Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
In Silicon Valley, investors don’t expect their portfolio companies to be profitable. “Blitzscaling: The Lightning-Fast Path to Building Massively Valuable Companies,” a bible for founders, instead calls for heavy spending on growth to scale in an Amazon -like fashion.
As for Wall Street, it’s shown an affinity for stock in Jeff Bezos’ business, despite the many years it spent navigating a path to profitability, as well as other money-losing endeavors. Why? Because it too is far less concerned with profitability than market opportunity.
Lyft, a ride-hailing company expected to go public this week, is not profitable. It posted losses of $911 million in 2018, a statistic that will make it the biggest loser amongst U.S. startups to have gone public, according to data collected by The Wall Street Journal. On the other hand, Lyft’s $2.2 billion in 2018 revenue places it atop the list of largest annual revenues for a pre-IPO business, trailing behind only Facebook and Google in that category.
Wall Street, in short, is betting on Lyft’s revenue growth, assuming it will narrow its loses and reach profitability… eventually.
Lyft, losses notwithstanding, is growing rapidly and Wall Street is paying attention. On the second day of its road show, reports emerged that its IPO was already oversubscribed. As a result, Lyft is said to have upped the cost of its stock, with new plans to raise more than $2 billion at a valuation upwards of $25 billion. That represents a revenue multiple of more than 11x, a step up multiple of more than 1.6x from its most recent private valuation of $15.1 billion and, of course, Wall Street’s insatiable desire for unicorns, profitable or not.
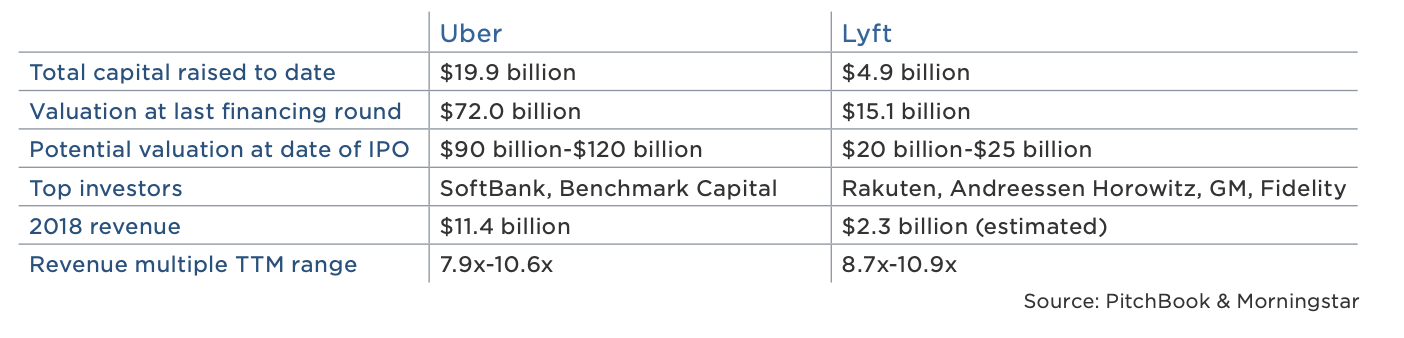
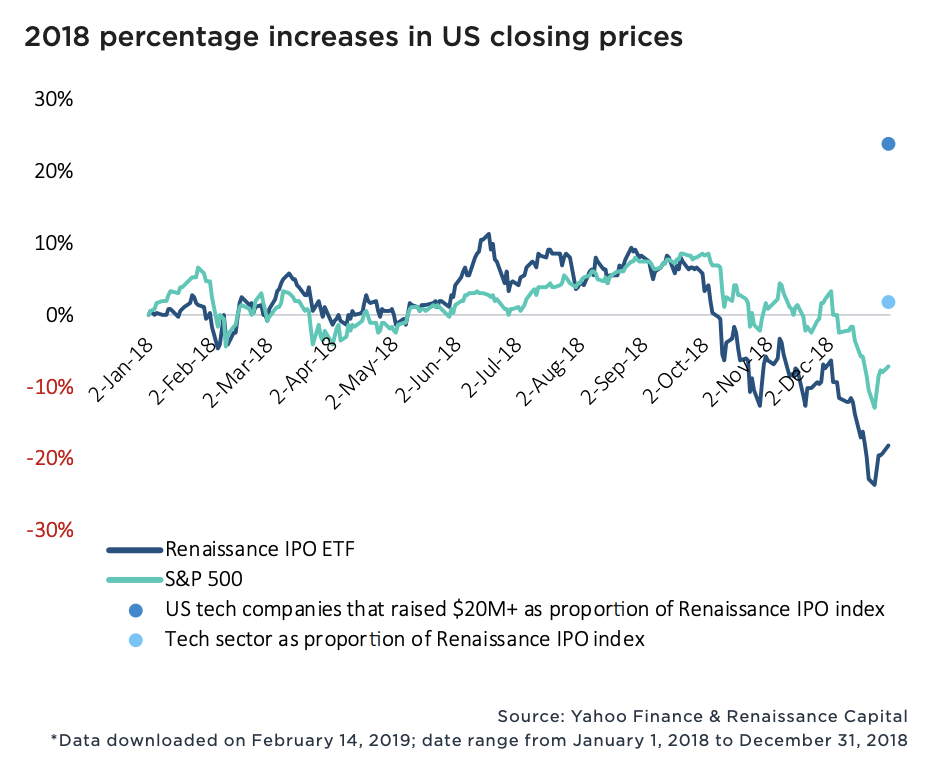
New data from PitchBook exploring the performance of billion-dollar-plus VC exits confirms Wall Street’s leniency toward unprofitable tech companies. Sixty-four percent of the 100+ companies valued at more than $1 billion to complete a VC-backed IPO since 2010 were unprofitable, and in 2018, money-losing startups actually fared better on the stock exchange than money-earning businesses. Moreover, U.S. tech companies that had raised more than $20 million traded up nearly 25 percent of 2018, while the S&P 500 technology sector posted flat returns.
