Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
A new auto-injecting pill might soon become a replacement for subcutaneous injection treatments.
The idea for this so-called robotic pill came out of a research project around eight years ago from InCube Labs — a life sciences lab operated by Rani Therapeutics Chairman and CEO Mir Imran, who has degrees in electrical and biomedical engineering from Rutgers University. A prominent figure in life sciences innovation, Imran has founded more than 20 medical device companies and helped develop the world’s first implantable cardiac defibrillator.
In working on the technology behind San Jose-based Rani Therapeutics, Imran and his team wanted to find a way to relieve some of the painful side effects of subcutaneous (or under-the-skin) injections, while also improving the treatment’s efficacy. “The technology itself started with a very simple thesis,” said Imran in an interview. “We thought, why can’t we create a pill that contains a biologic drug that you swallow, and once it gets to the intestine, it transforms itself and delivers a pain-free injection?”
Rani Therapeutics’ approach is based on inherent properties of the gastrointestinal tract. An injecting mechanism in their pill is surrounded by a pH-sensitive coating that dissolves as the capsule moves from a patient’s stomach to the small intestine. This helps ensure that the pill starts injecting the medicine in the right place at the right time. Once there, the reactants mix and produce carbon dioxide, which in turn inflates a small balloon that helps create a pressure difference to help inject the drug-loaded needles into the intestinal wall. “So it’s a really well-timed cascade of events that results in the delivery of this needle,” said Imran.
Despite its somewhat mechanical procedure, the pill itself contains no metal or springs, reducing the chance of an inflammatory response in the body. The needles and other components are instead made of injectable-grade polymers, that Imran said has been used in other medical devices as well. Delivering the injections to the upper part of the small intestine also carries little risk of infection, as the prevalence of stomach acid and bile from the liver prevent bacteria from readily growing there.
One of Imran’s priorities for the pill was to eliminate the painful side effects of subcutaneous injections. “It wouldn’t make sense to replace them with another painful injection,” he said. “But biology was on our side, because your intestines don’t have the kind of pain sensors your skin does.” What’s more, administering the injection into the highly vascularized wall of the small intestine actually allows the treatment to work more efficiently than when applied through subcutaneous injection, which typically deposits the treatment into fatty tissue.
Imran and his team have plans to use the pill for a variety of indications, including the growth hormone disorder acromegaly, diabetes and osteoporosis. In January 2020, their acromegaly treatment, Octreotide, demonstrated both safety and sustained bioavailability in primary clinical trials. They hope to pursue future clinical trials for other indications, but chose to prioritize acromegaly initially because of its well-established treatment drug but “very painful injection,” Imran said.
At the end of last year, Rani Therapeutics raised $69 million in new funding to help further develop and test their platform. “This will finance us for the next several years,” said Imran. “Our approach to the business is to make the technology very robust and manufacturable.”
Early Stage is the premier ‘how-to’ event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear first-hand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company-building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in – there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Eco, which has built out a digital global cryptocurrency platform, announced Friday that it has raised $26 million in a funding round led by a16z Crypto.
Founded in 2018, the SF-based startup’s platform is designed to be used as a payment tool around the world for daily-use transactions. The company emphasizes that it’s “not a bank, checking account, or credit card.”
“We’re building something better than all of those combined,” it said in a blog post. The company’s mission has also been described as an effort to use cryptocurrency as a way “to marry savings and spending,” according to this CoinList article.
Eco users can earn up to 5% annually on their deposits and get 5% cash back when transacting with merchants such as Amazon, Uber and others. Next up: The company says it will give its users the ability to pay bills, pay friends and more “all from the same, single wallet.” That same wallet, it says, rewards people every time they spend or save.
After a “successful” alpha test with millions of dollars deposited, the company’s Eco App is now available to the public.
A slew of other VC firms participated in Eco’s latest financing, including Founders Fund, Activant Capital, Slow Ventures, Coinbase Ventures, Tribe Capital, Valor Capital Group and more than one hundred other funds and angels. Expa and Pantera Capital co-led the company’s $8.5 million funding round.
CoinList co-founder Andy Bromberg stepped down from his role last fall to head up Eco. The startup was originally called Beam before rebranding to Eco “thanks to involvement by founding advisor, Garrett Camp, who held the Eco brand,” according to Coindesk. Camp is an Uber co-founder and Expa is his venture fund.
For a16z Crypto, leading the round is in line with its mission.
