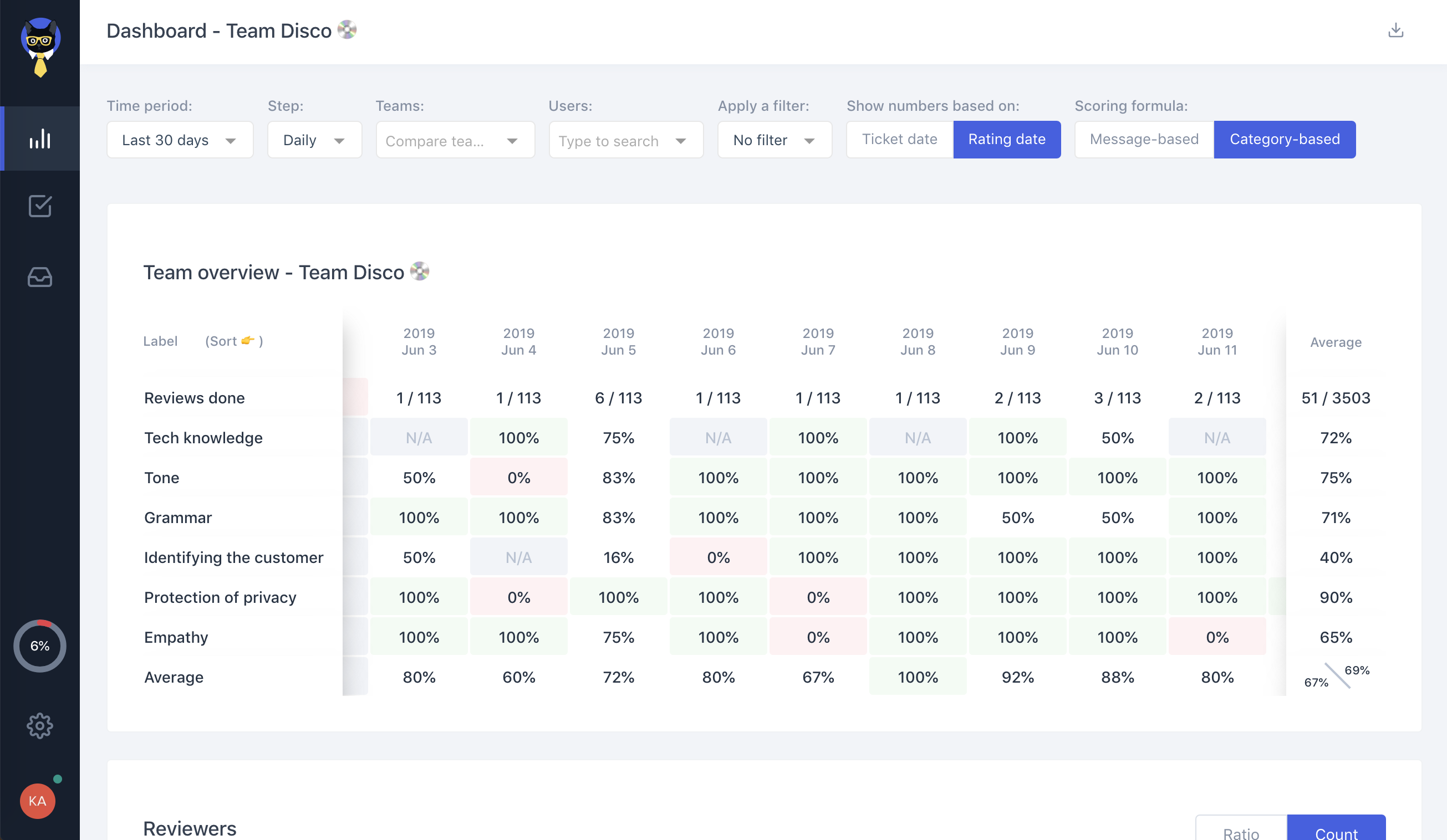
Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Larissa Russell and Fiona Lee founded a cookie startup called Green Pea Cookie in 2014. The cookies were 100% natural, vegan and “handcrafted with love.”
The company failed, but not because the cookies weren’t selling. The business couldn’t keep up with the antiquated wholesale food distribution system’s steep costs. Two incumbent players, United Natural Foods Inc. and KeHE Distributors, essentially controlled its only pathway to grocery stores across the country. So the founders shut down Green Pea and focused their efforts on building the tool Green Pea had needed to survive: Pod Foods, a distribution and logistics platform for emerging food brands.
“We were like so many other young entrepreneurs,” Russell, Pod Foods’ chief executive officer, tells TechCrunch. “I had studied government and economics and did the cookie company because I wanted to create something better for the world but we realized there was a much bigger issue at hand and it wasn’t enough to solve for the end product, we needed to solve for the way the product reached consumers.”
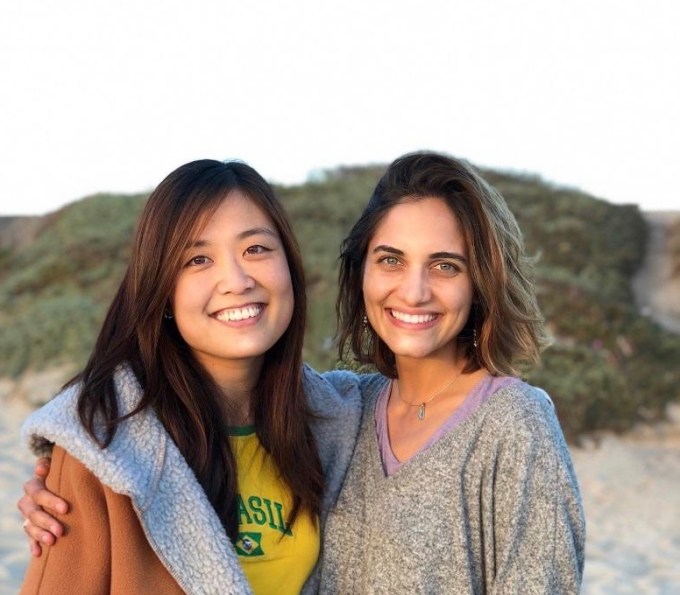

Pod Foods co-founders Fiona Lee (left) and Larissa Russell
“The distribution system hasn’t evolved since World War II,” Lee adds. “For so many years, there’s been little evolution in this space, even since the advent of technology and the internet.”