Wall Street is still adapting to the rapid growth of the tech industry; public markets investors, therefore, are willing to deal with negative to minimal cash flows for, well, a very long time.
There’s no doubt Lyft and its much larger competitor, Uber, will go public at monstrous valuations. The two IPOs, set to create a whole bunch of millionaires and return a number of venture capital funds, will provide Silicon Valley a lesson in Wall Street’s tolerance for outsized exits.

Much like a seed-stage investor must bet on a founder’s vision, Wall Street, given a choice of several unprofitable businesses, has to bet on potential market value. Fortunately, this strategy can work quite well. Take Floodgate, for example. The seed fund invested a small amount of capital in Lyft when it was still a quirky idea for ridesharing called Zimride. Now, it boasts shares worth more than $100 million. I’m sure early shareholders in Amazon — which went public as a money-losing company in 1997 — are pretty happy, too.
Ultimately, Wall Street’s appetite for unicorns like Lyft is a result of the shortage of VC-backed IPOs. In 2006, it was the norm for a company to make its stock market debut at 7.9 years old, per PitchBook. In 2018, companies waited until the ripe age of 10.9 years, causing a significant slowdown in big liquidity events and stock sales.
Fund sizes, however, have grown larger and the proliferation of unicorns continues at unforeseen rates. That may mean, eventually, an influx of publicly shared unicorn stock. If that’s the case, might Wall Street start asking more of these startups? At the very least, public market investors, please don’t be swayed by WeWork‘s eventual stock offering and its “community adjusted EBITDA.” Silicon Valley’s pixie dust can’t be that potent.
Powered by WPeMatico
Social investing and trading platform eToro announced that it has acquired Danish smart contract infrastructure provider Firmo for an undisclosed purchase price.
Firmo’s platform enables exchanges to execute smart financial contracts across various assets, including crypto derivatives, and across all major blockchains. Firmo founder and CEO Dr. Omri Ross described the company’s mission as “…enabl[ing] our users to trade any asset globally with instant settlement by tokenizing assets and executing all essential trade processes on the blockchain.” Firmo’s only disclosed investment, according to data from Pitchbook, came in the form of a modest pre-seed round from the Copenhagen Fintech Lab accelerator.
Firmo’s mission aligns well with that of eToro — which is equal parts trading platform, social network and educational resource for beginner investors — with the company having long communicated hopes of making the capital markets more open, transparent and accessible to all users and across all assets. By gobbling up Firmo, eToro will be able to accelerate its development of offerings for tokenized assets.
The acquisition represents the latest step in eToro’s broader growth plan, which has ramped up as of late. Earlier in March, the company launched a crypto-only version of its platform in the US, as well as a multi-signature digital wallet where users can store, send and receive cryptocurrencies.
The Firmo deal and eToro’s other expansion activities fit squarely into the company’s belief in the tokenization of assets and the immense, sector-defining opportunity that it creates. Etoro believes that asset tokenization and the movement of financial services onto the blockchain are all but inevitable and the company has employed the long-tailed strategy of investing heavily in related blockchain and crypto technologies despite the ongoing crypto winter.
“Blockchain and the tokenization of assets will play a major role in the future of finance,” said eToro co-founder and CEO Yoni Assia. “We believe that in time all investible assets will be tokenized and that we will see the greatest transfer of wealth ever onto the blockchain.” Assia expressed a similar sentiment in a recent conversation with TechCrunch, stating “We think [the tokenization of assets] is a bigger opportunity than the internet…”
After the acquisition, Firmo will operate as an internal R&D arm within eToro focused on developing blockchain-oriented trade execution and the infrastructure behind the digital representation of tokenized assets.
“The Firmo team has done ground-breaking work in developing practical applications for blockchain technology which will facilitate friction-less global trading,” said Assia.
“The adoption of smart contracts on the blockchain increases trust and transparency in financial services. We are incredibly proud and excited that [Firmo] will be joining the eToro family. We believe that together we have a very bright future and look forward to pursuing our shared goal to become the first truly global service provider allowing people to trade, invest and save.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Infinity Augmented Reality, an Israeli startup, has been acquired by Alibaba, the companies announced this weekend. The deal’s terms were not disclosed. Alibaba and InfinityAR have had a strategic partnership since 2016, when Alibaba Group led InfinityAR’s Series C. Since then, the two have collaborated on augmented reality, computer vision and artificial intelligence projects.
Founded in 2013, the startup’s augmented glasses platform enables developers in a wide range of industries (retail, gaming, medical, etc.) to integrate AR into their apps. InfinityAR’s products include software for ODMs and OEMs and a SDK plug-in for 3D engines.
Alibaba’s foray into virtual reality started three years ago, when it invested in Magic Leap and then announced a new research lab in China to develop ways of incorporating virtual reality into its e-commerce platform.
InfinityAR’s research and development team will begin working out of Alibaba’s Israel Machine Laboratory, part of Alibaba DAMO Academy, the R&D initiative into which it is pouring $15 billion with the goal of eventually serving two billion customers and creating 100 million jobs by 2036. DAMO Academy collaborates with universities around the world, and Alibaba’s Israel Machine Laboratory has a partnership with Tel Aviv University focused on video analysis and machine learning.
