Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Traditional MBA programs can be costly, lengthy and often lack the application of real-world skills. Meanwhile, big global brands and companies who need product managers to grow their businesses can’t sit around waiting for people to graduate. And the edtech space hasn’t traditionally catered to this sector.
This is perhaps why Product School says it has secured $25 million in growth equity investment from growth fund Leeds Illuminate (subject to regulatory approval) to accelerate its product and partnerships with client companies.
The growth funding for the company comes after bootstrapping since 2014, in large part because product managers (PMs) are no longer needed just inside tech companies but have become sought after across almost virtually all industries.
Product School provides certificates for individuals as well as team training, and says it has experienced an upwelling of business since COVID switched so many companies into digital ones. It also now counts Google, Facebook, Netflix, Airbnb, PayPal, Uber and Amazon amongst its customers.
“Product managers have an outsized role in driving digital transformation and innovation across all sectors,” said Susan Cates, managing partner of Leeds Illuminate. “Having built the largest community of PMs in the world validates Product School’s certification as the industry standard for the market and positions the company at the forefront of upskilling top-notch talent for global organizations.”
Carlos Gonzalez de Villaumbrosia, CEO and founder of Product School, who started the company after moving from Spain, said: “There has never been a better time in history to build digital products and Product School is excited to unlock value for product teams across the globe to help define the future. Our company was founded on the basis that traditional degrees and MBA programs simply don’t equip PMs with the real-world skills they require on the job.”
Product School has also produced the The Product Book, The Proddy Awards and ProductCon.
Its main competitor is MindTheProduct, a community and training platform, which has also boostrapped.
Powered by WPeMatico
Reducing global greenhouse gas emissions is an important goal, but another challenge awaits: lowering the levels of CO2 and other substances already in the atmosphere. One promising approach turns the gas into an ordinary mineral through entirely natural processes; 44.01 hopes to perform this process at scale using vast deposits of precursor materials and a $5 million seed round to get the ball rolling.
The process of mineralizing CO2 is well known among geologists and climate scientists. A naturally occurring stone called peridotite reacts with the gas and water to produce calcite, another common and harmless mineral. In fact this has occurred at enormous scales throughout history, as witnessed by large streaks of calcite piercing peridotite deposits.
Peridotite is normally found miles below sea level, but on the easternmost tip of the Arabian peninsula, specifically the northern coast of Oman, tectonic action has raised hundreds of square miles of the stuff to the surface.
Talal Hasan was working in Oman’s sovereign investment arm when he read about the country’s coast having the largest “dead zone” in the world, a major contributor to which was CO2 emissions being absorbed by the sea and gathering there. Hasan, born into a family of environmentalists, looked into it and found that, amazingly, the problem and the solution were literally right next to each other: the country’s mountains of peridotite, which theoretically could hold billions of tons of CO2.
Around that time, in fact, The New York Times ran a photo essay about Oman’s potential miracle mineral, highlighting the research of Peter Kelemen and Juerg Matter into its potential. As the Times’ Henry Fountain wrote at the time:
If this natural process, called carbon mineralization, could be harnessed, accelerated and applied inexpensively on a huge scale — admittedly some very big “ifs” — it could help fight climate change.
That’s broadly speaking the plan proposed by Hasan and, actually, both Kelemen and Matter, who make up the startup’s “scientific committee.” 44.01 (the molecular weight of carbon dioxide, if you were wondering) aims to accomplish mineralization economically and safely with a few novel ideas.
First is the basic process of accelerating the natural reaction of the materials. It normally occurs over years as CO2 and water vapor interact with the rock — no energy needs to be applied to make the change, since the reaction actually results in a lower energy state.
“We’re speeding it up by injecting a higher CO2 content than you would get in the atmosphere,” said Hasan. “We have to drill an engineered borehole that’s targeted for mineralization and injection.”
The holes would maximize surface area, and highly carbonated water would be pumped in cyclically until the drilled peridotite is saturated. Importantly, there’s no catalyst or toxic additive, it’s just fizzy water, and if some were to leak or escape, it’s just a puff of CO2, like what you get when you open a bottle of soda.
Second is achieving this without negating the entire endeavor by having giant trucks and heavy machinery pumping out new CO2 as fast as they can pump in the old stuff. To that end Hasan said the company is working hard at the logistics side to create a biodiesel-based supply line (with Wakud) to truck in the raw material and power the machines at night, while solar would offset that fuel cost at night.