In a blog post co-written by Katie Haun and Arianna Simpson, the firm outlined why it’s pumped about Eco and its plans.
“One of the challenges in any new industry — crypto being no exception — is building things that are not just cool for the sake of cool, but that manage to reach and delight a broad set of users,” they wrote. “Technology is at its best when it’s improving the lives of people in tangible, concrete ways…At a16z Crypto, we are constantly on the lookout for paths to get cryptocurrency into the hands of the next billion people. How do we think that will happen? By helping them achieve what they already want to do: spend, save, and make money — and by focusing users on tangible benefits, not on the underlying technology.”
Eco is not the only crypto platform offering rewards to users. Lolli gives users free bitcoin or cash when they shop at over 1,000 top stores.
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico
Insurance agents spend hours handling paperwork and grabbing client information over the phone. A new seed-stage startup, InsurGrid, has developed a software solution to help ease the process, and make it easier for agents to serve existing clients — and secure new ones.
InsurGrid gives agents a personalized platform to collect information from clients, such as date of birth, driver’s license information and policy declaration. This platform helps agents avoid sitting on long calls or managing back-to-back emails, and instead gives them one spot to understand how all their different clients function. It is starting with property and casualty management.
The startup integrates with 85 insurance carriers, serving as the software layer instead of the provider. Using the InsurGrid platform, insurers can ask clients to upload information and within seconds be registered as a policyholder. This essentially turns into a living Rolodex that insurers can use to access information on the account, and offer quotes on a faster rate.
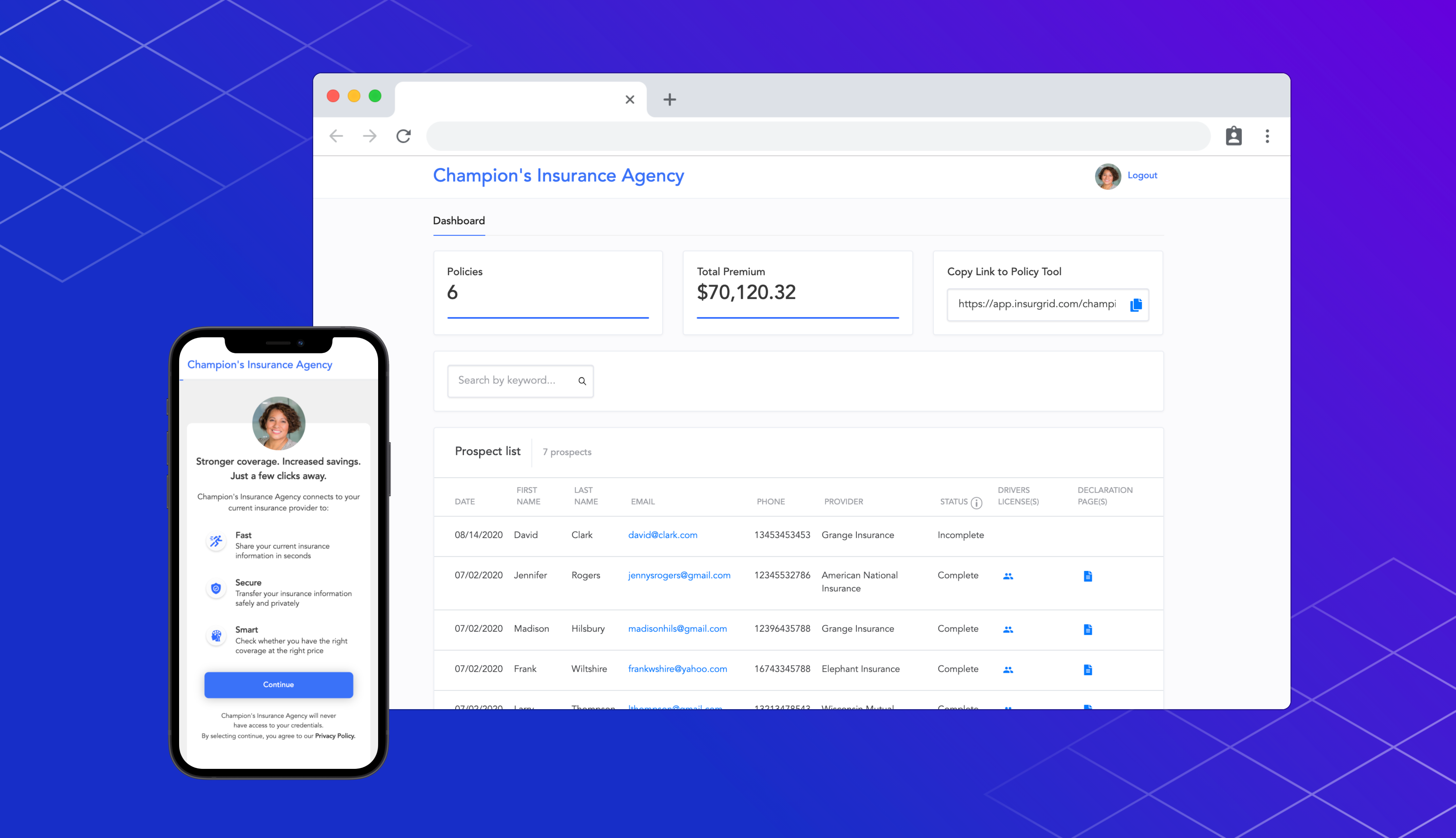
Image Credits: InsurGrid
There’s a monetary benefit in providing better service. Eden Insurance, a customer of InsurGrid, said that people who submit information through the platform converted at an 82% higher rate than those who don’t. Jeremy Eden, the agency owner of Eden Insurance, said they were able to show consumers that its plan was $300 cheaper than its existing rate.
