Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
SmartNews, a Tokyo-headquartered news aggregation website and app that’s grown in popularity despite hefty competition from built-in aggregators like Apple News, today announced it has closed on $230 million in Series F funding. The round brings SmartNews’ total raise to date to over $400 million and values the business at $2 billion — or as the company touts in its press release, a “double unicorn.” (Ha!)
The funding included new U.S. investors Princeville Capital and Woodline Partners, as well as JIC Venture Growth Investments, Green Co-Invest Investment, and Yamauchi-No.10 Family Office in Japan. Existing investors participating in this round included ACA Investments and SMBC Venture Capital.
Founded in 2012 in Japan, the company launched to the U.S. in 2014 and expanded its local news footprint early last year. While the app’s content team includes former journalists, machine learning is used to pick which articles are shown to readers to personalize their experience. However, one of the app’s key differentiators is how it works to pop users’ “filter bubbles” through its “News From All Sides” feature, which allows its users to access news from across a range of political perspectives.
It has also developed new products, like its COVID-19 vaccine dashboard and U.S. election dashboard, that provide critical information at a glance. With the additional funds, the company says it plans to develop more features for its U.S. audience — one of its largest, in addition to Japan — that will focus on consumer health and safety. These will roll out in the next few months and will include features for tracking wildfires and crime and safety reports. It also recently launched a hurricane tracker.
The aggregator’s business model is largely focused on advertising, as the company has said before that 85-90% of Americans aren’t paying to subscribe to news. But SmartNews’ belief is that these news consumers still have a right to access quality information.
In total, SmartNews has relationships with more than 3,000 global publishing partners whose content is available through its service on the web and mobile devices.
To generate revenue, the company sells inline ads and video ads, where revenue is shared with publishers. Over 75% of its publishing partners also take advantage of its “SmartView” feature. This is the app’s quick-reading mode, an alternative to something like Google AMP. Here, users can quickly load an article to read, even if they’re offline. The company promises publishers that these mobile-friendly stories, which are marked with a lightning bolt icon in the app, deliver higher engagement — and its algorithm rewards that type of content, bringing them more readers. Among SmartView partners are well-known brands like USA Today, ABC, HuffPost and others. Currently, over 70% of all SmartNews’ pageviews are coming from SmartView first.
SmartNews’ app has proven to be very sticky, in terms of attracting and keeping users’ attention. The company tells us, citing App Annie July 2021 data, that it sees an average time spent per user per month on U.S. mobile devices that’s higher than Google News or Apple News combined.
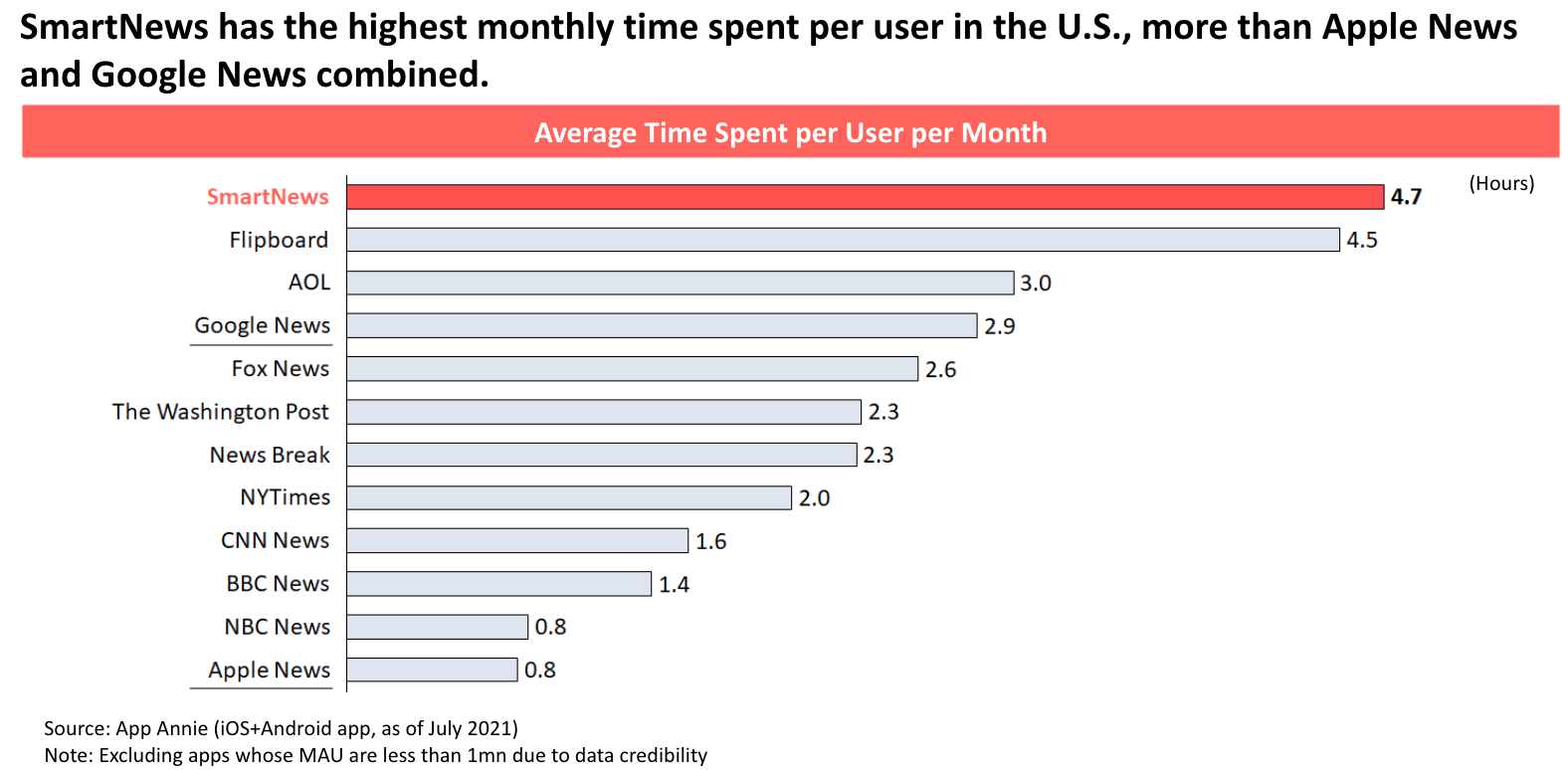
Image Credits: App Annie data provided by SmartNews
The company declined to share its monthly active users (MAUs), but had said in 2019 it had grown to 20 million in the U.S. and Japan. Today, it says its U.S. MAUs doubled over the last year.