It sounds like a lot to build up, but Hasan points out that a lot of this is already done by the oil industry, which as you might guess is fairly ubiquitous in the region. “It’s similar to how they drill and explore, so there’s a lot of existing infrastructure for this,” he said, “but rather than pulling the hydrocarbon out, we’re pumping it back in.” Other mineralization efforts have broken ground on the concept, so to speak, such as a basalt-injection scheme up in Iceland, so it isn’t without precedent.
Third is sourcing the CO2 itself. The atmosphere is full of it, sure, but it’s not trivial to capture and compress enough to mineralize at industrial scales. So 44.01 is partnering with Climeworks and other carbon capture companies to provide an end point for their CO2 sequestration efforts.
Plenty of companies are working on direct capture of emissions, be they at the point of emission or elsewhere, but once they have a couple million tons of CO2, it’s not obvious what to do next. “We want to facilitate carbon capture companies, so we’re building the CO2 sinks here and operating a plug and play model. They come to our site, plug in, and using power on site, we can start taking it,” said Hasan.
How it would be paid for is a bit of an open question in the exact particulars, but what’s clear is a global corporate appetite for carbon offsetting. There’s a large voluntary market for carbon credits beyond the traditional and rather outdated carbon credits. 44.01 can sell large quantities of verified carbon removal, which is a step up from temporary sequestration or capture — though the financial instruments to do so are still being worked out. (DroneSeed is another company offering a service beyond offsets that hopes to take advantage of a new generation of emissions futures and other systems. It’s an evolving and highly complex overlapping area of international regulations, taxes and corporate policy.)
For now, however, the goal is simply to prove that the system works as expected at the scales hoped for. The seed money is nowhere near what would be needed to build the operation necessary, just a step in that direction to get the permits, studies and equipment necessary to properly perform demonstrations.
“We tried to get like-minded investors on board, people genuinely doing this for climate change,” said Hasan. “It makes things a lot easier on us when we’re measured on impact rather than financials.” (No doubt all startups hope for such understanding backers.)
Apollo Projects, a early-stage investment fund from Max and Sam Altman, led the round, and Breakthrough Energy Ventures participated. (Not listed in the press release but important to note, Hasan said, were small investments from families in Oman and environmental organizations in Europe.)
Oman may be the starting point, but Hasan hinted that another location would host the first commercial operations. While he declined to be specific, one glance at a map shows that the peridotite deposits spill over the northern border of Oman and into the eastern tip of the UAE, which no doubt is also interested in this budding industry and, of course, has more than enough money to finance it. We’ll know more once 44.01 completes its pilot work.
Powered by WPeMatico
Just months after raising $28 million, Jerry announced today that it has raised $75 million in a Series C round that values the company at $450 million.
Existing backer Goodwater Capital doubled down on its investment in Jerry, leading the “oversubscribed” round. Bow Capital, Kamerra, Highland Capital Partners and Park West Asset Management also participated in the financing, which brings Jerry’s total raised to $132 million since its 2017 inception. Goodwater Capital also led the startup’s Series B earlier this year. Jerry’s new valuation is about “4x” that of the company at its Series B round, according to co-founder and CEO Art Agrawal.
“What factored into the current valuation is our annual recurring revenue, growing customer base and total addressable market,” he told TechCrunch, declining to be more specific about ARR other than to say it is growing “at a very fast rate.” He also said the company “continues to meet and exceed growth and revenue targets” with its first product, a service for comparing and buying car insurance. At the time of the company’s last raise, Agrawal said Jerry saw its revenue surge by “10x” in 2020 compared to 2019.
Jerry, which says it has evolved its model to a mobile-first car ownership “super app,” aims to save its customers time and money on car expenses. The Palo Alto-based startup launched its car insurance comparison service using artificial intelligence and machine learning in January 2019. It has quietly since amassed nearly 1 million customers across the United States as a licensed insurance broker.
“Today as a consumer, you have to go to multiple different places to deal with different things,” Agrawal said at the time of the company’s last raise. “Jerry is out to change that.”
The new funding round fuels the launch of the company’s “compare-and-buy” marketplaces in new verticals, including financing, repair, warranties, parking, maintenance and “additional money-saving services.” Although Jerry also offers a similar product for home insurance, its focus is on car ownership.
Image Credits: Jerry
“Access to reliable and affordable transportation is critical to economic empowerment,” said Rafi Syed, Jerry board member and general partner at Bow Capital, which also doubled down on its investment in the company. “Jerry is helping car owners make the most of every dollar they earn. While we see Jerry as an excellent technology investment showcasing the power of data in financial services, it’s also a high-performing investment in terms of the financial inclusion it supports.”