At the heart of InsurGrid is a bet from the founding team that legacy insurance agents aren’t going anywhere. Co-founder/CEO Chase Beach pointed out that the majority of the $684 billion of annual property and casualty insurance premiums in the United States is distributed by approximately 800,000 agents working in 16,000 brokerages. So far, InsurGrid works with more than 150 of those agencies.
When asked if InsurGrid ever had plans to offer its own insurance, similar to insurtech giants Hippo, Lemonade and Root, Beach said that it is solely working on innovating around the sales process for now. He said that these big companies, which have either recently gone public or are planning to, still rely on agents to be successful.
“Instead of us replacing the insurance agent, what if we gave them that same level of technology of a Hippo or large carrier,” Beach said. “And provide them with the digital experiences so they can compete in 2021.”
As time goes on, he sees insurance agents taking the same role that financial advisors or real estate agents take: “very much involved in the process because they are that expert.”
Other startups that have popped up in this space include Gabi, Trellis and Canopy Connect. The differentiator, the team sees, is that Beach comes from a 144-year-old insurance legacy, giving him key insights on how to sell to agents in a successful and effective way. It is starting with sales, but expect InsurGrid to expand to other parts of the insurance process as well.
To help them compete with new and old startups, InsurGrid recently raised $1.3 million in pre-seed financing to help it fulfill its goal to be the “underdog for the underdogs,” Beach said. Investors include Engineering Capital, Hustle Fund, Vess Capital, Sahil Lavingia and Trevor Kienzle.
Powered by WPeMatico
Dija, the London-based grocery delivery startup, is officially launching today and confirming that it raised £20 million in seed funding in December — a round that we first reported was partially closed the previous month.
Backing the company is Blossom Capital, Creandum and Index Ventures, with Dija seemingly able to raise pre-launch. In fact, there are already rumours swirling around London’s venture capital community that the upstart may be out raising again already — a figure up to £100 million was mooted by one source — as the race to become the early European leader in the burgeoning “dark” grocery store space heats up.

Image Credits: Dija
Over the last few months, a host of European startups have launched with the promise of delivering grocery and other convenience store items within 10-15 minutes of ordering. They do this by building out their own hyper-local, delivery-only fulfilment centres — so-called “dark stores” — and recruiting their own delivery personnel. This full-stack or vertical approach and the visibility it provides is then supposed to produce enough supply chain and logistics efficiency to make the unit economics work, although that part is far from proven.
Earlier this week, Berlin-based Flink announced that it had raised $52 million in seed financing in a mixture of equity and debt. The company didn’t break out the equity-debt split, though one source told me the equity component was roughly half and half.
Others in the space include Berlin’s Gorillas, London’s Jiffy and Weezy, and France’s Cajoo, all of which also claim to focus on fresh food and groceries. There’s also the likes of Zapp, which is still in stealth and more focused on a potentially higher-margin convenience store offering similar to U.S. unicorn goPuff. Related: goPuff itself is also looking to expand into Europe and is currently in talks to acquire or invest in the U.K.’s Fancy, which some have dubbed a mini goPuff.
