Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Our body is continuously storing and consuming energy to keep us alive — but understanding which fuels are being used and why is the Holy Grail of things like weight loss and body hacking. Today’s weight-loss market is saturated with generic products because — guess what — trying to tailor-make a solution for an individual is usually hard and expensive.
For a while now there’s been a technology around which can measure the metabolic gases found in your breath. The theory goes that if you can do that, everyone can work out what they should be eating and when. A few startups have tried, but nothing really took off. Now a new startup is having a crack and has secured significant funding to go for it.
Lumen is a pocket-sized device that measures the gases in your breath and translates that reading via an app into advice that gives you daily personalized meal plans.
As I said, this technology was tried by a startup called PATH Breath+Band, which had a similar device in 2016, but which didn’t take off.
The difference with Lumen is that it’s raised a decent war chest, as well as blowing up on Indiegogo.
It’s now raised a total of $7 million over the past four and a half years, from a host of investors. These include Disruptive VC, Oren Zeev, Red Swan Ventures, Resolute Ventures, Gigi Levy, Sir Ronald Cohen, Avishai Abrahami (Wix Founder) and RiverPark Funds. As part of that funding it’s also – in the last few days – raised more than $1 million on Indiegogo.
The founders are Merav Mor, a doctor of physiology (PhD) and cell biology and her twin sister, Michal Mor, also a doctor of physiology (PhD) and cell biology. CEO Daniel Tal is also a co-founder and also founded Wibiya, which was acquired by Conduit. It probably doesn’t hurt that the renowned Frog design helped in the, well, design.
As endurance athletes, the Mors began researching if there was a way for them to understand the impact of their nutrition and workouts on their bodies to improve their athletic performance. They came across a metabolic measurement called RQ (Respiratory Quotient), which is the gold standard for measuring the metabolic fuel usage of an individual. Top-performing athletes have been using this measurement for years, but the methods for measuring it are invasive (blood test), lengthy (1+ hour in metabolic chambers) and expensive (upwards of a few hundred dollars).
After four years of research and development they developed Lumen, with the ability to measure an individual’s RQ in one breath. What once took over an hour to measure, and a team of nutritionists and scientists to analyze, can now be done in less than three minutes. Michal and Merav’s technology is patent-pending.
So far Lumen says more than 300 beta users have lost an average of 6.8 lbs within the first 30 days of using the device.
Now, they do have competitors. These include Habit, which does pre-packaged personalized meals; Breezing, a technology that requires three minutes of continual breathing and the purchase of new cartridges with every measurement ($5); and Levl, which is a small home-lab setup that measures metabolism and ketosis and costs between $100-150/month. Then there is Ketonix, a computer-connected device that will only provide data on fat burn for users on a strict ketogenic diet.
But with Lumen you just buy the device and the app is free. No cartridges, filters or replacements.
All in all it’s quite a compelling proposition, so it will be interesting to see if Lumen can succeed where others have failed.
Powered by WPeMatico
A company called Rentlogic has raised $2.4 million to take the guesswork out of determining whether that cheap, beautiful New York apartment is actually a deathtrap wrapped in a brownstone’s clothing.
Renting in New York is murder already, but using Rentlogic, apartment hunters can figure out if their new housing situation could actually kill them (or put them at significant risk of bodily or property harm… or even minor inconveniences).
Investors in the company’s seed round include the Urban-X accelerator (which is a partnership between Urban.US and Mini); Urban.Us, an investor in urban technologies; the millennial-entrepreneur-focused investment firm, Kairos; and Seagram beverage company scion Edgar Bronfman, Jr.
Rentlogic already provides a grade for every building in New York — more than 1 million properties — but has added an inspection feature that it charges landlords for so that they can display a rating outside of their building. It’s like the city’s scoring grades for restaurants in neighborhoods.
“We grade every single property in New York,” says Yale Fox, the company’s founder and chief executive. “We have inspected 103 properties. Everybody is really happy with it and everybody is going to re-sign and we’re going to start scaling this out to every property in New York.”

Rentlogic scores buildings on a combination of around 150 different variables, including the ability to provide continuous heat and hot water, and whether or not a building has evidence of bed bugs or rodents.
The looks of the building doesn’t matter, Fox says. It’s more about the conditions of the building.
“It’s the same way a building would get LEED-certified,” says Fox. “It’s a good way for one landlord to differentiate their property as higher quality than a competitor’s in the same neighborhood.”