In a press statement, the laboratory’s head, Lihi Zelnik-Manor, said “Alibaba is delighted to be working with InfinityAR as one team after three years of partnership. The talented team brings unique knowhow in sensor fusion, computer vision and navigation technologies. We look forward to exploring these leading technologies and offering additional benefits to customers, partners and developers.”
Powered by WPeMatico
One of the hottest Y Combinator startups just raised a big seed round to clean up the mess created by Uber, Postmates and the gig economy. Catch sells health insurance, retirement savings plans and tax withholding directly to freelancers, contractors, or anyone uncovered. By building and curating simplified benefits services, Catch can offer a safety net for the future of work.
“In order to stay competitive as a society, we need to address inequality and volatility. We think Catch is the first step to offering alternatives to the mandate that benefits can only come from an employer or the government,” writes Catch co-founder and COO Kristen Tyrrell. Her co-founder and CEO Andrew Ambrosino, a former Kleiner Perkins design fellow, stumbled onto the problem as he struggled to juggle all the paperwork and programs companies typically hire an HR manager to handle. “Setting up a benefits plan was a pain. You had to become an expert in the space, and even once you were, executing and getting the stuff you needed was pretty difficult.” Catch does all this annoying but essential work for you.
Now Catch is getting its first press after piloting its product with tens of thousands of users. TechCrunch caught wind of its highly competitive seed round closing, and Catch confirms it has raised $5.1 million at a $20.5 million post-money valuation co-led by Khosla Ventures, Kindred Ventures, and NYCA Partners. This follow-up to its $1 million pre-seed will fuel its expansion into full heath insurance enrollment, life insurance and more. Catch is part of a growing trend that sees the best Y Combinator startup fully funded before Demo Day even arrives.
“Benefits, as a system built and provided by employers, created the mid-century middle class. In the post-war economic boom, companies offering benefits in the form of health insurance and pensions enabled familial stability that led to expansive growth and prosperity,” recalls Tyrrell, who was formerly the director of product at student debt repayment benefits startup FutureFuel.io. “Emboldened by private-sector growth (and apparent self-sufficiency), the 1970s and 80s saw a massive shift in financial risk management from the government to employers. The public safety net contracted in favor of privatized solutions. As technological advances progressed, employers and employees continued to redefine what work looked like. The bureaucratic and inflexible benefits system was unable to keep up. The private safety net crumbled.”
That problem has ballooned in recent years with the advent of the on-demand economy, where millions become Uber drivers, Instacart shoppers, DoorDash deliverers and TaskRabbits. Meanwhile, the destigmatization of remote work and digital nomadism has turned more people into permanent freelancers and contractors, or full-time employees without benefits. “A new class of worker emerged: one with volatile, complex income streams and limited access to second-order financial products like automated savings, individual retirement plans, and independent health insurance. We entered the new millennium with rot under the surface of new opportunity from the proliferation of the internet,” Tyrrell declares. “The last 15 years are borrowed time for the unconventional proletariat. It is time to come to terms and design a safety net that is personal, portable, modern and flexible. That’s why we built Catch.”

Catch co-founders Andrew Ambrosino and Kristen Tyrrell
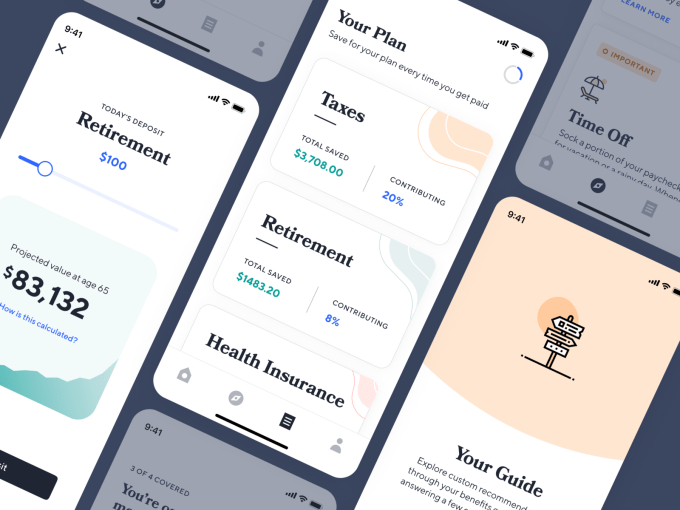
Currently Catch offers the following services, each with their own way of earning the startup revenue:
These and the rest of Catch’s services are curated through its Guide. You answer a few questions about which benefits you have and need, connect your bank account, choose which programs you want and get push notifications whenever Catch needs your decisions or approvals. It’s designed to minimize busy work so if you have a child, you can add them to all your programs with a click instead of slogging through reconfiguring them all one at a time. That simplicity has ignited explosive growth for Catch, with the balances it holds for tax withholding, time off and retirement balances up 300 percent in each of the last three months.