According to data provided to us by Apptopia, the SmartNews app has seen around 85 million downloads since its October 2014 launch, and 14 million of those took place in the past 365 days. Japan is the largest market for installs, accounting for 59% of lifetime downloads, the firm noted.
“This latest round of funding further affirms the strength of our mission, and fuels our drive to expand our presence and launch features that specifically appeal to users and publishers in the United States,” said SmartNews co-founder and CEO Ken Suzuki. “Our investors both in the U.S. and globally acknowledge the tremendous growth potential and value of SmartNews’s efforts to democratize access to information and create an ecosystem that benefits consumers, publishers and advertisers,” he added.
The company says the new funds will be used to invest in further U.S. growth and expanding the company’s team. Since its last fundraise in 2019, where it became a unicorn, the company more than doubled its headcount to approximately 500 people globally. it now plans to double its headcount of 100 in the U.S., with additions across engineering, product, and leadership roles.
The Wall Street Journal reports SmartNews is exploring an IPO, but the company declined to comment on this.
The SmartNews app is available on iOS and Android across more than 150 countries worldwide.
Powered by WPeMatico
Relyance AI, an early-stage startup that is helping companies stay in compliance with privacy laws at the code level, announced a $25 million Series A today. At the same time, they revealed a previously unannounced $5 million seed round.
Menlo Ventures and Unusual Ventures led the A round, while Unusual was sole lead on the seed. Serial entrepreneur Jyoti Bansal from Unusual will join the board under the terms of the deal. His partner John Vrionis had previously joined after the seed round. Matt Murphy from Menlo is coming on as a board observer. The company has now raised $30 million.
Relyance takes an unusual approach to verifying that data stays in compliance working at the code level, while ingesting contracts and existing legal requirements as code to ensure that a company is in compliance. Company co-CEO and co-founder Abhi Sharma says that code-level check is key to the solution. “For the first time, we are building the legal compliance and regulation into the source code,” Sharma told me.
He added, “Relyance is actually embedded within the DevOps pipeline of our customers’ infrastructure. So every time a new ETL pipeline is built or a machine learning model is receiving new source code, we do a compiler-like analysis of how personal sensitive data is flowing between internal microservices, data lakes and data warehouses, and then get a metadata analysis back to the privacy and compliance professionals [inside an organization].”
Leila R. Golchehreh, the other founder and co-CEO, brings a strong compliance background to the equation and has experienced the challenge of keeping companies in compliance firsthand. She said that Relyance also enables companies to define policy and contracts as code.
“Our approach is specifically to ingest contracts. We’ve actually created an algorithm around how [you] actually write a good data protection agreement. We’ve extracted those relevant provisions and we will compare that against [your] operational reality. So if there’s a disconnect, we will be able to raise that as an intelligent insight of a data misalignment,” she said.
With 32 employees, the co-founders hope to double or perhaps even triple that number in the next 12-18 months. Golchehreh and Sharma are a diverse co-founder team and they are attempting to build a company that reflects that. They believe being remote-first gives them a leg up in this regard, but they also have internal policies to drive it.
“The recruiters we work with have a mandate internally to say, ‘Hey, we really want to hire good people and diverse people.’ Relyance as a company is the genesis of two individuals from two completely different ends of the spectrum coming together. And I think hopefully, we can do our job of relaying that into the company as we scale,” Sharma said.
The two founders have been friends for several years and began talking about forming a company together in 2019 over a pizza dinner. The idea began to gel and they launched the company in February 2020. They spent some time talking to compliance pros to understand their requirements better, then in July 2020 began building the solution they have today. They released a beta in February and began quietly selling it in March.
Today they have a number of early customers working with their software, including Dialpad, Patreon, Samsara and True.
Powered by WPeMatico
Ascend on Wednesday announced a $5.5 million seed round to further its insurance payments platform that combines financing, collections and payables.
First Round Capital led the round and was joined by Susa Ventures, FirstMark Capital, Box Group and a group of angel investors, including Coalition CEO Joshua Motta, Newfront Insurance executives Spike Lipkin and Gordon Wintrob, Vouch Insurance CEO Sam Hodges, Layr Insurance CEO Phillip Naples, Anzen Insurance CEO Max Bruner, Counterpart Insurance CEO Tanner Hackett, former Bunker Insurance CEO Chad Nitschke, SageSure executive Paul VanderMarck, Instacart co-founders Max Mullen and Brandon Leonardo and Houseparty co-founder Ben Rubin.
This is the first funding for the company that is live in 20 states. It developed payments APIs to automate end-to-end insurance payments and to offer a buy now, pay later financing option for distribution of commissions and carrier payables, something co-founder and co-CEO Andrew Wynn, said was rather unique to commercial insurance.