However, let’s get back to Dija. Founded by Alberto Menolascina and Yusuf Saban, who both spent a number of years at Deliveroo in senior positions, the company has opened up shop in central London and promises to let you order groceries and other convenience products within 10 minutes. It has hubs in South Kensington, Fulham and Hackney, and says it plans to open 20 further hubs, covering central London and Zone 2, by the summer. Each hub carries around 2,000 products, claiming to be sold at “recommended retail prices”. A flat delivery fee of £1.99 is charged per order.
“The only competitors that we are focused on are the large supermarket chains who dominate a global $12 trillion industry,” Dija’s Menolascina tells me when I ask about competitors. “What really sets us apart from them, besides our speed and technology, is our team, who all have a background in growing and disrupting this industry, including myself and Yusuf, who built and scaled Deliveroo from the ground up”.
Menolascina was previously director of Corporate Strategy and Development at the takeout delivery behemoth and held several positions before that. He also co-founded Everli (formerly Supermercato24), the Instacart-styled grocery delivery company in Italy, and also worked at Just Eat. Saban is the former chief of staff to CEO at Deliveroo and also worked at investment bank Morgan Stanley.
During Dija’s soft-launch, Menolascina says that typical customers have been doing their weekly food shop using the app, and also fulfilling other needs, such as last-minute emergencies or late night cravings. “The pain points Dija is helping to solve are universal and we built Dija to be accessible to everyone,” he says. “It’s why we offer products at retail prices, available in 10 minutes — combining value and convenience. Already, Dija is becoming a key service for parents who are pressed for time working from home and homeschooling, as one example”.
Despite the millions of dollars being pumped into the space, a number of VCs I’ve spoken to privately are skeptical that fresh groceries with near instant delivery can be made to work. The thinking is that fresh food perishes, margins are lower and basket sizes won’t be large enough to cover the costs of delivery.
“This might be the case for other companies, but almost everyone at Dija comes from this industry and knows exactly what they are doing, from buying and merchandising to data and marketing,” Menolascina says, pushing back. “It’s also worth pointing out that we are a full-stack model, so we’re not sharing our margin with other parties. In terms of the average basket size, it varies depending on the customer’s need. On one hand, we have customers who do their entire grocery shop through Dija, while on the other hand, our customers depend on us for emergency purchases e.g. nappies, batteries etc.”
On pricing, he says that, like any retail business, Dija buys products at wholesale prices and sells them at recommended retail prices. “Going forward, we have a clear roadmap on how we generate additional revenue, including strategic partnerships, supply chain optimisation and technology enhancements,” adds Menolascina.

Image Credits: TechCrunch
Meanwhile, TechCrunch has learned that prior to launching its own app, Dija ran a number of experiments on takeout marketplace Deliveroo, including selling various convenience store items, such as potato chips and over-the-counter pharmaceuticals. If you’ve ever ordered toiletry products from “Baby & Me Pharmacy” or purchased chocolate sweets from “Valentine’s Vows,” you have likely and unknowingly shopped at Dija. Those brands, and a number of others, all delivered from the same address in South Kensington.
“Going direct to consumer without properly testing pick & pack is a big risk,” Menolascina told me in a WhatsApp message a few weeks ago, confirming the Deliveroo tests. “We created disposable virtual brands purely to learn what to sell and how to replenish, pick & pack, and deliver”.
Powered by WPeMatico
It’s not uncommon these days to hear of U.S.-based investors backing Latin American startups.
But it’s not every day that we hear of Latin American VCs investing in U.S.-based startups.
Berkeley-based fintech Flourish has raised $1.5 million in a funding round led by Brazilian venture capital firm Canary. Founded by Pedro Moura and Jessica Eting, the startup offers an “engagement and financial wellness” solution for banks, fintechs and credit unions with the goal of helping them engage and retain clients.
Also participating in the round were Xochi Ventures, First Check Ventures, Magma Capital and GV Angels as well as strategic angels including Rodrigo Xavier (former Bank of America CEO in Brazil), Beth Stelluto (formerly of Schwab), Gustavo Lasala (president and CEO of The People Fund) and Brian Requarth (founder of Viva Real).
With clients in the U.S., Bolivia and Brazil, Flourish has developed a solution that features three main modules:
In the U.S., Flourish began by testing end-user mechanics with organizations such as CommonWealth and Opportunity Fund. In 2019, it released a B2C version of the Flourish app (called the Flourish Savings App) as a pilot for its banking platform, which can integrate with banks through an SDK or an API. It is also now licensing its engagement technology to banks, retailers and fintechs across the Americas. Flourish has piloted or licensed its solution to U.S.-based credit unions, Sicoob (Brazil’s largest credit union) and BancoSol in Bolivia.
