Fundings & Exits
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Berlin-based Mobius Labs has closed a €5.2 million (~$6.1M) funding round off the back of increased demand for its computer vision training platform. The Series A investment is led by Ventech VC, along with Atlantic Labs, APEX Ventures, Space Capital, Lunar Ventures plus some additional angel investors.
The startup offers an SDK that lets the user create custom computer vision models fed with a little of their own training data — as an alternative to off-the-shelf tools which may not have the required specificity for a particular use-case.
It also flags a ‘no code’ focus, saying its tech has been designed with a non-technical user in mind.
As it’s an SDK, Mobius Labs’ platform can also be deployed on premise and/or on device — rather than the customer needing to connect to a cloud service to tap into the AI tool’s utility.
“Our custom training user interface is very simple to work with, and requires no prior technical knowledge on any level,” claims Appu Shaji, CEO and chief scientist.
“Over the years, a trend we have observed is that often the people who get the maximum value from AI are non technical personas like a content manager in a press and creative agency, or an application manager in the space sector. Our no-code AI allows anyone to build their own applications, thus enabling these users to get close to their vision without having to wait for AI experts or developer teams to help them.”
Mobius Labs — which was founded back in 2018 — now has 30 customers using its tools for a range of use cases.
Uses include categorisation, recommendation, prediction, reducing operational expense, and/or “generally connecting users and audiences to visual content that is most relevant to their needs”. (Press and broadcasting and the stock photography sector have unsurprisingly been big focuses to date.)
But it reckons there’s wider utility for its tech and is gearing up for growth.
It caters to businesses of various sizes, from startups to SMEs, but says it mainly targets global enterprises with major content challenges — hence its historical focus on the media sector and video use cases.
Now, though, it’s also targeting geospatial and earth observation applications as it seeks to expand its customer base.
The 30-strong startup has more than doubled in size over the last 18 months. With the new funding it’s planning to double its headcount again over the next 12 months as it looks to expand its geographical footprint — focusing on Europe and the US.
Year-on-year growth has also been 2x but it believes it can dial that up by tapping into other sectors.
“We are working with industries that are rich in visual data,” says Shaji. “The geospatial sector is something that we are focussing on currently as we have a strong belief that vast amounts of visual data is being produced by them. However, these huge archives of raw pixel data are useless on their own.
“For instance, if we want to track how river fronts are expanding, we have to look at data collected by satellites, sort and tag them in order to analyse them. Currently this is being done manually. The technology we are creating comes in a lightweight SDK, and can be deployed directly into these satellites so that the raw data can be detected and then analysed by machine learning algorithms. We are currently working with satellite companies in this sector.”
On the competitive front, Shaji names Clarifai and Google Cloud Vision as the main rivals it has in its sights.
“We realise these are the big players but at the same time believe that we have something unique to offer, which these players cannot: Unlike their solutions, our platform users can be outside the field of computer vision. By democratising the training of machine learning models beyond simply the technical crowd, we are making computer vision accessible and understandable by anyone, regardless of their job titles,” he argues.
“Another core value that differentiates us is the way we treat client data. Our solutions are delivered in the form of a Software Development Kit (SDK), which runs on-premise, completely locally on clients’ systems. No data is ever sent back to us. Our role is to empower people to build applications, and make them their own.”
Computer vision startups have been a hot acquisition target in recent years and some earlier startups offering ‘computer vision as a service’ got acquired by IT services firms to beef up their existing offerings, while tech giants like Amazon and (the aforementioned) Google offer their own computer vision services too.
But Shaji suggests the tech is now at a different stage of development — and primed for “mass adoption”.
“We’re talking about providing solutions that empower clients to build their own applications,” he says, summing up the competitive play. “And that [do that] with complete data privacy, where our solutions run on-premise, and we don’t see our clients data. Coupled with that is the ease of use that our technology offers: It is a lightweight solution that can be deployed on many ‘edge’ devices like smartphones, laptops, and even on satellites.”