Launched initially in 2013, Rentlogic was born out of Fox’s own tragic experience as a new renter in New York. The Canadian transplant (and the son of a family of real estate professionals and small scale landlords) had come to the city for a new job and was looking at an apartment in the West Village.
After shelling out a $12,000 deposit for first month’s rent, last month’s rent and a security deposit, Fox settled into his abode in the tree-lined luxury of one of Manhattan’s most sought-after neighborhoods. The love affair with the building didn’t last long.
Unexpectedly, Fox started to become sick. Several visits to the doctor couldn’t identify a cause for his illness, until, finally, his physician suggested a mold-related illness.
“I asked the landlord to fix it and I wound up having to take the landlord to court,” says Fox.
By the time the court date arrived, Fox had paid to fix the mold problem himself and had little in the way of solid evidence to show a judge. So he built an app that would track the public complaints filed against the landlord and the public assessments that had been done on the building.
“I went to court and I showed the judge this model that I had put together and he said, ‘Welcome to New York and I’m sorry this happened to you… and you should definitely build an app, because New York City needs this.’”

Rentlogic founder Yale Fox
Fox, already enrolled in the TED Fellows program, built the app, initially called “RentCheck” and began marketing it to landlords and renters. “It was just a hobby because I was so angry about how things had happened to me,” says Fox. “We didn’t want to charge renters fees to the site. We thought having equal access to information could prevent this from happening in the future.”
Things continued as a nonprofit for a while until last year Fox hit on a business model. He designed a ratings card for the building based on the data his company had collected and showed it to his current landlord. “She said, ‘How much would you charge for it?’” Fox recalled.
Thus RentCheck became Rentlogic and a business was born. Fox charges landlords for assessments and to display a ratings placard that indicates the building’s grade.
Renters are willing to pay up to an additional $45 per month, according to a white paper, to sign a lease in a building that’s been independently certified. “People are willing to pay a little bit more just to not deal with the constant headaches that happen in certain kinds of buildings,” he said.
Fox appears to have launched Rentlogic at the right time. The market for housing in New York has softened as luxury apartments flood the market and demand softens, meaning that rents are coming down across the board.
But beyond being more competitive there’s a defensive aspect to getting rated in a market filled with demanding, complaint-prone consumers that have no qualms savaging any business, from landlords to local restaurants (although oftentimes the landlords and restaurants deserve it).
“A lot of times landlords are purchasing this because there’s no way to prove they’re not a one-star landlord,” Fox says. “This is accessible for big landlords and small landlords. In a zero-transparency and low-accountability marketplace, there’s no incentive for bad actors to improve their behavior, but with Rentlogic there is.”
The company is already making institutional moves. Fox has inked a deal with Blackstone about providing ratings for their $5.5 billion Stuyvesant Town acquisition on the Lower East Side, according to Fox. In addition, the company has partnered with a number of real estate brokers and roommate-hunting services like Nooklyn and Roomi to use its ratings.
While Rentlogic is scrupulous about using data to train its algorithm, it’s also transparent about how the algorithm works, according to Fox.
“Algorithms control so much what’s going on in the world and people just don’t understand them,” he says. So in the interest of full transparency, the company is putting together a building simulator where users can add problems and see how it affects a building’s rating on the Rentlogic site. The company also has an algorithmic review committee that reviews the results coming from the building assessments.
And while Rentlogic is starting in New York, the company has plans to use its machine learning system to hoover up publicly available data and provide grades for real estate across the United States.
Ultimately, Fox just wants to help improve the tenant-landlord relationship, he says. “I was in a terrible situation with a landlord who went to jail… I launched this site so no one would have to go through what I went through.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Sometimes smart contracts can be pretty dumb.
All of the benefits of a cryptographically secured, publicly verified, anonymized transaction system can be erased by errant code, malicious actors or poorly defined parameters of an executable agreement.
Hoping to beat back the tide of bad contracts, bad code and bad actors, Sagewise, a new Los Angeles-based startup, has raised $1.25 million to bring to market a service that basically hits pause on the execution of a contract so it can be arbitrated in the event that something goes wrong.
