Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
The Daily Crunch is TechCrunch’s roundup of our biggest and most important stories. If you’d like to get this delivered to your inbox every day at around 9am Pacific, you can subscribe here:
1. Nvidia launches the $349 GeForce RTX 2060
Nvidia broke with tradition and put a new focus on gaming at CES. Last night the company unveiled the RTX 2060, a $349 low-end version of its new Turing-based desktop graphics cards. The RTX 2060 will be available on Jan. 15.
2. Elon Musk’s vision of spaceflight is gorgeous
This spring SapceX intends to launch the next phase in its space exploration plans. The newly named Starship rocket, previously known as the BFR, intends to to be rocket to rule them all. And it’s going to look good doing it.
3. Apple’s increasingly tricky international trade-offs
Far from its troubles in emerging markets like China, Apple is starting to face backlash from a European population that’s crying foul over the company’s perceived hypocrisy on data privacy. It’s become clear that Apple’s biggest success is now its biggest challenge in Europe.

Photo by Justin Sullivan/Getty Images
4. Marc Andreessen: audio will be “titanically important” and VR will be “1,000” times bigger than AR
In a recently recorded podcast Marc Andreesen gave some predictions on the future of the tech industry. Surprisingly, the all-start investor is continuing his support of the shaky VR industry saying that expanding the immersive world will require us to remove the head-mounted displays we’ve become accustomed to.
5. Fitness marketplace ClassPass acquires competitor GuavaPass
ClassPass, the five-year-old fitness marketplace, is in the midst of an expansion sprint. The company announced yesterday that it’s acquiring one it competitors, GuavaPass, for an undisclosed amount to expand into Asia. The move now puts ClassPass in more than 80 markets across the 11 countries, with plans to expand to 50 new cities in 2019.
6. Apple shows off new smart home products from HomeKit partners
Apple gave a snapshot of its future smart home ecosystem at CES. Looks like an array of smart light switches, door cameras, electrical outlets and more are on the way and will be configurable through the Home app and Siri.
7. Parcel Guard’s smart mailbox protects your packages from porch thieves
Danby is showing off its newly launched smart mailbox called Parcel Guard at CES, which allows deliveries to be left securely at customers’ doorsteps. Turns out you won’t need a farting glitter bomb to protect your packages after all. The Parcel Guard starts at $399 and pre-orders are will be available this week.
Powered by WPeMatico
Gousto, the U.K. cook-at-home meal kit service that competes most directly with HelloFresh, has raised a further £18 million in funding. The round is backed by Instagram “health influencer” Joe Wicks, along with existing investors Unilever Ventures, Hargreave Hale, BGF Ventures, MMC Ventures, and Angel CoFund.
The new funding brings the total raised by Gousto to £75 million since being founded in 2012, and follows a £28.5 million fund raise last March, which it used to invest in its machine learning and factory automation.
The startup also recently launched a customer-facing AI recipe recommendation tool, through which half of customer orders are now placed. Gousto says it will continue to prioritize the majority of its investment in technology to accelerate growth.
In a call, Gousto founder and CEO Timo Boldt told me the startup is now delivering over 1.5 million meals a month to customers, and is seeing 170 percent year-on-year growth. However, he declined to break out specific customer numbers, monthly active or otherwise.
Noteworthy, Gousto says two-thirds of customers are families, and Boldt says this proves that a meal kit service that offers the right mixture of choice, personalization and, crucially, price point, can become a viable alternative to the weekly grocery shop for busy families.
The thinking behind meal kit services more generally is that because they send you correctly portioned fresh ingredients matched to each recipe, you save money by only buying what is needed.
Meanwhile, the services themselves have the potential to run a lot more efficiently than a national grocery store chain’s offline or online offering, including throwing significantly less food away.
To that end, Boldt says that Gousto offers more choice to customers than competitors and is further ahead in terms of driving factory and logistics efficiencies through the use of automation and data. The meal kit service offers over 30 weekly recipes and delivers 7 days per a week. It also claims the shortest lead time of 3 days, and the lowest price point, starting at £2.98 per meal.
The investment in Gousto by “body coach” Joe Wicks is also worth noting, as the startup places more emphasis on healthy eating. The pair had already announced they are working together and this month will launch a co-branded range of nutritious meal kits. This will see a minimum of four new Wicks-branded recipes offered per week, including Joe’s Veggie Spag Bol’ and Satay Chicken Lettuce Wraps, along with Herby Crusted Fish, Root Veg Chips & Peas, and 10-Min Nifty Veggie Noodles.