Goodwater Capital Partner Chi-Hua Chien said the firm’s recurring revenue model makes it stand out from lead generation-based car insurance comparison sites.
CEO Agrawal agrees, noting that Jerry’s high-performing annual recurring revenue model has made the company “attractive to investors” in addition to the fact that the startup “straddles” the auto, e-commerce, fintech and insurtech industries.
“We recognized those investment opportunities could drive our business faster and led to raising the round earlier than expected,” he told TechCrunch. “We’re eager to launch new categories to save customers time and money on auto expenses and the new investment shortens our time to market.”
Agrawal also believes Jerry is different from other auto-related marketplaces out there in that it aims to help consumers with various aspects of car ownership (from repair to maintenance to insurance to warranties), rather than just one. The company also believes it is set apart from competitors in that it doesn’t refer a consumer to an insurance carrier’s site so that they still have to do the work of signing up with them separately, for example. Rather, Jerry uses automation to give consumers customized quotes from more than 45 insurance carriers “in 45 seconds.” The consumers can then sign on to the new carrier via Jerry, which can then cancel former policies on their behalf.
Jerry makes recurring revenue from earning a percentage of the premium when a consumer purchases a policy on its site from carriers such as Progressive.
Powered by WPeMatico
OwnBackup, the late-stage startup that helps companies in the Salesforce ecosystem back up their data, announced a $240 million Series E today at a $3.35 billion valuation. The latter is up from $1.4 billion in January when the company announced a $167.5 million Series D.
Alkeon Capital and B Capital Group co-led today’s investment, which also included BlackRock Private Equity Partners and Tiger Global along with existing investors Insight Partners, Salesforce Ventures, Sapphire Ventures and Vertex Ventures. The company has now raised close to $500 million, with more than $455 million coming since last July.
That’s a lot of capital, but OwnBackup CEO Sam Gutmann says that as the Salesforce ecosystem has grown, which includes not only Salesforce itself, but companies like Veeva and nCino, business has been booming, growing 100% year-over-year since 2018. That kind of growth gets investor attention, and Gutmann reported a lot of inbound investor interest in this round.
What’s more, the company announced that it will now support the same type of backup for Microsoft Dynamics 365 customers, thereby greatly expanding its potential market. “We’re also announcing that we are expanding into the Microsoft ecosystem specifically around Microsoft Dynamics 365’s huge ecosystem. I think it’s the second-largest B2B SaaS ecosystem beyond Salesforce. We’re just getting started there, but super excited about the opportunity,” he said.
The company also sees the opportunity to grow the business through acquisition. Over the last year, it bought two small companies, but he says that was more focused on acquiring specific talent to develop the platform, while future acquisitions could be more focused on expanding the business itself.
As the company takes on this kind of investment, Gutmann sees an IPO possibility at some point in the future, but for now he’s concentrating on growth. “We’re not focused on exiting. We’ve really focused on developing what is already a huge market and growing into an even bigger market, continuing to expand with a business that has great unit economics and continues to grow nicely,” he said.
The company has ballooned to 500 employees this year, with plans to double that number in the next year. As he does that, Gutmann says that hiring in general is challenging, but he is always looking to find ways to diversify his workforce. “It’s really, really hard. Our hiring managers definitely focus on [diversity], but at the end of the day, we want the best employees for the job. I think we’ve made a lot of strides. We’re working with one of our largest investors, Insight, who is co-sponsoring a program to train, more on the junior side, some underrepresented minorities in technical fields and bring them on as full-time employees after that program,” Gutmann said.
Gutmann says his offices have remained open throughout the pandemic, but nobody was required to come in. In fact, he says that his company is one of the few that has actually added office space to make it easier to distance. The company, which is located in New Jersey, has also expanded space outdoors for working outside when the weather permits.
Powered by WPeMatico
Upscribe founder and CEO Dileepan Siva watched the retail industry make a massive shift to subscription e-commerce for physical products over the past decade, and decided to get in it himself in 2019.
The Los Angeles-based company, developing subscription software for direct-to-consumer e-commerce merchants, is Siva’s fourth startup experience and first time as founder. He closed a $4 million seed round to go after two macro trends he is seeing: buying physical products, like consumer-packaged goods, on a recurring basis, and new industries offering subscriptions, like car and fashion companies.
