Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Whatnot, a livestreaming shopping platform for collectors to buy and sell things like rare Pokémon cards and Funko Pops, has closed a $150 million Series C — its third round of fundraising in 2021 alone. This round pins Whatnot’s valuation at $1.5 billion, earning it a spot on the ever-growing list of unicorns.
So what’s a Whatnot? The app captures a trend that had been growing popular on platforms like Instagram in the U.S. (and was already hugely popular in China): live shopping. Verified sellers can go on the air at any time, hosting on-the-fly video auctions for their goods. Sometimes buyers know exactly what they’re getting. Other times it’s more of a mystery bag; with the popular “card break” concept, for example, users buy assigned portions of an unopened (and often itself rare) box of Pokémon or sports cards and watch its contents revealed live.
This round was funded by return investors a16z and Y Combinator’s Continuity Fund, along with one new firm joining them: CapitalG (which was known as Google Capital before the Google/Alphabet name change.) They’ve also added a few well-known names to their list of angel investors, including Andre Iguodala of the Golden State Warriors, Zion Williamson of the New Orleans Pelicans and Logan Paul of the YouTube. Initial word of this round broke last week, via The Information.
Whatnot originally started as a more standard (less live) resale platform, at first focused on authenticating just one kind of collectable: Funko Pops. As the pandemic took over and everyone was suddenly stuck at home, they leaned hard into live shopping — and grew rapidly as a result.
Meanwhile, the company has been quickly expanding its scope; it grew from just Funko Pops to all sorts of other collectables, including Pokémon cards, pins, vintage clothing, sneakers and more. Whatnot co-founder Grant Lafontaine tells me that its biggest driver is sports cards, followed by Pokémon and Funko Pops. With each category it dives into, Whatnot focuses on onboarding sellers that are already known and trusted in their respective community; each streamer on the platform is currently vetted by the company before they can go live, helping them keep fraud to a minimum. Doing anything sketchy just means getting booted off the platform and burning your own reputation in the process.
A few other key bits from my conversation with Lafontaine:
This round brings the company’s total funds raised to $225 million — pretty much all of that in the last year. Meanwhile, competition in the space is heating up; competitors like Popshop have been raising millions for their platforms, and Miami’s Loupe raised $12 million back in June (and is opening a physical retail space soon) with its focus laser-locked on sports cards live sales. Existing giants want in on it too: YouTube is playing with the live shopping concept, and Amazon has been bringing in influencers to host live sessions. In other words: watch this space. Maybe watch it via livestream.
Powered by WPeMatico
Fiberplane, an Amsterdam-based early-stage startup that is building collaborative notebooks for SREs (site reliability engineers) to collaborate around an incident in a similar manner to group editing in a Google Doc, announced a €7.5 million (approximately $8.8 million USD) seed round today.
The round was co-led by Crane Venture Partners and Notion Capital, with participation from Northzone, System.One and Basecase Capital.
Micha Hernandez van Leuffen (known as Mies) is founder and CEO at Fiberplane. When his previous startup, Werker, was sold to Oracle in 2017, Hernandez van Leuffen became part of a much larger company where he saw people struggling to deal with outages (which happen at every company).
“We were always going back and forth between metrics, logs and traces, what I always call this sort of treasure hunt, and figuring out what was the underlying root cause of an outage or downtime,” Hernandez van Leuffen told me.
He said that this experience led to a couple of key insights about incident response: First, you needed a centralized place to pull all the incident data together, and secondly that as a distributed team managing a distributed system you needed to collaborate in real time, often across different time zones.
When he left Oracle in August 2020, he began thinking about the idea of giving DevOps teams and SREs the same kind of group editing capabilities that other teams inside an organization have with tools like Google Docs or Notion and an idea for his new company began to take shape.
What he created with Fiberplane is a collaborative notebook for SRE’s to pull in the various data types and begin to work together to resolve the incident, while having a natural audit trail of what happened and how they resolved the issue. Different people can participate in this notebook, just as multiple people can edit a Google Doc, fulfilling that original vision.
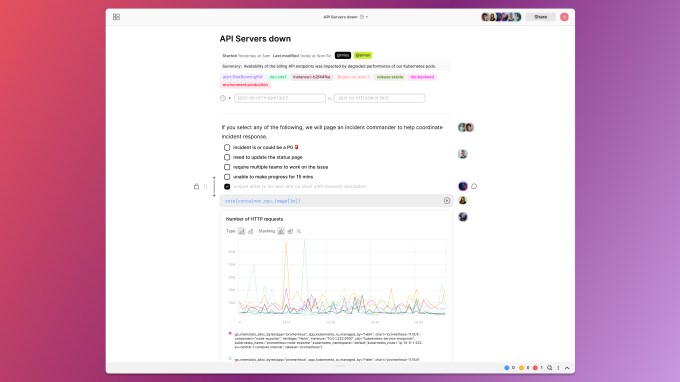
Fiberplane collaborative notebook example with multiple people involved. Image Credit: Fiberplane
He doesn’t plan to stop there though. The longer-term vision is an operational platform for SREs and DevOps teams to deal with every aspect of an outage. “This is our starting point, but we are planning to expand from there as more I would say an SRE workbench, where you’re also able to command and control your infrastructure,” he said.