Today, Pod Foods is announcing a $3 million seed round led by Moment Ventures, with participation from M12 and Unshackled Ventures to fuel the growth of its software and data-enabled platform. The capital follows a $250,000 pre-seed investment from Unshackled, a venture capital firm that invests in immigrant founders and, if necessary, helps them navigate the complex visa process.
Lee immigrated to the U.S. from Singapore five years ago to double down on Green Pea Cookie. Her business partner, Russell, had been handling operations in the U.S. while she helped build the business from her home country. With Pod Foods up and running, the founders now have the opportunity to bring Green Pea back from the dead. Instead, they tell me their focus and efforts are entirely on scaling their B2B software upstart. Green Pea is gone for good.
Pod Foods is an end-to-end platform that connects retailers with manufacturers, facilitating the overly complex wholesale-food distribution market. The startup works with a third-party network that handles both fulfillment and logistics to create a tool beneficial to emerging brands, big retailers and consumers. The company charges retailers on a subscription basis and takes a cut of each transaction. The end goal is to simplify an age-old process, allow startup brands the opportunity to sell products inside big retailers and make great products accessible to customers at a lower price.
The San Francisco-based startup has launched in the Bay Area and Chicago. Currently, it’s working with 350 food brands and 100 retailers. With a fresh funding deal, Pod Foods plans to scale 10x in the next 12 months.
“We want to change the way food is distributed,” Russell said. “We want to turn [the system] on its head so the consumer can get what they would like to buy in retail stores at an affordable price.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Spacetech startup NSLComm is gearing up to put its first satellite into orbit, aboard a Russian Soyuz rocket launching this Friday at 1:42 AM ET. Not only is the launch a first for the company, but it’s also the first deployment of a new kind of satellite technology, an expandable antenna solution created by NSLComm which is the secret ingredient that will unlock a number of different lines of business for the fledgling Israeli startup.
“Satellite communication is too expensive,” explained NSLComm CEO and co-founder Raz Itzhaki in an interview. “And this is the case, because satellites are expensive. A communication satellite is basically a dish in space, you want more communication, you need a larger dish. But a larger dish requires a larger satellite, and a larger launcher, so everything becomes more expensive. This is why if you launch a geostationary communication satellite you have to launch it for 20 years, because it has an ROI of more than 10 years. It weighs tons because it needs to live for 15-20 years, and when you sell the capacity, you pay hundreds of billions per megabit per second per month, because you need to return the amount of investment in the satellite.”
What Raz and his team saw was that much of the size and weight for these high-powered communication satellites was actually due to the antennas they need to use to ensure they can achieve a good signal from space. These are either large and fixed, requiring a lot of extra launch hardware and protection as they make their way to space (which is not needed once in orbit), or, for unfolding antennas that existed previously, they require a lot of additional hardware to actually do the unfolding antenna deployment in space, adding again a bunch of bulk and weight. All of which translates to higher launch costs, the need for longer productive life spans for the satellites and higher costs for connectivity consumers.
NSLComm’s solution was to develop a new kind of antenna that can deploy on its own, without the help of any additional heavy machinery, and that can extend to the sizes needed to provide truly high-throughput connectivity on a satellite that’s small and much easier to launch, providing about 100 times faster connectivity than the fastest nano-satellites in the same size class today at about one-tenth the launch cost.
“Our approach was to develop an antenna based on SMP — that’s a shape memory polymer,” Itzhaki said. “This antenna is actually a 3D spring; it memorizes its shapes, it needs no opening mechanism, because the antenna itself is its own opening mechanism. So when you open a hatch, it jumps out like a jack-in-the-box. We have an antenna that is compacted to a volume that is so small, that it fits less than 1U [around the space of one rack in a multi-rack server configuration, or about 1.75 inches tall] for a 60 centimeter [about two feet] diameter dish. And the antenna weighs 140 grams. Well, this changes the economics of satellite communication.”
NSLComm intends to launch 30 satellites by 2021 and hundreds in total by 2023, but launching its own network is only one part of its business plan, and there are other ways it intends to generate revenue in the more immediate term. Itzhaki explained that, in fact, the startup has four primary ways of doing business, including first offering cost-effective ways for customer companies to build their constellations using the startup’s technology. Next, there’s a “turnkey” option for customers that can purchase satellite terminals and ground stations for specific use, including one client already who is using this for an IoT application. Itzhaki says there are already “many” of these types of arrangements in the pipeline.
Third, NSLComm intends to offer a “private constellation” offering, where, for example, a cruise ship operator could build, launch and operate its own network constellation for its customers at minimal cost. Finally, there’s a “constellation as a service” model, where NSLCom would launch the constellation itself, partner with an operator and sell the capacity of the network on a subscription basis.
To date, NSLComm has raised $16 million, including $12 million from VCs, including Jerusalem Venture Partners, OurCrowd, Cockpit Innovation and Liberty Technology Venture Capital. It’s also backed by the Israel Space Agency and the Office of the Chief Scientist in Israel, which provided the remaining $4 million in initial funding.
Powered by WPeMatico
“No bad conversations between companies and their customers is what we’re shooting for,” Kair Käsper tells me. He’s the head of Growth of a relatively new startup called Klaus, which he founded together with old high school friend Martin Kõiva.
Most recently the pair were employees at Pipedrive, holding the roles of director of Product Marketing and global head of Customer Support, respectively. Many years prior to that they shared a flat together and worked on a number of projects. One of those was an applicant-tracking startup called Jobkitten “that didn’t really go anywhere.”
The latest Käsper and Kõiva venture, however, appears to already be on firmer footing. Described as a “conversation review and QA tool for support teams,” Klaus is designed to help companies improve the quality of customer service. Two years in the making but only launched formally six months ago, customers already include Automattic, Wistia and Soundcloud. And today the Estonian startup is disclosing $1.9 million in seed funding led by Creandum, the first Baltic investment by the Swedish VC firm and the first from its new fund.