Cue statement from Wicks: “It was clear from when I first approached Gousto that they were a purpose driven business, with a passion for getting more people cooking and in turn improving the health of the nation. As a customer before becoming an investor, I know that Gousto is having a lasting and hugely positive impact on the way families consume and eat food. I’m delighted to join forces and offer my knowledge to a company who has brought huge and much-needed innovation to an industry”.
Powered by WPeMatico
There’s been plenty of fanfare surrounding Uber and Lyft’s initial public offerings — slated for early 2019 — since the two companies filed confidential IPO paperwork with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission in early December. On top of that, public and private investors have had plenty to say about Slack and Pinterest’s rumored 2019 IPOs but those aren’t the only “unicorn” exits we should expect to witness in the year ahead.
Using its proprietary company rating algorithm, data provider CB Insights ranked five billion dollar companies most likely to perform IPOs next year in its latest tech IPO report. The algorithm analyzes non-traditional public signals, including hiring activity, web traffic and mobile app data to make its predictions. These are the startups that topped their list.

Peloton Co-Founder and CEO John Foley speaks onstage during TechCrunch Disrupt SF 2018 on September 6, 2018 in San Francisco, California. (Photo by Kimberly White/Getty Images for TechCrunch).
Peloton, dubbed the “Netflix of fitness,” has raised nearly $1 billion in venture capital funding in the six years since it was founded by John Foley, most recently raising $550 million at a $4 billion valuation. The manufacturer of tech-enabled exercise equipment is more than doubling in size every year and is “weirdly profitable,” an unusual characteristic for a venture-backed business of its age. Headquartered in New York, Peloton doesn’t have any public IPO plans, though Foley recently told The Wall Street Journal that 2019 “makes a lot of sense” for its stock market debut.
Select investors: L Catterton, True Ventures, Tiger Global

Cloudflare co-founder and CEO Matthew Prince appears on stage at the 2014 TechCrunch Disrupt Europe/London. (Photo by Anthony Harvey/Getty Images for TechCrunch)
Cybersecurity unicorn Cloudflare is likely to transition to the public markets in the first half of 2019 in what is poised to be a strong year for IPOs in the security industry. The web performance and security platform is said to be preparing for an IPO at a potential valuation of more than $3.5 billion after last raising capital in 2015 at a $1.8 billion valuation. Since it was founded in 2009, the San Francisco-based company has raised just north of $250 million in VC funding. CrowdStrike, another security unicorn, is also on track to go public next year and it wouldn’t be surprising to see Illumio and Lookout make the jump to the public markets as well.
Select investors: Pelion Venture Partners, NEA, Venrock

San Jose-based Zoom Video Communications has reportedly tapped Morgan Stanley to lead its upcoming IPO.
Zoom, a provider of video conferencing services, online meeting and group messaging tools that’s raised $160 million in VC cash to date, is eyeing a multi-billion IPO in 2019 and has reportedly hired Morgan Stanley to lead the offering. Founded in 2011, the company most recently brought in a $100 million Series D financing, entirely funded by Sequoia, at a $1 billion valuation in early 2017. Based in San Jose, Zoom is hoping to garner a valuation significantly larger than $1 billion when it IPOs, according to Reuters.
Select investors: Sequoia, Emergence Capital Partners, Horizons Ventures

Data management company Rubrik co-founder and CEO Bipul Sinha.
Data management company Rubrik has quietly made moves indicative of an impending IPO. The startup, which provides data backup and recovery services for businesses across cloud and on-premises environments, hired former Atlassian chief financial officer Murray Demo as its CFO earlier this year, as well as its first chief legal officer, Peter McGoff. Palo Alto-based Rubrik was valued at over of $1 billion with a $180 million funding round in 2017. The company has raised nearly $300 million to date.
Select investors: Lightspeed Venture Partners, Greylock, Khosla Ventures
Medallia, a customer experience management platform that’s nearly two decades old, may finally become a public company in 2019. The San Mateo-based company, which has been rumored to be planning an IPO for several years, hired a new CEO this year and reported $250 million in GAAP revenue for the year ending Jan. 31, 2018, according to Forbes. Medallia hasn’t raised capital since 2015, when it secured a $150 million funding deal at a $1.2 billion valuation. It has raised a total of just over $250 million.
Select investor: Sequoia
Powered by WPeMatico
A Juul is not a cigarette. It’s much easier than that. Through devilishly slick product design I’ll discuss here, the startup has massively lowered the barrier to getting hooked on nicotine. Juul has dismantled every deterrent to taking a puff.
The result is both a new $38 billion valuation thanks to a $12.8 billion investment from Marlboro Cigarettes-maker Altria this week, and an explosion in popularity of vaping amongst teenagers and the rest of the population. Game recognize game, and Altria’s game is nicotine addiction. It knows it’s been one-upped by Juul’s tactics, so it’s hedged its own success by handing the startup over a tenth of the public corporation’s market cap in cash.