Today the company has 13 employees and is growing, and as they do, they are exploring ways to make sure they are building a diverse company, looking at concrete strategies to find more diverse candidates.
“To hire diversely, we’re re-examining our top of the funnel processes. Our efforts include posting our jobs in communities of underrepresented people, running our job descriptions through a gender decoder and facilitating a larger time frame for jobs to remain open,” Elena Boroda, marketing manager at Fiberplane said.
While Hernandez van Leuffen is based in Amsterdam, the company has been hiring people in the U.K., Berlin, Copenhagen and the U.S., he said. The plan is to have Amsterdam as a central hub when offices reopen as the majority of employees are located there.
Powered by WPeMatico
APIs are the grease turning the gears and wheels for many organizations’ IT systems today, but as APIs grow in number and use, tracking how they work (or don’t work) together can become complex and potentially critical if something goes awry. Now, a startup that has built an innovative way to help with this is announcing some funding after getting traction with big enterprises adopting its approach.
Tyk, which has built a way for users to access and manage multiple internal enterprise APIs through a universal interface by way of GraphQL, has picked up $35 million, an investment that it will be using both for hiring and to continue enhancing and expanding the tools that it provides to users. Tyk has coined a term describing its approach to managing APIs and the data they produce — “universal data graph” — and today its tools are being used to manage APIs by some 10,000 businesses, including large enterprises like Starbucks, Societe Generale and Domino’s.
Scottish Equity Partners led the round, with participation also from MMC Ventures — its sole previous investor from a round in 2019 after boostrapping for its first five years. The startup is based out of London but works in a very distributed way — one of the co-founders is living in New Zealand currently — and it will be hiring and growing based on that principle, too. It has raised just over $40 million to date.
Tyk (pronounced like “tyke”, meaning small/lively child) got its start as an open source side project first for co-founder Martin Buhr, who is now the company’s CEO, while he was working elsewhere, as a “load testing thing,” in his words.
The shifts in IT toward service-oriented architectures, and building and using APIs to connect internal apps, led him to rethink the code and consider how it could be used to control APIs. Added to that was the fact that as far as Buhr could see, the API management platforms that were in the market at the time — some of the big names today include Kong, Apigee (now a part of Google), 3scale (now a part of RedHat and thus IBM), MuleSoft (now a part of Salesforce) — were not as flexible as his needs were. “So I built my own,” he said.
It was built as an open source tool, and some engineers at other companies started to use it. As it got more attention, some of the bigger companies interested in using it started to ask why he wasn’t charging for anything — a sure sign as any that there was probably a business to be built here, and more credibility to come if he charged for it.
“So we made the gateway open source, and the management part went into a licensing model,” he said. And Tyk was born as a startup co-founded with James Hirst, who is now the COO, who worked with Buhr at a digital agency some years before.
The key motivation behind building Tyk has stayed as its unique selling point for customers working in increasingly complex environments.
“What sparked interest in Tyk was that companies were unhappy with API management as it exists today,” Buhr noted, citing architectures using multiple clouds and multiple containers, creating more complexity that needed better management. “It was just the right time when containerization, Kubernetes and microservices were on the rise… The way we approach the multi-data and multi-vendor cloud model is super flexible and resilient to partitions, in a way that others have not been able to do.”
“You engage developers and deliver real value and it’s up to them to make the choice,” added Hirst. “We are responding to a clear shift in the market.”
One of the next frontiers that Tyk will tackle will be what happens within the management layer, specifically when there are potential conflicts with APIs.
“When a team using a microservice makes a breaking change, we want to bring that up and report that to the system,” Buhr said. “The plan is to flag the issue and test against it, and be able to say that a schema won’t work, and to identify why.”
Even before that is rolled out, though, Tyk’s customer list and its growth speak to a business on the cusp of a lot more.
“Martin and James have built a world-class team and the addition of this new capital will enable Tyk to accelerate the growth of its API management platform, particularly around the GraphQL focused Universal Data Graph product that launched earlier this year,” said Martin Brennan, a director at SEP, in a statement. “We are pleased to be supporting the team to achieve their global ambitions.”
Keith Davidson, a partner at SEP, is joining the Tyk board as a non-executive director with this round.
