Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
With COVID-19 disrupting the entire manufacturing supply chain including semiconductor shortages, companies across multiple industries have been struggling to seek a procurement solution that can rebalance the gap between supply and demand.
CADDi, a Tokyo-based B2B ordering and supply platform in the manufacturing and procurement industry, helps both procurement (demand side) and manufacturing facilities (supply side) by aggregating and rebalancing supply and demand via its automated calculation system for manufacturing costs and databases of fabrication facilities across Japan.
The company announced this morning a $73 million Series B round co-led by Globis Capital Partners and World Innovation Lab (WiL), with participation from existing investors DCM and Global Brain. Six new investors also have joined the round including Arena Holdings, DST Global, Minerva Growth Partners, Tybourne Capital Management, JAFCO Group and SBI Investment.
CADDi was founded by CEO Yushiro Kato and CTO Aki Kobashi in November 2017.
The post-money valuation is estimated at $450 million, according to sources close to the deal.
The new funding brings CADDi’s total raised so far to $90.5 million. In December 2018, the company closed a $9 million Series A round led by DCM and followed by Globis Capital Partners and WiL and Global Brain.
The funding proceeds will be used for accelerating digital transformation of the platform, hiring and expanding to global markets.
“We enable integrated production of complete sets of equipment consisting of custom-made parts such as sheet metal, machined parts and structural frames. Using an automatic quotation system based on a proprietary cost calculation algorithm, we select the processing company that best matches the quality, delivery date and price of the order and build an optimal supply chain,” CEO and co-founder Yushiro Kato said.
The goal of CADDi’s ordering platform is to transform the manufacturing industry from a multiple subcontractor pyramid structure to a flat, connected structure based on each manufacturers’ individual strengths, thus creating a world where those on the front lines of manufacturing can spend more time on essential and creative work, Kato said.
CADDi’s ordering platform, backed by its unique technology including automatic cost calculation system, optimal ordering and production management system, and drawing management system, offers a 10%-15% cost reduction, stable capacity and balanced order placement to its more than 600 Japanese supply partners spanning a multitude of industries.
“The demand for CADDi’s services has seen significant acceleration. Our business has been growing very fast, and our latest orders have grown more than six times compared to the previous year, leading to the company’s expanded presence into both eastern and western Japan in order to meet this increase in demand,” Kato said.
“Going forward, in addition to continuously expanding our ordering platform, we will also start to provide purchases (manufacturers) and supply partners with our technology directly to promote digital transformation of their operations, for example, the production management system and drawing management system,” Kato continued.
“As a start point, in the near future, we are thinking about selling ‘Drawing Management SaaS,’” which has been used internally for CADDi’s ordering operation, to help customers solve operational pains in handling piles of drawings. “Our ‘Drawing Management SaaS’ technology will not only help manage drawings as documents properly but also allow utilization of data of drawings in a practical way for future decision-making and action in their procurement process.”
CADDi’s next axis of growth will be other growing markets, especially in Southeast Asia, Kato pointed out. “Many of our Japanese customers have subsidiaries and branches in these countries, so it’s a natural expansion opportunity for us to strengthen our value proposition and provide more continuity and seamless service to our customers,” Kato added.
Kato also said it wants to continue investing in hiring, especially engineers, to further the development of its platform CADDi and new business. It plans to hire 1,000 employees in the next three years. CADDi had 102 employees as of March 2021.
The company aims to become a global platform with sales of USD 9.1 billion (that is 1 trillion YEN) by 2030, Kato said.
COVID-19 had a different impact on different industries in the procurement and manufacturing sector, with “the automobile and machine tool industries were negatively affected by the pandemic and experienced an up to 90% temporary drop in sales, while other industries such as the medical and semiconductor industries have experienced explosive growth in demand. The overall result of COVID-19 is that the company has captured more demand because CADDi’s system rebalances receipts across multiple industries,” according to Kato.
Masaya Kubota, partner at World Innovation Lab, told TechCrunch, “CADDi’s solution of aggregating and rebalancing supply and demand has once again proven to be indispensable to both purchasers and manufacturers, with the pandemic disrupting the entire supply chain in manufacturing. We first invested in CADDi in 2018, because we strongly believed in their mission of digitally transforming one of the most analog industries, the $1 trillion procurement market.”
Another investor principal at DCM, Kenichiro Hara, also said in an email interview with TechCrunch, “The pandemic made the manufacturing industry’s supply chain vulnerabilities quite clear early on. For example, if a country is on lockdown or a factory stalls the operations, their customers cannot procure necessary parts to produce their products. This impact amplifies, and the entire supply chain is affected. Therefore, the demand for finding new, available and accessible suppliers in a timely manner increased in importance, which is CADDi’s primary value-add.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Y Combinator-backed Kapacity.io is on a mission to accelerate the decarbonization of buildings by using AI-generated efficiency savings to encourage electrification of commercial real estate — wooing buildings away from reliance on fossil fuels to power their heating and cooling needs.
It does this by providing incentives to building owners/occupiers to shift to clean energy usage through a machine learning-powered software automation layer.
The startup’s cloud software integrates with buildings’ HVAC systems and electricity meters — drawing on local energy consumption data to calculate and deploy real-time adjustments to heating/cooling systems which not only yield energy and (CO2) emissions savings but generate actual revenue for building owners/tenants — paying them to reduce consumption such as at times of peak energy demand on the grid.
“We are controlling electricity consumption in buildings, focusing on heating and cooling devices — using AI machine learning to optimize and find the best ways to consume electricity,” explains CEO and co-founder Jaakko Rauhala, a former consultant in energy technology. “The actual method is known as ‘demand response’. Basically that is a way for electricity consumers to get paid for adjusting their energy consumption, based on a utility company’s demand.