Juul argues it can help people switch from obviously dangerous smoking to supposedly healthier vaping. But in reality, the tiny aluminum device helps people switch from nothing to vaping…which can lead some to start smoking the real thing. A study found it causes more people to pick up cigarettes than put them down.

Photographer: Gabby Jones/Bloomberg via Getty Images
How fast has Juul swept the nation? Nielsen says it controls 75 percent of the U.S. e-cigarette market up from 27 percent in September last year. In the year since then, the CDC says the percentage of high school students who’ve used an e-cigarette in the last 30 days has grown 75 percent. That’s 3 million teens or roughly 20 percent of all high school kids. CNBC reports that Juul 2018 revenue could be around $1.5 billion.
The health consequences aside, Juul makes it radically simple to pick up a lifelong vice. Parents, regulators, and potential vapers need to understand why Juul works so well if they’ll have any hope of suppressing its temptations.
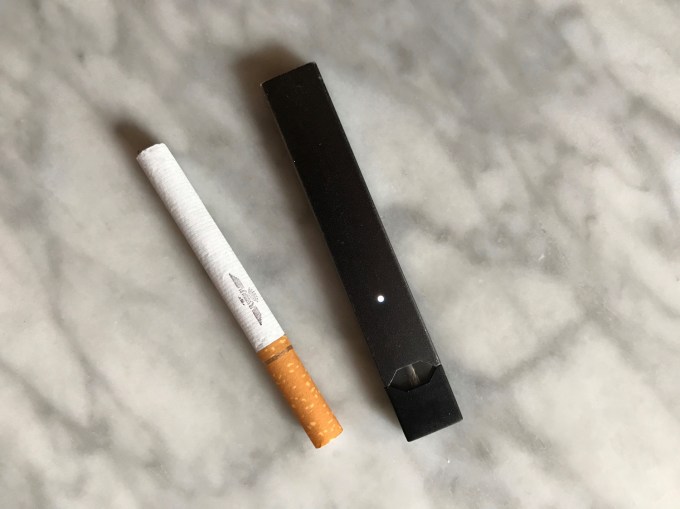
It’s tough to try a cigarette for the first time. The heat and smoke burn your throat. The taste is harsh and overwhelming. The smell coats your fingers and clothes, marking you as smoker. There’s pressure to smoke a whole one lest you waste the tobacco. Even if you want to try a friend’s, they have to ignite one first. And unlike bigger box mod vaporizers where you customize the temperature and e-juice, Juul doesn’t make you look like some dorky hardcore vapelord.
Juul is much more gentle on your throat. The taste is more mild and can be masked with flavors. The vapor doesn’t stain you with a smell as quickly. You can try just a single puff from a friend’s at a bar or during a smoking break with no pressure to inhale more. The elegant, discrete form factor doesn’t brand you as a serious vape users. It’s casual. Yet the public gesture and clouds people exhale are still eye catching enough to trigger the questions, “What’s that? Can I try?” There’s a whole other article to be written about how Juul memes and Instagram Stories that glamorized the nicotine dispensers contributed to the device’s spread.
And perhaps most insidiously, vaping seems healthier. A lifetime of anti-smoking ads and warning labels drilled the dangers into our heads. But how much harm could a little vapor do?
A friend who had never smoked tells me they burn through a full Juul pod per day now. Someone got him to try a single puff at a nightclub. Soon he was asking for drag off of strangers’ Juuls. Then he bought one and never looked back. He’d been around cigarettes at parties his whole life but never got into them. Juul made it too effortless to resist.
Lighting up a cigarette is a garish activity prohibited in many places. Not so with discretely sipping from a Juul.
Cigarettes often aren’t allowed to be smoked inside. Hiding it is no easy feat and can get you kicked out. You need to have a lighter and play with fire to get one started. They can get crushed or damp in your pocket. The burning tip makes them unruly in tight quarters, and the bud or falling ash can damage clothing and make a mess. You smoke a cigarette because you really want to smoke a cigarette.
Public establishments are still figuring out how to handle Juuls and other vaporizers. Many places that ban smoking don’t explicitly do the same for vaping. The less stinky vapor and more discrete motion makes it easy to hide. Beyond airplanes, you could probably play dumb and say you didn’t know the rules if you did get caught. The metal stick is hard to break. You won’t singe anyone. There’s no mess, need for an ashtray, or holes in your jackets or couches.