“The problem is that maintaining an even, high level of customer service quality is hard,” explains Käsper. “It becomes even harder if you have over 20,000 monthly conversations with customers and your support team is 100 people in three offices.
“As the head of customer support, you want everyone on your team to provide answers that meet with internal standards, regardless of how long they’ve been with the company or how seriously they take their job. You get very anxious in this situation, because you have no idea about what’s going on in those thousands of conversations. For you, no visibility means no control.”
He says that his and Kõiva’s firsthand experience at Pipedrive taught them that the key to quality assurance is going through past interactions and giving systematic feedback to agents. “Kind of like code review in engineering or the editorial process in writing,” he says. “Teams all over the world are discovering this now, but they almost always start with a manual process, managed in spreadsheets. They get stuck fast.”
To make this type of feedback loop more scalable, Klaus has created a purpose-built UI for giving internal feedback. Smartly, it also integrates with modern SaaS help desk solutions, such as Zendesk and Intercom.
“[The software also has] countless specialized features that allow you to focus on the actual feedback instead of managing a spreadsheet,” adds the Klaus head of Growth. They include the ability to easily filter out conversations for review, rate them based on a customized score card and notify agents of received feedback through email or Slack.
Meanwhile, the young company makes money by charging a monthly or yearly subscription fee based on how many users are connected to its app. In other words, just like Pipedrive before it, another classic enterprise SaaS play out of Estonia.
Update: An earlier version of this article wrongly said that Kair Käsper is CEO of Klaus; his job title is actually head of Growth.
Powered by WPeMatico
Cubyn, the Paris-based logistics startup that lets e-merchants outsource fulfillment and delivery logistics, has raised €12 million in new funding. The round is led by DN Capital, with participation from Partech Ventures, 360 Capital Partners, BNP Paribas Développement and the French investment bank BPI France.
The injection of capital is timed with the launch of “Cubyn Fulfillment,” as the company moves beyond pickup and delivery only. The new service is described as a fully integrated “first mile” solution that covers the entire fulfillment process, including keeping stock in Cubyn’s warehouses. It claims to be offered at a 30% lower price point than competitors.
“We want to make affordable world-class logistics accessible to every single e-merchant, whatever their size,” Cubyn co-founder and CEO Adrien Fernandez Baca tells TechCrunch. “Our typical customer is an e-merchant who sells across sales channels (marketplaces their own website). Size can go from 500 to 50,000 orders shipped per month.”
Launched in 2015, Cubyn says that in four years it has made more than 2 million shipments. It also reckons that because its tech is “built from the ground up,” the startup is well positioned to tackle fulfillment more efficiently than legacy players.
“Most direct competitors are the traditional third-party logistics players who missed the e-commerce revolution and lack technology intelligence,” says Baca. “We are 30% cheaper, with simpler multi-channel integrations and higher delivery quality. Less direct competitors are the fulfillment offer of marketplaces. They do offer a good logistics experience at a good price, but only for orders going through their marketplace.”
This, he argues, means there is a big gap in the market for a solution geared at multi-channel e-merchants. “We are marketplace agnostic and offer a seamless and high-quality multi-channel logistics,” adds the Cubyn CEO.
Specifically, the way the new Cubyn Fulfillment product works is as follows: An e-merchant signs up to Cubyn and plugs in their various sales channels, such as Amazon, Rakuten, eBay, Shopify etc. They then send Cubyn an appropriate amount of inventory to fulfill future orders, which is stored temporarily in a Cubyn warehouse. When an order is placed, Cubyn automatically packs the order and ships via the most suitable carrier to optimise for transit time and cost.
“Our customers pay based on the number of parcels they ship,” explains Baca. “Logistics is a game of volume and thanks to technology we can manage volumes that couldn’t be managed by historical players. This allow us to offer… cheaper prices and still have great margins.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Podimo, a Copenhagen-based startup building what it hopes will become Europe’s “Netflix for podcasts,” has raised €6 million in seed funding prior to launch. The round is co-led by Germany’s E.ventures and Denmark’s Heartcore, reflecting the young company’s two planned country launches later this year.
Founded by Morten Strunge, who has a track record in subscription media products via audio books service Mofibo (which he sold to Storytel), Podimo is hoping to capitalise on the rise in consumption in podcasts. Ambitiously, this will include both a free and paid version of its product, with the aim of creating a reliable revenue stream for podcast producers. The startup’s other founders are Nikolaj Koppel, Andreas Sachse and Sverre Dueholm.
“Podcasts have finally come of age and we are seeing a lot of demand for audio content globally across many different demographics,” Strunge tells me. “Consumers are increasingly looking for premium, ad-free services and we see a huge potential in the podcasting space.”
The Podimo app has been designed to provide a “superior experience” in discovery and recommendation compared to existing podcast streaming and download services. The idea, says Strunge, is to make it as seamless and easy as possible to find your next podcast.
“We believe that with the fast increasing amount of podcasts available, curation and discovery becomes more and more important to both unfold content in a relevant context and to the right individual user, which will benefit both podcast creators and consumers,” he says.
By launching a freemium model, where a paid version provides unlimited listening and features, Strunge believes there is an opportunity to work closely with podcast creators to strengthen the podcast ecosystem and make it less reliant on advertising revenue. “We want to become the preferred partner for creators, by both working closely with their content, curate and match it with each individual user, but also by offering a superior monetisation model,” he explains.
The hope then is that a more robust revenue stream will enable new podcasters to enter the market and allow existing ones to earn more. In turn that could give podcasters the financial headroom to invest even more time and effort into “creating great content.”
“Our dream is that with around 20% of people in Europe listening to podcasts on a weekly basis, many creators should be able to make a living out of creating podcasts, it shouldn’t just be for the few,” says Strunge, perhaps ignoring the fact that media often scales to become a hits-driven business. “We will offer revenue share to all existing podcasters out there, but also co-produce and produce original content,” he adds.
More broadly, Strunge says he remains a strong believer in audio as a format. He says not only is it easier to listen than it is to read but that podcasts are built for subscriptions. “It’s a short format, actuality driven, series driven and niche and broad at the same time,” says the Podimo CEO.