“For example if there is a lot of wind power production and suddenly the wind drops or the weather changes and the utility company is running power grids they need to balance that reduction — and the way to do that is either you can fire up natural gas turbines or you can reduce power consumption… Our product estimates how much can we reduce electricity consumption at any given minute. We are [targeting] heating and cooling devices because they consume a lot of electricity.”
“The way we see this is this is a way we can help our customers electrify their building stocks faster because it makes their investments more lucrative and in addition we can then help them use more renewable electricity because we can shift the use from fossil fuels to other areas. And in that we hope to help push for a more greener power grid,” he adds.
Kapcity’s approach is applicable in deregulated energy markets where third parties are able to play a role offering energy saving services and fluctuations in energy demand are managed by an auction process involving the trading of surplus energy — typically overseen by a transmission system operator — to ensure energy producers have the right power balance to meet customer needs.
Demand for energy can fluctuate regardless of the type of energy production feeding the grid but renewable energy sources tend to increase the volatility of energy markets as production can be less predictable versus legacy energy generation (like nuclear or burning fossil fuels) — wind power, for example, depends on when and how strongly the wind is blowing (which both varies and isn’t perfectly predictable). So as economies around the world dial up efforts to tackle climate change and hit critical carbon emissions reduction targets there’s growing pressure to shift away from fossil fuel-based power generation toward cleaner, renewable alternatives. And the real estate sector specifically remains a major generator of CO2, so is squarely in the frame for “greening”.
Simultaneously, decarbonization and the green shift looks likely to drive demand for smart solutions to help energy grids manage increasing complexity and volatility in the energy supply mix.
“Basically more wind power — and solar, to some extent — correlates with demand for balancing power grids and this is why there is a lot of talk usually about electricity storage when it comes to renewables,” says Rauhala. “Demand response, in the way that we do it, is an alternative for electricity storage units. Basically we’re saying that we already have a lot of electricity consuming devices — and we will have more and more with electrification. We need to adjust their consumption before we invest billions of dollars into other systems.”
“We will need a lot of electricity storage units — but we try to push the overall system efficiency to the maximum by utilising what we already have in the grid,” he adds.
There are of course limits to how much “adjustment” (read: switching off) can be done to a heating or cooling system by even the cleverest AI without building occupants becoming uncomfortable.
But Kapacity’s premise is that small adjustments — say turning off the boilers/coolers for five, 15 or 30 minutes — can go essentially unnoticed by building occupants if done right, allowing the startup to tout a range of efficiency services for its customers; such as a peak-shaving offering, which automatically reduces energy usage to avoid peaks in consumption and generate significant energy cost savings.
“Our goal — which is a very ambitious goal — is that the customers and occupants in the buildings wouldn’t notice the adjustments. And that they would fall into the normal range of temperature fluctuations in a building,” says Rauhala.
Kapacity’s algorithms are designed to understand how to make dynamic adjustments to buildings’ heating/cooling without compromising “thermal comfort”, as Rauhala puts it — noting that co-founder (and COO) Sonja Salo, has both a PhD in demand response and researched thermal comfort during a stint as a visiting researcher at UC Berkley — making the area a specialist focus for the engineer-led founding team.
At the same time, the carrots it’s dangling at the commercial real estate to sign up for a little algorithmic HVAC tweaking look substantial: Kapacity says its system has been able to achieve a 25% reduction in electricity costs and a 10% reduction in CO2-emissions in early pilots. Although early tests have been limited to its home market for now.
Its other co-founder, Rami El Geneidy, researched smart algorithms for demand response involving heat pumps for his PhD dissertation — and heat pumps are another key focus for the team’s tech, per Rauhala.
Heat pumps are a low-carbon technology that’s fairly commonly used in the Nordics for heating buildings, but whose use is starting to spread as countries around the world look for greener alternatives to heat buildings.
In the U.K., for example, the government announced a plan last year to install hundreds of thousands of heat pumps per year by 2028 as it seeks to move the country away from widespread use of gas boilers to heat homes. And Rauhala names the U.K. as one of the startup’s early target markets — along with the European Union and the U.S., where they also envisage plenty of demand for their services.
While the initial focus is the commercial real estate sector, he says they are also interested in residential buildings — noting that from a “tech core point of view we can do any type of building”.
“We have been focusing on larger buildings — multifamily buildings, larger office buildings, certain types of industrial or commercial buildings so we don’t do single-family detached homes at the moment,” he goes on, adding: “We have been looking at that and it’s an interesting avenue but our current pilots are in larger buildings.”
The Finnish startup was only founded last year — taking in a pre-seed round of funding from Nordic Makers prior to getting backing from YC — where it will be presenting at the accelerator’s demo day next week. (But Rauhala won’t comment on any additional fund raising plans at this stage.)
He says it’s spun up five pilot projects over the last seven months involving commercial landlords, utilities, real estate developers and engineering companies (all in Finland for now), although — again — full customer details are not yet being disclosed. But Rauhala tells us they expect to move to their first full commercial deals with pilot customers this year.
“The reason why our customers are interested in using our products is that this is a way to make electrification cheaper because they are being paid for adjusting their consumption and that makes their operating cost lower and it makes investments more lucrative if — for example — you need to switch from natural gas boilers to heat pumps so that you can decarbonize your building,” he also tells us. “If you connect the new heat pump running on electricity — if you connect that to our service we can reduce the operating cost and that will make it more lucrative for everybody to electrify their buildings and run their systems.
“We can also then make their electricity consumed more sustainable because we are shifting consumption away from hours with most CO2 emissions on the grid. So we try to avoid the hours when there’s a lot of fossil fuel-based production in the grid and try to divert that into times when we have more renewable electricity.
“So basically the big question we are asking is how do we increase the use of renewables and the way to achieve that is asking when should we consume? Well we should consume electricity when we have more renewable in the grid. And that is the emission reduction method that we are applying here.”