As long as your battery is charged, there’s no need for extra equipment and you won’t draw attention like with a lighter. Battery life is a major concern for heavy Juulers that smokers don’t have worry about, but I know people who now carry a giant portable charger just to keep their Juul alive. But there’s also a network effect that’s developing. Similar to iPhone cords, Juuls are becoming common enough that you can often conveniently borrow a battery stick or charger from another user.
And again, the modular ability to take as few or as many puffs as you want lets you absent-mindedly Juul at any moment. At your desk, on the dance floor, as you drive, or even in bed. A friend’s nieces and nephews say that they see fellow teens Juul in class by concealing it in the cuff of their sleeve. No kid would be so brazen as to try smoke in cigarette in the middle of a math lesson.
Gillette pioneered the brilliant razor and blade business model. Buy the sometimes-discounted razor, and you’re compelled to keep buying the expensive proprietary blades. Dollar Shave Club leveled up the strategy by offering a subscription that delivers the consumable blades to your door. Juul combines both with a product that’s physically addictive.
When you finish a pack of cigarettes, you could be done smoking. There’s nothing left. But with Juul you’ve still got the $35 battery pack when you finish vaping a pod. There’s a sunk cost fallacy goading you to keep buying the pods to get the most out of your investment and stay locked into the Juul ecosystem.

(Photo by Scott Olson/Getty Images)
One of Juul’s sole virality disadvantages compared to cigarettes is that they’re not as ubiquitously available. Some stores that sells cigs just don’t carry them yet. But more and more shops are picking them up, which will continue with Altria’s help. And Juul offers an “auto-ship” delivery option that knocks $2 off the $16 pack of four pods so you don’t even have to think about buying more. Catch the urge to quit? Well you’ve got pods on the way so you might as well use them. Whether due to regulation or a lack of innovation, I couldn’t find subscription delivery options for traditional cigarettes.
And for minors that want to buy Juuls or Juul pods illegally, their tiny size makes them easy to smuggle and resell. A recent South Park episode featured warring syndicates of fourth-graders selling Juul pods to even younger kids.
Juul co-founder James Monsees told the San Jose Mercury News that “The first phase is proving the value and creating a product that makes cigarettes obsolete.” But notice he didn’t say Juul wants to make nicotine obsolete or reduce the number of people addicted to it.

Juul co-founder James Monsees
If Juul actually cared about fighting addiction, it’d offer a regimen for weaning yourself off of nicotine. Yet it doesn’t sell low-dose or no-dose pods that could help people quit entirely. In the US it only sells 5% and 3% nicotine versions. It does make 1.7% pods for foreign markets like Israel where that’s the maximum legal strengths, though refuses to sell them in the States. Along with taking over $12 billion from one of the largest cigarette companies, that makes the mission statement ring hollow.
Juul is the death stick business as usual, but strengthened by the product design and virality typically reserved for Apple and Facebook.
Powered by WPeMatico
Social game developer Zynga has entered into an agreement to acquire Small Giant Games, the startup behind the popular mobile game Empires & Puzzles, in a deal expected to total $700 million.
Zynga, which has tumbled since its 2011 Nasdaq initial public offering, will initially acquire 80 percent of Small Giant Games for $560 million, composed of $330 million in cash and $230 million of unregistered Zynga common stock. Zynga will fund part of the transaction with a $200 million credit facility.
“We’ve been impressed by the quality and momentum of Empires & Puzzles as we add another Forever Franchise into Zynga’s portfolio,” Zynga chief executive officer Frank Gibeau said in a statement. “Small Giant has created an innovative game that delivers a unique player experience that engages over the long term.”
The deal is expected to close on January 1. Zynga will purchase the remaining 20 percent of Small Giant over the next three years “at valuations based on specified profitability goals.”
Helsinki-based Small Giant Games had raised $52 million in equity funding from EQT Ventures, Creandum, Spintop Ventures, Profounders and others since it was founded in 2013. The company reported $33 million of revenue for Empires & Puzzles, its most popular game, 10 months after its launch in 2017. Small Giant, which is also behind Alliance Wars and Season 2: Atlantis, says they exceeded 2017’s revenue just four months into 2018.
“Our studio was founded on the idea that small, skillful teams can accomplish giant things, and I am confident that partnering with Zynga is the right next step in our evolution,” Small Giant CEO Timo Soininen said in a statement. “We will now operate as a separate studio within Zynga, maintaining our identity, culture and creative independence. By leveraging the expertise and support from the wider Zynga team, we will amplify the reach of Empires & Puzzles and the new games in our development pipeline.”
Zynga, founded in 2007, is the developer of FarmVille, Zynga
Zynga expects to bring in $243 million in revenue in the fourth quarter of 2018.