The startup makes money through a partnership model that focuses on user activation and engagement.
Both immigrants, Moura and Eting met while in the MBA program at the Haas School of Business at UC Berkeley. Moura came to the U.S. from Brazil as a teen, while Eting is the daughter of a Filiponio father and mother of Mexican descent.
The pair bonded on their joint mission of building a business that empowered people to create positive money habits and understand their finances.
Currently, the 11-person team works out of the U.S., Mexico and Brazil. It plans to use its new capital to increase its number of customers in LatAm, do more hiring and develop new functionalities for the Flourish platform.
In particular, it plans to next focus on the Brazilian market, and will scale in a few select countries in the Americas.
“There are three things that make Latin America, and more specifically Brazil, attractive to us at this moment,” Moura said. “Currently, the B2B financial technology market is still in its nascency. This combined with open banking regulation and the need for more responsible products provides Flourish a unique opportunity in Brazil.”
Powered by WPeMatico
A lot of our communication these days with each other is digital, and today one of the companies enabling that — with APIs to build chat experiences into apps — is announcing a round of funding on the back of some very strong growth.
Stream, which lets developers build chat and activity streams into apps and other services by way of a few lines of code, has raised $38 million, funding that it will be using to continue building out its existing business as well as to work on new features.
Stream started out with APIs for activity feeds, and then it expanded to chat, which today can be integrated into apps built on a variety of platforms. Currently, its customers integrate third-party chatbots and use Dolby for video and audio within Stream, but over time, these are all areas where Stream itself would like to do more.
“End-to-end encryption, chatbots: We want to take as many components as we can,” said Thierry Schellenbach, the CEO who co-founded the startup with the startup’s CTO Tommaso Barbugli in Amsterdam in 2015 (the startup still has a substantial team in Amsterdam headed by Barbugli, but its headquarters is now in Boulder, Colorado, where Schellenbach eventually moved).

Image Credits: Stream (opens in a new window)
The company already has amassed a list of notable customers, including Ikea-owned TaskRabbit, NBC Sports, Unilever, Delivery Hero, Gojek, eToro and Stanford University, as well as a number of others that it’s not disclosing across healthcare, education, finance, virtual events, dating, gaming and social. Together, the apps Stream powers cover more than 1 billion users.
This Series B round is being led by Felicis Ventures’ Aydin Senkut, with previous backers GGV Capital and 01 Advisors (the fund co-founded by Twitter’s former CEO and COO, Dick Costolo and Adam Bain) also participating.
Alongside them, a mix of previous and new individual and smaller investors also participated: Olivier Pomel, CEO of Datadog; Tom Preston-Werner, co-founder of GitHub; Amsterdam-based Knight Capital; Johnny Boufarhat, founder and CEO of Hopin; and Selcuk Atli, co-founder and CEO of social gaming app Bunch (itself having raised a notable round of $20 million led by General Catalyst not long ago).
That list is a notable indicator of what kinds of startups are also quietly working with Stream.
The company is not disclosing its valuation but said chat revenue grew by 500% in 2020.
Indeed, the Series B speaks of a moment of opportunity: It is coming only about six months after the startup raised a Series A of $15 million, and in fact Stream wasn’t looking to raise right now.
“We were not planning to raise funding until later this year but then Aydin reached out to us and made it hard to say no,” Schellenbach said.
“More than anything else, they are building on the platforms in the tech that matters,” Senkut added in an interview, noting that its users were attesting to a strong return on investment. “It’s rare to see a product so critical to customers and scaling well. It’s just uncapped capability… and we want to be a part of the story.”
That moment of opportunity is not one that Stream is pursuing on its own.
Some of the more significant of the many players in the world of API-based communications services like messaging, activity streams — those consolidated updates you get in apps that tell you when people have responded to a post of yours or new content has landed that is relevant to you, or that you have a message, and so on — and chat include SendBird, Agora, PubNub, Twilio and Sinch, all of which have variously raised substantial funding, found a lot of traction with customers, or are positioning themselves as consolidators.
That may speak of competition, but it also points to the vast market there for the tapping.
Indeed, one of the reasons companies like Stream are doing so well right now is because of what they have built and the market demand for it.