Commenting on the funding in a statement, Stephan Wirries, partner at Ventech VC, added: “Appu and the team at Mobius Labs have developed an unparalleled offering in the computer vision space. Superhuman Vision is impressively innovative with its high degree of accuracy despite very limited required training to recognise new objects at excellent computational efficiency. We believe industries will be transformed through AI, and Mobius Labs is the European Deep Tech innovator teaching machines to see.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Homage, the caregiving-focused startup, has raised a $30 million Series C led by Sheares Healthcare Group, which is wholly-owned by investment firm Temasek. Other participants included new investors DG Daiwa Ventures and Sagana Capital, and returning backers East Ventures (Growth), HealthXCapital, SeedPlus, Trihill Capital and Alternate Ventures.
The new funding will be used to develop Homage’s technology, continue integrating with aged and disability care payer and provider infrastructure and speed-up its regional expansion through partnerships with hospitals and care providers. Homage currently operates in Singapore, Malaysia and Australia.
The Singapore-based company’s services include home visits from caregivers, nurses, therapists and doctors; telemedicine; and services for chronic illnesses. One of the reasons Homage’s platform is able to scale up is its matching engine, which helps clients, like older adults and people living with chronic conditions, find providers who are best suited to their needs (the final matches are made by Homage’s team).
The startup says the round was oversubscribed and one of the largest fundings raised by an on-demand care platform in Southeast Asia and Oceania so far. It brings Homage’s total raised to more than $45 million.
As part of Series C, Sheares Healthcare Group chief corporate development officer Khoo Ee Ping will join Homage’s board of directors.
Homage now has a regional network of more than 6,000 pre-screened and trained care professionals. It claims that its business outside of Singapore has grown more than 600% year-over-year in 2021, and it has more than tripled revenue over the past year.
Powered by WPeMatico
Forum Brands, an e-commerce acquisition platform, announced today that it has secured $100 million in debt funding from TriplePoint Capital.
The financing comes just over two months after the startup raised $27 million in an equity funding round led by Norwest Venture Partners.
Brenton Howland, Ruben Amar and Alex Kopco founded New York-based Forum Brands in the summer of 2020, during the height of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“We’re buying what we think are A+ high-growth e-commerce businesses that sell predominantly on Amazon and are looking to build a portfolio of standalone businesses that are category leaders, on and off Amazon,” Howland told me at the time of the company’s last raise. “A source of inspiration for us is that we saw how consumer goods and services changed fundamentally for what we think is going to be for decades and decades to come, accelerating the shift toward digital.”
Since we covered the company in June, Forum Brands says it has acquired several new brands, including Bonza, a seller of pet products, and Simka Rose, a baby-focused brand specializing in eco-friendly products. Simka sells in the U.S. and the EU and is an example of how Forum is expanding globally, Amar said.
Howland and Amar emphasize that the Forum team continues to focus on quality over quantity when evaluating potential acquisitions. Although they meet with 15-20 founders a week, they are selective in which companies they choose to acquire.
“We continue to be a quality-first buyer, and not quantity-driven,” Amar said, noting that the company will still help a company build its brand even if it does not yet meet Forum’s quality threshold or if the founders are just not ready to sell.
The new funds will be used to, naturally, acquire more e-commerce companies. As part of the debt financing, Sajal Srivastava, co-CEO and co-founder of TriplePoint Capital, will be joining Forum’s board of directors.
“We are impressed not only by Forum’s long-term strategy and ability to leverage technology and deep collective e-commerce and M&A experience but also by how Forum cultivates relationships with their sellers both before and after partnering with them,” he said in a written statement.
At the time of its June raise, Forum had about 20 employees. As of today, it has about 40.
Forum’s technology employs “advanced” algorithms and over 100 million data points to populate brand information into a central platform in real time, instantly scoring brands and generating accurate financial metrics.
On August 31, we covered the news that on the heels of Heroes announcing a $200 million raise to double down on buying and scaling third-party Amazon Marketplace sellers, another startup out of London aiming to do the same announced some significant funding of its own. Olsam, a roll-up play that is buying up both consumer and B2B merchants selling on Amazon by way of Amazon’s FBA fulfillment program, closed on $165 million — a combination of equity and debt that it will be using to fuel its M&A strategy, as well as continue building out its tech platform and to hire more talent.