In addition, production costs are low so it’s possible to keep to a price point below music and VOD services, and Strunge is convinced we will continue to see a significant increase in the number of podcasts produced. This will include the broader market, but also podcasts from more professional media players yet to invest strategically in the audio format.
Powered by WPeMatico
The new era of tech-enabled banks is coming, even in regulation-heavy Japan. Kyash, a fintech company with visions on becoming Japan’s first challenger bank, said today it has raised $14 million to continue its expansion.
To be clear, Kyash isn’t a bank. Yet. But it is currently applying for a host of licenses in Japan that could allow it to offer banking-style features, including checking accounts, ATM withdrawals and money remittance. Right now, it is a payment app that offers a connected Visa card in the style of Monzo, N26, Revolut (which has a Japan license) and others of that ilk.
The startup was founded in 2015 by Shinichi Takatori, a former banker and management consultant who saw the potential to merge tech and finance.
“I really noticed that information and communication has become ubiquitous but money itself hasn’t changed for a long time,” Takatori told TechCrunch in an interview.
The company took some time — two years — before it released a consumer product, but it quickly tied up with Visa to offer a prepaid debit card that connects to the Kyash app. That provides benefits like instant payment notifications, clear balance and lower fees for overseas spending, while costs are borne by merchants rather than users. They might seem elementary today, but they are still not standard among Japan’s traditional banks, Takatori explained.
The company declined to share its user numbers, but Takatori said this new round of funding — Kyash’s Series B — is a validation of the progress it has made.
The $14 million investment is co-led by Goodwater Capital, a U.S. investor that has backed fintech startups like Monzo, Stash and Toss in Korea, and Mitsubishi UFJ Capital, the investment arm of Japan’s largest bank.
Mitsubishi’s involvement means that Kyash counts Japan’s three largest banks as investors, with SMBC and Mizuho having previously put money into the company. Others that took part in this Series B include Toppan Printing, JAFCO and Shinsei Corporate Investment Limited.
So many banks on the cap table might seem like a strange thing for a disruptor — let alone the banks, which tend to behave territorially — but Takatori believes that there’s the potential for cooperation, not to mention that it will help the startup with its licensing efforts. Already, he revealed, Mitsubishi plans to integrate its card with the Kyash app to provide its customers with the best of both worlds.
“We’re not here to win over existing banks, but instead inform [them of] how money should work in next decade,” explained Takatori. “So why not collaborate in some way.”
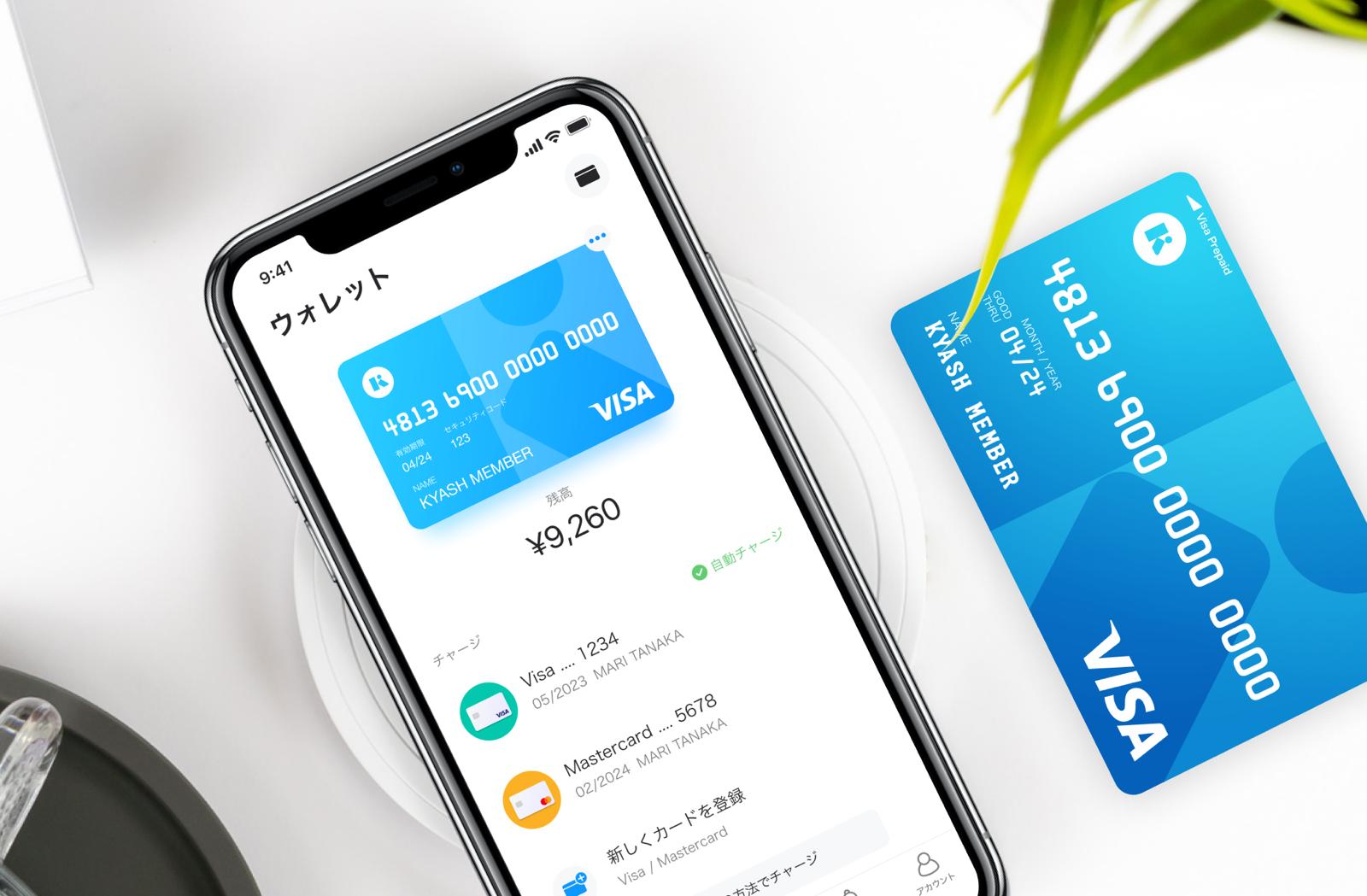
Kyash has a tie-up with Visa that allows it to offer its customers a connected debit card and also provide issuing services to other fintech startups
There’s also the fact that, even with a license, Kyash and others are unlikely to be able to offer full banking services. That means they will have to serve as complementary offerings to the industry, which would likely mean that cooperation is good — essential — for both sides.