Powered by WPeMatico
In less than a year after raising $25 million in Series B funding, technical assessment company CodeSignal announced a $50 million in Series C funding to offer new features for its platform that helps companies make data-driven hiring decisions to find and test engineering talent.
Similar to attracting a big investor lead for its B round — Menlo Ventures — it has partnered with Index Ventures to lead the C round. Menlo participated again and was joined by Headline and A Capital. This round brings CodeSignal’s total fundraising to $87.5 million.
Co-founder and CEO Tigran Sloyan got the idea for the company from an experience his co-founder and friend Aram Shatakhtsyan had while trying to find an engineering job. Both from Armenia, the two went in different paths for college, with Shatakhtsyan staying in Armenia and Sloyan coming to the U.S. to study at MIT. He then went on to work at Google.
“As companies were recruiting myself and my classmates, Aram was trying to get his resume picked up, but wasn’t getting attention because of where he went to college, even though he was the greatest programmer I had ever known,” Sloyan told TechCrunch. “Hiring talent is the No. 1 problem companies say they have, but here was the best engineer, and no one would bring him in.”
They, along with Sophia Baik, started CodeSignal in 2015 to act as a self-driving interview platform that directly measures skills regardless of a person’s background. Like people needing to take a driver’s test in order to get a license, Sloyan calls the company’s technical assessment technology a “flight simulator for developers,” that gives candidates a simulated evaluation of their skills and comes back with a score and highlighted strengths.
The need by companies to hire engineers has led to CodeSignal growing 3.5 times in revenue year over year and to gather a customer list that includes Brex, Databricks, Facebook, Instacart, Robinhood, Upwork and Zoom.
Sloyan said the company has not yet touched the money it received in its Series B, but wanted to jump at the opportunity to work with Nina Achadjian, partner at Index Ventures, whom he had known for many years since their time together at Google. To work together and for Achadjian to join the company’s board was something “I couldn’t pass up,” Sloyan said.
When Achadjian moved over to venture capital, she helped Sloyan connect to mentors and angel investors while keeping an eye on the company. Hiring engineers is “mission critical” for technology companies, but what became more obvious to her was that engineering functions have become necessary for all companies, Achadjian explained.
While performing due diligence on the space, she saw traditional engineering cultures utilizing CodeSignal, but then would also see nontraditional companies like banks and insurance companies.
“Their traction was undeniable, and many of our portfolio companies were using CodeSignal,” she added. “It is rare to see a company accelerate growth at the stage they are at.”
U.S. Department of Labor statistics estimate there is already a global talent labor shortage of 40 million workers, and that number will grow to over 85 million by 2030. Achadjian says engineering jobs are also expected to increase during that time, and with all of those roles and applicants, vetting candidates will be more important than ever, as will the ability for candidates to apply from wherever they are.
The new funding enabled the company to launch its Integrated Development Environment for candidates to interact with relevant assessment experiences like codes, files and a terminal on a machine that is familiar with them, so that they can showcase their skills, while also being able to preview their application. At the same time, employers are able to assign each candidate the same coding task based on the open position.
In addition, Sloyan intends to triple the company’s headcount over the next couple of months and expand into other use cases for skills assessment.
Powered by WPeMatico
Performance reviews eat up a lot of a manager’s time and are often the most dreaded part of work. OnLoop aims to bring some joy into the process by enabling information-gathering to happen behind the scenes and be easier for hybrid workforces.
The Singapore-based company designed a mobile-first product that consistently gathers employee feedback and goals so that the company has better insights into how both individuals and teams are doing. The feedback is also captured and converted into auto-generated reviews that lay out all of the content collected for managers to then quickly put together a finished product.
The platform was in private beta since January 2021, and after a successful run with 25 companies, OnLoop raised $5.5 million co-led by MassMutual Ventures and Square Peg Capital along with Hustle Fund and a group of angel investors including XA Network, BCG’s Aliza Knox, Uber’s Andrew Macdonald, Ready’s Allen Penn, Google’s Bambos Kaisharis, Ripple’s Brooks Entwistle, Robert Hoyt, Nordstar’s Eddie Lee, Nas Academy’s Alex Dwek and hedge fund managers John Candeto and Keshav Lall.
OnLoop co-founder and CEO Projjal Ghatak spent over three years at Uber and said he saw his fair share of productivity tools, but still struggled to develop his own team as tasks and communication were done differently by each employee.
“This is the one problem that companies consistently complain about — not having the right tool to develop teams,” he added.
As someone who began spending more and more time on his phone, Ghatak wanted his product to be mobile-native and eliminate the need for managers to start from scratch on performance reviews each time. Rather than spend days gathering the information, as the name suggests, OnLoop continuously and automatically captures the data and converts it into a well-written summary.