Communications services like Stream’s might be best compared to what companies like Adyen (another major tech force out of Amsterdam), Stripe, Rapyd, Mambu and others are doing in the world of fintech.
As with something like payments, the mechanics of building, for example, chat functionality can be complex, usually requiring the knitting together of an array of services and platforms that do not naturally speak to each other.
At the same time, something like an activity feed or a messaging feature is central to how a lot of apps work, even if they are not the core feature of the product itself. One good example of how that works are food ordering and delivery apps: they are not by their nature “chat apps” but they need to have a chat option in them for when you do need to communicate with a driver or a restaurant.
Putting those forces together, it’s pretty logical that we’d see the emergence of a range of tech companies that both have done the hard work of building the mechanics of, say, a chat service, and making that accessible by way of an API to those who want to use it, with APIs being one of the more central and standard building blocks in apps today; and a surge of developers keen to get their hands on those APIs to build that functionality into their apps.
What Stream is working on is not to be confused with the customer-service focused services that companies like Zendesk or Intercom are building when they talk about chat for apps. Those can be specialized features in themselves that link in with CRM systems and customer services teams and other products for marketing analytics and so on. Instead, Stream’s focus are services for consumers to talk to other consumers.
What is a trend worth watching is whether easy-to-integrate services like Stream’s might signal the proliferation of more social apps over time.
There is already at least one key customer — which I am now allowed to name — that is a steadily growing, still young social app, which has built the core of its service on Stream’s API.
With just a handful of companies — led by Facebook, but also including ByteDance/TikTok, Tencent, Twitter, Snap, Google (via YouTube) and some others depending on the region — holding an outsized grip on social interactions, easier, platform-agnostic access to core communications tools like chat could potentially help more of these, with different takes on “social” business models, find their way into the world.
“Stream’s technology addresses a common problem in product development by offering an easy-to-integrate and scalable messaging solution,” said Dick Costolo of 01 Advisors, and the former Twitter CEO, in a statement. “Beyond that, their team and clear vision set them apart, and we ardently back their mission.”
Updated to correct that the revenue growth is not related to the valuation figure.
Powered by WPeMatico
Hepster, an insurtech platform from Germany, has raised $10 million in a Series A funding round led by Element Ventures. Also participating was Seventure Partners, MBMV and GPS Ventures, as well as previous investors. The funds will be used to broaden the Hepster insurance ecosystem and scale up its network, with an emphasis on automation.
The German insurance market is famously slow at adopting new practices, and Hepster is part of a new wave of insurtech startups in the country taking advantage of this. It allows businesses to build insurance policies from scratch, matched specifically to the needs of their individual service or industry. E-commerce players, for instance, can then embed these insurance products into the e-commerce journey.
Its products are therefore better suited to the new sector of, for example, shared e-bike schemes and peer-to-peer rental platforms, which are rarely covered by traditional brokers in Germany. However, it also caters to traditional, established industries as well.
It now has more than 700 partners, including European bike retailers and rental companies Greenstorm Mobility and Baron Mobility, as well as Berlin-based cargo bike provider Citkar and Munich e-bike startup SUSHI.
Christian Range, Hepster co-founder and CEO, said in a statement: “Hepster is now a key player within the European insurance market. Our state-of-the-art technology with our API-driven ecosystem, as well as our highly service-oriented approach, sets us apart.”
In an interview he told me: “Germany is the toughest market with the most regulations, the most laws. We have a saying in Germany, if you can make it in Germany, you can make it everywhere. Also, it’s a big market in terms of selling insurance products because Germans really like insurance in every regard. So there is huge market potential in Germany I think.”
Michael McFadgen, partner at Element Ventures, said: “As new industries and business models emerge, companies need much more flexible insurance propositions than what is currently being offered by traditional brokers. Hepster is the breakout company in the space, and their focus on embedded insurance will pay dividends in years to come.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Healthcare is one of the most complex industries out there, creating frustration on the consumer side but also the opportunity for huge improvements from, in a way, rather simple methods. Halo Diagnostics (or Dx for short) has raised a $19 million Series A to improve diagnosis of several serious illnesses by crossing the streams from multiple tests and making the improved process easily available to providers. They’ve also taken the unusual step of taking out an eight-figure line of credit to buy outright the medical facilities they’ll need to do it.
As anyone who’s had to deal with major health concerns can attest, the care you get differs widely from one provider to another depending on many factors, not least of which are what your insurance covers and what methods are already in use by the provider.