Co-founded by a longtime lawyer, Amy Wan, whose experience runs the gamut from the U.S. Department of Commerce to serving as counsel for a peer-to-peer real estate investment platform in Los Angeles, and Dan Rice, a longtime entrepreneur working with blockchain, Sagewise works with both Ethereum and the Hedera Hashgraph (a newer distributed ledger technology, which purports to solve some of the issues around transaction processing speed and security which have bedeviled platforms like Ethereum and Bitcoin).
The company’s technology works as a middleware, including an SDK and a contract notification and monitoring service. “The SDK is analogous to an arbitration clause in code form — when the smart contract executes a function, that execution is delayed for a pre-set amount of time (i.e. 24 hours) and users receive a text/email notification regarding the execution,” Wan wrote to me in an email. “If the execution is not the intent of the parties, they can freeze execution of the smart contract, giving them the luxury of time to fix whatever is wrong.”
Sagewise approaches the contract resolution process as a marketplace where priority is given to larger deals. “Once frozen, parties can fix coding bugs, patch up security vulnerabilities, or amend/terminate the smart contract, or self-resolve a dispute. If a dispute cannot be self-resolved, parties then graduate to a dispute resolution marketplace of third party vendors,” Wan writes. “After all, a $5 bar bet would be resolved differently from a $5M enterprise dispute. Thus, we are dispute process agnostic.”
Wavemaker Genesis led the round, which also included strategic investments from affiliates of Ari Paul (Blocktower Capital), Miko Matsumura (Gumi Cryptos), Youbi Capital, Maja Vujinovic (Cipher Principles), Jordan Clifford (Scalar Capital), Terrence Yang (Yang Ventures) and James Sowers.
“Smart contracts are coded by developers and audited by security auditing firms, but the quality of smart contract coding and auditing varies drastically among service providers,” said Wan, the chief executive of Sagewise, in a statement. “Inevitably, this discrepancy becomes the basis for smart contract disputes, which is where Sagewise steps in to provide the infrastructure that allows the blockchain and smart contract industry to achieve transactional confidence.”
In an email, Wan elaborated on the thesis to me, writing that, “smart contracts may have coding errors, security vulnerabilities, or parties may need to amend or terminate their smart contracts due to changing situations.”
Contracts could also be disputed if their execution was triggered accidentally or due to the actions of attackers trying to hack a platform.
“Sagewise seeks to bring transactional confidence into the blockchain industry by building a smart contract safety net where smart contracts do not fulfill the original transactional intent,” Wan wrote.
Powered by WPeMatico
Crypto skeptics rejoice! A new way to short the cryptocurrency market is coming from dYdX, a decentralized financial derivatives startup. In two months it will launch its protocol for creating short and leverage positions for Ethereum and other ERC20 tokens that allow investors to amp up their bets for or against these currencies.
To get the startup there, dYdX recently closed a $2 million seed round led by Andreessen Horowitz and Polychain, and joined by Kindred and Abstract plus angels, including Coinbase CEO Brian Armstrong and co-founder Fred Ehrsam, and serial investor Elad Gil.
“The main use for cryptocurrency so far has been trading and speculation — buying and holding. That’s not how sophisticated financial institutions trade,” says dYdX founder Antonio Juliano. “The derivatives market is usually an order of magnitude bigger than the spot trading or buy/sell market. The cryptocurrency market is probably on the order of $5 billion to $10 billion in volume, so you’d expect the derivatives market would be 10X bigger. I think there’s a really big opportunity there.”
The idea is that you buy the short Ethereum token with ETH or a stable coin from an exchange or dYdX. The short Ethereum’s token price is inversely pegged to ETH, so it goes up in value when ETH goes down and vice versa. You can then sell the short Ethereum token for a profit if you correctly predicted an ETH price drop.
On the backend, lenders earn an interest rate by providing ETH as collateral locked into smart contracts that back up the short Ethereum tokens. Only a small number of actors have to work with the smart contract to mint or close the short Tokens. Meanwhile, dYdX also offers leveraged Ethereum tokens that let investors borrow to boost their profits if ETH’s price goes up.
The plan is to offer short and leveraged tokens for any ERC20 currency in the future. dYdX is building its own user-facing application for buying the tokens, but is also partnering with exchanges to offer the margin tokens “where people are already trading,” says Juliano.
“We think of it as more than just shorting your favorite shitcoin. We think of them as mature financial products.”