Powered by WPeMatico
After a 17-hour marathon through nearly 200 startup pitches, the Equity team was fired up to get back on Twitter and chat through some early trends and favorites from the first day of Y Combinator’s demo party. We’ll be back on the air tomorrow, so make sure you’re following the show on Twitter so you don’t miss out.
What did Natasha and Alex chat about? The following:
TechCrunch has extensive coverage of the day on the site, so there’s lots to dig into if you are in the mood. More tomorrow!
Equity drops every Monday at 7:00 a.m. PST, Wednesday, and Friday at 6:00 a.m. PST, so subscribe to us on Apple Podcasts, Overcast, Spotify and all the casts!
Powered by WPeMatico
In the customer service industry, your accent dictates many aspects of your job. It shouldn’t be the case that there’s a “better” or “worse” accent, but in today’s global economy (though who knows about tomorrow’s) it’s valuable to sound American or British. While many undergo accent neutralization training, Sanas is a startup with another approach (and a $5.5M seed round): using speech recognition and synthesis to change the speaker’s accent in near real time.
The company has trained a machine learning algorithm to quickly and locally (that is, without using the cloud) recognize a person’s speech on one end and, on the other, output the same words with an accent chosen from a list or automatically detected from the other person’s speech.
It slots right into the OS’s sound stack so it works out of the box with pretty much any audio or video calling tool. Right now the company is operating a pilot program with thousands of people in locations from the USA and UK to the Philippines, India, Latin America, and others. Accents supported will include American, Spanish, British, Indian, Filipino and Australian by the end of the year.
To tell the truth, the idea of Sanas kind of bothered me at first. It felt like a concession to bigoted people who consider their accent superior and think others below them. Tech will fix it… by accommodating the bigots. Great!
But while I still have a little bit of that feeling, I can see there’s more to it than this. Fundamentally speaking, it is easier to understand someone when they speak in an accent similar to your own. But customer service and tech support is a huge industry and one primarily performed by people outside the countries where the customers are. This basic disconnect can be remedied in a way that puts the onus of responsibility on the entry-level worker, or one that puts it on technology. Either way the difficulty of making oneself understood remains and must be addressed — an automated system just lets it be done more easily and allows more people to do their job.
It’s not magic — as you can tell in this clip, the character and cadence of the person’s voice is only partly retained and the result is considerably more artificial sounding:
But the technology is improving and like any speech engine, the more it’s used, the better it gets. And for someone not used to the original speaker’s accent, the American-accented version may very well be more easily understood. For the person in the support role, this likely means better outcomes for their calls — everyone wins. Sanas told me that the pilots are just starting so there are no numbers available from this deployment yet, but testing has suggested a considerable reduction of error rates and increase in call efficiency.
It’s good enough at any rate to attract a $5.5M seed round, with participation from Human Capital, General Catalyst, Quiet Capital, and DN Capital.
“Sanas is striving to make communication easy and free from friction, so people can speak confidently and understand each other, wherever they are and whoever they are trying to communicate with,” CEO Maxim Serebryakov said in the press release announcing the funding. It’s hard to disagree with that mission.
While the cultural and ethical questions of accents and power differentials are unlikely to ever go away, Sanas is trying something new that may be a powerful tool for the many people who must communicate professionally and find their speech patterns are an obstacle to that. It’s an approach worth exploring and discussing even if in a perfect world we would simply understand one another better.
Powered by WPeMatico
The digital transformation currently sweeping society has likely reached your favorite local restaurant.
Since 2013, Boston-based Toast has offered bars and eateries a software platform that lets them manage orders, payments and deliveries.
Over the last year, its customers have processed more than $38 billion in gross payment volume, so Alex Wilhelm analyzed the company’s S-1 for The Exchange with great interest.
“Toast was last valued at just under $5 billion when it last raised, per Crunchbase data,” he writes. “And folks are saying that it could be worth $20 billion in its debut. Does that square with the numbers?”
Full Extra Crunch articles are only available to members.
Use discount code ECFriday to save 20% off a one- or two-year subscription.
Airbnb, DoorDash and Coinbase each debuted at past Y Combinator Demo Days; as of this writing, they employ a combined 10,000 people.