Powered by WPeMatico
Gamelearn, which develops video games to deliver corporate training, has scored $5 million in Series A funding. Participating in the new financing round is previous backer Kibo Ventures, along with Oak3Capital, All Iron Ventures, UL Invest, and Inveready.
The Madrid-based startup says that it will use the new capital to boost the company’s production of “serious games” and reinforce its international presence. It currently has customer a base of 2,000 clients, spanning 50 countries. Those clients include LG, Thyssen Krupp, UPS, Hyundai, P&G, KPMG, Tetrapak, and Merck&Co.
Founded in 2007, Gamelearn is attempting to shake up the corporate training industry via its in-house developed game-based learning solutions and gamification for corporations. Its video games and simulators are designed to “train, communicate, inform, raise awareness and engage” employees. The company’s founders are Ibrahim Jabary, Mai Apraiz and Eduardo Monfort, each of whom has experience in corporate training.
Their take is that the startup’s bespoke video games and simulators can be used to meet a plethora of corporate needs, such as internal communication, digital transformation, management of change, leadership training, negotiation, time management, customer service, product training, project management or compliance.
“Corporate training is boring and non-engaging,” Gamelearn co-founder Mai Apraiz tells me. “Only 30 percent of e-learning courses are completed, meaning 3 out of 4 dollars invested in e-learning are wasted by corporations around the world. We create fun and engaging training experiences that allow our clients to achieve a 93 percent completion rate”.
Apraiz says these experiences are delivered through high-quality content, gamification, and simulation in a single product, which, she claims, no other company does. “The quality of our games is the best in the market. You can compare our products by checking our competitors’ websites against our own. That’s why we are the most awarded game-based learning company in the world”.
Proof that European tech companies are increasingly thinking globally, including pan-European, Gamelearn not only sells its products internationally, but offers “Customer Success” support in 4 different languages, and the startup’s games are translated into a dozen different languages.
On Gamelearn’s business model, Apraiz says the company sells licenses to play its games on the Gamelearn platform or on other commercial Learning Management Systems that it integrates with. “We sell projects as well as subscriptions,” she adds.
Powered by WPeMatico
M&A activity was brisk in the enterprise market this year, with 10 high-profile deals totaling almost $88 billion. Companies were opening up their wallets and pouring money into mega acquisitions. It’s worth noting that the $88 billion figure doesn’t include Dell paying investors more than $23 billion for VMware tracking stock to take the company public again or several other deals of over a billion dollars that didn’t make our list.
Last year’s big deals included Intel buying MobileEye for $15 billion and Cisco getting AppDynamics for $3.7 billion, but there were not as many big ones. Adobe, which made two large acquisitions this year, was mostly quiet last year, only making a minor purchase. Salesforce too was mostly quiet in 2017, only buying a digital creative agency, after an active 2016. SAP also made only one purchase in 2017, paying $350 million for Gigya. Microsoft was active buying nine companies, but these were primarily minor. Perhaps everyone was saving their pennies for 2018.
This year, by contrast, was go big or go home, and we saw action across the board from the usual suspects. Large companies looking to change their fortunes or grow their markets went shopping and came home with some expensive trinkets for their collections. Some of the deals are still waiting to pass regulatory hurdles and won’t be closing until 2019. Regardless, it’s too soon to judge whether these big-bucks ventures will pay the dividends that their buyers hope, or if they end up being M&A dust in the wind.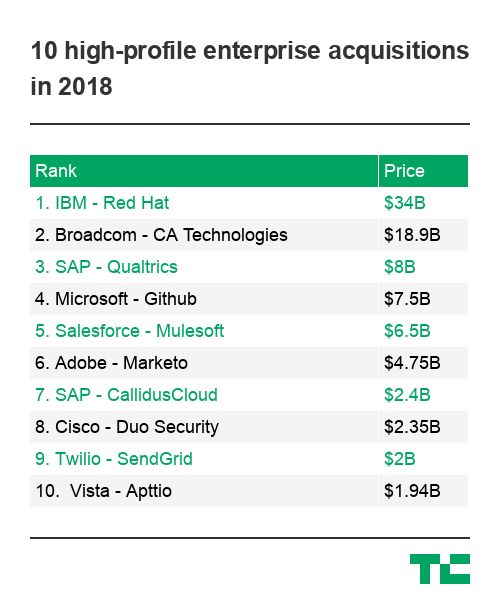
By far the biggest and splashiest deal of the year goes to IBM, which bet the farm to acquire Red Hat for a staggering $34 billion. IBM sees this acquisition as a way to build out its hybrid cloud business. It’s a huge bet and one that could determine the success of Big Blue as an organization in the coming years.
