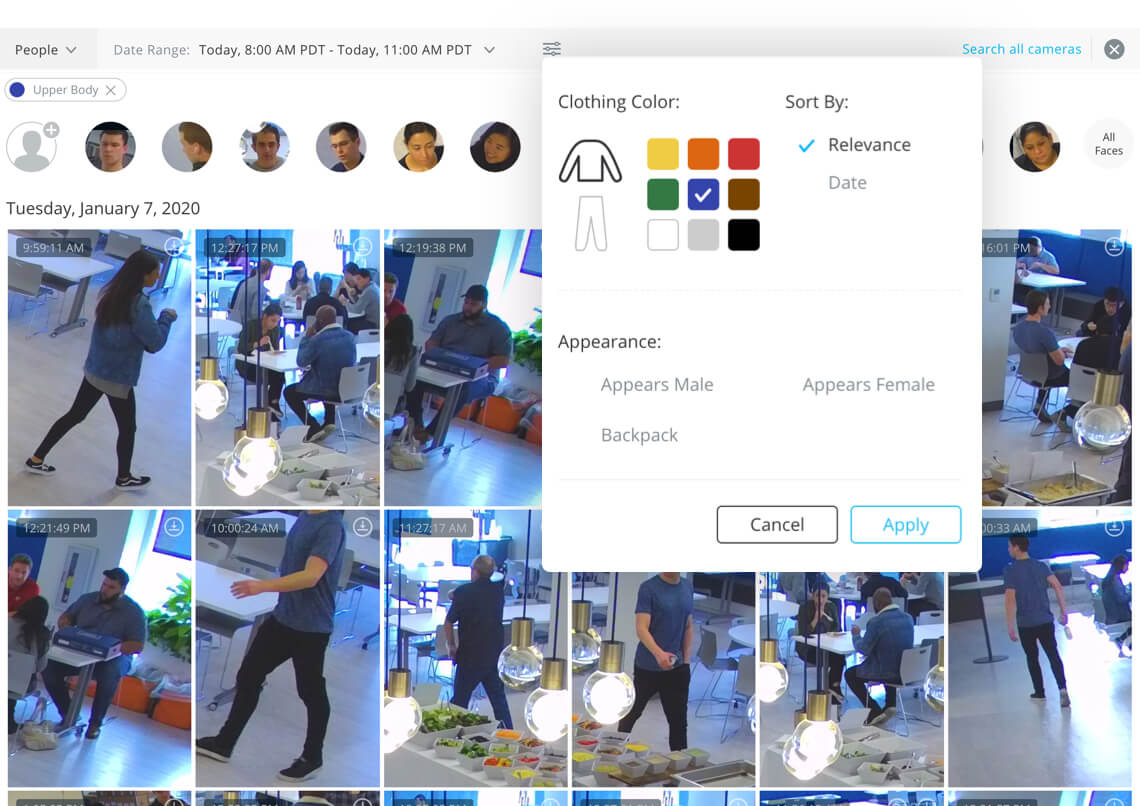
At first, few could see the vision through the slow upgrade cycles and basement security rooms common with most potential clients. “The seed and the A were extremely difficult rounds to raise compared to the later rounds because people didn’t believe we could execute what were are proposing,” Kaliszan glumly recalls.
But today Verkada receives a huge vote of confidence. It just raised an $80 million Series C at a stunning $1.6 billion post-money valuation thanks to lead investor Felicis Ventures writing Verkada its biggest check to date. The cash brings Verkada to $139 million in funding to sell dome cameras, fisheye lenses, footage viewing stations and the software to monitor it all from anywhere.
Why sink in so much cash at a valuation triple that of Verkada’s $540 million price tag after its April 2019 Series B? Because Verkada wants to bring two-factor authentication to doors with its new access control system that it’s announcing is now in beta testing ahead of a Spring launch. Instead of just allowing a stealable key fob or badge to open your office entryway, it could ask you to look into a Verkada camera too so it can match your face to your permissions.

“Our mission is to be the essential physical security software layer for every building, and the foundation of a larger enterprise IoT infrastructure,” Kaliszan tells me. By uniting security cameras and door locks in one system, it could keep banks, schools, hospitals, government buildings and businesses safe while offering new insights on how their spaces are used.
The founders’ pedigrees don’t hurt its efforts to sell that future to investors like Next47, Sequoia Capital and Meritech Capital, which joined the round. Robertson co-founded IT startup Meraki and sold it to Cisco for $1.2 billion. Kaliszan and his other co-founders Benjamin Bercovitz and James Ren started CourseRank for education software while at Stanford before selling it to Chegg.

Making a better product than what’s out there isn’t rocket science, though. Many building security systems only let footage be accessed from a control room in the building… which doesn’t help much if everyone’s trying to escape due to emergency or if a manager elsewhere simply wants to take a look. Verkada’s cloud lets the right employees keep watch from mobile, and data is also stored locally on the cameras so they keep recording even if the internet cuts out. “Our competitors stream unencrypted video and it’s on you to protect it. We’re responsible for handling that data,” Kaliszan says.
Verkada’s machine vision software can make sense of all the footage its cameras collect. “We can immediately show them all the video containing a particular person of interest rather than manually searching through hours of footage,” Kaliszan insists. “Our platform can use AI/machine learning to recognize patterns and behaviors that are out of the norm in real time.”
For example, a hostage negotiator was able to use Verkada’s system to assess whether a SWAT team needed to invade a building. Verkada can group all spottings of an individual together for review, or scan all the footage for people wearing a certain color or with other search filters.