Today and tomorrow, TechCrunch reporters will cover the proceedings at YC’s Summer 20201 Demo Day. In addition to writing up founder pitches, they’ll also rank their favorites.
Even remotely, I can feel a palpable sense of excitement radiating from our team — anything can happen at YC Demo Day, so sign up for Extra Crunch to follow the action.
Thanks very much for reading; I hope you have an excellent week.
Walter Thompson
Senior Editor, TechCrunch
@yourprotagonist

Image Credits: Ron Miller/TechCrunch
In August 2006, AWS activated its EC2 cloud-based virtual computer, a milestone in the cloud infrastructure giant’s development.
“You really can’t overstate what Amazon was able to accomplish,” writes enterprise reporter Ron Miller.
In the 15 years since, EC2 has enabled clients of any size to test and run their own applications on AWS’ virtual machines.
To learn more about a fundamental technological shift that “would help fuel a whole generation of startups,” Ron interviewed EC2 VP Dave Brown, who built and led the Amazon EC2 Frontend team.

Image Credits: Jasmin Merdan (opens in a new window)/ Getty Images
Most managers agree that OKRs foster transparency and accountability, but running a team effectively has different challenges when workers are attending all-hands meetings from their kitchen tables.
Instead of just discussing key metrics before board meetings or performance reviews, make them part of the day-to-day culture, recommends Jeremy Epstein, Gtmhub’s CMO.
“Strengthen your team by creating authentic workplace transparency using numbers as a universal language and providing meaning behind your team’s work.”
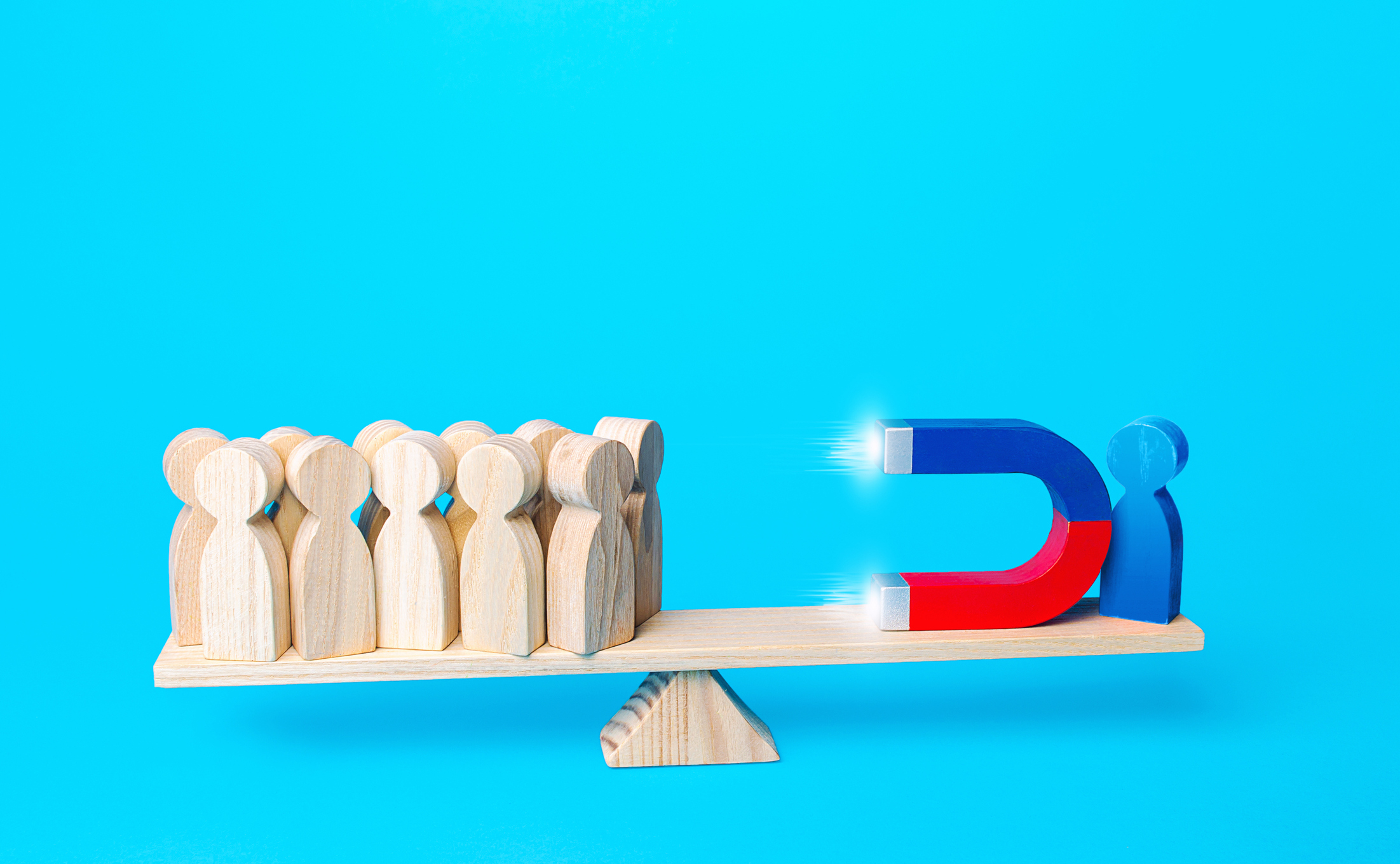

Image Credits: Getty Images under an Andrii Yalanskyi (opens in a new window) license
Many founders must overcome a few emotional hurdles before they’re comfortable pitching a potential investor face-to-face.
To alleviate that pressure, Unicorn Capital founder Evan Fisher recommends that entrepreneurs use pre-pitch meetings to build and strengthen relationships before asking for a check:
“This is the ‘we actually aren’t looking for money; we just want to be friends for now’ pitch that gets you on an investor’s radar so that when it’s time to raise your next round, they’ll be far more likely to answer the phone because they actually know who you are.”
Pre-pitches are good for more than curing the jitters: These conversations help founders get a better sense of how VCs think and sometimes lead to serendipitous outcomes.