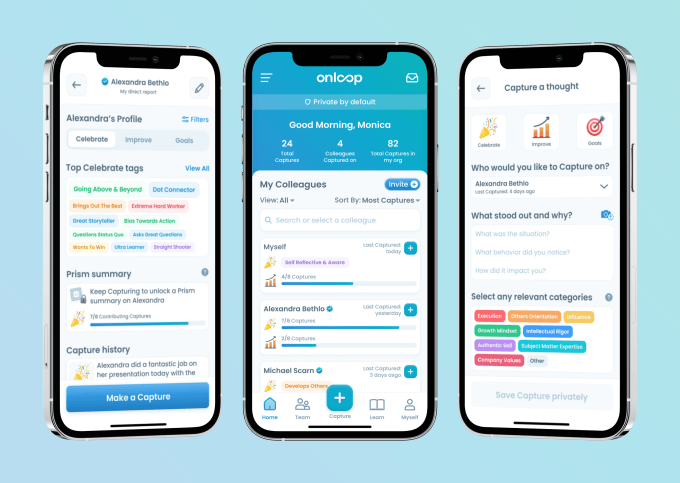
OnLoop app. Image Credits: OnLoop
Having that continuous loop of information is good for morale, he said. He points to data that shows regular self-reflection and feedback increased productivity by 20%, and a Gallup study where only 14% of employees thought their performance reviews inspired them to improve.
“A lot of company culture is set by the leaders, so as they want to drive this culture in their organizations, we are the tool that drives this,” Ghatak said. “Our job is to help educate the teams on how to do that well. We hear time and time again to make it fun and convenient. Teams don’t realize that if you are helping colleagues understand, showing them a light they didn’t have before, it will drive impact.”
The new funding will be mainly invested into product development and R&D, including expanding product, data and engineering teams. The company will also look at its sales and marketing framework. The company currently has 22 employees.
OnLoop was able to convert some of its early adopters into paying customers and is now focusing on figuring out a scalable way to get the product into the hands of more teams.
Piruze Sabuncu, partner at Square Peg Capital, experienced the pain of performance reviews when she was working in Stripe’s Southeast Asia and Hong Kong region. One of the challenges she faced working with regional teams was that an employee’s direct manager could be located elsewhere, yet work closely with a manager in their respective office.
Square Peg itself uses OnLoop, and Sabuncu said she liked that it is mobile-first and was designed in a way that people didn’t open it up and dread using it.
“Who your manager is, is a big question, but it shouldn’t matter,” she added. “It would still be my duty to be capturing and developing the person even if they were not my direct person. Everyone is talking about remote and hybrid work, and it is not going anywhere — it is here to stay. We believe this is a huge opportunity, a $400 billion market to disrupt, and OnLoop is providing better ways to communicate and give feedback.”
Editor’s note: Due to error, the round amount and lead investors were updated following the announcement.
Powered by WPeMatico
Tile, the maker of Bluetooth-powered lost item finder beacons and, more recently, a staunch Apple critic, announced today it has raised $40 million in non-dilutive debt financing from Capital IP. The funding will be put toward investment in Tile’s finding technologies, ahead of the company’s plan to unveil a new slate of products and features that the company believes will help it to better compete with Apple’s AirTags and further expand its market.
The company has been a longtime leader in the lost item finder space, offering consumers small devices they can attach to items — like handbags, luggage, bikes, wallets, keys and more — which can then be tracked using the Tile smartphone app for iOS or Android. When items go missing, the Tile app leverages Bluetooth to find the items and can make them play a sound. If the items are further afield, Tile taps into its broader finding network consisting of everyone who has the app installed on their phone and other access points. Through this network, Tile is able to automatically and anonymously communicate the lost item’s location back to its owner through their own Tile app.

Image Credits: Tile
Tile has also formed partnerships focused on integrating its finding network into over 40 different third-party devices, including those across audio, travel, wearables and PC categories. Notable brand partners include HP, Dell, Fitbit, Skullcandy, Away, Xfinity, Plantronics, Sennheiser, Bose, Intel and others. Tile says it’s seen 200% year-over-year growth on activations of these devices with its service embedded.
To date, Tile has sold more than 40 million devices and has over 425,000 paying customers — a metric it’s revealing for the first time. It doesn’t disclose its total number of users, both free and paid combined, however. During the first half of 2021, Tile says revenues increased by over 50%, but didn’t provide hard numbers.
While Tile admits that the COVID-19 pandemic had some impacts on international expansions, as some markets have been slower to rebound, it has still seen strong performance outside the U.S., and considers that a continued focus.
The pandemic, however, hasn’t been Tile’s only speed bump.