In terms of limitations, Kapacity’s software-focused approach can’t work in every type of building — requiring that real estate customers have some ability to gather energy consumption (and potentially temperature) data from their buildings remotely, such as via IoT devices.
“The typical data that we need is basic information on the heating system — is it running at 100% or 50% or what’s the situation? That gets us pretty far,” says Rauhala. “Then we would like to know indoor temperatures. But that is not mandatory in the sense that we can still do some basic adjustments without that.”
It also of course can’t offer much in the way of savings to buildings that are running 100% on natural gas (or oil) — i.e. with electricity only used for lighting (turning lights off when people are inside buildings obviously wouldn’t fly); there must be some kind of air conditioning, cooling or heat pump systems already installed (or the use of electric hot water boilers).
“An old building that runs on oil or natural gas — that’s a target for decarbonization,” he continues. “That’s a target where you could consider installing heat pumps and that is where we could help some of our customers or potential customers to say OK we need to estimate how much would it cost to install a heat pump system here and that’s where our product can come in and we can say you can reduce the operating cost with demand response. So maybe we should do something together here.”
Rauhala also confirms that Kapacity’s approach does not require invasive levels of building occupant surveillance, telling TechCrunch: “We don’t collect information that is under GDPR [General Data Protection Regulation], I’ll put it that way. We don’t take personal data for this demand response.”
So any guestimates its algorithms are making about building occupants’ tolerance for temperature changes are, therefore, not going to be based on specific individuals — but may, presumably, factor in aggregated information related to specific industry/commercial profiles.
The Helsinki-based startup is not the only one looking at applying AI to drive energy cost and emissions savings in the commercial buildings sector — another we spoke to recently is Düsseldorf-based Dabbel, for example. And plenty more are likely to take an interest in the space as governments start to pump more money into accelerating decarbonization.
Asked about competitive differentiation, Rauhala points to a focus on real-time adjustments and heat pump technologies.
“One of our key things is we’re developing a system so that we can do close to real-time control — very, very short-term control. That is a valuable service to the power grid so we can then quickly adjust,” he says. “And the other one is we are focusing on heat pump technologies to get started — heat pumps here in the Nordics are a very common and extremely good way to decarbonize and understanding how we can combine these to demand response with new heat pumps that is where we see a lot of advantages to our approach.”
“Heat pumps are a bit more technically complex than your basic natural gas boiler so there are certain things that have to be taken it account and that is where we have been focusing our efforts,” he goes on, adding: “We see heat pumps as an excellent way to decarbonize the global building stock and we want to be there and help make that happen.”
Per capita, the Nordics has the most heat pump installations, according to Rauhala — including a lot of ground source heat pump installations which can replace fossil fuel consumption entirely.
“You can run your building with a ground source heat pump system entirely — you don’t need any supporting systems for it. And that is the area where we here in Europe are more far ahead than in the U.S.,” he says on that.
“The U.K. government is pushing for a lot of heat pump installations and there are incentives in place for people to replace their existing natural gas systems or whatever they have. So that is very interesting from our point of view. The U.K. also has a lot of wind power coming online and there have been days when the U.K. has been running 100% with renewable electricity which is great. So that actually is a really good thing for us. But then in the longer term in the U.S. — Seattle, for example, has banned the use of fossil fuels in new buildings so I’m very confident that the market in the U.S. will open up more and quickly. There’s a lot of opportunities in that space as well.
“And of course from a cooling perspective air conditioning in general in the U.S. is very widespread — especially in commercial buildings so that is already an existing opportunity for us.”
“My estimate on how valuable electricity use for heating and cooling is it’s tens of billions of dollars annually in the U.S. and EU,” he adds. “There’s a lot of electricity being used already for this and we expect the market to grow significantly.”
On the business model front, the startup’s cloud software looks set to follow a SaaS model but the plan is also to take a commission of the savings and/or generated income from customers. “We also have the option to provide the service with a fixed fee, which might be easier for some customers, but we expect the majority to be under a commission,” adds Rauhala.
Looking ahead, were the sought-for global shift away from fossil fuels to be wildly successful — and all commercial buildings’ gas/oil boilers got replaced with 100% renewable power systems in short order — there would still be a role for Kapacity’s control software to play, generating energy cost savings for its customers, even though our (current) parallel pressing need to shrink carbon emissions would evaporate in this theoretical future.
“We’d be very happy,” says Rauhala. “The way we see emission reductions with demand response now is it’s based on the fact that we do still have fossil fuels power system — so if we were to have a 100% renewable power system then the electricity does nothing to reduce emissions from the electricity consumption because it’s all renewable. So, ironically, in the future we see this as a way to push for a renewable energy system and makes that transition happen even faster. But if we have a 100% renewable system then there’s nothing [in terms of CO2 emissions] we can reduce but that is a great goal to achieve.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Pry Financials wants to make startup finances approachable for its entire team, not just the people in charge of its accounting spreadsheets. The Y Combinator alum announced today it has raised $4.2 million from Global Founders Capital, Pioneer Fund, NOMO VC, Liquid2 and Hyphen Capital.
Launched in March, Pry now has more than 200 customers and claims it has grown 35% month-over-month since YC’s Demo Day. It was founded by Alex Sailer, Tiffany Wong, Hayden Jensen and Andy Su.
Before starting Pry, Su was co-founder of InDinero, another YC alum that started as a “Mint for small businesses” before pivoting to a full-service accounting company. InDinero launched while he was still a student at UC Berkeley, and Su eventually became responsible for its financial planning.

Pry Financials’ team. Image Credits: Pry Financials
He told TechCrunch that most startups can’t afford accounting software like Workday Adaptive Planning. Instead, they sometimes work with outsourced CFO services, but mostly rely on spreadsheets for everything: three-way forecasts, predicting runway, hiring and contractor budgets and investor updates.