Merchants use Upscribe’s technology to drive subscriber growth, reduce churn and enable their customers to personalize a subscription experience, like skipping shipments, swapping out products and changing the order frequency. Brands can also feature products for upsell purposes throughout the subscriber lifecycle, from checkout to post-purchase.
Upscribe also offers APIs for merchants to integrate tools like Klaviyo, Segment and Shopify — a new subscription offering for checkouts.
Uncork Capital led the seed round and was joined by Leaders Fund, The House Fund, Roach Capitals’ Fahd Ananta and Shippo CEO Laura Behrens Wu.
“As the market for D2C subscriptions booms, there is a need for subscription-first brands to grow and scale their businesses,” said Jeff Clavier, founder and managing partner of Uncork Capital, in a written statement. “We have spent a long time in the e-commerce space, working with D2C brands and companies who are solving common industry pain points, and Upscribe’s merchant-centric approach raised the bar for subscription services, addressing the friction in customer experiences and enabling merchants to engage subscribers and scale recurring revenue growth.”
Siva bootstrapped the company, but decided to go after venture capital dollars when Upscribe wanted to create a more merchant-centric approach, which required scaling with a bigger team. The “real gems are in the data layer and how to make the experience exceptional,” he added.
The company is growing 43% quarter over quarter and is close to profitable, with much of its business stemming from referrals, Siva said. It is already working with customers like Athletic Greens, Four Sigmatic and True Botanicals and across multiple verticals, including food and beverage, health and wellness, beauty and cosmetics and home care.
The new funding will be used to “capture the next wave of brands that are going to grow,” he added. Siva cites the growth will come as the DTC subscription market is forecasted to reach $478 billion by 2025, and 75% of those brands are expected to offer subscriptions in the next two years. As such, the majority of the funding will be used to bring on more employees, especially in the product, customer success and go-to-market functions.
Though there is competition in the space, many of those are focused on processing transactions, while Siva said Upscribe’s approach is customer relationships. The cost of acquiring new customers is going up, and subscription services will be the key to converting one-time buyers into loyal customers.
“It is really about customer relationships and the ongoing engagement between merchants and subscribers,” he added. “We are in a different world now. The first wave could play the Facebook game, advertising on social media with super low acquisition and scale. That is no longer the case anymore.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Trendyol, an e-commerce platform based in Turkey, has raised $1.5 billion in a massive funding round that values the company at $16.5 billion. General Atlantic, SoftBank Vision Fund 2, Princeville Capital and sovereign wealth funds, ADQ (UAE) and Qatar Investment Authority co-led the round.
The deal marks SoftBank’s first in the country.
The new financing also makes Trendyol Turkey’s first decacorn, and among the highest-valued private tech companies in Europe. It comes just months after strategic — and majority — backer Alibaba invested $350 million in the company at a $9.4 billion valuation.
Founded in 2010, Trendyol ranks as Turkey’s largest e-commerce company, serving more than 30 million shoppers and delivering more than 1 million packages per day. It claims to have evolved from marketplace to “superapp” by combining its marketplace platform (which is powered by Trendyol Express, its own last-mile delivery solution) with instant grocery and food delivery through its own courier network (Trendyol Go), its digital wallet (Trendyol Pay), consumer-to-consumer channel (Dolap) and other services.

Image Credits: Founder Demet Mutlu / Trendyol
Trendyol founder Demet Suzan Mutlu said the new capital will go toward expansion within Turkey and globally. Specifically, the company plans to continue investing in nationwide infrastructure, technology and logistics and toward accelerating digitalization of Turkish SMEs. She said the company was founded to create positive impact and that it intends to continue on that mission.
Evren Ucok, Trendyol’s chairman, added that part of the company’s goal is to create new export channels for Turkish merchants and manufacturers.
Melis Kahya Akar, managing director and head of consumer for EMEA at General Atlantic, said that Trendyol’s marketplace model — ranging from grocery delivery to mobile wallets — “brings convenience and ease to consumers” in Turkey and internationally.
“Turkey is one of the fastest growing economies in the world and benefits from attractive demographics, with a young population that is very active online,” wrote General Atlantic’s Kahya Akar via e-mail. “We expect its already sizable e-commerce market –$17 billion in 2020 – to continue to grow meaningfully on the back of growing online penetration. We think Trendyol is ideally positioned to meet the needs of consumers in Turkey and around the world as the company expands.”