When Apple announced its plans to compete with the launch of AirTags, Tile went on record to call it unfair competition. Unlike Tile devices, Apple’s products could tap into the iPhone’s U1 chip to allow for more accurate finding through the use of ultra-wideband technologies available on newer iPhone models. Tile, meanwhile, has plans for its own ultra-wideband-powered device, but hadn’t been provided the same access. In other words, Apple gave its own lost item finder early, exclusive access to a feature that would allow it to differentiate itself from the competition. (Apple has since announced it’s making ultra-wideband APIs available to third-party developers, but this access wasn’t available from day one of AirTag’s arrival.)
Image Credits: Tile internal concept art
Tile has been vocal on the matter of Apple’s anti-competitive behavior, having testified in multiple congressional hearings alongside other Apple critics, like Spotify and Match. As a result of increased regulatory pressure, Apple later opened up its Find My network to third-party devices, in an effort to placate Tile and the other rivals its AirTags would disadvantage.
But Tile doesn’t want to route its customers to Apple’s first-party app — it intends to use its own app in order to compete based on its proprietary features and services. Among other things, this includes Tile’s subscriptions. A base plan is $29.99 per year, offering features like free battery replacement, smart alerts and location history. A $99.99 per year plan also adds insurance of sorts — it pays up to $1,000 per year for items it can’t find. (AirTag doesn’t do that.)
Despite its many differentiators, Tile faces steep competition from the ultra-wideband-capable AirTags, which have the advantage of tapping into Apple’s own finding network of potentially hundreds of millions of iPhone owners.
However, Tile CEO CJ Prober — who joined the company in 2018 — claims AirTag hasn’t impacted the company’s revenue or device sales.
“But that doesn’t take away from the fact that they’re making things harder for us,” he says of Apple. “We’re a growing business. We’re winning the hearts and minds of consumers… and they’re competing unfairly.”
“When you own the platform, you shouldn’t be able to identify a category that you want to enter, disadvantage the incumbents in that category, and then advantage yourself — like they did in our case,” he adds.
Tile is preparing to announce an upcoming product refresh that may allow it to better take on the AirTag. Presumably, this will include the pre-announced ultra-wideband version of Tile, but the company says full details will be shared next week. Tile may also expand its lineup in other ways that will allow it to better compete based on look and feel, size and shape, and functionality.
Tile’s last round of funding was $45 million in growth equity in 2019. Now it’s shifted to debt. In addition to new debt financing, Tile is also refinancing some of its existing debt with this fundraise, it says.
“My philosophy is it’s always good to have a mix of debt and equity. So some amount of debt on the balance sheet is good. And it doesn’t incur dilution to our shareholders,” Prober says. “We felt this was the right mix of capital choice for us.”
The company chose to work with Capital IP, a group it’s had a relationship with over the last three years, and who Tile had considered bringing on as an investor. The group has remained interested in Tile and excited about its trajectory, Prober notes.
“We are excited to partner with the Tile team as they continue to define and lead the finding category through hardware and software-based innovations,” said Capital IP’s Managing Partner Riyad Shahjahan, in a statement. “The impressive revenue growth and fast-climbing subscriber trends underline the value proposition that Tile delivers in a platform-agnostic manner, and were a critical driver in our decision to invest. The Tile team has an ambitious roadmap ahead and we look forward to supporting their entry into new markets and applications to further cement their market leadership,” he added.
Powered by WPeMatico
Sorcero announced Thursday a $10 million Series A round of funding to continue scaling its medical and technical language intelligence platform.
The latest funding round comes as the company, headquartered in Washington, D.C. and Cambridge, Massachusetts, sees increased demand for its advanced analytics from life sciences and technical companies. Sorcero’s natural language processing platform makes it easier for subject-matter experts to find answers to their questions to aid in better decision making.
CityRock Venture Partners, the growth fund of H/L Ventures, and Harmonix Fund co-led the round and were joined by new investors Rackhouse, Mighty Capital and Leawood VC, as well as existing investors, Castor Ventures and WorldQuant Ventures. The new investment gives Sorcero a total of $15.7 million in funding since it was founded in 2018.
Prior to starting Sorcero, Dipanwita Das, co-founder and CEO, told TechCrunch she was working in public policy, a place where scientific content is useful, but often a source of confusion and burden. She thought there had to be a more effective way to make better decisions across the healthcare value chain. That’s when she met co-founders Walter Bender and Richard Graves and started the company.
“Everything is in service of subject-matter experts being faster, better and less prone to errors,” Das said. “Advances of deep learning with accuracy add a lot of transparency. We are used by science affairs and regulatory teams whose jobs it is to collect scientific data and effectively communicate it to a variety of stakeholders.”