Coinbase has proven to be an incredible incubator for blockchain startup founders. Juliano was employed there as a software engineer after briefly working at Uber and graduating in computer science from Princeton in 2015. “The first thing I started was a search engine for decentralized apps. I worked for months on it full-time, but nobody was building decentralized apps so no one was searching for them. It was too early,” Juliano explains.
 But along the way he noticed the lack of financial instruments for decentralized derivatives despite exploding consumer interest in buying and selling cryptocurrencies. He figured the big hedge funds would eventually come knocking if someone built them a bridge into the blockchain world.
But along the way he noticed the lack of financial instruments for decentralized derivatives despite exploding consumer interest in buying and selling cryptocurrencies. He figured the big hedge funds would eventually come knocking if someone built them a bridge into the blockchain world.
Juliano built dYdX to create a protocol to first begin offering margin tokens. It’s open source, so technically anyone can fork it to issue tokens themselves. But dYdX plans to be the standard-bearer, with its version offering the maximum liquidity to investors trying to buy or sell the margin tokens. His five-person team in San Francisco with experience from Google, Bloomberg, Goldman Sachs, NerdWallet and ConsenSys is working to find as many investors as possible to collateralize the tokens and exchanges to trade them. “It’s a race to build liquidity faster than anyone else,” says Juliano.
So how will dYdX make money? As is common in crypto, Juliano isn’t exactly sure, and just wants to build up usage first. “We plan to capture value at the protocol level in the future likely through a value adding token,” the founder says. “It would’ve been easy for us to rush into adding a questionable token as we’ve seen many other protocols do; however, we believe it’s worth thinking deeply about the best way to integrate a token in our ecosystem in a way that creates rather than destroys value for end users.”
“Antonio and his team are among the top engineers in the crypto ecosystem building a novel software system for peer-to-peer financial contracts. We believe this will be immensely valuable and used by millions of people,” says Polychain partner Olaf Carlson-Wee. “I am not concerned with short-term revenue models but rather the opportunity to permanently improve global financial markets.”
With the launch less than two months away, Juliano is also racing to safeguard the protocol from attacks. “You have to take smart contract security extremely seriously. We’re almost done with the second independent security audit,” he tells me.
 The security provided by decentralization is one of dYdX’s selling points versus centralized competitors like Poloniex that offer margin trading opportunities. There, investors have to lock up ETH as collateral for extended periods of time, putting it at risk if the exchange gets hacked, and they don’t benefit from shared liquidity like dYdX will.
The security provided by decentralization is one of dYdX’s selling points versus centralized competitors like Poloniex that offer margin trading opportunities. There, investors have to lock up ETH as collateral for extended periods of time, putting it at risk if the exchange gets hacked, and they don’t benefit from shared liquidity like dYdX will.
It also could compete for crypto haters with the CBOE that now offers Bitcoin futures and margin trading, though it doesn’t handle Ethereum yet. Juliano hopes that since dYdX’s protocol can mint short tokens for other ERC20 tokens, you could bet for or against a certain cryptocurrency relative to the whole crypto market by mixing and matching. dYdX will have to nail the user experience and proper partnerships if it’s going to beat the convenience of centralized exchanges and the institutional futures market.
If all goes well, dYdX wants to move into offering options or swaps. “Those derivatives are more often traded by sophisticated traders. We don’t think there are too many traders like that in the market right now,” Juliano explains. “The other types of derivatives that we’ll move to in the future will be really big once the market matures.” That “once the market matures” refrain is one sung by plenty of blockchain projects. The question is who’ll survive long enough to see that future, if it ever arrives.
[Featured Image via Nuzu and Bryce Durbin]
Powered by WPeMatico
Stampli, an invoice management platform, announced today the closing of a $6.7 million Series A funding round led by SignalFire, with participation from Bloomberg Beta, Hillsven Capital and UpWest Labs.
If you’ve ever freelanced for a company, you know that the long, instant ramen-filled days between filing an invoice and having it completed can be grueling. Brothers Eyal and Ofer Feldman launched Stampli in 2015 to help solve this problem and bridge the communication gap between accountants, related internal departments and vendors. Aimed at mid to large-size companies, to date Stampli has helped a wide range of companies (from fashion to tech) manage more than $4 billion in invoices through its AI-driven interface.
“Invoice management is like an elephant,” co-founder and CEO Eyal Feldman told TechCrunch. “One person sees the head, one person sees the tail, one person sees the legs. It’s a process that different people see different versions of but the whole picture should include everybody. The ability for all of these people to be involved is really the core of the process.”