“I was the chief technical officer and over the years, I also took on the finance function, so it was kind of a dual CTO/CFO role. This was 2010 through 2020 and as technology grew, the engineering and product teams got all sorts of new tools every six months or so, whereas the finance team was just stuck in Excel,” he said.
Started as a side project while Su was still at InDinero, Pry starts at just $50 a month and replaces those spreadsheets with easy-to-understand dashboards for accounting, financial planning and scenario modeling. The dashboards connect to QuickBooks, Xero or bank accounts, so numbers are continuously updated.
Pry’s clients typically start using it after they raise seed funding, because “for most first-time founders, that’s the most amount of money you have ever received, so you need to spend more time managing it and reviewing it every month. And you’re spending a lot of time on payroll each month,” Su said. Second-time founders, meanwhile, sign up for Pry because they are sick of Excel spreadsheets.
“Reviewing a spreadsheet is mind-numbingly hard,” said Su. “If you see a number that’s off, you get this weird formula if you didn’t do it yourself. Then you basically have to write a long email to the financial analyst who wrote it and hope that they get back to you before closing time.” For founders who need to update lenders or investors every month, this means a lot of work.
Pry makes the process more efficient by turning three-way reports — combinations of balance sheets, profit and loss statements and cashflow — into Financial Report dashboards, and then adding features like hiring plans, financial modeling and scenario planning.
The scenario planning feature serves as a sandbox, giving startup teams and their investors a way to predict how different situations will impact finances: for example, how much runway they have if they raise a certain amount of funding or adjust product pricing.
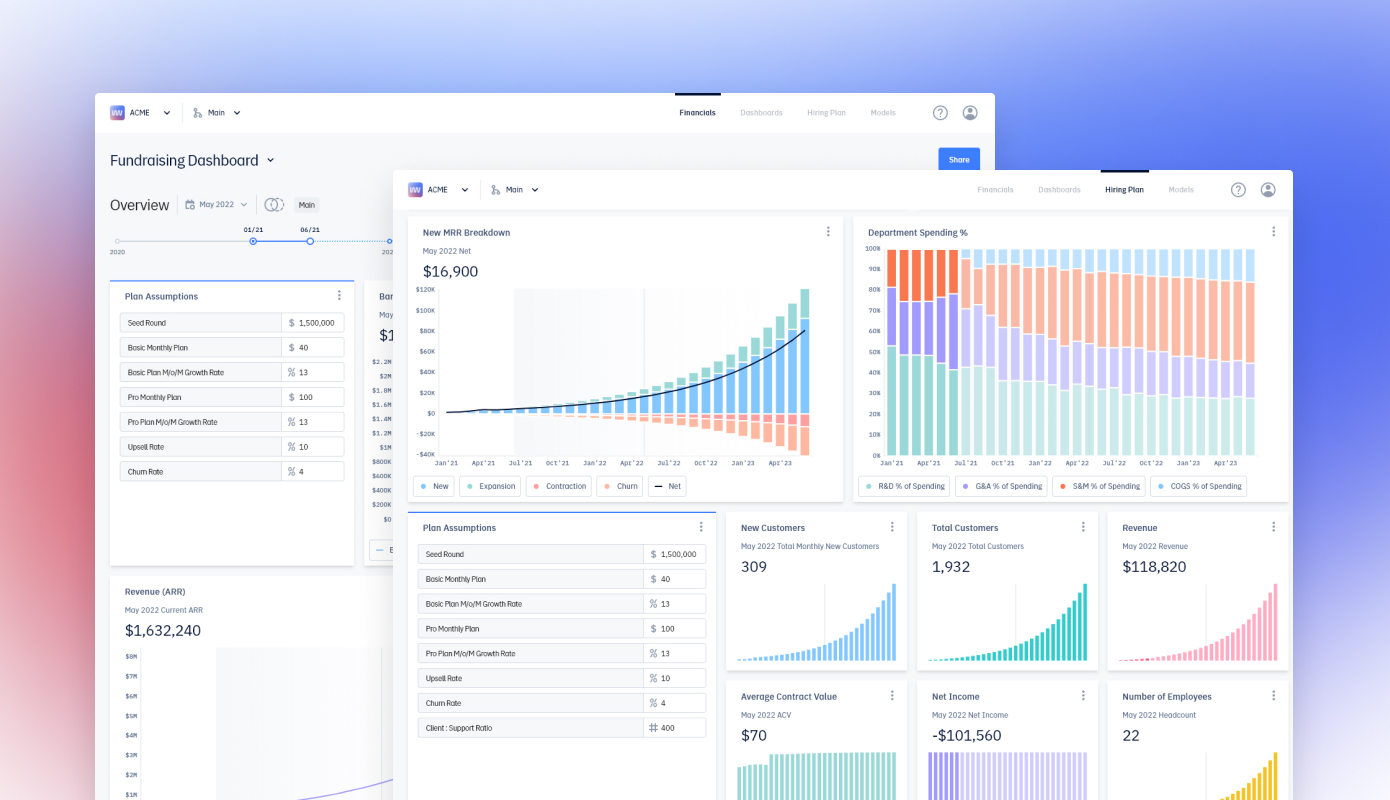
Fundraising dashboards created with Pry Financials. Image credits: Pry Financials
“We’re improving upon and trying to make decisions about the company in a collaborative way. The analogy we have is Git branching, where you have your main plan, and want to try something like a new revenue model or acquiring a business, but don’t want to mess with your current strategy,” said Su. “What you can do is create a completely new branch with, say, a new pricing strategy. You can make all the changes you want and then switch back to your old branch without worrying about overriding or conflicting with it.”