The total addressable market for language intelligence is big — Das estimated it to be $42 billion just for the life sciences sector. Due to the demand, the co-founders have seen the company grow at 324% year over year since 2020, she added.
Raising a Series A enables the company to serve more customers across the life sciences sector. The company will invest in talent in both engineering and on the commercial side. It will also put some funds into Sorcero’s go-to-market strategy to go after other use cases.
In the next 12 to 18 months, a big focus for the company will be scaling into product market fit in the medical affairs and regulatory space and closing new partnerships.
Oliver Libby, partner at CityRock Venture Partners, said Sorcero’s platform “provides the rails for AI solutions for companies” that have traditionally found issues with AI technologies as they try to integrate data sets that are already in existence in order to run analysis effectively on top of that.
Rather than have to build custom technology and connectors, Sorcero is “revolutionizing it, reducing time and increasing accuracy,” and if AI is to have a future, it needs a universal translator that plugs into everything, he said.
“One of the hallmarks in the response to COVID was how quickly the scientific community had to do revolutionary things,” Libby added. “The time to vaccine was almost a miracle of modern science. One of the first things they did was track medical resources and turn them into a hook for pharmaceutical companies. There couldn’t have been a better use case for Sorcero than COVID.”
Powered by WPeMatico
LinkedIn normalized the idea of making people’s resume’s visible to anyone who wanted to look at them, and today a startup that’s hoping to do the same for companies and how they are organized and run is announcing some funding. The Org, which wants to build a global, publicly viewable database of company organizational charts — and then utilize that database as a platform to power a host of other services — has raised $20 million, money that it will be using to hire more people, add on more org charts and launch new features, with a recruitment toolkit being first on the list.
The Series B is led by Tiger Global, with previous backers Sequoia, Founders Fund and Balderton Capital also participating alongside new investors Thursday Ventures, Lars Fjeldsoe-Nielsen (a former Balderton partner), Neeraj Arora (formative early WhatsApp exec), investor Gavin Baker, and more. From what we understand, the investment values The Org at $100 million.
Founders Fund led the company’s last round, a Series A in February 2020, and the whole world of work has really changed a lot in the interim because of COVID-19: companies have become more distributed (a result of offices shutting down); the make-up of businesses has changed because of new demands; and many of us have had our sense of connection to our jobs tested in ways that we never thought it would.
All of that has had a massive impact on The Org, and has played into its theory of why org charts are useful, and most useful as a tool for transparency.
“In many ways the pandemic has forced us to reevaluate the norms of how work happens. One of the misconceptions was the idea that you are only working when you are at the office, 9-5. But the future of work is a hybrid set up but you get a lot of issues that arise out of that, communication being one of them. Now it’s much more important to create alignment, a sense of connection, and really feeling a sense of belonging in your company,” Christian Wylonis, the CEO who co-founded the company with Andreas Jarbøl, said in an interview (the two are pictured below). “We think that a lot of these issues are rooted around transparency and that is what The Org is about. Who is doing what, and why?”

Image Credits: The Org
He said that when the coronavirus suddenly ramped up into a global issue — and it really was sudden; our conversation in February 2020 had nothing whatsoever to do with it, yet it was only weeks later that everything shut down — it wasn’t obvious that The Org would have a place in the so-called “new normal.”
“We were as nervous as anyone else, but the idea of what work would look like and how we enable people around that has gotten a lot higher on the agenda,” he said. “The appetite for new tools has improved dramatically, and we can see that in our traffic.”
The Org has indeed seen some very impressive growth. The company now hosts some 130,000 public org charts, sees 30,000 daily visitors and has more than 120,000 registered users. And more casual usage has boomed, too. Wylonis notes that The Org now has close to 1 million visitors each month versus just 100,000 in February 2020, when it only had 16,000 org charts on its platform.
Monetization is coming slowly for the startup. Building, editing and officially “claiming” a profile on the platform are all still free, but in the meantime The Org is working on its platform play and using the database that it is building to power other services. Job hunting is the first area that it will tackle.
Posting jobs will be free, and it’s integrating with Greenhouse to feed information into its system, but recruiters and HR pros are given an option to manage the sourcing and screening process through The Org, a kind of executive recruitment tool, which will come at a charge. Down the line there are plans for more communications and HR tools, Wylonis said. Some of this will be built by way of integrations and APIs with other services, and some tools — such as communications features — will be built in-house, from the ground up.
When I covered the company’s last round, I’d noted that there were some obvious hurdles for The Org, as well as potentially others like Charthop or Visier building business models on providing more transparency and information around hiring and how companies are run.