Wynn started the company in January 2021 with his co-founder Praveen Chekuri after working together at Instacart. They originally started Sheltr, which connected customers with trained maintenance professionals and was acquired by Hippo in 2019. While working with insurance companies they recognized how fast the insurance industry was modernizing, yet insurance sellers still struggled with customer experiences due to outdated payments processes. They started Ascend to solve that payments pain point.
The insurance industry is largely still operating on pen-and-paper — some 600 million paper checks are processed each year, Wynn said. He referred to insurance as a “spaghetti web of money movement” where payments can take up to 100 days to get to the insurance carrier from the customer as it makes its way through intermediaries. In addition, one of the only ways insurance companies can make a profit is by taking those hundreds of millions of dollars in payments and investing it.
Home and auto insurance can be broken up into payments, but the commercial side is not as customer friendly, Wynn said. Insurance is often paid in one lump sum annually, though, paying tens of thousands of dollars in one payment is not something every business customer can manage. Ascend is offering point-of-sale financing to enable insurance brokers to break up those commercial payments into monthly installments.
“Insurance carriers continue to focus on annual payments because they don’t have a choice,” he added. “They want all of their money up front so they can invest it. Our platform not only reduces the friction with payments by enabling customers to pay how they want to pay, but also helps carriers sell more insurance.”
Ascend app
Startups like Ascend aiming to disrupt the insurance industry are also attracting venture capital, with recent examples including Vouch and Marshmallow, which raised close to $100 million, while Insurify raised $100 million.
Wynn sees other companies doing verticalized payment software for other industries, like healthcare insurance, which he says is a “good sign for where the market is going.” This is where Wynn believes Ascend is competing, though some incumbents are offering premium financing, but not in the digital way Ascend is.
He intends to deploy the new funds into product development, go-to-market initiatives and new hires for its locations in New York and Palo Alto. He said the raise attracted a group of angel investors in the industry, who were looking for a product like this to help them sell more insurance versus building it from scratch.
Having only been around eight months, it is a bit early for Ascend to have some growth to discuss, but Wynn said the company signed its first customer in July and six more in the past month. The customers are big digital insurance brokerages and represent, together, $2.5 billion in premiums. He also expects to get licensed to operate as a full payment in processors in all states so the company can be in all 50 states by the end of the year.
The ultimate goal of the company is not to replace brokers, but to offer them the technology to be more efficient with their operations, Wynn said.
“Brokers are here to stay,” he added. “What will happen is that brokers who are tech-enabled will be able to serve customers nationally and run their business, collect payments, finance premiums and reduce backend operation friction.”
Bill Trenchard, partner at First Round Capital, met Wynn while he was still with Sheltr. He believes insurtech and fintech are following a similar story arc where disruptive companies are going to market with lower friction and better products and, being digital-first, are able to meet customers where they are.
By moving digital payments over to insurance, Ascend and others will lead the market, which is so big that there will be many opportunities for companies to be successful. The global commercial insurance market was valued at $692.33 billion in 2020, and expected to top $1 trillion by 2028.
Like other firms, First Round looks for team, product and market when it evaluates a potential investment and Trenchard said Ascend checked off those boxes. Not only did he like how quickly the team was moving to create momentum around themselves in terms of securing early pilots with customers, but also getting well known digital-first companies on board.
“The magic is in how to automate the underwriting, how to create a data moat and be a first mover — if you can do all three, that is great,” Trenchard said. “Instant approvals and using data to do a better job than others is a key advantage and is going to change how insurance is bought and sold.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Businesses and the tech companies that serve them are run on data. At best, it can be used to help with decision-making, to understand how well or badly an organization is doing and to build new systems to run the next generation of services. At its most challenging, though, data can represent a real headache: there is too much of it, in too many places, and too much of a task to bring it into any kind of order.
Enter a startup called Matillion, which has built a platform to help companies harness their data so that it can be used, and what’s more, the platform is not just for data scientists, but it’s written with a “low-code” approach that can be used by a wider group of users.
Today, it is announcing a big round of investment — $150 million at a $1.5 billion valuation — a sign not just of Matillion’s traction in this space, but of the market demand for the tech that it has built.
The company currently has “hundreds” of large enterprise customers, including Western Union, FOX, Sony, Slack, National Grid, Peet’s Coffee and Cisco for projects ranging from business intelligence and visualization through to artificial intelligence and machine learning applications.
General Atlantic is leading the funding, with Battery Ventures, Sapphire Ventures, Scale Venture Partners and Lightspeed Venture Partners — some of the biggest enterprise startup investors in the world — also participating. Matillion last raised money — a Series D of around $100 million — as recently as February this year, at what was an undisclosed valuation at the time.
Announcing this latest round at a $1.5 billion valuation is significant not just for Matillion. The startup was founded in Manchester (it now also has a base in Denver), and this makes it one of a handful of tech startups out of the city — others we’ve recently covered include The Hut Group, Peak AI and Fractory — now hitting the big leagues and helping to put it on the innovation map as an urban center to watch.
Matthew Scullion, the startup’s CEO and founder, explained that the crux of the issue Matillion is addressing is the diamond-in-the-rough promise of big data. Typically, large organizations are producing giant amounts of data every day, hugely valuable information as long as it can be tapped efficiently. The problem is that this data is often sitting across a lot of different places — typically large organizations might have over 1,000 data sources, apps sitting across multiple clouds and servers and storage across Snowflake, Amazon Redshift and Databricks. On top of this, while a lot of that data is very structured, those sources are not necessarily aligned with each other.