“Investors are opportunists by necessity,” says Fisher, “so if they like the cut of your business’s jib, you never know — the FOMO might start kicking hard.”

Image Credits: MirageC (opens in a new window) / Getty Images
FischerJordan’s Deeba Goyal and Archita Bhandari break down the pandemic’s impact on alternative lenders, specifically what they had to do to survive the crisis, taking a look at smaller lenders including Credibly, Kabbage, Kapitus and BlueVine.
“Only those who were able to find a way through the complexities of their existing capital sources were able to maintain their performance, and the rest were left to perish or find new funding avenues,” they write.
Image Credits: Nigel Sussman (opens in a new window)
Customer engagement software company Freshworks’ S-1 filing depicts a company that’s experiencing accelerating revenue growth, “a great sign for the health of its business,” reports Alex Wilhelm in this morning’s The Exchange.
“Most companies see their growth rates decline as they scale, as larger denominators make growth in percentage terms more difficult.”
Studying the company’s SEC filing, he found that “Freshworks isn’t a company where we need to cut it lots of slack, as we might with an adjusted EBITDA number. It is going public ready for Big Kid metrics.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Databricks this morning confirmed earlier reports that it was raising new capital at a higher valuation. The data- and AI-focused company has secured a $1.6 billion round at a $38 billion valuation, it said. Bloomberg first reported last week that Databricks was pursuing new capital at that price.
The Series H was led by Counterpoint Global, a Morgan Stanley fund. Other new investors included Baillie Gifford, UC Investments and ClearBridge. A grip of prior investors also kicked in cash to the round.
The new funding brings Databricks’ total private funding raised to $3.5 billion. Notably, its latest raise comes just seven months after the late-stage startup raised $1 billion on a $28 billion valuation. Its new valuation represents paper value creation in excess of $1 billion per month.
The company, which makes open source and commercial products for processing structured and unstructured data in one location, views its market as a new technology category. Databricks calls the technology a data “lakehouse,” a mashup of data lake and data warehouse.
Databricks CEO and co-founder Ali Ghodsi believes that its new capital will help his company secure market leadership.