This deal was unexpected, as Broadcom, a chip maker, spent the second largest amount of money in a year of big spending. What Broadcom got for its many billions was an old-school IT management and software solutions provider. Perhaps Broadcom felt it needed to branch out beyond pure chip making, and CA offered a way to do it, albeit a rather expensive one.
While not anywhere close to the money IBM or Broadcom spent, SAP went out and nabbed Qualtrics last month just before the company was about to IPO, still paying a healthy $8 billion. The company believes that the new company could help build a bridge between SAP operational data inside its back-end ERP systems and Qualtrics customer data on the front end. Time will tell if they are right.
In June, Microsoft swooped in and bought GitHub, giving it a key developer code repository. It was a lot of money to pay, and Diane Greene expressed regret that Google hadn’t been able to get it. That’s because cloud companies are working hard to win developer hearts and minds. Microsoft has a chance to push GitHub users toward its products, but it has to tread carefully because they will balk if Microsoft goes too far.
Salesforce wasn’t about to be left out of the party in 2018 and in March, the CRM giant announced it was buying API integration vendor Mulesoft for a cool $6.5 billion. It was a big deal for Salesforce, which tends to be acquisitive, but typically on smaller deals. This one was a key purchase though because it gives the company the ability to access data wherever it lives, on premises or in the cloud, and that could be key for them moving forward.
Adobe has built a strong company primarily on the strength of its Creative Cloud, but it has been trying to generate more revenue on the marketing side of the business. To that end, it acquired Marketo for $4.75 billion and immediately boosted its marketing business, especially when combined with the $1.68 billion Magento purchase earlier in the year.
SAP doesn’t do as many acquisitions as some of its fellow large tech companies mentioned here, but this year it did two. Not only did it buy Qualtrics for $8 billion, it also grabbed CallidusCloud for $2.4 billion. SAP is best known for managing back-office components with its ERP software, but this adds a cloud-based, front-office sales process piece to the mix.
Cisco has been hard at work buying up a variety of software services over the years, and this year it added to its security portfolio when it acquired Duo Security for $2.35 billion. The Michigan-based company helps companies secure applications using their own mobile devices and could be a key part of the Cisco security strategy moving forward.
Twilio got into the act this year too. While not in the same league as the other large tech companies on this list, it saw a piece it felt would enhance its product set and it was willing to spend big to get it. Twilio, which made its name as a communications API company, saw a kindred spirit in SendGrid, spending $2 billion to get the API-based email service.
Vista Equity Partners is the only private equity firm on the list, but it’s one with an appetite for enterprise technology. With Apttio, it gets a company that can help companies understand their cloud assets alongside their on-prem ones. The company had been public before Vista bought it for $1.94 billion last month.
Powered by WPeMatico
PetaGene, the Cambridge, U.K.-based genomics data compression startup, has raised $2.1 million in further funding. Leading the round is U.S. venture firm Romulus Capital, with participation from other unnamed investors Silicon Valley and London. It brings total funding to $3.2 million.
Previous investor Entrepreneur First, the company builder backed by Greylock Partners, also followed on. PetaGene is an alumnus of EF6, although notably its two founders Dan Greenfield and Vaughan Wittorff already knew each other from their time at the Computer Laboratory in Cambridge University. Both hold PhDs from Cambridge University, too.
The new funding will be used by the company to grow its technical team based in Cambridge, its global sales team, and further expand PetaGene’s product offerings. I’m also told the new funding comes off the back of signing a large contract with a major undisclosed pharmaceutical company.
“As whole genome sequencing becomes more and more commonplace, the amount of data it creates places great strain on infrastructure. We help organisations with managing that data,” says PetaGene co-founder Dan Greenfield. “Through our compression technology, we make that data up to ten times smaller and faster to transfer for research and analysis, democratising precision medicine in the process”.
As it stands, the storage and processing of genomics data adds a significant extra cost and acts as a bottleneck for how fast data can be worked with. By some estimates genomics data will reach 40 exabytes per year by 2025 (exabytes, by the way, is a lot of data!). Therefore, better file compression technology has the potential to be a major enabler of innovation and research based on genomics, including developing new personalised medicine and treatments.
Key to this, PetaGene says its software enables compression of huge amounts of genomic data without compromising on access and data quality. The company claims its products go beyond regular data reduction techniques.
“We have dedicated extensive R&D to building extremely high performance compressors for genomic data, the result being that we outperform existing state-of-the-art compression, sometimes by a factor of 6x or more,” explains Greenfield.