For men going in to get a prostate cancer screening, for instance, the common bloodwork and rectal exam haven’t changed in years, and really aren’t that great at predicting problems, leading to uncertainty and unnecessary procedures like biopsies.
Of course, if you’re lucky, your provider might offer multiparametric MRIs, which are much better at finding problems — and if you combine that MRI with a urine test that checks for genetic markers, the detection accuracy rises to practically foolproof levels.
But these tests are more expensive, take special facilities and personnel and may otherwise not fit into the provider’s existing infrastructure. Halo aims to provide that infrastructure by revamping the medical data stream to allow for this kind of multi-factor diagnosis.
“Basically doctors and imaging centers aren’t offering latest level of care. If you’re lucky you might get it, but in community medicine you’re not going to,” said Brian Axe, co-founder and chief product officer at Halo Dx. “As perverse as it sounds, what the healthcare industry needs to adopt the latest medical advancements is better financial alignment in addition to better outcomes. The challenge is the integrated diagnostic solution — how do you get these orders, go to market and talk with primary care providers?”
An added obstacle is that multi-modal testing isn’t really the kind of thing medical imaging or testing providers just decide to get into. An imaging center isn’t going to hear that a urine test improves reliability and think “well let’s buy the building next door and start doing that too!” It’s costly and complex to build out testing facilities, and getting the expertise to run them and combine the results is another hurdle.
So Halo Dx is parachuting in with tens of millions of dollars and purchasing the imaging and testing centers themselves (four so far), taking over their operations and combining them with other tests.
Assuming that much liability as a young company may seem like folly, but it helps that these imaging centers are strong businesses already — not derelict, half-paid-off MRI machines being operated at a loss.
“The imaging orders are coming in already; the centers are profitable. They’re coming on board because they see how technology is coming to disrupt them, and they want to help drive the change,” said Axe.
Prostate and breast cancers are the first target, but more and better data produce similarly improved diagnosis and treatment planning for more conditions, potentially (these are still being proven out), like Multiple Sclerosis, Parkinson’s and other neurodegenerative diseases.
With one company running multiple intake, imaging and testing facilities and integrating the results, it’s much more likely that providers will sign up. And Halo Dx is trying to bring some of the enterprise-grade software expertise to bear on the historically neglected field of medical data storage and communication.
Axe deferred to the company’s chief medical officer, Dr. John Feller, on the perils of that aspect of the field.
“Dr Feller describes this so well: ‘I have this state of the art MRI machine that can see inside your body, but because of the fragmented solutions that are out there, from intake to the storage centers, I feel like I’m living with pre-dot-com era tech and it’s crippling,’ ” Axe recalled. “If you want to look at records or recommend additional tests, software vendors don’t talk to each other or integrate. You have three providers that need to talk to each other and there’s a dozen systems between them.”
Axe compared the company’s approach here to One Medical’s — increasing efficiency and using that to make the relationship with the consumer lighter and easier, leading to more interactions.
In some ways it seems like a risky move, taking on nearly a hundred million in obligations and jumping into a hugely complex and highly regulated space. But the team is accomplished, the backers are notable, the potential for growth is there, and the success of the likes of One Medical have likely emboldened all involved.
Zola Global Investors led the round, and a who’s-who in medical and tech participated: Anne Wojcicki, Fred Moll, Stephen Pomeranz, Bob Reed, Robert Ciardi, Jim Pallotta and, believe it or not, Ronnie Lott of 49ers fame.
These and others involved make for a strong statement of confidence in both the model and the specific approach Halo Dx is taking to expanding and advancing care. Here’s hoping, however, that you won’t have to make use of their services.
Powered by WPeMatico
Fintech startup ClearGlass Analytics has closed a £2.6 million ($3.6 million) funding round for its platform, which aims to create greater transparency on fees in the long-term savings market, such as pensions and the wider asset management market.
The £2.6 million seed round includes European VC Lakestar and Outward VC, the venture arm of Investec, as well as several angels from both the asset management and pension fund worlds. These include Ruston Smith, a pension trustee; Richard Butcher, chair of the PLSA (U.K. pension trade body); Chris Wilcox, former Global Head of JP Morgan Asset Management; and Rob O’Rahilly, Sikander Ilyas and Alex Large, also former JP Morgan employees.