Indeed, 2,500 clients, including 25 Fortune 500 companies, are already using Verkada. In the last year it has tripled revenue, partnered with 1,100 resellers, launched nine new camera models, added people and vehicle analytics, opened its first London office and is on track to grow from 300 to 800 employees by the end of 2020.
“We call this reinvention,” says Felicis Ventures founder and managing director Aydin Senkut. “One thing people underestimate is how big this market is. Honeywell is valued at $110 billion-plus. There’s a Chinese company that’s over $50 billion. The opportunity to be the operating system for all buildings in the world? Sounds like that market couldn’t be better.” Senkut knows Verkada works because he had it installed in all his homes and offices.
Most enterprise software companies don’t have to worry about the complexities of hardware supply chains. There’s always a risk that its sales process stumbles, leaving it stuck with too many cameras. “We’re still burning money. We’re not there yet or we wouldn’t be raising venture. Because we’re going after a mature market, you can’t come at it with a model that doesn’t make sense. Investors come at it from a hard-nosed approach,” Robertson admits.
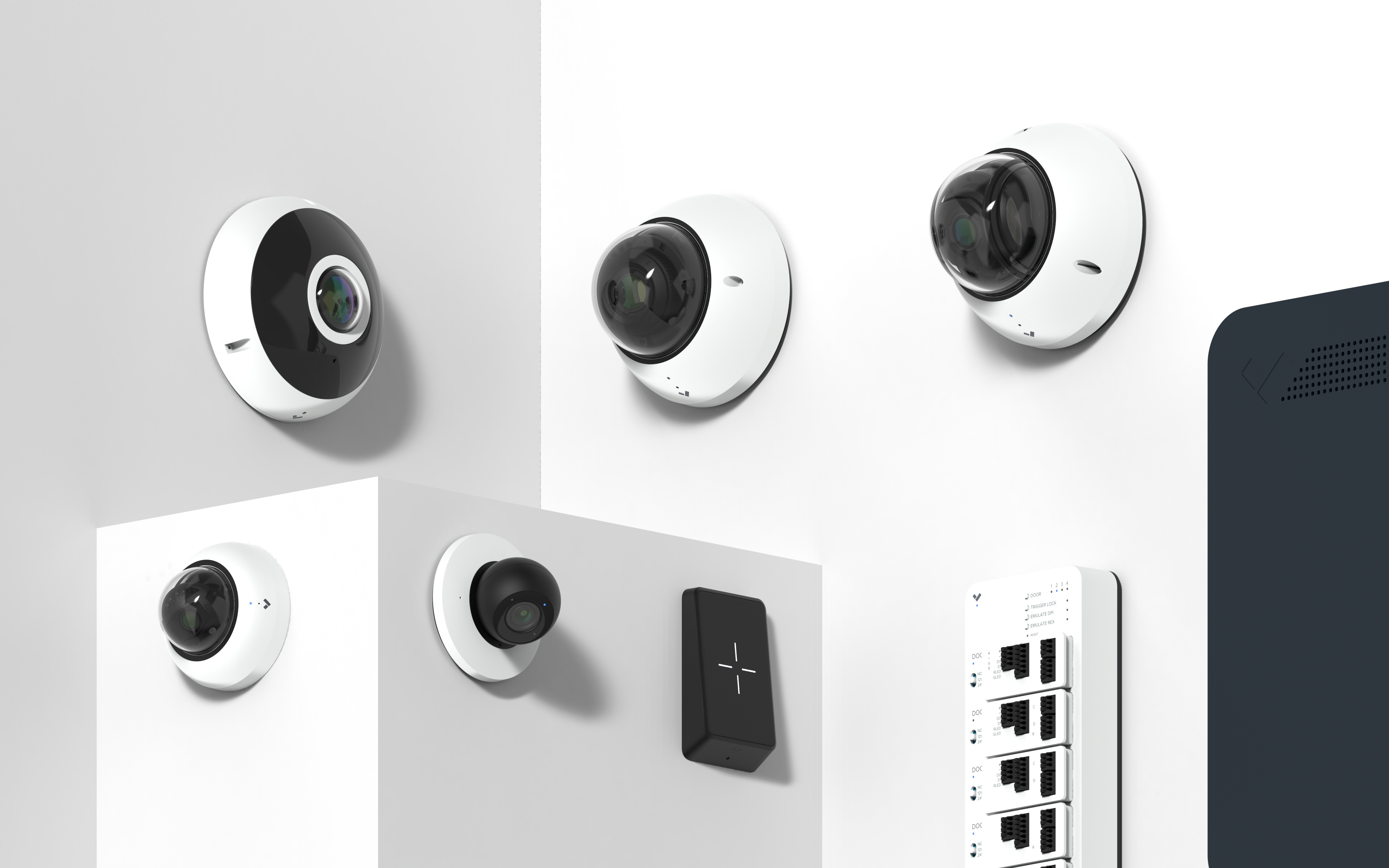

“People have a tendency to write off Verkada as a boring camera company. They don’t realize how access control as the second product is going to supercharge the company’s potential,” Senkut declares.
One bullet Verkada dodged is the one firmly lodged in Amazon’s chest. Ring security cameras have received stern criticism over Amazon’s cooperation with law enforcement that some see as a violation of privacy and expansion of a police state. “We don’t have any arrangements with law enforcement like Ring,” Kaliszan tells me. “We view ourselves as providing great physical security tools to the people that run schools, hospitals and businesses. The data that those organizations gather is their own.”
Powered by WPeMatico