Those speculative branches are also continuously updated with the company’s most recent bank account and payroll information, so founders don’t need to recreate them from scratch if they want to revisit a potential scenario later.
Pry plans to build more complex predictive tools and also integrate industry standards, like statistic and benchmarks, into templates to help founders understand what targets they should set.
Because Pry is easier to manage than a set of Excel spreadsheets, Su said it’s helped startups spot important things. For example, one founder was able to find a way to save $15,000 by catching a tax issue. Pry also helps everyone at a startup understand its finances’ even if they haven’t worked with accounting spreadsheets before. The platform will add roles and permissions soon, so founders can give or restrict access to different people, like leaders of specific departments.
Su said Pry does not compete with the accounting services many startups rely on until they can hire a head of finance, but makes it easier for startups to collaborate with them since they can share their dashboards.
“Usually early on, you can outsource to a CFO firm. That’s the norm in the business and it works pretty well for most companies. You get a part-time CFO to work really hard for a month and get your fundraising structure done,” said Su, adding “we fit into that ecosystem well.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Givz, which has developed an API-powered platform that gives brands a way to convert discounts into donations, has raised $3 million in seed funding.
Eniac and Accomplice co-led the financing for the New York-based startup. Additional investors include Supernode Ventures, Claude Wasserstein of Fine Day, Phoenix Club and Dylan Whitman.
Givz was founded in 2017 to make charitable giving more accessible and convenient for the masses. In March 2020, right before the COVID-19 pandemic hit, the company pivoted from B2C to B2B and used the technology rails it had built to create the e-commerce marketing platform that Givz is today.
The company aims to drive “full-price purchasing behavior” by giving consumers the ability to convert the money they would be saving if getting a discount, and donating it to their favorite charities.
Prior to the funding, Givz had been working with more than 80 enterprise, mid-market and SMB retail and e-commerce clients such as H&M, Tom Brady’s TB12, Seedlip and Terez, and accumulated more than 40,000 individual users. Since the shift last year, the company has helped drive more than $1 million to 1,100 charities, according to CEO and founder Andrew Forman.
It just launched on Shopify, which Forman says will give the startup access to the 1.7 million retailers that use Shopify as their e-commerce platform.
Givz operates under the premise that “donation-driven marketing” consistently outperforms discounts and costs less, “making it an attractive addition” to corporate marketing.
“We are creating a new marketing category and generating the largest sustainable charitable giving platform in the process,” he told TechCrunch.
An example of a company using Givz can be found in Tervis, which offered customers “For every $50 you spend, you’ll receive $15 to give to the charity of your choice.”
“They used Givz technology to allow consumers to choose the charity of their choice and make a turnkey disbursement to hundreds of charities,” Forman explained. “They saw a 20% lift in website conversion and a 17% increase in average order value as a result of this offer.”
Image Credits: Givz
Currently, Givz has eight employees with plans to more than double that number over the next year.
The company plans to use the new capital toward that hiring, and to do some marketing of its own.
“We also want to explore the full potential around the consumer behavior data we collect,” Forman said.
In the short term, Givz is focused on “Shopify growth” with direct to consumer brands.
“But we have successful use cases and huge potential with enterprise retailers and financial institutions,” Forman told TechCrunch. “In the future, we have our sights set on restaurants, the gaming industry and global expansion. I believe that using personalized donations to incentivize consumer behavior has endless application across industries, verticals and continents.”
Eniac partner Vic Singh said that there’s been a trend of brands experimenting with different ways to target the socially conscious consumer.
“We believe Givz’s donation-driven marketing platform offers brands the best way to attract the socially conscious consumer while elevating their brand, moving more inventory and driving increased order value rather than simplistic traditional discounting,” he added.
Accomplice’s TJ Mahony said that both he and Singh believed SMS would emerge as a new marketing category, which led to early investments in Attentive and Postscript, respectively.
“We both saw a similar opportunity with Givz,” he wrote via e-mail. “Discounting is a well worn marketing muscle, but it’s detrimental to the brand, margins and customer expectations. We believe continuous impact marketing becomes the alternative to discounting and marketers will begin to build teams and budget around thoughtful and persistent giving strategies.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Covering public companies can be a bit of a drag. They grow some modest amount each year, and their constituent analysts pester them with questions about gross margin expansion and sales rep efficiency. It can be a little dull. Then there are startups, which grow much more quickly — and are more fun to talk about.
That’s the case with Shelf.io. The company announced an impressive set of metrics this morning, including that from July 2020 to July 2021, it grew its annual recurring revenue (ARR) 4x. Shelf also disclosed that it secured a $52.5 million Series B led by Tiger Global and Insight Partners.
That’s quick growth for a post-Series A startup. Crunchbase reckons that the company raised $8.2 million before its Series B, while PitchBook pegs the number at $6.5 million. Regardless, the company was efficiently expanding from a limited capital base before its latest fundraising event.
What does the company’s software do? Shelf plugs into a company’s information systems, learns from the data and then helps employees respond to queries without forcing them to execute searches or otherwise hunt for information.
The company is starting with customer service as its target vertical. According to Shelf CEO Sedarius Perrotta, Shelf can absorb information from, say, Salesforce, SharePoint, legacy knowledge management platforms and Zendesk. Then, after training models and staff, the company’s software can begin to provide support staff with answers to customer questions as they talk to customers in real time.
The company’s tech can also power responses to customer queries not aimed at a human agent and provide a searchable database of company knowledge to help workers more quickly solve customer issues.
Per Perrotta, Shelf is targeting the sales market next, with others to follow. How might Shelf fit into sales? According to the company, its software may be able to offer staff already written proposals for similar-seeming deals and other related content. The gist is that at companies that have lots of workers doing similar tasks — clicking around in Salesforce, or answering support queries, say — Shelf can learn from the activity and get smarter in helping employees with their tasks. I presume that the software’s learning ability will improve over time, as well.