For context, since the 1980s, large companies have stored massive amounts of structured data in data warehouses. More recently, companies like Snowflake and Databricks have provided a similar solution for unstructured data called a data lake.
In Ghodsi’s view, combining structured and unstructured data in a single place with the ability for customers to execute data science and business-intelligence work without moving the underlying data is a critical change in the larger data market.
“[Data lakehouses are] a new category, and we think there’s going to be lots of vendors in this data category. So it’s a land grab. We want to quickly race to build it and complete the picture,” he said in an interview with TechCrunch.
Ghodsi also pointed out that he is going up against well-capitalized competitors and that he wants the funds to compete hard with them.
“And you know, it’s not like we’re up against some tiny startups that are getting seed funding to build this. It’s all kinds of [large, established] vendors,” he said. That includes Snowflake, Amazon, Google and others who want to secure a piece of the new market category that Databricks sees emerging.
The company’s performance indicates that it’s onto something.
Databricks has reached the $600 million annual recurring revenue (ARR) milestone, it disclosed as part of its funding announcement. It closed 2020 at $425 million ARR, to better illustrate how quickly it is growing at scale.
Per the company, its new ARR figure represents 75% growth, measured on a year-over-year basis.
That’s quick for a company of its size; per the Bessemer Cloud Index, top-quartile public software companies are growing at around 44% year over year. Those companies are worth around 22x their forward revenues.
At its new valuation, Databricks is worth 63x its current ARR. So Databricks isn’t cheap, but at its current pace should be able to grow to a size that makes its most recent private valuation easily tenable when it does go public, provided that it doesn’t set a new, higher bar for its future performance by raising again before going public.
Ghodsi declined to share timing around a possible IPO, and it isn’t clear whether the company will pursue a traditional IPO or if it will continue to raise private funds so that it can direct list when it chooses to float. Regardless, Databricks is now sufficiently valuable that it can only exit to one of a handful of mega-cap technology giants or go public.
Why hasn’t the company gone public? Ghodsi is enjoying a rare position in the startup market: He has access to unlimited capital. Databricks had to open another $100 million in its latest round, which was originally set to close at just $1.5 billion. It doesn’t lack for investor interest, allowing its CEO to bring aboard the sort of shareholder he wants for his company’s post-IPO life — while enjoying limited dilution.
This also enables him to hire aggressively, possibly buy some smaller companies to fill in holes in Databricks’ product roadmap, and grow outside of the glare of Wall Street expectations from a position of capital advantage. It’s the startup equivalent of having one’s cake and eating it too.
But staying private longer isn’t without risks. If the larger market for software companies was rapidly devalued, Databricks could find itself too expensive to go public at its final private valuation. However, given the long bull market that we’ve seen in recent years for software shares, and the confidence Ghodsi has in his potential market, that doesn’t seem likely.
There’s still much about Databricks’ financial position that we don’t yet know — its gross margin profile, for example. TechCrunch is also incredibly curious what all its fundraising and ensuing spending have done to near-term Databricks operating cash flow results, as well as how long its gross-margin adjusted CAC payback has evolved since the onset of COVID-19. If we ever get an S-1, we might find out.
For now, winsome private markets are giving Ghodsi and crew space to operate an effectively public company without the annoyances that come with actually being public. Want the same thing for your company? Easy: Just reach $600 million ARR while growing 75% year over year.
Powered by WPeMatico
One of the consequences of rising CO2 levels in our atmosphere is that levels also rise proportionately in the ocean, harming wildlife and changing ecosystems. Heimdal is a startup working to pull that CO2 back out at scale using renewable energy and producing carbon-negative industrial materials, including limestone for making concrete, in the process, and it has attracted significant funding even at its very early stage.
If the concrete aspect seems like a bit of a non sequitur, consider two facts: concrete manufacturing is estimated to produce as much as 8% OF all greenhouse gas emissions, and seawater is full of minerals used to make it. You probably wouldn’t make this connection unless you were in some related industry or discipline, but Heimdal founders Erik Millar and Marcus Lima did while they were working in their respective masters programs at Oxford. “We came out and did this straight away,” he said.