ClearGlass is targeting the £1.5 trillion mature “Defined Benefit” pension schemes market and claims to now work with more than 500 DB pension funds. It will use the funding to expand into the U.K. Defined Contribution pension market, and consolidate its early footprint in Europe and Africa.
How ClearGlass works is that it acts as a data interface between asset managers and their clients. Pension funds then use the platform to see all of their investment costs in one place, thus getting more data than usual from more asset managers and other suppliers. This helps the funds see the “true cost” of what they are paying for the management of their investments. ClearGlass claims to be able to uncover the kinds of costs of asset management that, in some instances, can be more than double those expected.
The startup recently did an analysis of the cost and performance of more than 400 asset managers. It found that while most U.K. asset managers were meeting minimum standards for data delivery, quality and accuracy, 30 (including some powerful players) did not pass their tests.
The company was founded by Dr. Christopher Sier, a World Bank and FCA expert who previously developed the cost transparency standard at the request of the FCA, and co-founders Ritesh Singhania and Kunal Varma.
Sier, founder and CEO, said: “Finding your costs are so much larger is shocking, but also something to be celebrated. These incremental costs were always there, they just weren’t exposed, and now you can identify those and bring about change. You can’t manage what you don’t measure.”
In an interview with TechCrunch, Ritesh Singhania, COO, said getting the data about pension funds is normally “super challenging and complicated. And second of all, even when you got the data, you couldn’t make head nor tail of it because you can’t compare it across funds. What we have done is that we have been the line of communication between the manager and the pension fund. So we have built a piece of technology that helps with the communication between the asset managers, and the pension funds to be able to collect that data, check that data. And finally, give them something that doesn’t require them to spend 20 hours to understand it.”
ClearGlass was incubated by the Founders Factory accelerator.
Powered by WPeMatico
Colombian startup Elenas says it’s helping tens of thousands of women make money by selling products online. And today, it announced that it has raised $6 million in Series A funding.
That’s on top of the $2 million seed round that Elenas announced last fall. Founder and CEO Zach Oschin said that demand continues to grow, particularly with high unemployment levels (particularly among women), while consumers remain nervous about in-person shopping during the pandemic.
“We’ve been able to provide opportunities for tens of thousands of women to earn extra income,” Oschin said.
He suggested that Elenas is essentially a reinvention of the direct sales/catalog sales model that 11 million women participate in across the Latin America. The idea is that independent seller/entrepreneurs (often but not always women) can browse a catalog of products in categories like beauty, personal care and electronics, from more than 250 distributors and brands, all available at a discounted wholesale price. They decide what they want to sell, how much they want to mark the price up and then promote the products on social channels like WhatsApp and Facebook.
Besides its digital focus, Oschin said Elenas is better for the resellers because there’s less risk: “We don’t hold inventory for the company, which is very different than traditional direct sales, and our entrepreneurs don’t ever hold inventory.” Nor do those entrepreneurs need to get involved in things like payment collection or delivery, because Elenas and its distributor partners handle all of that.
“For us, the goal is to provide this backend operating system that gives women everything they need to run their store,” he added.
Elenas offers an automated on-boarding process for the sellers, but Oschin said that within the app, “we do a lot of work to train our sellers how to sell.”

Elenas CEO Zach Oschin. Image Credits: Elenas
The company (which participated in our Latin American Startup Battlefield in 2018) says it’s now paid out more than $7 million to its sellers. It doesn’t limit participation by gender, but Oschin estimated that more than 95% of sellers are women, with 80% of them under the age of 30 and about a third of them without any previous direct sales experience.
The new funding comes from Leo Capital, FJ Labs, Alpha4 Ventures and Meesho. Oschin said the company’s investors have a presence across six different continents, reflecting its international vision. Indeed, one of its next steps is expanding across Latin America, starting with Mexico and then Peru.
“Having seen the meteoric growth of social commerce in India and China we are excited to partner with Elenas as they have demonstrated the right product and operating model for the region,” said Leo Capital co-founder Shwetank Verma in a statement. “The Elenas team has built a solution that’s inclusive, impactful and is well positioned for exponential growth.”
Early Stage is the premier “how-to” event for startup entrepreneurs and investors. You’ll hear firsthand how some of the most successful founders and VCs build their businesses, raise money and manage their portfolios. We’ll cover every aspect of company building: Fundraising, recruiting, sales, product-market fit, PR, marketing and brand building. Each session also has audience participation built-in — there’s ample time included for audience questions and discussion.
Powered by WPeMatico