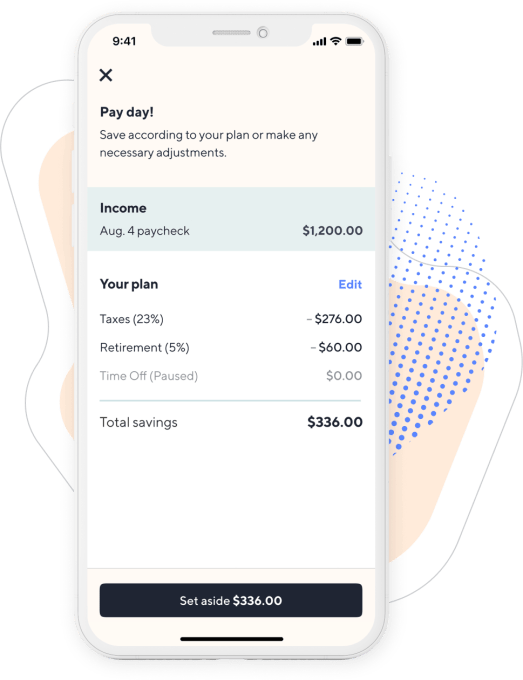 In 2019 it plans to add Catch-branded student loan refinancing, vision and dental enrollment plus payments via existing providers, life insurance through a partner such as Ladder or Ethos and full health insurance enrollment plus subsidies and premium payments via existing insurance companies like Blue Shield and Oscar. And in 2020 it’s hoping to build out its own blended retirement savings solution and income-smoothing tools.
In 2019 it plans to add Catch-branded student loan refinancing, vision and dental enrollment plus payments via existing providers, life insurance through a partner such as Ladder or Ethos and full health insurance enrollment plus subsidies and premium payments via existing insurance companies like Blue Shield and Oscar. And in 2020 it’s hoping to build out its own blended retirement savings solution and income-smoothing tools.
If any of this sounds boring, that’s kind of the point. Instead of sorting through this mind-numbing stuff unassisted, Catch holds your hand. Its benefits Guide is available on the web today and it’s beta testing iOS and Android apps that will launch soon. Catch is focused on direct-to-consumer sales because “We’ve seen too many startups waste time on channels/partnerships before they know people truly want their product and get lost along the way,” Tyrrell writes. Eventually it wants to set up integrations directly into where users get paid.
Catch’s biggest competition is people haphazardly managing benefits with Excel spreadsheets and a mishmash of healthcare.gov and solutions for specific programs. Twenty-one percent of Americans have saved $0 for retirement, which you could see as either a challenge to scaling Catch or a massive greenfield opportunity. Track.tax, one of its direct competitors, charges a subscription price that has driven users to Catch. And automated advisors like Betterment and Wealthfront accounts don’t work so well for gig workers with lots of income volatility.
So do the founders think the gig economy, with its suppression of benefits, helps or hinders our species? “We believe the story is complex, but overall, the existing state of the gig economy is hurting society. Without better systems to provide support for freelance/contract workers, we are making people more precarious and less likely to succeed financially.”
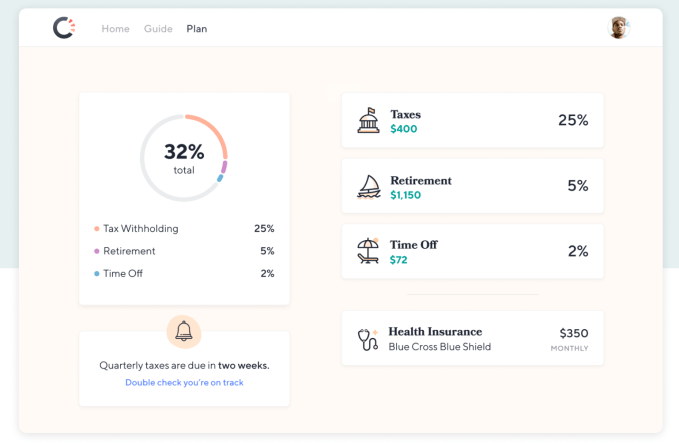
When I ask what keeps the founders up at night, Tyrrell admits “The safety net is not built for individuals. It’s built to be distributed through HR departments and employers. We are very worried that the products we offer aren’t on equal footing with group/company products.” For example, there’s a $6,000/year IRA limit for individuals while the corporate equivalent 401k limit is $19,000, and health insurance is much cheaper for groups than individuals.
To surmount those humps, Catch assembled a huge list of angel investors who’ve built a range of financial services, including NerdWallet founder Jake Gibson, Earnest founders Louis Beryl and Ben Hutchinson, ANDCO (acquired by Fiverr) founder Leif Abraham, Totem founder Neal Khosla, Commuter Club founder Petko Plachkov, Playable (acquired by Stripe) founder Tad Milbourn and Synapse founder Bruno Faviero. It also brought on a wide range of venture funds to open doors for it. Those include Urban Innovation Fund, Kleiner Perkins, Y Combinator, Tempo Ventures, Prehype, Loup Ventures, Indicator Ventures, Ground Up Ventures and Graduate Fund.
Hopefully the fact that there are three lead investors and so many more in the round won’t mean that none feel truly accountable to oversee the company. With 80 million Americans lacking employer-sponsored benefits and 27 million without health insurance and median job tenure down to 2.8 years for people ages 25 to 34 leading to more gaps between jobs, our workforce is vulnerable. Catch can’t operate like a traditional software startup with leniency for screw-ups. If it can move cautiously and fix things, it could earn labor’s trust and become a fundamental piece of the welfare stack.
Powered by WPeMatico

HoneyBook co-founders Oz and Naama Alon
HoneyBook, a customer-relationship management platform aimed at small businesses in creative fields, announced today it has raised a $28 million Series C led by Citi Ventures. All of its existing investors, including Norwest Venture Partners, Aleph, Vintage Investment Partners and Hillsven Capital, also returned for the round. Citi is a strategic partner for HoneyBook and this will enable it to offer new financial products to freelancers, its co-founder and CEO Oz Alon told TechCrunch.