Sometimes the companies in question don’t actually want to have more transparency. And any database that is based around self-reporting runs the risk of being only as good as the data that is put into it — meaning it may be incomplete, or simply wrong, or just presented to the contributors’ best advantage, not that of the company itself. (This is one of the issues with LinkedIn, too: Even with people’s resumes being public, it’s still very easy to lie about what you actually do, or have done.)
So far, the theory is that some of this will be resolved by way of who The Org is targeting and how it is growing. Today the company’s “sweet spot” is early-stage startups with about 50-200 employees, and generally org charts are created for these businesses in part by The Org itself, and then largely by way of wiki-style user-edited content (anyone with a company email can get involved).
The plan is both to continue working with those smaller startups as they scale up, but also target bigger and bigger businesses. These, however, can be trickier to snag — not least because they will stretch into the realm of public companies, but also because their charts will be more complicated to map and manage consistently. For that reason, The Org is also adding in more features around how companies can “claim” their profiles, including managing permissions for who can edit profiles.
This might mean more managed public profiles, but the idea is that it will be a start, and once more companies post more information, we will see more transparency overall, not unlike how LinkedIn evolved, Wylonis said.
The LinkedIn analogy is interesting for another reason. It seems a no-brainer that LinkedIn, which is at its heart a massive database of information about the world of professional work, and the people and companies involved in it, would have wanted to build its own version of org charts at some point. And yet it hasn’t.
Some of this might be down to how LinkedIn has fundamentally built and organised its own database and knowledge graph, but Wylonis believes it might also be a conceptual difference.
“We think that this might be the fundamental difference between us and them,” Wylonis said of LinkedIn. “They are a database of resumes. ‘I can say whatever I want.’ But for us, the atomic unit is the organization itself. That is an important distinction because it’s a one to many relationship. It can’t be only me editing my profile. And allows us to build structures.”
He added that this was one of the reasons that Keith Rabois — who was an early exec at LinkedIn — became an early investor in The Org: “LinkedIn has been looking at this forever, but they haven’t been able to build it, and so that is how we caught his attention.”
Powered by WPeMatico
CoderSchool, a Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam-based online coding school startup, announced today $2.6 million in pre-Series A funding to scale up its online coding school platform.
This round was led by Monk’s Hill Ventures, with participation from returning seed investors Iterative, XA Network and iSeed Ventures. CoderSchool raised a seed round led by TRIVE Ventures in 2018.
CoderSchool will use the funding to accelerate its online teaching platform growth and technology infrastructure expansion for the company’s technical education programs that guarantee employment upon graduation.
The company, founded in 2015 by Charles Lee and Harley Trung, who previously worked as software engineers, pivoted from offline to online in early 2020 to bring high-quality technical training to everyone, everywhere. After switching to a fully online learning program, the company recorded 100% quarter-over-quarter (QoQ) growth in fully online enrollment, it said in a statement.
“Coding is the future. At CoderSchool, we believe everyone in Southeast Asia deserves a chance to be part of that future,” the company co-founder and CEO Lee said.
In Vietnam, the demand for IT talent is dramatically increasing by 47% a year, while supply is only increasing by 8% year-on-year.
“The need for strong engineers and developers in Southeast Asia has never been as pertinent as it is today with the growth of tech companies and digital businesses,” said Michele Daoud, partner of Monk’s Hill Ventures. “We have been impressed by the team’s focus on setting the standard for coding education in the region. We are excited to partner with CoderSchool to provide both opportunity and access to the millions of aspiring students in Vietnam.”
Given the strong engineer demand in Vietnam, the domestic market size is estimated between $100 million – $200 million, and still increasing every year, according to Lee. CoderSchool has been focusing on Vietnam for the last six years, but plans to enter the global market following the next round, Lee said, without providing exact timetable.
CoderSchool, which offers full-stack web development, machine learning and data sciences courses at a lower cost, has trained more than 2,000 alumni up to date, and recorded over 80% job placement rate for full-time graduates, getting jobs at companies such as BOSCHE, Microsoft, Lazada, Shopee, FE Credit, FPT Software, Sendo, Tiki and Momo.
“After having taught over 2,000 students, we’ve been able to refine our [coding education] content. We rewrote our full-stack web development course — from Ruby, Phyton to JavaScript — in two years, and added new machine learning and data science courses to our program,” Lee told TechCrunch.
CorderSchool’s online program enables students to interact with instructors and classmates before, during and after scheduled class sessions with its human-driven learning strategy. CoderSchool currently has 15 instructional staff, and plans to hire 35 additional instructors by Q4 2022.
CoderSchool’s data analytics has improved individual student performance while also allowing CoderSchool to increase its classroom size at scale, reaching a peak of 107 enrollments in a data science class.