A 2020 report by JPMorgan found that e-commerce represented only 5.3% of the overall Turkish retail market at the time but that Turkish e-commerce had notched impressive leaps in revenues in recent years: 2018 alone saw the market jump by 42%, followed by 31% in 2019. As of 2020, 67% of the Turkish population were making purchases online.
Powered by WPeMatico
We’ve all been there. (Or at least I have.)
You’re getting ready to vacate a property you’ve rented, only to be told by the landlord that you won’t be getting your security deposit back.
This happened to me the first time I ever rented a place in the late 90s. I was shocked, but more than anything, I was angry at the injustice because I knew that what the landlord claimed was not true. It was her word against mine and my roommate’s. Still, we took her to small claims court, not so much over the $800 she was trying to keep but more to prove her wrong. In the end, we won.
But it was a lot of work, and a lot of time spent. If only there was some kind of technology available to have helped us make our case.
Well, today there is. RentCheck, a startup that is out to help solve the “he said, she said” challenge in these situations with an automated property inspection platform, has recently raised $2.6 million in seed money.
Lydia Winkler and Marco Nelson started the company in mid-2019 after Winkler experienced a similar situation to mine and ended up suing her landlord in small claims court. She was working on getting her JD/MBA at Tulane University at the time.
“It was an injustice for me not to pursue it,” she told TechCrunch. “I took meticulous photos of the move-out condition of my apartment. The process took 18 months. But not everyone has the time or knowledge to fight in court.”
She then met Nelson, who had bought several properties that he ended up renting out. He had issues with security deposits too, but the opposite ones. He had to settle disputes over deposits, and found himself documenting properties’ condition at the time of move-out.
“I met Lydia and we realized we were passionate about the same problem,” Nelson recalled.
And so New Orleans-based RentCheck was born.

Image Credits: RentCheck; Co-founders Marco Nelson and Lydia Winkler
There are an estimated 48 million rental units in the U.S., with an average deposit of $1,000.
“A good chunk of that is being fought after on aggregate,” Winkler said. “And so many need that money to put down a deposit on another unit.”
To address the problem, RentCheck built a web app for property managers that they believe also benefits tenants. The company’s digital platform works by providing a way for property managers to facilitate and conduct remote, guided property inspections. For obvious reasons, the company saw increased demand upon the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, considering that the platform was automated and contactless. It saw 1,000% — mostly organic — growth in terms of the number of properties on the platform.
“What we do is, using a guided inspection process, prompt users and guide them room by room, telling them exactly what to take photos of so that floors, ceilings, windows and walls are all accounted for,” Winkler said.
Everything is done within the app so that users can’t upload photos that were previously on their camera roll “to ensure the integrity of the inspection” and that everything is time stamped. Once the inspection is complete, whoever does it signs off on it that they completed it accurately and honestly. Then the property manager can also sign off on it so both parties can agree on the move-out condition.
The company operates as a SaaS business, and charges property management companies a subscription fee based on the number of properties that they have on the RentCheck platform. They can then conduct “as many inspections as they want,” Nelson says, “whether the residents are doing them, their internal teams are doing them, or a third-party vendor, or a hybrid of the three.”
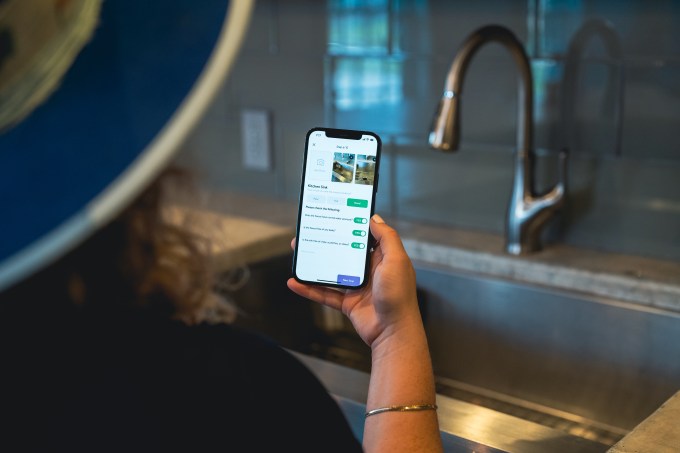

Image Credits: RentCheck/Bryce Ell Photography
The startup has attracted some large-name investors since its inception, first catching the attention of James “Jim” Coulter, the founder of TPG Capital, when the company won New Orleans Entrepreneurship Week. Coulter subsequently became one of the company’s first investors in its $1 million pre-seed round.