They both firmly believe that climate change is an existential threat to humanity, but were disappointed at the lack of permanent solutions to its many and various consequences across the globe. Carbon capture, Millar noted, is frequently a circular process, meaning it is captured only to be used and emitted again. Better than producing new carbons, sure, but why aren’t there more ways to permanently take them out of the ecosystem?
The two founders envisioned a new linear process that takes nothing but electricity and CO2-heavy seawater and produces useful materials that permanently sequester the gas. Of course, if it was as easy that, everyone would already be doing it.
“The carbon markets to make this economically viable have only just been formed,” said Millar. And the cost of energy has dropped through the floor as huge solar and wind installations have overturned decades-old power economies. With carbon credits (the market for which I will not be exploring, but suffice it to say it is an enabler) and cheap power come new business models, and Heimdal’s is one of them.
The Heimdal process, which has been demonstrated at lab scale (think terrariums instead of thousand-gallon tanks), is roughly as follows. First the seawater is alkalinized, shifting its pH up and allowing the isolation of some gaseous hydrogen, chlorine and a hydroxide sorbent. This is mixed with a separate stream of seawater, causing the precipitation of calcium, magnesium and sodium minerals and reducing the saturation of CO2 in the water — allowing it to absorb more from the atmosphere when it is returned to the sea. (I was shown an image of the small-scale prototype facility but, citing pending patents, Heimdal declined to provide the photo for publication.)
So from seawater and electricity, they produce hydrogen and chlorine gas, calcium carbonate, sodium carbonate and magnesium carbonate, and in the process sequester a great deal of dissolved CO2.
For every kiloton of seawater, one ton of CO2 is isolated, and two tons of the carbonates, each of which has an industrial use. MgCO3 and Na2CO3 are used in, among other things, glass manufacturing, but it’s CaCO3, or limestone, that has the biggest potential impact.
As a major component of the cement-making process, limestone is always in great demand. But current methods for supplying it are huge sources of atmospheric carbon. All over the world industries are investing in carbon reduction strategies, and while purely financial offsets are common, moving forward the preferred alternative will likely be actually carbon-negative processes.
To further stack the deck in its favor, Heimdal is looking to work with desalination plants, which are common around the world where fresh water is scarce but seawater and energy are abundant, for example the coasts of California and Texas in the U.S., and many other areas globally, but especially where deserts meet the sea, like in the MENA region.
Desalination produces fresh water and proportionately saltier brine, which generally has to be treated, as to simply pour it back into the ocean can throw the local ecosystem out of balance. But what if there were, say, a mineral-collecting process between the plant and the sea? Heimdal gets the benefit of more minerals per ton of water, and the desalination plant has an effective way of handling its salty byproduct.
“Heimdal’s ability to use brine effluent to produce carbon-neutral cement solves two problems at once,” said Yishan Wong, former Reddit CEO, now CEO of Terraformation and individually an investor in Heimdal. “It creates a scalable source of carbon-neutral cement, and converts the brine effluent of desalination into a useful economic product. Being able to scale this together is game-changing on multiple levels.”
Terraformation is a big proponent of solar desalination, and Heimdal fits right into that equation; the two are working on an official partnership that should be announced shortly. Meanwhile a carbon-negative source for limestone is something cement makers will buy every gram of in their efforts to decarbonize.
Wong points out that the primary cost of Heimdal’s business, beyond the initial ones of buying tanks, pumps and so on, is that of solar energy. That’s been trending downwards for years and with huge sums being invested regularly there’s no reason to think that the cost won’t continue to drop. And profit per ton of CO2 captured — already around 75% of over $500-$600 in revenue — could also grow with scale and efficiency.
Millar said that the price of their limestone is, when government incentives and subsidies are included, already at price parity with industry norms. But as energy costs drop and scales rise, the ratio will grow more attractive. It’s also nice that their product is indistinguishable from “natural” limestone. “We don’t require any retrofitting for the concrete providers — they just buy our synthetic calcium carbonate rather than buy it from mining companies,” he explained.
All in all it seems to make for a promising investment, and though Heimdal has not yet made its public debut (that would be forthcoming at Y Combinator’s Summer 2021 Demo Day) it has attracted a $6.4 million seed round. The participating investors are Liquid2 Ventures, Apollo Projects, Soma Capital, Marc Benioff, Broom Ventures, Metaplanet, Cathexis Ventures and, as mentioned above, Yishan Wong.