This brings HoneyBook’s total raised so far to $72 million. It is using the funds to grow its teams in San Francisco and Tel Aviv and build new features for its user base, including small companies, people who work by themselves (“solopreneurs”) and freelancers. Like other CRMs, HoneyBook helps them develop relationships with potential new clients, manage projects, send invoices and accept payments, but with tools scaled for their business’ needs.
Alon told TechCrunch in an email that one segment HoneyBook is focused on is millennials (he cites a survey that found 49 percent of people under 40 plan to start their own business). HoneyBook currently claims tens of thousands of customers and has passed $1 billion in business booked using its software, along with 75,000 members in Rising Tide, the company’s online community for creative entrepreneurs.
Other management software platforms competing for the attention of entrepreneurs and freelancers include Tave, Dubsado and 17hats. One of the main ways HoneyBook differentiates is by enabling its users to accept online payments without integrating with a third-party service. Thanks to this, its users “transact more than 80 percent of their business online, significantly more than any other payments platform serving this audience, Alon said. Its partnership with Citi will also allow the company to develop more unique services for its target customers, he added.
In a prepared statement, Citi Ventures’ Israel director and venture investing lead Omit Shinar said, “We are in the midst of a period of extensive changes in societal structures and economic models. The fintech ecosystem is producing more and more breakthrough innovations that serve the needs of modern consumers, and we believe, as a pioneer in its space, HoneyBook can become a market leader in the U.S.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Cookie-cutter corporate housing turns people into worker drones. When an employee needs to move to a new city for a few months, they’re either stuck in bland, giant apartment complexes or Airbnbs meant for shorter stays. But Zeus lets any homeowner get paid to host white-collar transient labor. Through its managed ownership model, Zeus takes on all the furnishing, upkeep, and risk of filling the home while its landlords sit back earning cash.
Zeus has quietly risen to a $45 million revenue run rate from renting out 900 homes in 23 cities. That’s up 5X in a year thanks to Zeus’ 150 employees. With a 90 percent occupancy rate, it’s proven employers and their talent want more unique, trustworthy, well-equipped multi-month residences that actually make them feel at home.
Now while Airbnb is distracted with its upcoming IPO, Zeus has raised $24 million to steal the corporate housing market. That includes a previous $2.5 million seed round from Bowery, the new $11.5 million Series A led by Initialized Capital whose partner Garry Tan has joined Zeus’ board, and $10 million in debt to pay fixed costs like furniture. The plan is to roll up more homes, build better landlord portal software, and hammer out partnerships or in-house divisions for cleaning and furnishing.

“In the first decade out of school people used to have two jobs. Now it’s four jobs and it’s trending to five” says Zeus co-founder and CEO Kulveer Taggar. “We think in 10 years, these people won’t be buying furniture.” He imagines they’ll pay a premium for hand-holding in housing, which judging by the explosion in popularity of zero-friction on-demand services, seems like an accurate assessment of our lazy future. Meanwhile, Zeus aims to be “the quantum leap improvement in the experience of trying to rent out your home” where you just punch in your address plus some details and you’re cashing checks 10 days later.
“When I sold my first startup, I bought a home for my mom in Vancouver” Taggar recalls. It was payback for when she let him remortgage her old house while he was in college to buy a condo in Mumbai he’d rent out to earn money. “Despite not having much growing up, my mom was a travel agent and we got to travel a lot” which Taggar says inspired his goal to live nomadically in homes around the world. Zeus could let other live that dream.

Zeus co-founder and CEO Kulveer Taggar
After Oxford and working as an analyst at Deutsche Bank, Taggar built student marketplace Boso before moving to the United States. There, he co-founded auction tool Auctomatic with his cousin Harjeet Taggar and future Stripe co-founder Patrick Collison, went through Y Combinator, and sold it to Live Current Media for $5 million just 10 months later. That gave him the runway to gift a home to his mom and start tinkering on new ideas.
With Y Combinator’s backing again, Taggar started NFC-triggered task launcher Tagstand, which pivoted into app settings configurer Agent, which pivoted into automatic location sharing app Status. But when his co-founder Joe Wong had to move an hour south from San Francisco to Palo Alto, Taggar was dumbfounded by how distracting the process was. Listing and securing a new tenant was difficult, as was finding a medium-term rental without having to deal with exhorbitant prices or sketchy Cragislist. Having seen his former co-founder go on to great success with Stripe’s dead-simple payments integration, Taggar wanted to combine that vision with OpenDoor’s easy home sales to making renting or renting out a place instantaneous. That spawned Zeus.
To become a Zeus landlord, you just type in your address, how many bedrooms and bathrooms, and some aesthetic specs, and you get a monthly price quote for what you’ll be paid. Zeus comes in and does a 250-point quality assessment, collects floor plans, furnishes the property, and handles cleaning and maintenance. It works with partners like Helix mattresses, Parachute sheets, and Simple Human trash cans to get bulk rates. “We raised debt because we had these fixed investments into furniture. It’s not as dilutive as selling pure equity” Taggar explains.
Zeus quickly finds a tenant thanks to listings in Airbnb and relationships with employers like Darktrace and ZS Associates with lots of employees moving around. After passing background checks, tenants get digital lock codes and access to 24/7 support in case something doesn’t look right. The goal is to get someone sleeping there in just 10 days. “Traditional corporate housing is $10,000 a month in SF in the summer or at extended stay hotels. Airbnb isn’t well suited [for multi-month stays]. ” Taggar claims. “We’re about half the price of traditional corporate housing for a better product and a better experience.”