The company’s seed round included participation from Cox Enterprises, for its operations in the multifamily housing space, and angels such as Jim Payne, who previously sold MoPub to Twitter, and MAX to AppLovin; Ken Goldman, the former CFO of Yahoo, and who currently runs Hillspire, Eric and Wendy Schmidt’s family office; Mark Zaleski and John Kuolt of BCG Digital Ventures, and Brian Long, the founder of Attentive, who previously sold TapCommerce to Twitter. It also included institutional investors such as Irongrey, Context Ventures and Techstars.
“What we love about RentCheck is that it’s using very clever technology to automate and solve arguably the industry’s biggest problem in terms of money and time for both property managers and tenants,” said Kuolt, former managing director at BCG Digital Ventures and an early RentCheck investor. “The deposit deduction issue needs a technology-based solution, and almost everyone, at some time, has felt like they’ve been screwed over on their deposit by a landlord. When you see and use RentCheck’s solution, it makes you think: ‘Why didn’t I think of this?’ ”
Powered by WPeMatico
Back in December 2020 we covered the launch of a new kind of smartphone app-based search engine, Xayn.
“A search engine?!” I hear you say? Well, yes, because despite the convenience of modern search engines’ ability to tailor their search results to the individual, this user-tracking comes at the expense of privacy. This mass surveillance might be what improves Google’s search engine and Facebook’s ad targeting, to name just two examples, but it’s not very good for our privacy.
Internet users are admittedly able to switch to the U.S.-based DuckDuckGo, or perhaps France’s Qwant, but what they gain in privacy, they often lose in user experience and the relevance of search results, through this lack of tailoring.
What Berlin-based Xayn has come up with is personalized, but a privacy-safe web search on smartphones, which replaces the cloud-based AI employed by Google et al. with the innate AI in-built into modern smartphones. The result is that no data about you is uploaded to Xayn’s servers.
And this approach is not just for “privacy freaks”. Businesses that need search but don’t need Google’s dominant market position are increasingly attracted by this model.
And the evidence comes today with the news that Xayn has now raised almost $12 million in Series A funding led by the Japanese investors Global Brain and KDDI (a Japanese telecommunications operator), with participation from previous backers, including the Earlybird VC in Berlin. Xayn’s total financing now comes to more than $23 million.
It would appear that Xayn’s fusion of a search engine, a discovery feed and a mobile browser has appealed to these Asian market players, particularly because Xayn can be built into OEM devices.
The result of the investment is that Xayn will now also focus on the Asian market, starting with Japan, as well as Europe.
Leif-Nissen Lundbæk, co-founder and CEO of Xayn said: “We proved with Xayn that you can have it all: great results through personalization, privacy by design through advanced technology and a convenient user experience through clean design.”
He added: “In an industry in which selling data and delivering ads en masse are the norm, we choose to lead with privacy instead and put user satisfaction front and center.”
The funding comes as legislation such as the EU’s GDPR or California’s CCPA have both raised public awareness about personal data online.
Since its launch, Xayn says its app has been downloaded around 215,000 times worldwide, and a web version of its app is expected soon.
Over a call, Lundbæk expanded on the KDDI aspect of the fund-raising: “The partnership with KDDI means we will give users access to Xayn for free, while the corporate — such as KDDI — is the actual customer but gives our search engine away for free.”
The core features of Xayn include personalized search results; a personalized feed of the entire internet, which learns from their Tinder-like swipes, without collecting or sharing personal data; and an ad-free experience.
Naoki Kamimeada, partner at Global Brain Corporation said: “The market for private online search is growing, but Xayn is head and shoulders above everyone else because of the way they’re re-thinking how finding information online should be.”
Kazuhiko Chuman, head of KDDI Open Innovation Fund, said: “This European discovery engine uniquely combines efficient AI with a privacy-protecting focus and a smooth user experience. At KDDI, we’re constantly on the lookout for companies that can shape the future with their expertise and technology. That’s why it was a perfect match for us.”
In addition to the three co-founders (Leif-Nissen Lundbæk, chief executive officer, Professor Michael Huth, chief research officer, and Felix Hahmann, chief operations officer), Dr Daniel von Heyl will come on board as chief financial officer. Frank Pepermans will take on the role of chief technology officer and Michael Briggs will join as chief growth officer.
Powered by WPeMatico
Canopy Servicing announced this morning it recently closed a $15 million Series A. The startup sells software to fintechs and others, allowing customers to create loan programs and service the resulting products.