Powered by WPeMatico
A 22-month-old startup that is helping millions of blue- and gray-collar workers in India learn new skills and find jobs has become the youngest firm to join the coveted unicorn status in the world’s second-largest internet market.
Apna announced on Thursday that it has raised $100 million in a round led by Tiger Global. The new round — a Series C — valued Apna at $1.1 billion. TechCrunch reported last month that Tiger Global, an existing investor in Apna, was in talks to lead a $100 million financing round in the startup at the unicorn valuation.
Owl Ventures, Insight Partners, Sequoia Capital India, Maverick Ventures and GSV Ventures also participated in the new round, which is the third investment secured by Apna this year. Apna was valued at $570 million in its Series B round in June this year.
The investors’ excitement comes as Apna has demonstrated an impressive growth in recent months. The startup has amassed over 16 million users on its 15-month-old eponymous Android app, up from 10 million in June this year.
Indian cities are home to hundreds of millions of low-skilled workers who hail from villages in search of work. Many of them have lost their jobs amid the coronavirus pandemic that has slowed several economic activities in the South Asian market.
Apna has built a platform that provides a community to these workers. In the community, they engage with each other, exchange notes to perform better at interviews and share tips to negotiate better compensation.
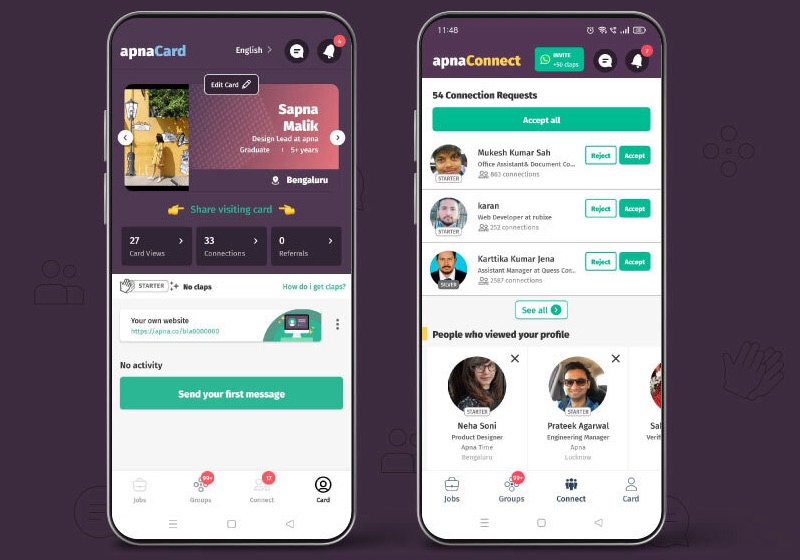
Image Credits: Apna
On top of this, Apna connects these workers to potential employers. In an interview with TechCrunch, Apna founder and chief executive Nirmit Parikh said more than 150,000 employers — including Zomato, Bharti AXA, Urban Company, BYJU’S, PhonePe, Burger King, Delhivery, Teamlease and G4S Global — are on the platform, and over 5 million jobs are active.
The startup, whose name is inspired from a cheerful 2019 Bollywood song, has facilitated over 18 million job interviews in the past 30 days, he said. Apna is currently operational in 28 Indian cities.
The idea for Apna came, Parikh has said, after he was puzzled to find that even as there are hundreds of millions of blue- and gray-collar workers in India, locating them when you need assistance with a task often proves very difficult.
Prior to starting Apna, Parikh, who previously worked at Apple, met these workers and went undercover as an electrician and floor manager to understand the problems they were facing. The problem, he found, was the disconnect. Workers had no means to find who needed them for jobs, and they were also not connected with one another. The community aspect of Apna, which now has over 70 such groups, is aimed at addressing this challenge.
The Apna app allows these workers to learn new skills to become eligible for more work opportunities. Apna has emerged as one of the fastest growing upskilling platforms — and that would explain why GSV Ventures and Owl Ventures, two high-profile firms known to back edtech startups, are investing in the Bangalore-based firm.
“Apna’s viral adoption is driven by a novel social and interactive approach to connecting employers with job seekers. We expect job seekers in search of meaningful connections and vetted opportunities to drive Apna’s continued explosive growth across India — and the world,” said Griffin Schroeder, partner at Tiger Global, in a statement.
Now the startup, which has started to monetize the platform, is ready to aggressively expand. Parikh said Apna will continue to expand to more cities in India and by early next year, Apna will begin its global expansion. Parikh said the startup is eyeing expansion in the USA, South East Asia and Middle East and Africa.
“We have already created a dent. Now we want to impact the lives of 2.3 billion,” he said. “We will require crazy amounts of resources and a world-class team to deliver. It’s a herculean task, and is going to take a village. But somebody has to solve it.”
Powered by WPeMatico