“Data has become the new currency, and the world is pivoting to that,” he said. “It’s changing all aspects of how we work, and it is happening very fast. But the problem is that the world’s ability to innovate with data is constrained. It’s not the shortage of data or demand to put it to work, but the point is the world’s ability to make that data useful.”
Matillion has answered that with a framework and system that can both identify data sources and basically bring order to them, without needing to move the data from one place to another in order to be used. It’s an ETL (extract, transform and load) provider, and it is far from being the only one in the market, with others like Dataiku, Talent, SnapLogic, as well as cloud providers like AWS and Microsoft, among the many trying to address this area.
The difference with Matillion, Scullion said, is that it has a democratized platform, so that organizations don’t have to rely on data scientists to get involved in order to use it, by building a low-code interface around it.
“We have made it accessible, intuitive and easy to use by bringing in a low-code approach,” he said. “We’ve developed a platform and data operating system that has all the things in the kit bag that an organization needs to make it useful.”
This is important because, as big data analytics and the tools to build these processes become more mainstream and themselves take on low-code interfaces, Matillion is providing a way for those less technical users to source and use their data, too. This means more efficiency, less cost, and more time for data scientists to work on more difficult problems and do less busy work.
“As organizations look for ways to harness data to make better business decisions, the market for cloud data integration and transformation is expanding,” said Chris Caulkin, managing director and head of Technology for EMEA at General Atlantic. “We believe that Matillion’s low-code ETL platform simplifies the process of constructing data pipelines and preparing data for analysis, enabling citizen data scientists and data engineers alike to play a valuable role in extracting data-based insights. We look forward to supporting the team through its next phase of growth and expansion.”
Powered by WPeMatico
In order to support a buildout of renewable energy, which tends to over-generate electricity at certain times of day and under-generate at others, the grid is going to need a lot of batteries. While lithium-ion works fine for consumer electronics and even electric vehicles, battery startup EnerVenue says it developed a breakthrough technology to revolutionize stationary energy storage.
The technology itself — nickel-hydrogen batteries — isn’t actually new. In fact, it’s been used for decades in aerospace applications, to power everything from satellites to the International Space Station and the Hubble Telescope. Nickel-hydrogen had been too expensive to scale for terrestrial applications, until Stanford University professor (and now EnerVenue chairman) Yi Cui determined a way to adapt the materials and bring the costs way, way down.
Nickel-hydrogen has a number of key benefits over lithium-ion, according to EnerVenue: it can withstand super-high and super-low temperatures (so no need for air conditioners or thermal management systems); it requires very little to no maintenance; and it has a far longer lifespan.
The technology has caught the eye of two giants in the oil and gas industry, energy infrastructure company Schlumberger and Saudi Aramco’s VC arm, which together with Stanford University have raised $100 million in Series A funding. The investment comes around a year after EnerVenue raised a $12 million seed. The company is planning on using the funds to scale its nickel-hydrogen battery production, including a Gigafactory in the U.S., and has entered a manufacturing and distribution agreement with Schlumberger for international markets.
“I spent almost three and a half years prior to EnerVenue looking for a battery storage technology that I thought could compete with lithium-ion,” CEO Jorg Heinemann told TechCrunch in a recent interview. “I had essentially given up.” Then he met with Cui, who had managed through his research to bring the cost down from around $20,000 per kilowatt hour to $100 per kilowatt hour within line of sight — a jaw-dropping decrease that puts it on-par with existing energy storage technology today.

EnerVenue CEO Jorg Heinemann Image Credits: EnerVenue (opens in a new window)
Think of a nickel-hydrogen battery as a kind of battery-fuel cell hybrid. It charges by building up hydrogen inside a pressure vessel, and when it discharges, that hydrogen gets reabsorbed in water, Heinemann explained. One of the key differences between the batteries in space and the one’s EnerVenue is developing on Earth is the materials. The nickel-hydrogen batteries in orbit use a platinum electrode, which Heinemann said accounts for as much as 70% of the cost of the battery. The legacy technology also uses a ceramic separator, another high cost. EnerVenue’s key innovation is finding new, low-cost and Earth-abundant materials (though the exact materials they aren’t sharing).
Heinemann also hinted that an advanced team within the company is working on a separate technology breakthrough that could bring the cost down even further, to the range of around $30 per kilowatt hour or less.
Those aren’t the only benefits. EnerVenue’s batteries can charge and discharge at different speeds depending on a customer’s needs. It can go from a 10-minute charge or discharge to as slow as a 10-20 hour charge-discharge cycle, though the company is optimizing for a roughly two-hour charge and four- to eight-hour discharge. EnerVenue’s batteries are also designed for 30,000 cycles without experiencing a decline in performance.
“As renewables get cheaper and cheaper, there’s lots of time of the day where you’ve got, say, a one- to four-hour window of close to free power that can be used to charge something, and then it has to be dispatched fast or slow depending on when the grid needs it,” he said. “And our battery does that really well.”
It’s notable that this round was funded by two companies that loom large in the oil and gas industry. “I think nearly 100% of the oil and gas industry is now pivoting to renewables in a huge way,” Heinemann added. “They all see the future as, the energy mix is shifting. We’re going to be 75% renewable by mid-century, most think it’s going to happen quicker, and those are based on studies that the oil and gas industry did. They see that and they know they need a new play.”

Image Credits: EnerVenue
Don’t expect nickel-hydrogen to start appearing in your iPhone anytime soon. The technology is big and heavy — even scaled down as much as possible, a nickel-hydrogen battery is still around the size of a two-liter water flask, so lithium-ion will definitely still play a major role in the future.