But, beyond the consumer play, a notable piece of Kyash’s business that has investors excited is its B2B payment business.
The company developed its own payment processing system to reduce costs, which is one reason it took time to launch. Thanks to a tie-up with Visa, it offers both issuing and processing of prepaid Visa cards to fintech companies in Japan that want to go down the payment route.
That’s increasingly popular, given the government push to make the country a “cashless society” ahead of the 2020 Olympic Games next year. It also could appeal to crypto companies in Japan, which offers the world’s most robust licensing, that want to follow the example of the Coinbase card in Europe or startups like Crypto.com and TenX, which offer similar prepaid cards.
Takatori said Kyash is “in discussions” with crypto companies, but that it has not made a decision on how to proceed yet. The company is also eyeing potential overseas expansions, although that is some way down the line.
“We have open eyes for globalization, it’s just a matter of when,” he told TechCrunch. “We still have a far way to go [in Japan, but] maybe after the Olympics.”
More pressingly, he sees the company looking to raise a “pretty quick” Series C round to give it acceleration into next year. That’s likely to go to more expansion and user acquisition as the licenses the startup has applied for are unlikely to be granted this year.
Powered by WPeMatico
Kabbage, the AI-based small business loans platform backed by SoftBank and others, is adding more firepower to its lending machine: the Atlanta-based startup has secured an additional $200 million in the form of a revolving credit facility from an unnamed subsidiary of a large life insurance company, managed and administered by 20 Gates Management, and Atalaya Capital Management.
The money comes on the heels of a $700 million securitization Kabbage secured just three months ago and it is notable not just for its size but its terms: it’s a four-year facility, a length of time that underscores a level of confidence in the company’s performance.
Kabbage, which loans up to $250,000 in a single deal to small and medium businesses, has built a platform that harnesses the long tail of big data from across the web. It uses not just indicators from a company’s own public activities, but also sources comparative information from across a wider group of similar companies, with “2 million live data connections” currently helping to feed its algorithm.
Together, these help Kabbage determine whether to provide the loans, and at what rates. Notably, the whole process takes mere minutes, making Kabbage disruptive to the traditional route of applying for loans from banks, which can come at higher rates, often take longer to close and may never get approved.
The company was last valued at $1.2 billion in its most recent equity round from the Vision Fund in 2017, with about $500 million raised in equity to date from it and other investors, including BlueRun Ventures and Mohr Davidow Ventures. Rob Frohwein, the co-founder and CEO, confirmed to me via email that there are “no plans on the equity side right now.” We’ve asked about IPO plans and will update if we learn anything more on that front.
More importantly, alongside its equity story is the company’s business story: Kabbage has to date loaned out $7 billion in capital — amassed through securitizations and other facilities alongside that — to 185,000 businesses, and the company has seen an acceleration of business activity over the last two years. Nearly $700 million was loaned out in Q2 of this year, passing the record in Q1 of $600 million. This puts Kabbage on track to loan out between $2.4 billion and $3 billion this year.
“This transaction further diversifies Kabbage’s committed sources of funding and prepares us to meet the escalating demand for capital access among small businesses,” said Kabbage head of Capital Markets, Deepesh Jain, in a statement. “2019 has proven to be a tide-shifting year as customers accessed more than $670 million from Kabbage in Q2 2019, well surpassing our previously set record last quarter.”
While a lot of Kabbage’s business has come out of its direct consumer relationships, it’s also been expanding by way of more third-party relationships. It has white-label partnerships with banks to power their own loan offerings for SMBs, and earlier this year it was also tapped by e-commerce giant Alibaba to provide loans to its small business customers of up to $150,000 to help finance purchases, part of the latter company’s redoubled efforts to build out its business in the U.S. by way of its quiet acquisition of OpenSky.
Powered by WPeMatico
Even as much of the world is digitizing its governance, in small towns and villages of India, data about its citizens is still being largely logged on long and thick notebooks. Have they received the subsidized cooking gas cylinders? How frequent are the power cuts in the village? If these data points exist at all, they are probably stored in big paperbacks stacked in a corner of some agency’s office.
Five years ago, two young entrepreneurs — Prukalpa Sankar and Varun Banka — set out to modernize this system. They founded SocialCops, a startup that builds tools that make it easier for government officials — and anyone else — to quickly conduct surveys and maintain digital records that could be accessed from anywhere.
The Indian government was so impressed with SocialCops’ offering that it partnered with the startup on National Data Platform, a project to connect and bring more transparency within many of the state-run initiatives; and Ujjwala Yojana, a project to deliver subsidized cooking gas cylinders to poor women across the nation.
“This is a crucial step towards good governance through which we will be able to monitor everything centrally,” India’s Prime Minister Narendra Modi said of National Data Platform. “It will enable us to effectively monitor every village of the country.”
Two years ago, the duo wondered if the internal tools that they built for their own teams to manage their projects could help data teams around the world? The early results are in: Atlan, a startup they founded using learnings from SocialCops, has secured more than 200 customers from over 50 nations and has raised $2.5 million in pre-Series A funding led by Waterbridge Ventures, an early stage venture fund.
The startup, which employs about 80 people, has also received backing from Ratan Tata, Chairman Emeritus of conglomerate Tata Sons, Rajan Anandan, the former head of Google Southeast Asia, and 500 Startups. On Tuesday, Singapore-headquartered Atlan moved out of stealth mode.
The premise of Atlan’s products is simple. It’s built on the assumption that the way most people in enterprises deal with data is inefficient and broken, Sankar and Banka told TechCrunch in an interview. Typically, there is no central system to keep track of all these data points that often live in their own silos. This often results in people spending days to figure out what their compliance policy is, for instance.
