Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Robotic process automation (RPA) has found a strong foothold in the world of enterprise IT through its effective use of AI and other technology to help automate repetitive tasks to free up people to focus on more complicated work. Today, a startup called Infinitus is coming out of stealth to apply this concept to the world of healthcare — specifically, to speed up the process of voice communication between entities in the fragmented U.S. healthcare industry.
Infinitus uses “voice RPA” to become the machine-generated voice that makes calls from, say, healthcare providers or pharmacies to insurance companies to go through a series of questions (directed at humans at the other end) that typically need to be answered before payments are authorized and other procedures can take place. Those conversations are then ingested into Infinitus’s platform to parse them for relevant information that is input into the right fields to trigger whatever actions need to happen as a result of the calls.
The startup is coming out of “stealth mode” today but it has been around for a couple of years already and has signed on a number of large healthcare companies as customers — for example, the wholesale drug giant AmerisourceBergen — and is in some cases contributing its technology to public health efforts around the current coronavirus pandemic, with one organization currently using it to automate a mass calling system across several states to get a better idea of vaccine availability to help connect the earliest doses with the most vulnerable groups that need them the fastest.
It made 75,000 calls on behalf of 12,000 providers in January alone.
Infinitus’ public launch is also coming with a funding kicker: it has picked up $21.4 million in Series A funding from a group of big-name investors to build the business.
The round is being co-led by Kleiner Perkins and Coatue, with Gradient Ventures (Google’s early-stage AI fund), Quiet Capital, Firebolt Ventures and Tau Ventures also participating, along with individual investments from a selection of executives across the worlds of AI and big tech: Ian Goodfellow, Gokul Rajaram, Aparna Chennapragada and Qasar Younis.
Coatue is shaping up to be a huge investor in the opportunity in RPA. Earlier this week, it emerged that it co-led the latest investment in UiPath, one of the leaders in the space, having been a part of previous rounds as well.
“Coatue is proud to have led the Series A in Infinitus,” says Yanda Erlich, a general partner at Coatue. “We are big believers in the transformative power of RPA and Enterprise Automation. We believe Infinitus’ VoiceRPA solution enables healthcare organizations to automate previously costly and manual calls and faxes and empowers these organizations to see benefits from end-to-end process automation.”
The problem that Infinitus is addressing is the fact that healthcare, in particular in the privatized U.S. market, has a lot of time-consuming and often confusing red tape when it comes to getting things done. And a lot of the most immediate pain points of that process can be found in voice calls, which are the primary basis of critical communications between different entities in the ecosystem.
Voice calls are used to initiate most processes, whether it’s to obtain critical information, follow up on a form or previous communication, or pass on some data, or of course provide clearance for a payment.
There are 900 million calls of these kinds made in the U.S., with the average length of each call 35 minutes, and with the average healthcare professional who works in an administrative role to make those calls dedicating some 4.5 hours each day to being on the phone.
All of this ultimately adds to the exorbitant costs of healthcare services in the U.S. (and likely some of those inscrutable lines of fees that you might see on bills), not to mention delays in giving care. (And those volumes underscore just what a small piece Infinitus touches today.)
Founder and CEO Ankit Jain — a repeat entrepreneur and ex-Googler who held senior roles in engineering and was a founding partner at Gradient at the search giant — told TechCrunch in an interview that the idea for Infinitus first occurred to him a couple of years ago, when he was still at Gradient.
“We were starting to see a lot of improvements in voice communications technology, turning text into speech and speech into text. I realised that it would soon be possible to automate phone calls where a machine could carry out a full conversation with someone.”
Indeed, around that time, Google itself had launched Duplex, a service built around the same principle, but aimed at consumers, for people to book appointments, restaurant tables and other services.
He determined that just being able to talk like a human and understand natural language wasn’t the only issue, and not even the main one, in enterprises applications like healthcare environments, which rely on specific jargon and particular scenarios that are probably less rather than more like actual human interactions.
“I thought, if someone wanted to build this for healthcare it would change it,” he said. And so he decided to do just that.
Jain said that Infinitus is using public cloud speech to text systems but the natural language processing and flows to triage and use of the information gained from the conversations are built in house. The specialization of the content and interactions potentially is also one reason why Infinitus might not worry so soon about cannibalization from bigger RPA players, at least for now.
The fact that services like these — the new generation of robocalls, as it were — can sound “lifelike”, like actual humans, has been something that consumer versions have aspired to, although that hasn’t always worked out for the best. Duplex, for example, in its early days came under criticism for how its excellent quality might actually be deceptive, because it wasn’t clear to users they were speaking to a machine logging their responses in a data harnessing exercise. Jain notes that Infinitus is actually intentionally choosing voices that sound like bots to help make that clear to those taking the calls.
He said that this also “helps reduce the level of chatter” on the conversation and keeps the person speaking focused on business.
On that front, it seems that while Infinitus works like other voice RPA services, connected up with live, human agents who can take over calls if they get tricky, that hasn’t really needed to be used.
“Today we don’t need to triage with humans because we see high enough success rates with our system,” he said.
You might wonder, why hasn’t the healthcare industry just moved past voice altogether? Surely there are ways of exchanging data between entities so that calls could become obsolete? Turns out that at least for now that isn’t something that will change quickly, Jain said.
Part of it is because the fragmentation in the market means it’s hard to implement new standards across the board, covering hundreds of insurance payers, healthcare providers, pharmaceutical groups, billing and collections organisations and more. And when it comes down to it, a phone call ends up being the easiest route for many admins who might have to typically deal with 100 different payment companies and other entities, each with a different logging mechanism. “It’s a lot of cognitive load, so it’s often easier to just pick up the phone,” Jain said.