Stationary energy storage may have a different future. EnerVenue is currently in “late-stage” discussions on the site and partner for a United States factory to produce up to one gigawatt-hour of batteries annually, with the goal of eventually scaling even beyond that. Heinemann estimates that the tooling cap-ex per megawatt hour should be just 20% that of lithium ion. Under the partnership with Schlumberger, the infrastructure company will also be separately manufacturing batteries and selling them in Europe and the Middle East.
“It’s a technology that works today,” Heinemann said. “We’re not waiting on a technology breakthrough, there’s no science project in our future that we have to go achieve in order to prove out something. We know it works.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Cross-border commerce company Zonos raised $69 million in a Series A, led by Silversmith Capital Partners, to continue building its APIs that auto classify goods and calculate an accurate total landed cost on international transactions.
St. George, Utah-based Zonos is classifying the round as a minority investment that also included individual investors Eric Rea, CEO of Podium, and Aaron Skonnard, co-founder and CEO of Pluralsight. The Series A is the first outside capital Zonos has raised since it was founded in 2009, Clint Reid, founder and CEO, told TechCrunch.
As Reid explained it, “total landed cost” refers to the duties, taxes, import and shipping fees someone from another country might pay when purchasing items from the U.S. However, it is often difficult for businesses to figure out the exact cost of those fees.
Global cross-border e-commerce was estimated to be over $400 billion in 2018, but is growing at twice the rate of domestic e-commerce. This is where Zonos comes in: The company’s APIs, apps and plugins simplify cross-border sales by providing an accurate final price a consumer pays for an item on an international purchase. Businesses can choose which one or multiple shipping carriers they want to work with and even enable customers to choose at the time of purchase.
“Businesses can’t know all of a country’s laws,” Reid added. “Our mission is to create trust in global trade. If you are transparent, you bring trust. This was traditionally thought to be a shipping problem, but it is really a technology problem.”
As part of the investment Todd MacLean, managing partner at Silversmith Capital Partners, joined the Zonos board of directors. One of the things that attracted MacLean to the company was that Reid was building a company outside of Silicon Valley and disrupting global trade far from any port.
He says while looking into international commerce, he found people wound up being charged additional fees after they have already purchased the item, leading to bad customer experiences, especially when a merchant is trying to build brand loyalty.
Even if someone chooses not to purchase the item due to the fees being too high, MacLean believes the purchasing experience will be different because the pricing and shipping information was provided up front.
“Our diligence said Zonos is the only player to take the data that exists out there and make sense of it,” MacLean said. “Customers love it — we got the most impressive customer references because this demand is already out there, and they are seeing more revenue and their customers have more loyalty because it just works.”
In fact, it is common for companies to see 25% to 30% year over year increase in sales, Reid added. He went on to say that due to fees associated with shipping, it doesn’t always mean an increase in revenue for companies. There may be a small decrease, but a longer lifetime value with customers.
Going after venture capital at this time was important to Reid, who saw global trade becoming more complex as countries added new tax laws and stopped using other trade regulations. However, it was not just about getting the funding, but finding the right partner that recognizes that this problem won’t be solved in the next five years, but will need to be in it for the long haul, which Reid said he saw in Silversmith.
The new investment provides fuel for Zonos to grow in product development and go-to-market while also expanding its worldwide team into Europe and Asia Pacific. Eighteen months ago, the company had 30 employees, and now there are over 100. It also has more than 1,500 customers around the world and provides them with millions of landed cost quotes every day.
“Right now, we are the leader for APIs in cross-border e-commerce, but we need to also be the technology leader regardless of the industry,” Reid added. “We can’t just accept that we are good enough, we need to be better at doing this. We are looking at expanding into additional markets because it is more than just servicing U.S. companies, but need to be where our customers are.”
Powered by WPeMatico
When Kleiner Perkins led Stord’s $12.4 million Series A in 2019, its founders were in their early 20s and so passionate about their startup that they each dropped out of their respective schools to focus on growing the business.
Fast-forward two years and Stord — an Atlanta-based company that has developed a cloud supply chain — is raising more capital in a round again led by Kleiner Perkins.
This time, Stord has raised $90 million in a Series D round of funding at a post-money valuation of $1.125 billion — more than double the $510 million that the company was valued at when raising $65 million in a Series C financing just six months ago.
In fact, today’s funding marks Stord’s third since early December of 2020, when it raised its Series B led by Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund, and brings the company’s total raised since its 2015 inception to $205 million.
Besides Kleiner Perkins, Lux Capital, D1 Capital, Palm Tree Crew, BOND, Dynamo Ventures, Founders Fund, Lineage Logistics and Susa Ventures also participated in the Series D financing. In addition, Michael Rubin, Fanatics founder and founder of GSI Commerce; Carlos Cashman, CEO of Thrasio; Max Mullen, co-founder of Instacart; and Will Gaybrick, CPO at Stripe, put money in the round. Previous backers include BoxGroup, Susa Ventures, Dynamo, Revolution and Rise of the Rest Seed Fund, among others.
Founders Sean Henry, 24, and Jacob Boudreau, 23, met while Henry was at Georgia Tech and Boudreau was in online classes at Arizona State (ASU) but running his own business, a software development firm, in Atlanta.
Over time, Stord has evolved into a cloud supply chain that can give companies a way to compete and grow with logistics, and provides an integrated platform “that’s available exactly when and where they need it,” Henry said. Stord combines physical logistics services such as freight, warehousing and fulfillment in that platform, which aims to provide “complete visibility, rapid optimization and elastic scale” for its users.
About two months ago, Stord announced the opening of its first fulfillment center, a 386,000-square-foot facility, in Atlanta, which features warehouse robotics and automation technologies. “It was the first time we were in a building ourselves running it end to end,” Henry said.