“Atlan wants to democratize data inside organizations,” said Sankar.
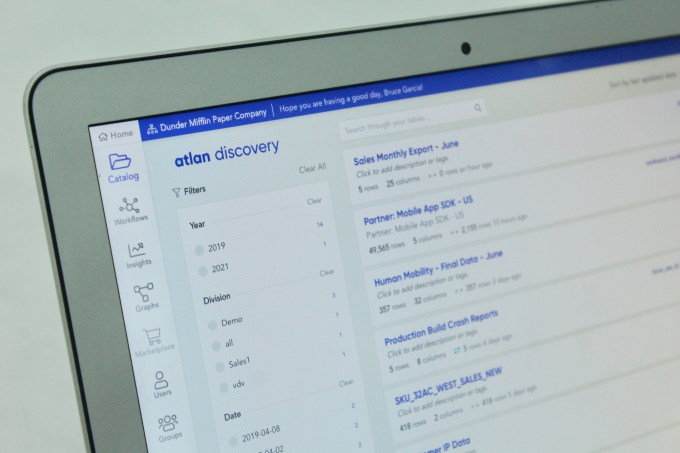
Teams within a typical company currently use a number of different tools to gather and manage data. Atlan has built products — dubbed Discovery, Grid, and Workflows — to create a collaboration layer, bringing together diverse data (from internal and external sources), tools and people to one interface.
“We are reimagining every human interaction with data. For instance, code has a profile on GitHub—what would a “profile” of data look like? What if you could share data as easily as a Google Sheets link, without worrying about the size or format? Or what would a data versioning and approval workflow look like? What if data scientists could acquire external data within minutes, instead of the months it takes right now?” said Banka.
The startup has also built a product called Collect that allows an organization to quickly deploy apps to collect granular data. These apps can collect data even when there is no internet connection. All of these data points, too, then find their way to the interface.
Atlan intends to use the capital it has raised on product development and sign more customers. It has already won some big names including Unilever, Milkbasket, Barbeque Nation, WPP and GroupM, Mahindra Group and InMobi in India, Chuan Lim Construction in Singapore, ServeHaiti in Haiti, Swansea University in the UK, the Ministry of Environment in Costa Rica, and Varun Beverages in Zambia.
In a prepared statement, Manish Kheterpal, Managing Partner at WaterBridge Ventures, said, “companies are struggling to overcome the friction that arises when diverse individuals need to collaborate, leading to project failure. The IPOs of companies like Slack and Zoom are proof that we live in the era of consumerization of the enterprise. With its sharp focus on data democratization, Atlan is well-positioned to reimagine the future of how data teams work.”
As for SocialCops, Sankar said it will live on as a data science community and pursue its signature “social good” mission.
Powered by WPeMatico
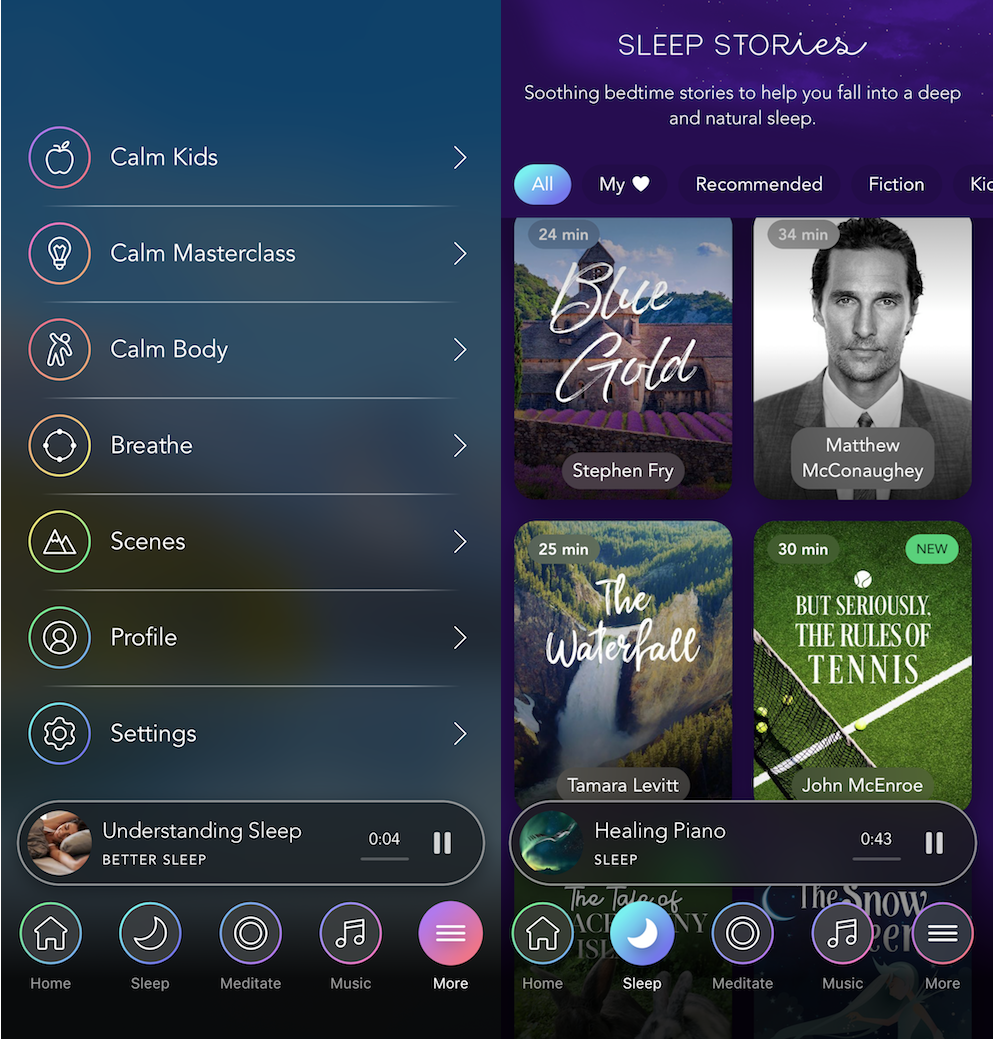
Meditation app unicorn Calm wants you to doze off to the dulcet tones of actor Matthew McConaughey’s southern drawl or writer Stephen Fry’s English accent. Calm’s Sleep Stories feature that launched last year is a hit, with more than 150 million listens from its 2 million paid subscribers and 50 million downloads. While lots of people want to meditate, they need to sleep. The seven-year-old app has finally found its must-have feature that makes it a habit rather than an aspiration.