Shelf, around 100 people today, hopes to double in size by the end of the year, and then double again next year.
That’s where the new capital comes in. Hiring folks in the worlds of machine learning and data science is very expensive. And because the company wants to scale those hires quickly, it will need a large bank balance to lean on.
Quick ARR growth was not the only reason Shelf was able to secure such an outsized Series B, at least when compared to how much capital it had raised before. Per Perrotta, Shelf has 130% net dollar retention and no churn to report, meaning its customers are both sticky and expand organically.
While Shelf is interesting today and has certainly found niches it can sell into in its current form, I am more curious about how far the company can take its machine learning system, called MerlinAI. If its tech can get sufficiently smart, its ability to prompt and help employees could reduce onboarding time and the overall cost of employee training. That would be a huge market.
This is the sort of deal that we expect to see Tiger in — an outsized investment (compared to prior rounds) into a high-growth company that has lots of market room. Whatever price Tiger just paid for the company’s stock, a few years of continued growth should de-risk the investment. By our read, Tiger is really just the market-leading bull on software market growth in the long term. Shelf fits into that thesis neatly.
Powered by WPeMatico
As more companies provide more API-first services, Moesif has developed a way for those companies to learn how their customers are utilizing them.
The San Francisco-based startup is adding to its capital raise Monday with the announcement of a $12 million Series A round led by David Sacks and Arra Malekzadeh of Craft Ventures. Existing investor Merus Capital, which led Moesif’s $3.5 million seed round in 2019, also participated in the round, bringing the company’s total raise to $15.5 million, Moesif co-founder and CEO Derric Gilling told TechCrunch.
Gilling and Xing Wang founded Moesif in 2017 and went through the Alchemist Accelerator in 2018.
Companies seeking data around API usage and workflow traditionally had to build that capability in-house on top of a tech like Snowflake, Gilling said. One of the problems with that was if someone wanted a report, the process was ad hoc, meaning they would file a ticket and wait until a team had time to run the report. In addition, companies find it difficult to accurately bill customers on usage or manage when someone exceeds the rate limits.
“We started to see people build on top of our platform and pull data on APIs, and they started asking us how to directly serve customers, like making them aware if they are hitting a rate limit,” Gilling added. “We started to build new functionality and a way to customize the look and feel of the platform.”
Moesif provides self-service analytics that can be accessed daily and features to scale analytics in a more cost-effective manner. Customers use it to monitor features to better understand when there are issues with the API, and there are additional capabilities to understand who is using the API, how often and who may be likely to stop using a product based on how they are using it.
The company is also now seeing its revenue grow over 20% month over month this year and adoption by more diverse use cases and larger companies. At the time of the seed round, the company was just getting started with analytics and user trials, Gilling said. Today, it boasts a customer list that includes UPS, Tomorrow.io, Symbl.ai and Deloitte.
The company has also gone from a team of two to nine employees, and Gilling expects to use the new funding to bolster that roster across engineering, sales, developer relations and customer success.
He is also focusing on being a thought leader in the space and is pushing go-to-market and building out a new set of features to monetize APIs and improve its dashboard to better differentiate Moesif from competitors, which he said focus more on server health versus customer usage.
As part of the investment, Craft Ventures’ Malekzadeh is joining Moesif’s board. She was introduced to Gilling by another portfolio company and felt Moesif fit into Crafts’ thesis on SaaS companies.
Malekzadeh’s particular interest is in developer tools, and while in her previous position working at a startup developing APIs, she felt firsthand the pain point of not being able to know how those APIs were being used, how much customers should be billed and “was always bugging the product and engineering teams for reports.”
Moesif didn’t exist at the time she worked at the startup, and instead, her company had to build it own tools that turned out to be clunky, while at the same time recruiting top engineers that didn’t want to take up their time with building something that wasn’t the company’s core product.
“The two founders are highly technical, but they provided great content on their website that helped me learn about them,” Malekzadeh added. “One of the interesting things about them is that even though they are technical, they speak the same language as a business user, which makes them special as a developer-first company. Just the growth in their revenue was super impressive, and their customer references were glowing.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Chinese-backed and Africa-focused fintech company OPay raised $400 million in new financing led by SoftBank Vision Fund 2, Bloomberg reported Monday, valuing the company at $2 billion.
The round, which marks the fund’s first investment in an African startup, drew participation from existing investors like Sequoia Capital China, Redpoint China, Source Code Capital and Softbank Ventures Asia. Other investors, including DragonBall Capital and 3W Capital, also took part in the new financing round.
This news comes three months after The Information reported that the company was in talks to raise “up to $400 million at a $1.5 billion valuation” from a group of Chinese investors. The new financing also comes two years after OPay announced two funding rounds in 2019 — $50 million in June and a $120 million Series B in November.
In an emailed statement, OPay CEO Yahui Zhou said OPay “wants to be the power that helps emerging markets reach a faster economic development.” The company, founded in 2018, had an exclusive presence in Nigeria before last year.
While the company started with providing customers with digital services in their everyday life, from mobility and logistics to e-commerce and fintech at cheap rates, those super app plans have been largely underwhelming.
Right now, it’s the company’s mobile money and payment arm that thrives the most. By simply allowing unbanked and underbanked users in Nigeria to send and receive money and pay bills through a network of thousands of agents, OPay has grown at an exponential rate.
The company plays in an extremely competitive fintech market. Nigeria is Africa’s most populous nation, and with a large share of its people underbanked and unbanked, fintech is the most promising digital sector in the country. The same can be said for the continent as a whole. Mobile money services have long catered to the needs of the underbanked. Per GSMA, Africa had more than 160 million active mobile money users generating over $495 billion in transaction value last year.