The company raised a $3.5 million seed round in 2020. Canaan led its Series A, with participation from Homebrew, Foundation and BoxGroup, among others. Per Canopy, its valuation grew by 5x from its seed round to its Series A.
The company has raised $18.5 million to date.
So far this reads much like any other post announcing a new startup funding round, kicking off with an array of information concerning the round and who chipped into the transaction. Next, we’d probably note the competitors, growth and what investors in the company in question have to say about their recent purchase. This morning, however, I want to riff a bit on the future of fintech and how the financial tech stack of the future may be built.
TechCrunch chatted with Canopy CEO Matt Bivons last week. He has an interesting take on where fintech is headed. Let’s discuss it and work through what Canopy does.
As with many startups, Canopy was built to scratch an itch. Bivons had run into issues regarding loan servicing in prior jobs. He went on to found a startup that aimed to build a student credit card. But after working on that project, Bivons and co-founder Will Hanson pivoted the company to a B2B-focused concern building loan servicing technology.
Behind the decision was market research undertaken by the Canopy crew that uncovered that a great number of fintech startups wanted to get into the credit market. That makes sense; credit products can provide far more attractive economics to fintech startups than, say, checking and savings accounts. Knowing that loan servicing was a bear and a half to manage, Canopy decided to focus on it.
Bivons framed Canopy as a modern API for loan servicing that can be used to create and manage loans at any point in their lifecycle. He noted that what the startup is doing is akin to what several successful fintech companies have done, namely taking a piece of the fintech world and making it better for developers.
This is where Bivons’ view of the future of fintech products comes into play. According to the CEO, in the future, companies will not buy a monolithic financial technology stack. Instead, he thinks, they will buy the best API for each slice of the fintech world that they need to implement. This matters because we could argue that Canopy is targeting too small a product space. Not that its market isn’t large — debt and its servicing are massive problem spaces — but seeing a company find a niche to focus on makes more sense when its leaders expect focused fintech products to win out over large bundles of services.
Bivons added that much of the fintech focus of the last five years has been on debit, citing Chime, Step and Greenlight as examples. The next decade, he said, is going to focus on credit products. That would be good news for Canopy.

Canopy co-founders via the company. CTO Will Hanson (left) and CEO Matt Bivons (right).
Critically, and for the finance nerds out there, Bivons told TechCrunch that its loan servicing technology does not require the company to take on any credit risk, and that it has gross margins of around 90%. I never trust a too-round number, but the figure indicates that what Canopy has built could grow into an attractive business.
Today, Canopy is a traditional SaaS, though Bivons said that it wants to move toward usage-based pricing in time. Its service costs around 50 cents per account per month, or around $6 per year in its current form. Today, around 40% of Canopy’s customers are seed and Series A-scale startups, though Bivons noted that it is moving up the customer size chart over time.
The resulting growth is impressive. Canopy’s customer count grew 4.5x from February to May of 2021. Of course, Canopy is a young company, so its overall customer base could not have been massive at the start of the year. Still, that’s the sort of growth that makes investors sit up and pay attention, making the Canopy Series A somewhat unsurprising.
Fintech growth doesn’t seem to be slackening much, meaning that the market for what Canopy is selling should expand. Provided that its view that best-of-breed, more particular fintech products will beat larger stacks in the market, it could have an interesting trajectory ahead of it. And now that it has raised its Series A, we can start to annoy it with more concrete questions about its growth from here on out.
Powered by WPeMatico
James Evans, Richard Freling and Vinay Ayyala, co-founders at CommandBar, were working on a software product when they hit a wall while trying to access certain functionalities within the software.
That’s when the lightbulb moment happened and, in 2020, the team shifted to building an embeddable search widget to make software easier to use.
“We thought this paradigm feels like it could be useful, but it is hard to build well, so we built it,” Evans told TechCrunch.
On Monday, CommandBar emerged from beta and announced its $4.8 million seed round, led by Thrive Capital, with participation from Y Combinator, BoxGroup and a group of angel investors including, AngelList’s Naval Ravikant, Worklife Ventures’ Brianne Kimmel, StitchFix president Mike Smith and others.
CommandBar’s business-to-business tool, referred to as “command k,” was designed to make software simpler and faster to use. The technology is a search interface that sits on top of web-based apps so that users can access functionalities by searching simple keywords. It can also be used to boost new users with recommended prompts like referrals.