Zeus signs minimum two-year leases with landlords and tries to extend them to five years when possible. It gets one free month of rent as is standard for property managers, but doesn’t charge an additional rate. For example, Zeus might lease your home for $4,000 per month but gets the first month free, and rent it out for $5,000 so it earns $60,000 but pays you $44,000. That’s a tidy margin if Zeus can get homes filled fast and hold down its upkeep costs.
“Zeus has been instrumental for my company to start the process of re-location to the Bay Area and to host our visiting employees from abroad now that we are settled” writes Zeus client Meitre’s Luis Caviglia. “I particularly like the ‘hard truths’ featured in every property, and the support we have received when issues arose during our stays.”
There’s no shortage of competitors chasing this $18 billion market in the US alone. There are the old-school corporations and chains like Oakwood and Barbary Coast that typically rent out apartments from vast, generic complexes at steep rates. Stays over 30 days made up 15 percent of Airbnb’s business last year, but the platform wasn’t designed for peace-of-mind around long-term stays. There are pure marketplaces like UrbanDoor that don’t always take care of everything for the landlord or provide consistent tenant experiences. And then there are direct competitors like $130 million-funded Sonder, $66 million-funded Domio, recently GV-backed 2nd Address, and European entants like MagicStay, AtHomeHotel, and Homelike.
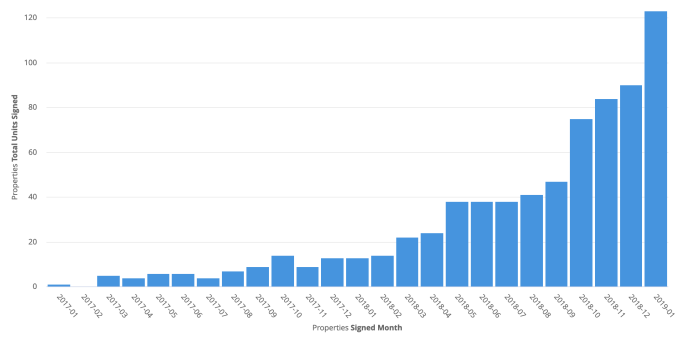
Zeus’ property unit growth
There’s plenty of pie, though. With 330,000 housing units in SF alone, Zeus has plenty of room to grow. The rise of remote work means companies whose employee typically didn’t relocate may now need to bring in distant workers for a multi-month sprint. A recession could make companies more expense-cautious, leading them to rethink putting up staffers in hotels for months on end. Regulatory red tape and taxes could scare landlords away from short-term rentals and towards coprorate housing. And the need to expand into new businesses could tempt the big vacation rental platforms like Airbnb to make acquisitions in the space — or try to crush Zeus.
Winners will be determined in part by who has the widest and cheapest selection of properties, but also by which makes people most comfortable in a new city. That’s why Taggar is taking a cue from WeWork by trying to arrange more community events for its tenants. Often in need of friends, Zeus could become a favorite by helping people feel part of a neighborhood rather than a faceless inmate in a massive apartment block or hotel. That gives Zeus network effect if it can develop density in top markets.

Taggar says the biggest challenge is that “I feels like I’m running five startups at once. Pricing, supply chain, customer service, B2B. We’ve decided to make everything custom — our own property manager software, our own internal CRM. We think these advantages compound, but I could be wrong and they could be wasted effort.”
The benefits of Zeus‘ success would go beyond the founder’s bank account. “I’ve had friends in New York get great opportuntiies in San Francisco but not take them because of the friction of moving” Taggar says. Routing talent where it belongs could get more things built. And easy housing might make people more apt to live abroad temporarily. Taggar concludes, “I think it’s a great way to build empathy.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Nested, the London-based “data-driven” estate agency that provides a cash advance to help you buy a new home before you’ve sold your old one, has laid off 20 percent of its workforce, TechCrunch has learned.
According to sources, the more than 15 staff being let go were informed earlier today. The majority of departures are within Nested’s operations team, including sales, although I understand they also include a number of engineers and other product people.
Contacted by TechCrunch, Nested co-founder Matt Robinson confirmed the departures, citing the uncertainty of Brexit, and the impact this is having on liquidity in the housing market. It is understood that the layoffs are designed to place Nested in a better financial position and enable it to continue weathering the Brexit storm, and ultimately position the company to reach profitability in the future.
Robinson provided the following statement:
We have come off a record year and quarter but with continued uncertainty around Brexit market volumes have fallen significantly. We will continue to grow share, however, given the external environment we must remain cautious as we build the business for the coming years.
Launched in late 2016, Nested competes with high-end estate agents by providing all of the services needed to sell your house, but with a key difference. In addition to handling valuation, marketing and sales, the startup will loan you between 90 and 95 percent of the market value of your property as a cash advance so you can purchase a new home prior to your old one selling.
Before Brexit and the uncertainty it has caused with regards to U.K. house prices, that figure was “up to 97 percent” of the market value of the property.
More broadly, the idea behind Nested is to eliminate much of the stress and uncertainty of selling and buying a home, including what your final budget will be, and also ensure that you’re never caught up in the dreaded property “chain” and miss out on your desired home. By becoming a cash buyer, it also puts you in a stronger position to negotiate your onward purchase.
Related to this, it is unknown to what extent the downward pressure on house prices in the U.K. has affected Nested’s market fit, or its ability to use data to accurately value the properties it lends cash against. However, the core value-add of not being stuck in a chain would seem to be just as useful in a downturn as it is in an overheated market.