Traditional invoice management between vendors and internal departments in a company can be a tangled mess of email exchanges, lost messages and ultimately delayed payments. But, Stampli’s interface (which can be integrated directly into a company’s enterprise resource planning software like NetSuite, Intuit QuickBooks or SAP) allows for every step of the invoice’s journey to have a central landing page on which every relevant party can collaborate.
“We found that 85 percent of our users are not accounting people,” said Feldman. “[They] are all the managers around and all the other people involved. What we found in our research is that when the process works for them is when accounting is happy.”
This landing page not only provides easy access to pertinent information between departments, but Stampli’s built-in AI, Billy the Bot, helps invoice managers fill in relevant information by first learning the structure of the invoice and then learning through observation the user’s behavior and work flow. When Billy passes an 80 percent confidence threshold for its decision, it goes ahead and auto-fills the information. But, if it’s feeling unsure about its choice, Billy will leave it as a suggestion instead to avoid introducing any errors to the paperwork.
The more invoices users process through Stampli, the more Billy learns how to best streamline the process for that company.
In the arena of invoice management, Stampli faces competition from companies like Determine and Concur, which also offer all-in-one platforms for invoice management and, in the case of Concur, also incorporate machine learning to capture invoices.
According to Feldman, what helps Stampli stand apart from the competition is its emphasis on company collaboration and its no-fee installation of the software. With no upfront cost, the company only charges per invoice.
Powered by WPeMatico
A mere sprinkling of autonomous vehicles exist in a few dozen cities today. A smattering in San Francisco and Silicon Valley. A dusting in the greater Phoenix area and Pittsburgh. A few drops in Boston, Detroit, Gothenburg, Shenzhen and Singapore.
And none of them — at least not yet — have been deployed as a true commercial enterprise.
While the bulk of this nascent industry fixates on the system of sensors, maps and AI necessary for vehicles to drive without a human behind the wheel, the founders of startup RideOS are directing their efforts to the day when fleets of self-driving cars hit the streets.
It’s there, where human-driven and automated vehicles will be forced to mingle, that RideOS co-founders Chris Blumenberg and Justin Ho see opportunity. And so do investors.
The company, which has existed for all of 12 months, has raised $25 million in a Series B funding round led by Next47, the venture arm of Siemens. Sequoia, an existing investor, and Singapore-based ST Ventures, also participated in the round.
The Series B round brings the company’s total funding to $34 million. RideOS announced in June that it was partnering with Ford Motor subsidiary Autonomic and had raised $9 million in a Series A round led by Sequoia Capital.
In July, RideOS announced it had partnered with ST Engineering to accelerate the deployment of autonomous vehicles in Singapore.
Blumenberg and Ho contend that unless there’s a coordinating layer that can communicate information between all automated vehicles — like say how air traffic control works in aviation — there will be traffic congestion and accidents.
The founders, who met at Uber Advanced Technologies Group, have developed a cloud-based fleet-management platform that pulls mapping, traffic and detection data to suggest to all self-driving vehicles operating in a given geography the safest, most efficient routes. The aim is to be an independent platform that can orchestrate communication between self-driving vehicle services that may be competitors.
RideOS is taking a similar approach to Waze, explained Blumenberg, the company’s CTO and a veteran of Apple. “Except we’re not relying on human input; we’re relying on things that can be detected automatically such as critical interventions or what is captured from computer vision or GPS data.”
However, RideOS isn’t sitting around for a day when automated vehicles hit the road en mass. The company’s platform is designed to work for human-driven fleets too. RideOS has already signed partnerships with mobility companies, Ho said without naming them.
“We’re working on this grand future, but there are many, many use cases we can support prior to that,” Ho said.
RideOS plans to use the additional funds to expand its services to global transportation markets. It just so happens that a team within Next47 is dedicated to helping startups tap into Siemens’ global network. In other words, RideOS stands to benefit from Siemens’ global footprint and partnerships, in addition to its access to capital.
Next47 will also join the RideOS board and will be integral in guiding RideOS in European transportation markets, the company said.
“There’s a tremendous amount of innovation in AVs at the moment,” Mike Vernal, a new partner at Sequoia Capital who led the company’s Series A round, told TechCrunch. “There’s probably 50, 60, 70 teams working on getting a single autonomous vehicle working. But no one is focused on what happens next.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Marketers are increasingly looking for social media celebrities and influencers who can promote their products with more authenticity (or at least, the appearance of authenticity) than a traditional ad.