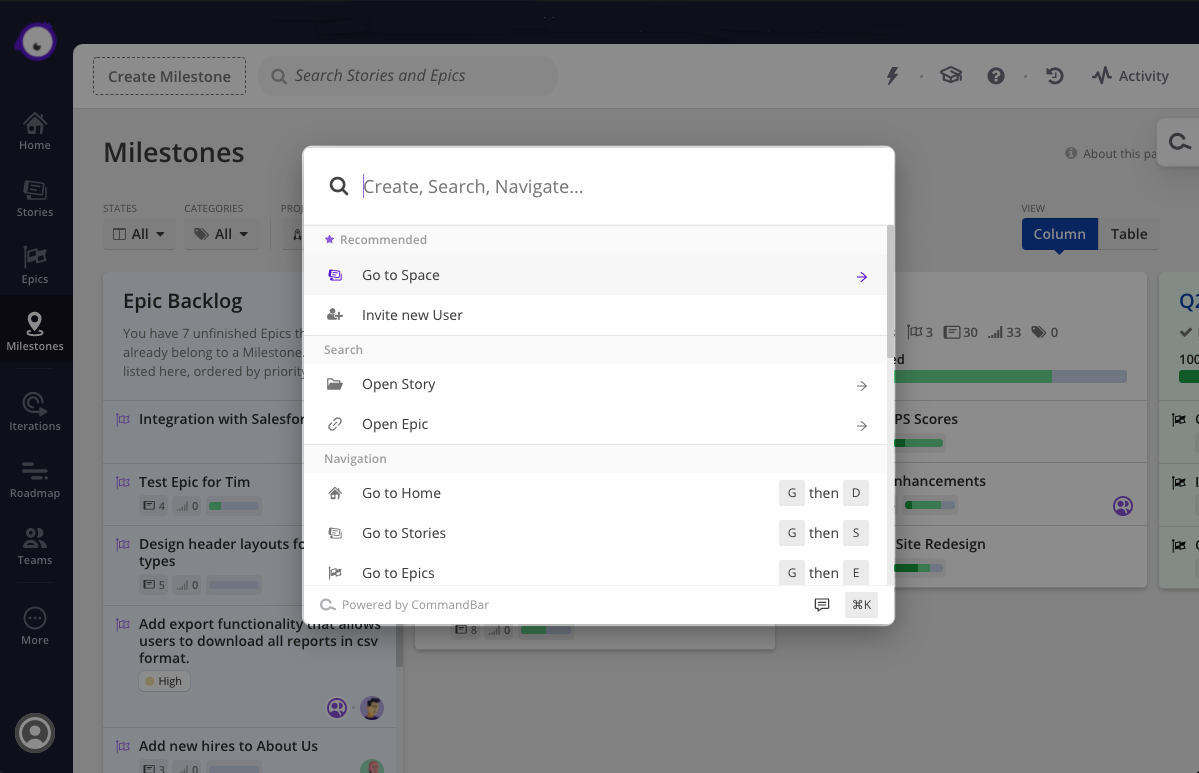
CommandBar in Clubhouse. Image Credits: CommandBar
Companies integrate CommandBar by pasting in a line of code and using configuration tools to quickly add commands relevant to their apps. The product was purposefully designed as low-code so that product and customer success teams can add configurations without relying on engineering support, Evans said.
Initially, it was a difficult sell: One of the more challenging parts in the early days of the company was helping customers and investors understand what CommandBar was doing.
“It was hard to describe over the phone, we had to try to get people on Zoom so they could see it,” he said. “It is easier now to sell the product because they can see it being used in an app. That is where many new users come from.”
CommandBar is already being used by companies like Clubhouse.io, Canix and Stacker that are serving hundreds of thousands of users. The most common use case for CommandBar so far is onboarding new software users.
He intends to use the new funding to grow the team, hiring across engineering, sales and marketing. The beta testing was successful in receiving good feedback from the early customers, and Evans wants to reflect that in new products and functionalities that will come out later this year.
Vince Hankes, an investor at Thrive Capital, was introduced to CommandBar through one of its pre-seed investors.
His interest is in B2B software companies and applications, and one of the things that became obvious to him while looking into the space was the natural tension between the simplicity and functionality of apps.
Apps are sometimes hard for even a power user to navigate, he said, but CommandBar makes something as simple as resetting a password easier by being able to search for that term and go right to that page if it is configured that way by the company.
“The types of companies interested in their product are impressive,” Hankes said. “We began to see demand from a broad range of companies that weren’t obvious. In fact, they are using CommandBar as a tool for deeper customer engagement.”
Powered by WPeMatico