Keen to capitalize on solving the insomnia problems plaguing people around the world, Lightspeed tells TechCrunch it has just invested $27 million into a Series B extension round in Calm alongside some celebrity angels at a $1 billion valuation. The cash will help the $70 per year subscription app further expand from guided meditations into more self-help masterclasses, stretching routines, relaxing music, breathing exercises, stories for children and celebrity readings that lull you to sleep.
The funding adds to Calm’s $88 million Series B led by TPG that was announced in February that was also at a $1 billion valuation, bringing the full B round to $115 million and Calm’s total funding to about $141 million. Lightspeed partner Nicole Quinn confirms the fund started talks with Calm around the same time as TPG, but took longer to finish due diligence, which is why the valuation didn’t grow despite Calm’s progress since February.
“Nicole and Lightspeed are valuable partners as we continue to double down on entertainment through our content,” Calm’s head of communications Alexia Marchetti tells me. The startup plans to announce more celebrity content tie-ins later this summer.
Broadening its appeal is critical for Calm amidst a crowded meditation app market that includes Headspace, Simple Habit and Insight Timer, plus newer entrants like Peloton’s mindfulness sessions and Journey’s live group classes. It’s become easy to find guided meditations online for free, so Calm needs to become a holistic mental wellness hub.
While it risks diluting its message by doing so much, Calm’s plethora of services could make it a gateway to more of your personal health spend, including therapy, meditation retreats and health merchandise from airy clothing to yoga mats. But subscription fees alone are powering a big business. Calm quadrupled revenue in 2018 to reach $150 million in ARR and hit profitability.
Calm is poised to keep up its rapid revenue growth. After the launch of Sleep Stories, “it was incredible to see the engagement spike up and also the retention,” says Quinn. Users can choose from having McConaughey describe the wonders of the cosmos, John McEnroe walk them through the rules of tennis, fairy tales like The Little Mermaid and more.
Quinn tells me “Sleep Stories is now a huge percentage of the business, and also the length of time people spend on the app has gone up dramatically.” She tells me that so many startups are “trying to invent a problem where there isn’t one.” But difficulty snoozing is so widespread and detrimental that users are eager to pay for an app instead of a sleeping pill. Having the Interstellar actor talk about the universe until I pass out sounds alright, alright, alright.

Powered by WPeMatico
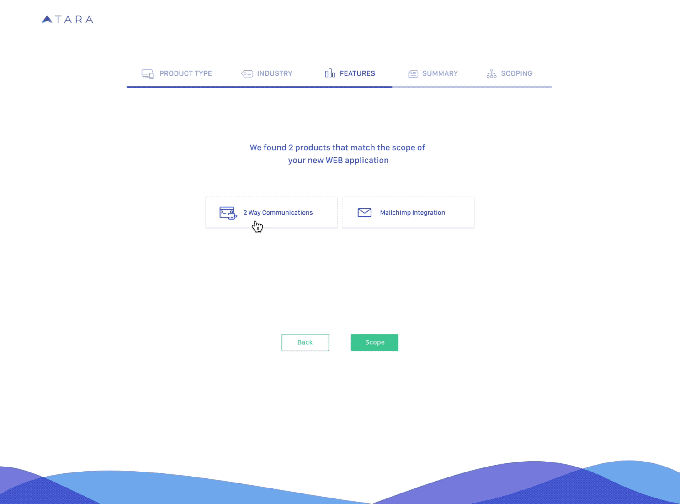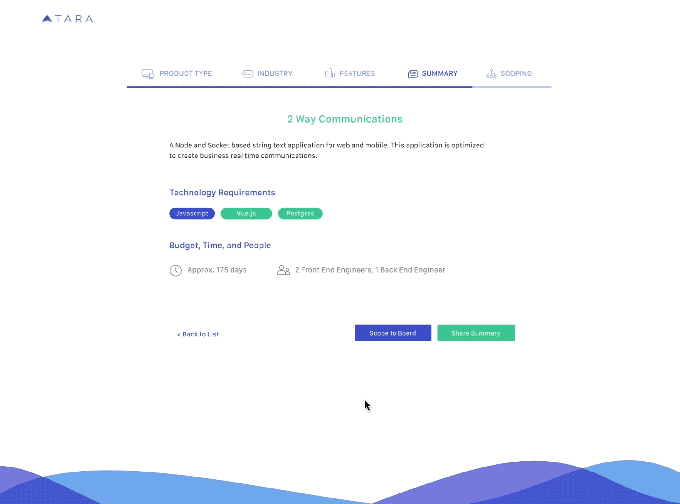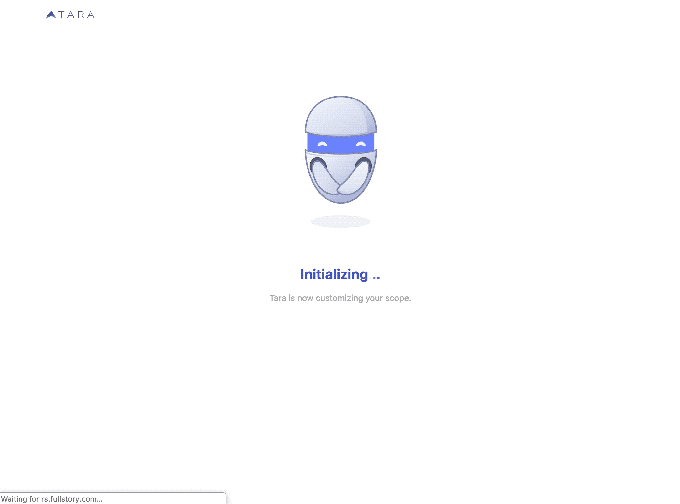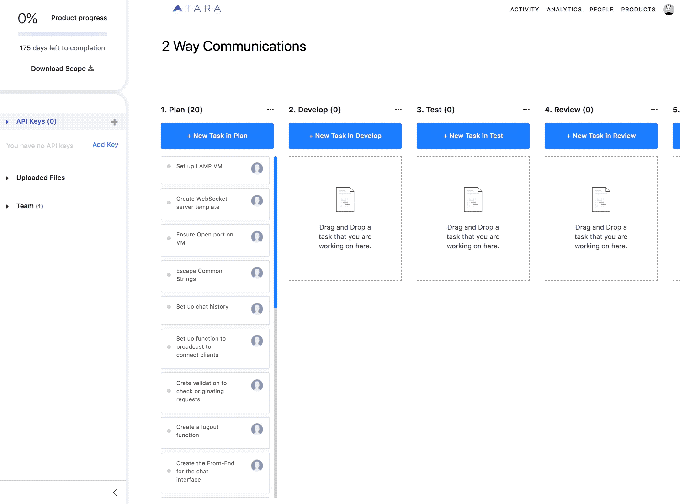
Artificial intelligence has become an increasingly important component of how a lot of technology works; now it’s also being applied to how technologists themselves work. Today, one of the startups building such a tool has raised some capital, Tara.ai, a platform that uses machine learning to help an organization get engineering projects done — from identifying and predicting the work that will need to be tackled, to sourcing talent to execute that, and then monitoring the project of that project — has raised a Series A of $10 million to continue building out its platform.