Meanwhile, the downsizing of Nested comes just four months after the startup raised a further £120 million in funding, a combination of £20 million equity financing and £100 million in debt. The equity part of the round was led by Northzone and Balderton Capital, while the source of the debt financing, to be used primarily for the cash advances Nested provides to sellers, was not disclosed.
Previous backers in Nested include Rocket Internet’s Global Founders Capital, and London-based Passion Capital. The current listed directors are CEO Robinson, Rocket Internet’s Oliver Samwer, COO James Turford and Northzone’s Jeppe Heinrich Zink.
Separately — and unrelated to today’s layoffs — TechCrunch has learned that Phil Cowans, who co-founded Nested alongside CEO Robinson and COO Turford, stepped down as CTO of Nested in the last few weeks, although he remains at the company in a different role and as co-founder. He also resigned as a director of Nested on the 25th of February, according to a regulatory filing with the U.K.’s Companies House.
Powered by WPeMatico
Pan-African e-commerce company Jumia filed for an IPO on the New York Stock Exchange today, per SEC documents and confirmation from CEO Sacha Poignonnec to TechCrunch.
The valuation, share price and timeline for public stock sales will be determined over the coming weeks for the Nigeria-headquartered company.
With a smooth filing process, Jumia will become the first African tech startup to list on a major global exchange.
Poignonnec would not pinpoint a date for the actual IPO, but noted the minimum SEC timeline for beginning sales activities (such as road shows) is 15 days after submitting first documents. Lead adviser on the listing is Morgan Stanley .
There have been numerous press reports on an anticipated Jumia IPO, but none of them confirmed by Jumia execs or an actual SEC, S-1 filing until today.
Jumia’s move to go public comes as several notable consumer digital sales startups have faltered in Nigeria — Africa’s most populous nation, largest economy and unofficial bellwether for e-commerce startup development on the continent. Konga.com, an early Jumia competitor in the race to wire African online retail, was sold in a distressed acquisition in 2018.
With the imminent IPO capital, Jumia will double down on its current strategy and regional focus.
“You’ll see in the prospectus that last year Jumia had 4 million consumers in countries that cover the vast majority of Africa. We’re really focused on growing our existing business, leadership position, number of sellers and consumer adoption in those markets,” Poignonnec said.
The pending IPO creates another milestone for Jumia. The venture became the first African startup unicorn in 2016, achieving a $1 billion valuation after a $326 funding round that included Goldman Sachs, AXA and MTN.
Founded in Lagos in 2012 with Rocket Internet backing, Jumia now operates multiple online verticals in 14 African countries, spanning Ghana, Kenya, Ivory Coast, Morocco and Egypt. Goods and services lines include Jumia Food (an online takeout service), Jumia Flights (for travel bookings) and Jumia Deals (for classifieds). Jumia processed more than 13 million packages in 2018, according to company data.
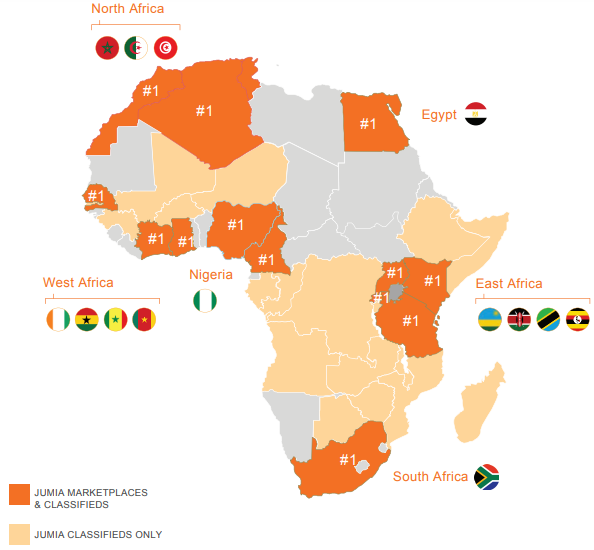 Starting in Nigeria, the company created many of the components for its digital sales operations. This includes its JumiaPay payment platform and a delivery service of trucks and motorbikes that have become ubiquitous with the Lagos landscape.
Starting in Nigeria, the company created many of the components for its digital sales operations. This includes its JumiaPay payment platform and a delivery service of trucks and motorbikes that have become ubiquitous with the Lagos landscape.
Jumia has also opened itself up to traders and SMEs by allowing local merchants to harness Jumia to sell online. “There are over 81,000 active sellers on our platform. There’s a dedicated sellers page where they can sign-up and have access to our payment and delivery network, data, and analytic services,” Jumia Nigeria CEO Juliet Anammah told TechCrunch.
The most popular goods on Jumia’s shopping mall site include smartphones (priced in the $80 to $100 range), washing machines, fashion items, women’s hair care products and 32-inch TVs, according to Anammah.
E-commerce ventures, particularly in Nigeria, have captured the attention of VC investors looking to tap into Africa’s growing consumer markets. McKinsey & Company projects consumer spending on the continent to reach $2.1 trillion by 2025, with African e-commerce accounting for up to 10 percent of retail sales.
Jumia has not yet turned a profit, but a snapshot of the company’s performance from shareholder Rocket Internet’s latest annual report shows an improving revenue profile. The company generated €93.8 million in revenues in 2017, up 11 percent from 2016, though its losses widened (with a negative EBITDA of €120 million). Rocket Internet is set to release full 2018 results (with updated Jumia figures) April 4, 2019.
Jumia’s move to list on the NYSE comes during an up and down period for B2C digital commerce in Nigeria. The distressed acquisition of Konga.com, backed by roughly $100 million in VC, created losses for investors, such as South African media, internet and investment company Naspers .