Parent company Opera reported that OPay’s monthly transactions grew 4.5x to over $2 billion in December last year. OPay also claims to process about 80% of bank transfers among mobile money operators in Nigeria and 20% of the country’s nonmerchant point of sales transactions. Last year, the company also said it acquired an international money transfer license with a WorldRemit partnership also in the works.
Per Bloomberg, the company’s monthly transaction volumes exceed $3 billion at the moment.
Last year, OPay expanded to Egypt, and according to the company, that’s an entry point to the Middle East market.
In a statement, Kentaro Matsui, a managing director at SoftBank Group Corp, said, “We believe our investment will help the company extend its offering to adjacent markets and replicate its successful business model in Egypt and other countries in the region.”
SoftBank joins a growing list of high-flying investors (Dragoneer, Sequoia and SVB Capital, among others) that have cut their first checks in African ventures this year. As the continent continues to show promise, fintech remains its poster child. This year up to half of the total investments raised have emerged from the sector; it contributed to more than 25% last year.
In addition, fintech has produced the most mega-rounds so far. TymeBank raised $109 million in February, Flutterwave bagged a $170 million round in March and Chipper Cash secured $100 million in May.
OPay’s fundraise is the largest of the lot in terms of size and value, making it the second African fintech unicorn after Flutterwave and the third African unicorn after e-commerce giant Jumia. The three make up the five billion-dollar tech companies on the continent, which include Interswitch and Fawry.
Powered by WPeMatico
Figuring out size and cut of clothes through a website can suck the fun out of shopping online, but Revery.ai is developing a tool that leverages computer vision and artificial intelligence to create a better online dressing room experience.
Under the tutelage of University of Illinois Center for Computer Science advisrr David Forsyth, a team consisting of Ph.D. students Kedan Li, Jeffrey Zhang and Min Jin Chong, is creating what they consider to be the first tool using existing catalog images to process at a scale of over a million garments weekly, something previous versions of virtual dressing rooms had difficulty doing, Li told TechCrunch.

Revery.ai co-founders Jeffrey Zhang, Min Jin Chong and Kedan Li. Image Credits: Revery.ai
California-based Revery is part of Y Combinator’s summer 2021 cohort gearing up to complete the program later this month. YC has backed the company with $125,000. Li said the company already has a two-year runway, but wants to raise a $1.5 million seed round to help it grow faster and appear more mature to large retailers.
Before Revery, Li was working on another startup in the personalized email space, but was challenged in making it work due to free versions of already large legacy players. While looking around for areas where there would be less monopoly and more ability to monetize technology, he became interested in fashion. He worked with a different adviser to get a wardrobe collection going, but that idea fizzled out.
The team found its stride working with Forsyth and making several iterations on the technology in order to target business-to-business customers, who already had the images on their websites and the users, but wanted the computer vision aspect.
Unlike its competitors that use 3D modeling or take an image and manually clean it up to superimpose on a model, Revery is using deep learning and computer vision so that the clothing drapes better and users can also customize their clothing model to look more like them using skin tone, hair styles and poses. It is also fully automated, can work with millions of SKUs and be up and running with a customer in a matter of weeks.
Its virtual dressing room product is now live on many fashion e-commerce platforms, including Zalora-Global Fashion Group, one of the largest fashion companies in Southeast Asia, Li said.

Revery.ai landing page. Image Credits: Revery.ai
“It’s amazing how good of results we are getting,” he added. “Customers are reporting strong conversion rates, something like three to five times, which they had never seen before. We released an A/B test for Zalora and saw a 380% increase. We are super excited to move forward and deploy our technology on all of their platforms.”
This technology comes at a time when online shopping jumped last year as a result of the pandemic. Just in the U.S., the e-commerce fashion industry made up 29.5% of fashion retail sales in 2020, and the market’s value is expected to reach $100 billion this year.
Revery is already in talks with over 40 retailers that are “putting this on their roadmap to win in the online race,” Li said.
Over the next year, the company is focusing on getting more adoption and going live with more clients. To differentiate itself from competitors continuing to come online, Li wants to invest body type capabilities, something retailers are asking for. This type of technology is challenging, he said, due to there not being much in the way of diversified body shape models available.
He expects the company will have to collect proprietary data itself so that Revery can offer the ability for users to create their own avatar so that they can see how the clothes look.
“We might actually be seeing the beginning of the tide and have the right product to serve the need,” he added.
Powered by WPeMatico
Like other areas of healthcare, the dental industry is steadily embracing technology. But while much of it is in the orthodontic realm, other startups, like Adra, are bringing artificial intelligence into a dentist’s day-to-day workflow, particularly in finding cavities, of what will be a $435.08 billion global dental services market this year.
The Singapore-based company was founded in 2021, but was an idea that started last year. Co-founder Hamed Fesharaki has been a dentist for over a decade and owns two clinics in Singapore.
He said dentists learn to read X-rays in dental school, but it can take a few years to get good at it. Dentists also often have just minutes to read them as they hop between patients.
As a result, dentists end up misdiagnosing cavities up to 40% of the time, co-founder Yasaman Nematbakhsh said. Her background is in imaging, where she developed an artificial intelligence machine identifying hard-to-see cancers, something Fesharaki thought could also be applied to dental medicine.
Providing the perspective of a more experienced dentist, Adra’s intent is to make every dentist “a super dentist,” Fesharaki told TechCrunch. Its software detects cavities and other dental problems on dental X-rays faster and 25% more accurately, so that clinics can use that time to better serve patients and increase revenue.