“At the same time our customers want to be assured that the original file can be exactly recovered. Other compression solutions unfortunately aren’t able to restore the original file, and can even sometimes discard or modify internal content without telling their users. We’ve spent a great deal of effort to make sure we preserve the original file bit-for-bit, even providing commercial guarantees to our customers. I can’t really go into the details of our secret sauce here, but we’re very proud of our industry-leading performance, and we continue to keep improving it”.
Krishna K. Gupta, founder and general partner of Romulus Capital, says he was impressed by the part of the genomics value chain PetaGene is targeting, which led the firm to first invest in 2017. “Since then, their ability to successfully develop their product for the cloud and the strong interest from potential customers have only served to reinforce our view,” he says.
Meanwhile, PetaGene’s target customers span pharmaceutical companies, academic research institutions, clinical labs in hospitals, and genomic sequencing companies.
“Our clients pay for our software according to the savings they make,” adds the PetaGene co-founder. “The greater the reduction in size of their data files, the more revenue we receive, and the more they are saving in storage and data transfer costs. We don’t charge our clients for accessing or decompressing the compressed data”.
Powered by WPeMatico
Dataiku wants to turn buzzwords into an actual service. The company has been focused on data tools for many years, before everybody started talking about big data, data science and machine learning.
And the company just raised $101 million in a round led by Iconiq Capital, with Alven Capital, Battery Ventures, Dawn Capital and FirstMark Capital also participating.
If you’re generating a lot of data, Dataiku helps you find a meaning behind data sets. First, you import your data by connecting Dataiku to your storage system. The platform supports dozens of database formats and sources — Hadoop, NoSQL, images, you name it.
You can then use Dataiku to visualize your data, clean your data set, run some algorithms on your data in order to build a machine learning model, deploy it and more. Dataiku has a visual coding tool, or you can use your own code.
But Dataiku isn’t just a tool for data scientists. Even if you’re a business analyst, you can visualize and extract data from Dataiku directly. And because of its software-as-a-service approach, your entire team of data scientists and data analysts can collaborate on Dataiku.
Clients use it to track churn, detect fraud, forecast demand, optimize lifetime values and more. Customers include General Electric, Sephora, Unilever, KUKA, FOX and BNP Paribas.
With today’s funding round, the company plans to double its staff. The company currently works with 200 people in New York, Paris and London. It plans to open offices in Singapore and Sydney, as well.
Powered by WPeMatico
Our distinct skill sets and shortcomings mean people and robots will join forces for the next few decades. Robots are tireless, efficient and reliable, but in a millisecond through intuition and situational awareness, humans can make decisions machine can’t. Until workplace robots are truly autonomous and don’t require any human thinking, we’ll need software to supervise them at scale. Formant comes out of stealth today to “help people speak robot,” says co-founder and CEO Jeff Linnell. “What’s really going to move the needle in the innovation economy is using humans as an empowering element in automation.”
Linnell learned the grace of uniting flesh and steel while working on the movie Gravity. “We put cameras and Sandra Bullock on dollies,” he bluntly recalls. Artistic vision and robotic precision combined to create gorgeous zero-gravity scenes that made audiences feel weightless. Google bought his startup Bot & Dolly, and Linnell spent four years there as a director of robotics while forming his thesis.
Now with Formant, he wants to make hybrid workforce cooperation feel frictionless.
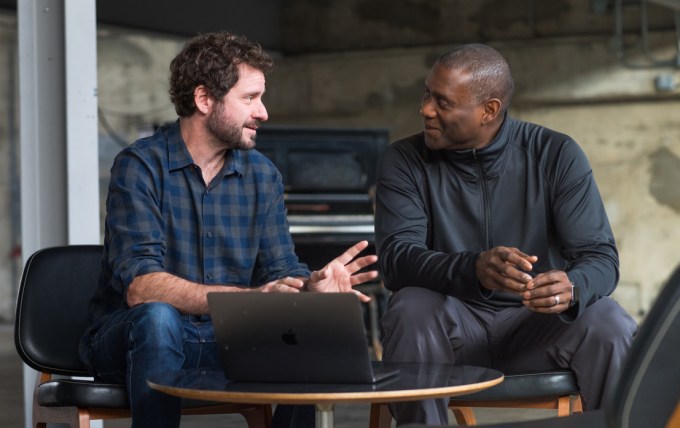

The company has raised a $6 million seed round from SignalFire, a data-driven VC fund with software for recruiting engineers. Formant is launching its closed beta that equips businesses with cloud infrastructure for collecting, making sense of and acting on data from fleets of robots. It allows a single human to oversee 10, 20 or 100 machines, stepping in to clear confusion when they aren’t sure what to do.