And today, the company is announcing it has acquired Connecticut-based Fulfillment Works, a 22-year-old company with direct-to-consumer (DTC) experience and warehouses in Nevada and in its home state.
With FulfillmentWorks, the company says it has increased its first-party warehouses, coupled with its network of over 400 warehouse partners and 15,000 carriers.
While Stord would not disclose the amount it paid for Fulfillment Works, Henry did share some of Stord’s impressive financial metrics. The company, he said, in 2020 delivered its third consecutive year of 300+% growth, and is on track to do so again in 2021. Stord also achieved more than $100 million in revenue in the first two quarters of 2021, according to Henry, and grew its headcount from 160 people last year to over 450 so far in 2021 (including about 150 Fulfillment Works employees). And since the fourth quarter is often when people do the most online shopping, Henry expects the three-month period to be Stord’s heaviest revenue quarter.
For some context, Stord’s new sales were up “7x” in the second quarter of 2020 compared to the same period last year. So far in the third quarter, sales are up almost 10x, according to Henry.
Put simply, Stord aims to give brands a way to compete with the likes of Amazon, which has set expectations of fast fulfillment and delivery. The company guarantees two-day shipping to anywhere in the country.
“The supply chain is the new competitive battleground,” Henry said. “Today’s buying expectations set by Amazon and the rise of the omni-channel shopper have placed immense pressure on companies to maintain more nimble and efficient supply chains… We want every company to have world-class, Prime-like supply chains.”
What makes Stord unique, according to Henry, is the fact that it has built what it believes to be the only end-to-end logistics network that combines the physical infrastructure with software.
That too is one of the reasons that Kleiner Perkins doubled down on its investment in the company.
Ilya Fushman, Stord board director and partner at Kleiner Perkins, said even at the time of his firm’s investment in 2019, that Henry displayed “amazing maturity and vision.”
At a high level, the firm was also just drawn to what he described as the “incredibly large market opportunity.”
“It’s trillions of dollars of products moving around with consumer expectation that these products will get to them the same day or next day, wherever they are,” Fushman told TechCrunch. “And while companies like Amazon have built amazing infrastructure to do that themselves, the rest of the world hasn’t really caught up… So there’s just amazing opportunity to build software and services to modernize this multitrillion-dollar market.”
In other words, Fushman explained, Stord is serving as a “plug and play” or “one stop shop” for retailers and merchants so they don’t have to spend resources on their own warehouses or building their own logistics platforms.
Stord launched the software part of its business in January 2020, and it grew 900% during the year, and is today one of the fastest-growing parts of its business.
“We built software to run our logistics and network of hundreds of warehouses,” Henry told TechCrunch. “But if companies want to use the same system for existing logistics, they can buy our software to get that kind of visibility.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Canva is now valued at $40 billion following a fresh capital injection of $200 million (USD) in a round led by T. Rowe Price. New and existing investors participated in the round, including Franklin Templeton, Sequoia Capital Global Equities, Bessemer Venture Partners, Greenoaks Capital, Dragoneer Investments, Blackbird, Felicis and AirTree Ventures.
This round solidifies Canva as one of the most valuable private software companies out there, and it also propels the Australian tech scene forward.
Co-founder and CEO Melanie Perkins and her team started working on Canva in 2012, and launched the product in 2013. The premise behind it was relatively simple, but the technology itself… not so much.
Canva allows anyone to design. Presentations, t-shirts, brochures, flyers… you name it. The first step in this is creating a truly simple user interface, where folks can simply drag and drop components into their designs, complete with hundreds of thousands of templates, without doing a lot of fine tuning. The second step is creating a massive library of content, from fonts to templates to imagery, gifs and videos. The third step is to make that product accessible to everyone, whether it’s a platform or device or language or price.
Going after everyone, instead of just designers, has proved incredibly fruitful for the company. To be clear, designers still use Canva to lay out components they’ve designed in other products, such as Figma and Sketch, and Canva actually plays nicely with a variety of design software products. But Canva has no intention of going head to head with Figma, Adobe or Sketch.
Perkins described it with the example of a business card. Designers will create the components of a business card in their design platform of choice, and then lay out the template for business cards in Canva, sharing that template with the entire organization. That way, when someone gets a title change or a new employee comes on, they can actually edit the card themselves without the help of a designer and send it to print.
TechCrunch asked Perkins why Canva hasn’t extended the platform more aggressively into the workflow of professional designers.
“We would like to replace PDF,” said Perkins. “Rather than people sending PDFs backwards and forwards between the designer and the client, designers can just create a template for organization use. It’s less important for us to absolutely excel at things like vector design because there are amazing programs on the market that may be there. We really want to focus on that collaboration piece.”
Though a bottoms-up enterprise strategy is relatively popular these days, Canva was an early master of the model. Canva launched as a free product, and over time the company introduced enterprise layers into the mix.
As of now, Canva has more than 60 million monthly active users across 190 countries, with big-name companies on the enterprise plan. This includes Salesforce, Marriott International, PayPal and American Airlines. Canva expects to exceed $1 billion in annualized revenue by the end of 2021. More than 500,000 teams are paying for the product in some capacity.
With a 2,000-person team, Canva will use the fresh funding to double its workforce in the next year.
Canva also shared its DEI numbers, with females representing 42% of the workforce. The company did not share any stats around people of color on the team.
Perkins explained to TechCrunch that a huge part of the company’s growth has to do with an obsession over creating a highly valuable free product.
“We intentionally make our free product extremely generous for a number of reasons,” said Perkins. “It’s critical both for our marketing and towards our mission of empowering people to design. But, as part of our marketing, it means that people are able to love the product, share it with their friends and family, and promote it on social media. And then that virality really rapidly fuels our growth.”