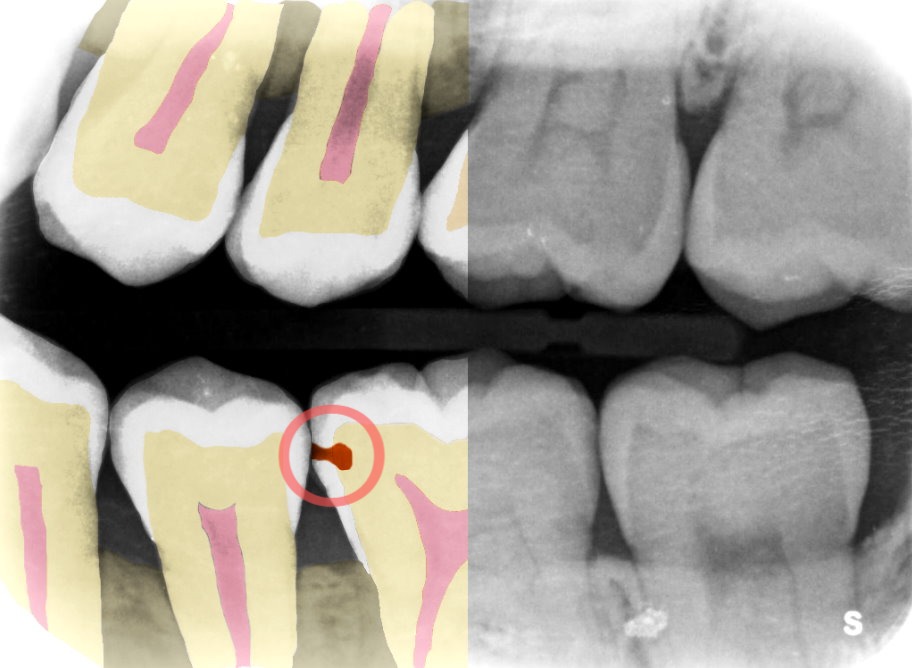
Example of Adra’s software. Image Credits: Adra
“We are coming from the eye of an experienced dentist to help illustrate the problems by turning the X-rays into images to better understand what to look for,” he added. “Ultimately, the dentist has the final say, but we bring the experience element to help them compare and give them suggestions.”
By quickly pointing out the problem and the extent of it, dentists can decide in what way they want to treat it — for example, do a filling, a fluoride treatment or wait.
Along with third co-founder Shifeng Chen, the company is finishing up its time in Y Combinator’s summer cohort and has raised $250,000 so far. Fesharaki intends to do more formalized seed fundraising and wants to bring on more engineers to tackle user experience and add more features.
The company has a few clinics doing pilots and wants to attract more as it moves toward a U.S. Food and Drug Administration clearance. Fesharaki expects it to take six to nine months to receive the clearance, and then Adra will be able to hit the market in late 2022 or early 2023.
Powered by WPeMatico
Servicing one’s car personally is a time-consuming, expensive and painstaking process. It’s a cycle that can lead to more expensive repairs and safety issues down the line, and no car owner likes that.
Egypt and Dubai-based auto tech startup Odiggo is a platform addressing this problem. It allows car owners to get the help they need by finding car services and parts suppliers from providers around them. Then for the suppliers, it increases their sales and reaches more customers without necessarily spending on marketing.
Odiggo is part of the current YC Summer batch and has secured a $2.2 million seed round before Demo Day. The rosters of existing investors participating in the round are Y Combinator, 500 Startups, and Plug and Play Ventures. Regional VCs like Seedra Ventures, LoftyInc Capital, and Essa Al-Saleh (CEO of Volta-Tucks) also took part.
Ahmed Omar and Ahmed Nasser launched Odiggo in December 2019. The company operates a marketplace that connects car owners with service providers who can solve their problems, from servicing and repair to washing and maintenance. A commission-based model is used and Odiggo charges the car suppliers 20% commission on every transaction.
Over 50,000 car owners across three markets — Egypt, the UAE and Saudi Arabia — use Odiggo. The company also works directly with over 300 merchants. It claims merchant numbers have grown 40% month-on-month while its user base has increased 200% since the start of the pandemic.
“We believe we are at a watershed moment. It is incredible that since COVID hit, Odiggo has experienced over 10 times growth in the last year,” said co-founder Omar.
CEO Omar said with this new round, Odiggo’s priority will be to attain consistent growth while expanding its team across the UEA, Saudi Arabia and Egypt.

L-R: Ahmed Nassir (co-founder) & Ahmed Omar (co-founder and CEO)
He adds that since Odiggo taps into a mix of data sources — including car metrics and internal software, it will use that same information to provide more product offerings.
Odiggo will use part of the funding to continue developing its tech and dashboard software, he said.
“For example, the platform would be hooked up to the car owner’s vehicle and link the vehicle to the marketplace and provide frequent updates of your vehicle condition so you’ll be informed if the tires are low, the oil needs changing, or if a service is required.”
The pandemic has upended the mobility and logistics sectors, especially in MENA, making players like Odiggo gain much visibility from investors. In an industry today worth over $61 billion in the Middle East and Africa alone, Odiggo is looking to become a market leader. It has even more lofty plans to go public in the next three years.
“We are also aiming to be fully focused on spending more on our product and technology, as building an ecosystem to monetize requires more capital. Our target is to go for IPO by 2024 and achieve one billion services booked, and this requires a lot of network effects, infrastructure and technology,” the CEO said.
“We aim to be the first $100 billion company coming out of the region,” added Nasser.
Some of its investors, Idris Ayodeji Bello, managing partner at LoftyInc, and Essa Al-Saleh, are onboard with the startup’s plan despite early days.
“We are excited to back Odiggo through our Afropreneurs Funds in its quest to transform the automotive parts market and provide superior service to clients, starting from MENA. The leadership team of Omar and Nasser, supported by the rest of the employees, have been a joy to work with and we are on a countdown to the IPO,” said Bello in a statement.
Powered by WPeMatico