Heimdal has already signed LOIs with several large cement and glass manufacturers, and is planning its first pilot facility at a U.S. desalination plant. After providing test products to its partners on the scale of tens of tons, they plan to enter commercial production in 2023.
Powered by WPeMatico
With so much startup activity in the software-as-a-service (SaaS) space it can be a challenge for businesses to figure out which of these SaaS (SaaSes?) are actually useful and worth continuing to shell out for. Well, Cologne-based startup Sastrify is here to help — offering what it describes as a “highly automated” platform (covering some 20,000+ SaaS solutions) to help other businesses with procurement and management of third-party services.
It may not sound the sexist startup business to be in, but despite only launching earlier this year, Sastrify is already cash-flow positive — and can tout “a high six-digit recurring revenue” just a few months post-launch. Not bad for a startup that was only founded last summer.
Today it’s announcing closing a $7 million seed round from HV Capital and the founders of FlixMobility, Personio and SumUp. That follows a $1.3 million pre-seed raised back in late 2020, ahead of its launch.
Sastrify tells us it has around 50 customers at this stage — including “unicorn startups like Gorillas”. It says its approach works best for growing companies with 100+ employees, and is perhaps especially suited to European tech scale-ups.
On the competitive front the startup points to U.S.-based Vendr and Tropic, which may further explain the regional focus (although it’s not only selling in Europe).
Sastrify’s sales pitch to SMEs includes that current customers have seen an average 6.5x return on their investment — in addition to what it bills as “thousands of working hours” saved from “wasted” activities related to SaaS procurement.
Cost savings are another carrot — which the startup is claiming its customers are “typically” saving around 20-30% of their SaaS cost.
So how does it actually make it easier for businesses to navigate the pros & cons of the smorgasbord of SaaS(es) now out there?
“Our main mantra is: ‘Effective procurement asks the right questions at the right time’,” says co-founder Sven Lackinger, who previously co-founded a SaaS startup himself of course (evopark), exiting that company back in 2018.
“To ensure that we’ve defined and implemented a five-step process into our platform, covering the whole life-cycle of SaaS applications within enterprises. Our clients can search for the suitable SaaS solutions while we guide them through the right evaluation process per use case and tool (e.g. what are similar companies using?).
“We then take over the whole buying process, aka automatically reaching out to different vendors, AI-/OCR-based comparing and benchmarking for offers. Once the tool is implemented, we make sure to track usage frequently (via regular, automated surveys to tool owners) and re-evaluate over time so there is no ongoing waste of licenses.”
“We have a more automated platform [than Vendr and Tropic] and can also resell licenses to our customers directly (e.g. for Google, Microsoft and others) to ensure best prices and fast delivery,” he also tells us. “This allows us to offer a faster and cheaper solution which is more suited to the European market (where the average SaaS expense per company is still smaller than in the US).”
If you’re outsourcing all this other stuff to SaaS providers, why not get a specialist service to stay on top of how you do that too, is the basic idea.
The 30-strong Sastrify team will be using the seed funding to accelerate sales, marketing and product dev so it can expand its SaaS management service to more companies in Europe and beyond.
Commenting on the funding in a statement, Jasper Masemann, partner at HV Capital, added: “Cloud software adoption is massively accelerating and almost every company nowadays uses SaaS products but does not buy and manage them efficiently. Sastrify’s astonishing growth underlines the broad customer value the team has already created. It is early days but Sastrify could create an SAP Arriba with a payment solution for SMB – a massive market just in Europe.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Hello and welcome back to Equity, TechCrunch’s venture capital-focused podcast, where we unpack the numbers behind the headlines.
Natasha and Alex and Grace and Chris were joined by none other than TechCrunch’s own Mary Ann Azevedo, in her first-ever appearance on the show. She’s pretty much the best person and we’re stoked to have her on the pod.
And it was good that Mary Ann was on the show this week as she wrote about half the dang site. Which meant that we got to include all sorts of her work in the rundown. Here’s the agenda:
Powered by WPeMatico