So Altru CEO Alykhan Rehmatullah wondered: Why can’t businesses do something similar with recruiting?
And that’s what Altru is trying to accomplish, powering a page on a company’s website that highlights videos from real employees answering questions that potential hires might be asking. The videos are searchable (thanks to Altru’s transcriptions), and they also can be shared on social media.
The startup was part of the recent winter batch at Techstars NYC, and it’s already working with companies like L’Oréal, Dell and Unilever. Today, Altru is announcing that it’s raised $1.3 million in new funding led by Birchmere Ventures.
Rehmatullah contrasted Altru’s approach with Glassdoor, which he said features “more polarized” content (since it’s usually employees with really good or really bad experiences who want to write reviews) and where companies are often forced to “play defense.”
On Altru, on the other hand, employers can take the informal conversations that often take place when someone’s deciding whether to accept a job and turn them into an online recruiting tool. Over time, Rehmatullah said the platform could expand beyond recruiting to areas like on-boarding new employees.
Since these videos are posted to the company website, with the employees’ name and face attached, they may not always feel comfortable being completely honest, particularly about a company’s flaws. But at least it’s a message coming from a regular person, not the corporate-speak of a recruiter or manager.
Rehmatullah acknowledged that there’s usually “an educational process” involved in making employers more comfortable with this kind of content.
“These conversations are already happening outside your organization,” he said. “In the long-term, candidates expect more authenticity, more transparency, more true experiences.”
Powered by WPeMatico
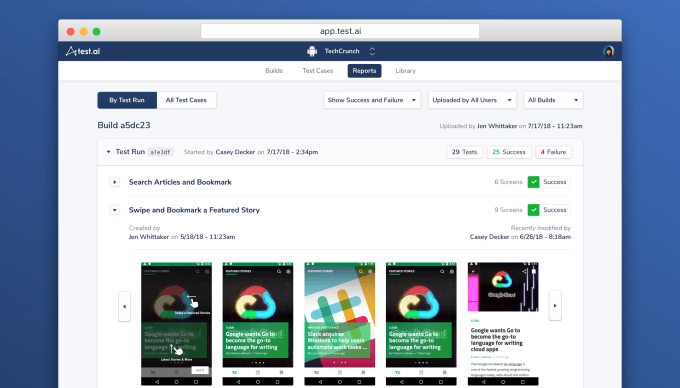
For developers, the process of determining whether every new update is going to botch some core functionality can take up a lot of time and resources, and things get far more complicated when you’re managing a multitude of apps.
Test.ai is building a comprehensive system for app testing that relies on bots, not human labor, to see whether an app is ready to start raking in the downloads.
The startup has just closed an $11 million Series A round led by Gradient Ventures, Google’s AI-focused venture fund. Also participating in the round were e.ventures, Uncork Capital and Zetta Venture Partners. Test.ai, which was founded in 2015, has raised $17.6 million to date.
“Every advancement in training AI systems enables an advancement in user testing, and test.ai is the leader in AI-powered testing technology. We’re excited to help them supercharge their growth as they test every app in the world,” Gradient Ventures founder Anna Patterson said in a statement. “In a couple years, AI testing will be ingrained into every company’s product flow.”
The company’s technology doesn’t just leverage AI to cut down on how long it takes for an app to be tested; there are much lengthier processes it helps eliminate when it comes to developers readying lists of scenarios to be tested. Test.ai has trained their bots on “tens of thousands of apps” to help it understand what an app looks like and what interface patterns they’re typically composed of. From there, they’re able to build their own scenario list and find what works and what doesn’t.
That can mean, in the case of an app like our own, tracking down a bookmark button and then deducing that there are certain process that users would go through to use its functionality.
Right now, the utility is in the fact that bots scale so broadly and so quickly. While a startup working on a single app may have the flexibility to choose amongst a few options, larger enterprises with several aging products having to grapple with updated systems are in a bit more of a bind. Some of Test.ai’s larger unnamed partners that “make app stores” or devices are working at the stratospheric level having to verify tens of thousands of apps to ensure that everything is in working order.
“That’s an easy sell for us, almost too easy, because they don’t have the resources to individually test ten thousand apps every time something like Android gets updated,” CEO Jason Arbon tells TechCrunch.