 In late 2018, Nigerian online sales platform DealDey shut down. And TechCrunch reported this week that consumer-focused venture Gloo.ng has dropped B2C e-commerce altogether to pivot to e-procurement. The CEO cited better unit economics from B2B sales.
In late 2018, Nigerian online sales platform DealDey shut down. And TechCrunch reported this week that consumer-focused venture Gloo.ng has dropped B2C e-commerce altogether to pivot to e-procurement. The CEO cited better unit economics from B2B sales.
As demonstrated in other global startup markets, consumer-focused online retail can be a game of capital attrition to outpace competitors and reach critical mass before turning a profit. With its unicorn status and pending windfall from an NYSE listing, Jumia could be better positioned than any venture to win on e-commerce at scale in Africa.
Powered by WPeMatico
Time is Ltd., a Prague-based startup offering “productivity software analytics” to help companies gain insights from employees’ use of Slack, Office 365, G Suite and other enterprise software, has raised €3 million in funding.
Leading the round is Mike Chalfen — who previously co-founded London venture capital firm Mosaic Ventures but has since decided to operate as a solo investor — with participation from Accel. The investment will be used by Time is Ltd. to continue building the platform for large enterprises that want to better understand the patterns of behaviour hidden inside the various cloud software on which they run.
“Time is Ltd. was founded… to help large corporations and companies get a view into insights and productivity of teams,” co-founder and CEO Jan Rezab tells me. “Visualising insights around calendars, time and communication will help companies to understand real data behind their productivity.”
Powered by machine learning, the productivity software analytics platform plugs into the cloud software tools that enterprises typically use to collaborate across various departments. It then analyses various metadata pulled from these software tools, such as who is communicating with whom and time spent on Slack, or which teams are meeting, where and for how long as per various calendars. The idea is to enable managers to gain a better understanding of where productivity is lost or could be improved and to tie to business goals changes in these patterns.
Rezab cites the example of a large company undergoing “agile” transformation. “If you want to steer a massive company of 5,000 plus people, you really should understand the impact of your actions a bit more much earlier, not after the fact,” he says. “One of the hypothesis of an agile transformation is, for example, that managers really get involved a bit less and things work a bit more streamlined. You see from our data that this is or is not happening, and you can take corrective action.”
Or it could be something as simple as a large company with multiple offices that is conducting too many meetings. Time is Ltd. is able to show how the number of meetings held is increasing and which departments or teams are instigating them. “You can also show the inter-departmental video meeting efficiency, and if the people, for example, often need to travel to these meetings, how long does that takes versus digital meetings — so you can generally help and recommend the company take specific actions,” explains Rezab.
Sales is another area that could benefit from productivity analytics, with Time is Ltd. revealing that most sales teams actually spend the majority of their meeting time inside the company, not outside as you would think. “The structure of these internal meetings varies; planning for these events or just on-boarding and education,” says the Time is Ltd. CEO. “You can, so to speak, follow the time from revenue to different teams… and then see over time how it changes, and how it impacts sales productivity.”
Meanwhile, investor Mike Chalfen describes the young startup as a new breed of data-driven services that use “significant but under-utilised datasets.” “Productivity is one of the largest software markets globally, but lacks deep enterprise analytics to drive intelligent operational management for large businesses,” he says in a statement.
That’s not to say Time is Ltd. isn’t without competition, which includes Microsoft itself. “Our biggest competitor is Microsoft Workplace Analytics,” says Rezab. “However, Microsoft does not integrate other than MS products. Our advantage is that we are a productivity platform to integrate all of the cloud tools. Starting with Slack, SAP Success Factors, Zoom and countless others.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Unmind, a U.K.-based startup that offers a mental health platform for the workplace, has raised £3 million in new funding. The round is led by London-based venture capital firm Felix Capital, with co-investment from Michael Whitfield and Chris Bruce, the founders of Thomsons Online Benefits.
Founded in 2016, Unmind is a B2B service that provides “clinically backed” tools, training and assessments for company employees in a bid to improve workplace mental health. The digital platform, delivered through the Unmind mobile app, includes bite-sized exercises for “everyday wellbeing,” personalised assessments, and customised programmes for improving areas such as stress, focus, and sleep.
“There is not enough support in society for people’s mental health, and this is especially true in the workplace,” explains co-founder and CEO Dr Nick Taylor, who is a Clinical Psychologist. “Everyone has mental health — and supporting it is integral to a successful workforce — but most provisions are highly reactive and heavily stigmatised, leading to low uptake amongst employees.”

To help remedy this, Unmind is designed to offer a “positive, preventative solution” that anyone can use to bolster their mental health. Designed to be anonymous, Taylor says employees can use the platform to proactively measure, manage and improve their mental health and well-being.
“The digital platform offers personalised assessments, bite-sized tools, online interventions and confidential signposting to other services,” he explains. “Employees can anonymously access Unmind at anytime, anywhere, on any device.”
To date, Unmind has partnered with organisations such as John Lewis & Partners, Made.com, Square Enix, William Hill, Yorkshire Building Society, Thomsons Online Benefits and Pentland Brands, to name just a few. “Unmind is now used in many countries around the world, which is an exciting place to be given the early stage of the company,” says Taylor. “We are focused on working with enterprise clients with 1,000 plus employees.”
Meanwhile, Unmind says the new investment will be used to improve the startup’s “consumer grade, mobile first product,” whilst increasing its library of proprietary content. The broader vision, says the company, is to help create a workplace environment where mental health is “universally understood, nurtured and celebrated.”
Powered by WPeMatico