Alongside growing the team, Canva also has plans to further build out the product in the next year, launching website design soon. This will allow users to turn existing and new presentations and designs into a website, and even search for and buy a domain for that site.
Canva is also working on a new video editor and an offline mode.
Perkins says that Canva has two goals, and that each fuels the other. The first is to become one of the world’s most valuable companies, and the other is to do the most good that it can do.
The company has already joined the 1% pledge and has several efforts around being a force for good, including giving the premium product to more than 130,000 nonprofits, allocating more than 45,000 volunteering hours each year and launching Print One, Plant One, which is a project that plants a tree for every single print order placed through Canva.
With today’s funding announcement, cofounders Perkins and Cliff Obrecht are committing the vast majority of their own equity in the company (around 30%) to doing good in the world, with plans to do this through the Canva Foundation.
Perkins will be joining us at Disrupt to talk about the new funding, valuation, what’s in store for Canva, and share her broader thoughts on design as a category.
Powered by WPeMatico
When you’re hot, you’re hot. And 1047 Games is making the most of the heat generated by Splitgate, its first game and now a breakout success. After working on a shoestring for years, the team has since May raised three rounds, the latest for a massive $100 million.
Co-founder and CEO Ian Proulx credited a dedicated community and, as he described it, “taking a Silicon Valley approach to running a game business.”
At the time 1047 Games was founded, about five years ago, free to play (F2P) PC games were a niche genre. While games like World of Tanks and Warframe were seeing success, and of course many mobile games relying on in-app purchases, Fortnite had yet to show the industry that F2P could be so ludicrously profitable.
“Five years ago it was very hit-driven: You spend years developing a product, put all this money into hyping the launch and then hope it’s a success,” Proulx explained. “Our process was, there’s no way we can take that risk — if we spent our entire budget and got it wrong, we’re out of business. So we thought, let’s do a soft launch, put it out there and see what happens, learn, listen, look at the data. Why would I spend money marketing a product that I have no idea about whether it will be a success? If we wanted to spend money, and we didn’t have a lot, I’d rather spend it on a product that has great metrics and KPIs.”
If you’re not familiar with it, Splitgate is a multiplayer online competitive shooter with a lot of DNA from the old-school arena shooters like Quake 3, Unreal Tournament and Halo. Those games are frenetic enough, but Splitgate adds the ability to bend space with portals, like the eponymous Portal, adding a truly ridiculous amount of mobility to the action.
Proulx said investors shut the door on him repeatedly because they didn’t see Splitgate competing in any of the popular genres, battle royales and hero shooters, for instance. But he felt confident that this update to a familiar formula would be a success partly because the demand was there, just sleeping. “People grew up playing these games, and the reason [the market] is dead is not because they stopped loving them,” he said. “No one has moved the needle because there hasn’t been a lot of innovation, and there hasn’t been something that’s accessible to the masses. Quake Arena is great, but it’s extremely difficult. No 12-year-old Fortnite kid is gonna play it. We really do fill this void.”
While gameplay-wise Splitgate is most obviously similar to classic shooters, Proulx said a better comparison would be Rocket League, another huge success story in gaming that took a great concept and provided it as cheaply as possible, making money off cosmetic items and other totally optional perks.
“You can just have fun, turn your brain off and play, but there’s this limitless skill ceiling,” he explained.
It didn’t spring fully formed from 1047 in 2019, though. The team put out the gaming equivalent of a minimum viable product. “It was fun, and the basics were there,” he said, “but we learned there’s way more to running a business and free-to-play than just having a fun game.”
The danger for any game is simply that people stop playing, so the team focused on retention and on listening to feedback from the community to make Splitgate a “forever game” that can go years, with “seasons,” new features and maps, and so on.
The original MVP release saw some traction, around 600,000 downloads in its first month, but the big multiplatform relaunch — still as an “open beta” — this summer made a huge splash, pulling in more than 10 million in July.
Suddenly the tables had turned and 1047 was holding, as Proulx put it, “lightning in a bottle.”
“Our first round six months ago was extremely difficult. We talked to every investor on the planet and they all said no,” he recalled. But the hard work paid off: “We got lucky and ended up with the perfect partners — I can’t stress enough how supportive our investors have been.”
The next round (with Human Capital, just as Splitgate was taking off, went from phone call to funding over a weekend. This third round, with 1047 picking and choosing, was led by Lightspeed Venture Partners with participation from “Insight Partners, Anthos Capital, and earlier seed round investors Galaxy Interactive, VGames, Human Capital, Lakestar, DraperDragon, and Draper University” (from the press release).
One wonders what a team of fewer than 10 people could possibly do with $100 million ($116 million if you count the two previous rounds). But the bet investors are making is not that 1047 is going to suddenly make Assassin’s Creed, but rather that they think 10 million (and rising) people playing a unique game is potentially a huge opportunity — if the developers have the chance to follow through. This post-hype period is the valley of death for many games, the developers starved for cash after streamers and curious casuals move on. But the funding means that, for 1047, it’s license to hire like mad and double down.
“The scope of what we can do is now through the roof,” said Proulx. “There’s so much we couldn’t think about because we were a tiny team with a tiny budget, but now everything is on the table. We’re focusing on the long term — I look at the game as being 25% done. We don’t need to be Fortnite tomorrow, but now it really is about building the next Riot Games, the next big games business.”
In the meantime, Splitgate itself is still on the road to 1.0 and Proulx says the team can now truly focus on making it the game they and the community have been shaping it to be for years. He noted that many players have stuck by the team for years and helped make the game what it is, and that their input is just as important now.