The funding for the company cofounded by Iba Masood (she is the CEO) and Syed Ahmed comes from an interesting group of investors that point to Tara’s origins, as well as how it sees its product developing over time.
The round was led by Aspect Ventures (the female-led firm that puts a notable but not exclusive emphasis on female-founded startups) with participation also from Slack, by way of its Slack Fund. Previous investors Y Combinator and Moment Ventures also participated in the round. (Y Combinator provides an avenue to companies from its cohorts to help them source their Series A rounds, and Tara.ai went through this process.)
Tara.ai was originally founded as Gradberry out of Y Combinator, with its initial focus on using an AI platform for organizations to evaluate and help source engineering talent: Tara.ai was originally that name of its AI engine.
(The origin of how Masood and Ahmed identified this problem was through their own direct experience: both were grads (she in finance, he in engineering) from the American University of Sharjah in the U.A.E. that had problems getting hired because no one had ever heard of their university. Even so, they had won an MIT-affiliated startup competition in Morocco and relocated to Boston. The idea with Gradberry was to cut through the big names and focus just on what people could do.)
Masood and Syed (who eventually got married) eventually realised that using that engine to evaluate the wider challenges of executing engineering projects came as a natural progression once the team started digging into the challenges and identifying what actually needed to be solved.
A study that McKinsey (where Masood once worked) conducted across some 5,000 projects found that $66 billion dollars were identified as “lost” due to projects running past the expected completion time, lack of adequate talent and just overall poor planning.
“We realised that recruiting was actually the final decision you make, not the first, and we wanted to be involved earlier in the decision-making process,” Masood said in an interview. “We saw a much bigger opportunity looking not at the people, but the whole project.”
In action, that means that Tara.ai is used not just to scope out the nature of the problem that needed to be solved, or the goal that an organization wanted to achieve; it is also used to suggest which frameworks will need to be used to execute on that goal, and then suggest a timeline to follow.
Then, it starts to evaluate a company’s own staff expertise, along with that from other recruiting platforms, to figure out which people to source from within the company. Eventually, that will also be complemented with sourcing information from outside the organization — either contractors or new hires.
Masood noted that a large proportion of users in the tech world today use Jira and platforms like it to manage projects. While there are some tools in Jira to help plan out projects better, Tara is proposing its platform as a kind of virtual project manager, or an assistant to an existing project manager, to conceive of the whole project, not just help with the admin of getting it done.
Notably, right now she says that some 75% of Tara.ai’s users — customers include Cisco, Orange Silicon Valley and Mower Digital — are “not technical,” meaning they themselves do not ship or use code. “This helps them understand what could be considered and the dependencies that can be expected out of a project,” she notes.
Lauren Kolodny, the partner at Aspect who led the investment, said that one of the things that stood out for her, in fact, with Tara.ai, was precisely how it could be applied exactly in those kinds of scenarios.
Today, tech is such a fundamental part of how a lot of businesses operate, but that doesn’t mean that every business is natively a technology one (think here of food and beverage companies as an example, or government agencies). In those cases, these companies would have traditionally had to turn to outside consultants to identify opportunities, and then build and potentially long-term operate whatever the solutions become. Now there is an opportunity to rethink how technology is used in these kinds of organizations.
“Projects have been hacked together from multiple systems, not really built in combination,” Kolodny said of how much development happens at these traditional businesses. “We are really excited about the machine learning scoping and mapping of internal and external talent, which is looking to be particularly important as traditional enterprises are required to get level with newer businesses, and the amount of talent they need to execute on these projects becomes challenging.”
Tara.ai’s next steps will involve essentially taking the building blocks of what you can think of as a very powerful talent and engineering project search engine, and making it more powerful. That will include integrating databases of external consultants and figuring out how best to have these in tandem with internal teams while keeping them working well together. And soon to come also will be bug prediction: how to identify these before they arise in a project. The company is releasing an updated AI engine to coincide with the funding.
The Slack investment is also a notable nod to what direction Tara.ai will take. Masood said that Slack was one of three “big tech” companies interested in investing in this round, and she and Syed chose Slack because from what they could see of its existing and target customers, many were already using it and some have already started requesting closer collaboration so that events in one could come up as updates in the other.
“Our largest customers are heavy Slack users and they are already having conversations in Slack related to projects in Tara.ai,” she said. “We are tackling the scoping element and now seeing how to link up even command line interfaces between the two.”
She noted that this does not rule out closer integrations with communications and other platforms that people use on a daily basis to get their work done: the idea is to become a tool to work better overall.
Powered by WPeMatico