The startup’s capabilities operate on a much more quantitative scale than human-powered competitors like UserTesting, which tend to emphasize testing for feedback that’s a bit more qualitative in nature. Test.ai’s founders believe that their system will be able to grapple with more nebulous concepts in the future as it analyzes more apps, and that it’s already gaining insights into concepts like whether a product appears “trustworthy,” though there are certainly other areas where bots are trailing the insights that can be delivered by human testers.
The founders say they hope to use this latest funding to scale operations for their growing list of enterprise clients and hire some new people.
Powered by WPeMatico
Gusto, which sells payroll, benefits and human resources management and monitoring services to small businesses, has raised $140 million in its latest round of funding.
The company said it will use the money to add new services to increase payment flexibility for employees. The company launched a new service called Flexible Pay, which gives employees a way to get paid no matter when a company’s pay schedule dictates. It seems sort of like a payday loan, where a percentage of the salary is taken by Gusto for providing money upfront.
The late-stage round was led by T. Rowe Price Associates portfolio, MSD Capital (the family investment fund for Michael Dell), Dragoneer Investment Group and Y Combinator’s Continuity Fund.
Previous investors, including General Catalyst, CapitalG, Kleiner Perkins, 137 Ventures and Emergence Capital, also participated in the round.
The company claims that it processes tens of billions of dollars in payroll and offers a range of benefits, including health insurance, 401(k) plans and college savings plans.
Powered by WPeMatico
Marc Piette had a revelation as he buzzed in and out of the Palo Alto Airport in pursuit of his pilot’s license. Instead of freedom, he saw restraint. He also saw potential.
“It became pretty apparent that there were major issues with the general aviation industry with smaller aircraft,” Piette said in a recent interview with TechCrunch. “And yet it had enormous potential to change the way people moved around.”
Now, Piette’s two-year-old autonomous-aviation startup Xwing is ramping up to unlock that potential. The company, which has kept a low profile since its founding, isn’t building autonomous helicopters and planes. Instead, it’s focused on the software stack that will enable pilotless flight of small passenger aircraft.
The company announced Tuesday that it has raised $4 million in a seed round led by Eniac Ventures. Array Ventures, along with Stripe founders John and Patrick Collison and Nat Friedman of Xamarin, Microsoft and GitHub, also participated in the round.
The funding will be used by the San Francisco-based company to scale operations and continue to hire aerospace and software talent.
The startup has about a dozen employees, including some uniquely talented folks who have experience with optionally piloted vehicles, unmanned systems and certified avionics. For example, the company’s CTO, Maxime Gariel, worked on autonomous-aviation projects such as DARPA Gremlins and the AgustaWestland SW4 Solo autonomous helicopter. Other members of the small team previously worked at Rockwill Collins, with the Naval Research Lab, Google, and McKinsey.
Piette, whose last company Locu was acquired by GoDaddy, sees several restraints to small passenger aircraft: the skill level required to fly a plane and the cost of earning a pilot’s license and accessing a plane. The relatively puny sales volume of small aircraft — just 3,293 general aviation aircraft, including helicopters, were delivered last year worldwide, in contrast to more than 80 million cars — has depressed innovation and kept prices high.
And even when people have both a license and an aircraft, they still must travel from a small airport to their final destination.
The company is focusing on the key functions of autonomous flight, such as sensing, reasoning and control.
Xwing isn’t pinned to one kind of aircraft. Piette said the system is designed to work across different kinds of aircraft. For instance, the company spent 18 months testing on a subscale fixed-wing aircraft. It tested on a helicopter more recently.
Xwing is developing and integrating those technologies for rotorcraft, general aviation fixed-wing and the emerging electric vertical takeoff and landing (known as eVTOL) aircraft.
The company’s sensor integration software enables aircraft to perceive the world around it and reliably detect ground-based and airborne hazards and precisely determine the vehicle’s position.
This perception technology is the building block for autonomous aircraft, and also can be used to increase the operational envelope of current-day piloted aircraft, according to Xwing.
From here, the company’s Autonomy Flight Management System (AFMS) allows the aircraft to act upon the information from its surroundings. The system will integrate with air traffic control, generate flight paths to navigate the airspace, monitor system health and address all contingencies to ensure passenger safety, the company says.
Now, Xwing is in discussion with various, and still unnamed, large companies about integrating the system into their aircraft.
Powered by WPeMatico