“We read everything, we’re listening — keep the feedback coming. We’re still operating like the indie team that had to stay close with our community. We’re still in that mindset,” Proulx said, “but now we just have a ridiculous amount of money.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Millions.co, a social commerce platform geared toward professional and semi-professional athletes wanting help to monetize their fanbase by selling merch and/or on-demand video, has grabbed $10 million in funding led by Boston-based Volition Capital.
The round is being loosely pegged as a Series A as the seasoned team behind Millions self-funded the first wave of development to get the platform launched.
The founding team includes CEO Matt Whitteker, a boxing gym owner who co-founded the supply chain data management unicorn Assent Compliance and NoNotes.com; CMO Brandon Austin, co-founder of Go-Fish Cam; and, in advisor roles, Adrian Salamunovic, co-founder of DNA 11 and CanvasPop; Scott Whitteker (Fight for the Cure) and Bruce Buffer (a veteran sports announcer).
Millions launched its fan engagement social commerce platform in April — with an initial three products for pro/semi-pro athletes to pitch at their followers: Namely custom merchandize (including a free design service); ask-me-anything personalized videos; and a pay-per-view streaming offering that lets fans pay to tune into a livestream of their favorite sportsperson.
The startup’s initial plan had been to build just an e-commerce and merchandising platform but, having built that component, Salamunovic says the team decided to bundle in video products — such as personalized videos and “democratising” pay-per-view (PPV).
“Our biggest advantage and differentiator is that we are strictly focused on the sports world and fan engagement,” he tells TechCrunch. “The obvious indirect competitors are Twitch (heavily focused on e-sports/gaming), Patreon (focused on creators), Represent.com (focused on merch drops for ‘influencers’), and even OnlyFans (we know who they focus on) but we’re laser-focused on the multibillion-dollar sports market.”
“Cameo has a very similar product to our video ‘Ask Me Anything’ platform — but we don’t focus on birthday shout-outs we focus on allowing fans to ask their favorite athletes questions around their training, their success, predictions (we’ve seen a lot of gamblers use our platform to get tips) and less on things like shout-outs,” he adds. “We love Cameo, but we’re really different and focused on sports.”
“Instagram, TikTok, Snapchat, Facebook are all great social media platforms that allow athletes to engage and interact with their fans but it’s not a great place to monetize your audience,” Salamunovic also argues. “We help athletes create a brand, build a merch line, sell video content (personalized videos and watch parties all on a single platform). We’re not trying to replace any of these platforms, we’re complementing them by allowing the athletes to provide a single link and landing page for deeper interaction and monetization. The fans seem to love it too.”
At this stage, Millions only has around 300 athlete profiles live but says it has “thousands” who’ve registered interest across a variety of sports categories.
Its first focus — including for partnerships with agencies and sports leagues — has been on “combat sports and gyms”. But the platform has a long list of sports types in the search filter — from lacrosse to water polo to baseball or gymnastics — so the ambition is to go after a very broad funnel of pro/semi sportspeople.
And for every Michael Jordan or Cristiano Ronaldo — aka, those top-tier athletes who can command hundreds of millions in sponsorship fees by inking partnerships with top brands to promote their products and who you certainly won’t find selling hats on Millions — there are scores of athletes who aren’t able to cut such sweet deals and who will have far more modest fanbases.
It’s that broad field of players and performers who Millions hopes will flock to its platform — and take up its dedicated offer of social commerce tools and tech to engage with and monetize their followers.
Commenting on the funding in a statement, Sean Cantwell, managing partner at Volition Capital, suggested: “Athletes are always looking for ways to connect on a deeper level with fans, generate additional revenue streams and build their personal brands and Millions offers all of this on a single platform. We think that Millions is the future of fan engagement.”
To help grease the funnel of sportspeople it needs to drive eyeballs to its platform, Millions is offering athletes a “signing bonus” when they join and start selling — with a variety of tiers of bonus (of up to $5K) per sportsperson.
“We initially wanted to stay hyper-focused on combat sports and not try to ‘boil the ocean’. Now we’re releasing new athletes’ profiles daily and introducing new sports like football, volleyball, golf and more,” notes Salamunovic. “Really, this platform is designed for any athlete who wants to reach their fans and create new monetization channels without having to put a ton of effort into things like page design, technology, design or logistics… we take care of all that so they can focus on engaging with their fans and most importantly on their sport and training.”
“We’re looking to build the most important sports tech company in history,” he adds. “We’re going to be the Etsy ($21 billion market cap) of sports. That’s an ambitious statement but it’s true; 98% of athletes NEED our product/platform.”
Chasing that scale is why Millions is raising now. And while the early focus has been on North America — where about 90% of the onboarded sportspeople hail from currently — it reckons there’s “huge growth potential” in Europe and Asia so is very much gunning to build a global business.
It says it’ll be splashing Series A cash on growing its product engineering team and recruiting to expand its team generally, as well as spending on marketing to get the word out to athletes and get more signed up to build their own brands and sell direct to fans.
“I believe a powerful thing we’re doing, past just the product offering, is enabling athletes to have a team,” adds Austin. “With Millions, athletes get a marketing team, a personal account manager, and a design team that they can use to build their brand and product line, and to promote to, and further build, their fan base. We allow the athlete to focus on training, playing/fighting, and winning while we help take care of everything else, and coach them on how to brand and market themselves.”
Millions’ business model is to take a 20% cut of all sales athletes make via the platform — with the split remaining the same for merchandise or video sales.
For the former, Millions is using a global network of print-on-demand suppliers to do the fulfilment.
While products the platform can customize for athletes to sell as their own brand merch include t-shirts, caps and hoodies.
Powered by WPeMatico