“The tooling is 10 years behind the web,” Linnell explains. “If you build a data company today, you’ll use AWS or Google Cloud, but that simply doesn’t exist for robotics. We’re building that layer.”
“This is going to sound completely bizarre,” Formant CTO Anthony Jules warns me. “I had a recurring dream [as a child] in which I was a ship captain and I had a little mechanical parrot on my should that would look at situations and help me decide what to do as we’d sail the seas trying to avoid this octopus. Since then I knew that building intelligent machines is what I would do in this world.”
So he went to MIT, left a robotics PhD program to build a startup called Sapient Corporation that he built into a 4,000-employee public company, and worked on the Tony Hawk video games. He too joined Google through an acquisition, meeting Linnell after Redwood Robotics, where he was COO, got acquired. “We came up with some similar beliefs. There are a few places where full autonomy will actually work, but it’s really about creating a beautiful marriage of what machines are good at and what humans are good at,” Jules tells me.
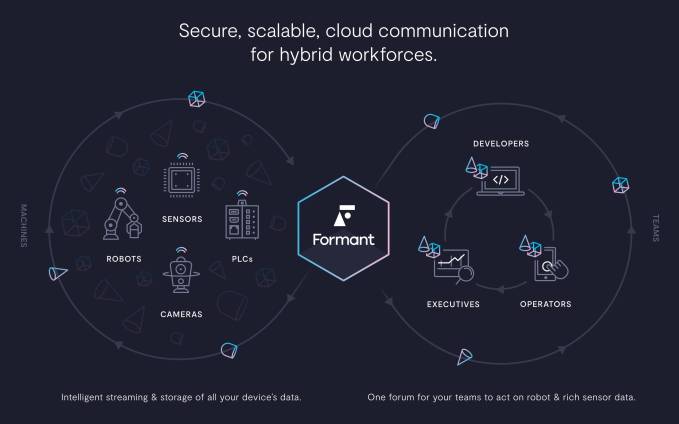
Formant now has SaaS pilots running with businesses in several verticals to make their “robot-shaped data” usable. They range from food manufacturing to heavy infrastructure inspection to construction, and even training animals. Linnell also foresees retail increasingly employing fleets of robots not just in the warehouse but on the showroom floor, and they’ll require precise coordination.
What’s different about Formant is it doesn’t build the bots. Instead, it builds the reins for people to deftly control them.
First, Formant connects to sensors to fill up a cloud with LiDAR, depth imagery, video, photos, log files, metrics, motor torques and scalar values. The software parses that data and when something goes wrong or the system isn’t sure how to move forward, Formant alerts the human “foreman” that they need to intervene. It can monitor the fleet, sniff out the source of errors, and suggest options for what to do next.
For example, “when an autonomous digger encounters an obstacle in the foundation of a construction site, an operator is necessary to evaluate whether it is safe for the robot to proceed or stop,” Linnell writes. “This decision is made in tandem: the rich data gathered by the robot is easily interpreted by a human but difficult or legally questionable for a machine. This choice still depends on the value judgment of the human, and will change depending on if the obstacle is a gas main, a boulder, or an electrical wire.”
Any single data stream alone can’t reveal the mysteries that arise, and people would struggle to juggle the different feeds in their minds. But not only can Formant align the data for humans to act on, it also can turn their choices into valuable training data for artificial intelligence. Formant learns, so next time the machine won’t need assistance.
With rock-star talent poached from Google and tides lifting all automated boats, Formant’s biggest threat is competition from tech giants. Old engineering companies like SAP could try to adapt to the new real-time data type, yet Formant hopes to out-code them. Google itself has built reliable cloud scaffolding and has robotics experience from Boston Dynamics, plus buying Linnell’s and Jules’ companies. But the enterprise customization necessary to connect with different clients isn’t typical for the search juggernaut.
 Linnell fears that companies that try to build their own robot management software could get hacked. “I worry about people who do homegrown solutions or don’t have the experience we have from being at a place like Google. Putting robots online in an insecure way is a pretty bad problem.” Formant is looking to squash any bugs before it opens its platform to customers in 2019.
Linnell fears that companies that try to build their own robot management software could get hacked. “I worry about people who do homegrown solutions or don’t have the experience we have from being at a place like Google. Putting robots online in an insecure way is a pretty bad problem.” Formant is looking to squash any bugs before it opens its platform to customers in 2019.
With time, humans will become less and less necessary, and that will surface enormous societal challenges for employment and welfare. “It’s in some ways a continuation of the industrial revolution,” Jules opines. “We take some of this for granted but it’s been happening for 100 years. Photographer — that’s a profession that doesn’t exist without the machine that they use. We think that transformation will continue to happen across the workforce.”
Powered by WPeMatico