Bringing in voiceRPA like Infinitus’s is part of that long haul to update the bigger system.
“By automating one side we are showing the other side that it can be done,” Jain said. “Right now, there are just too many players and getting them to agree on one standard is a gargantuan task, so trying to win one small piece after another is how it’s done. It should not be voice, but by the time standards bodies agree on something else, the world has moved on.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Virtual health and wellness platforms have grown increasingly popular throughout the pandemic, but a new startup wants to focus that effort exclusively on senior citizens. Bold, a digital health and wellness service, plans to prevent chronic health problems in older adults through free and personalized exercise programs. Co-founded by Amanda Rees and her partner Hari Arul, Bold picked up $7 million this week in seed funding led by Julie Yoo of Silicon Valley-based Andreessen Horowitz.
Rees said in an interview that the idea for Bold came from time she spent caring for her grandmother, helping her through health challenges like falls. “I kept thinking about solutions we could build to keep someone healthier longer, rather than waiting for until they have a fall or something else goes off the rails to intervene,” she said. Rees started Bold to use what she’d learned from her own experience in dance and yoga to help her grandmother practice maintaining balance to prevent future falls. “My passion really was around ways to sort of widen the aperture and make these solutions more accessible and built for older people.”
The member experience is pretty straightforward. Users fill out some brief fitness information on the web-based platform, outlining their goals and current baseline. From that information, Bold creates a personalized program that ranges from a short, seated Tai Chi class once a week, to cardio and strength classes meeting multiple times each week. “The idea is to really meet a member where they are, and then through our programming, help them along their journey of doing the types of exercises that are going to have the most immediate benefit for them,” said Rees.
Bold’s funding round comes at a time of concern around ballooning healthcare expenses for older populations, and a focus on how to reduce these costs for both current and future generations. While falls alone aren’t necessarily complex medical incidents, they have the potential to lead to fractures and other serious injuries. Bold’s preventative approach to falls is a more active solution than necklace or bracelet monitors that send a signal to emergency services when they detect a fall. And by offering virtual programs, they can help at-risk older populations engage in exercise while avoiding potential COVID-19 exposure at gyms.
Research shows that this works. Even simple, low-intensity exercise can improve balance and strength enough to reduce the incidence of falls, which is currently the leading cause of injury and injury death among older adults.
Fewer injuries would mean less need for medical care, which would lead to money saved for hospitals and health insurers alike. That’s why in addition to their seed funding, Bold has plans to start rolling out partnerships with Medicare Advantage organizations and risk-bearing providers, which will help make their exercise programs available to users for free.
Powered by WPeMatico
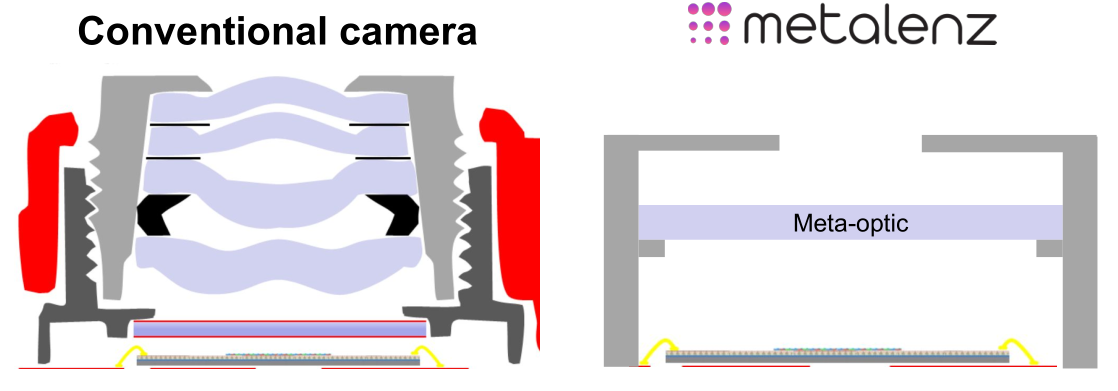
As impressive as the cameras in our smartphones are, they’re fundamentally limited by the physical necessities of lenses and sensors. Metalenz skips over that part with a camera made of a single “metasurface” that could save precious space and battery life in phones and other devices… and they’re about to ship it.
The concept is similar to, but not descended from, the “metamaterials” that gave rise to flat beam-forming radar and lidar of Lumotive and Echodyne. The idea is to take a complex 3D structure and accomplish what it does using a precisely engineered “2D” surface — not actually two-dimensional, of course, but usually a plane with features measured in microns.
In the case of a camera, the main components are of course a lens (these days it’s usually several stacked), which corrals the light, and an image sensor, which senses and measures that light. The problem faced by cameras now, particularly in smartphones, is that the lenses can’t be made much smaller without seriously affecting the clarity of the image. Likewise sensors are nearly at the limit of how much light they can work with. Consequently, most of the photography advancements of the last few years have been done on the computational side.
Using an engineered surface that does away with the need for complex optics and other camera systems has been a goal for years. Back in 2016 I wrote about a NASA project that took inspiration from moth eyes to create a 2D camera of sorts. It’s harder than it sounds, though — usable imagery has been generated in labs, but it’s not the kind of thing that you take to Apple or Samsung.
Metalenz aims to change that. The company’s tech is built on the work of Harvard’s Federico Capasso, who has been publishing on the science behind metasurfaces for years. He and Rob Devlin, who did his doctorate work in Capasso’s lab, co-founded the company to commercialize their efforts.
“Early demos were extremely inefficient,” said Devlin of the field’s first entrants. “You had light scattering all over the place, the materials and processes were non-standard, the designs weren’t able to handle the demands that a real world throws at you. Making one that works and publishing a paper on it is one thing, making 10 million and making sure they all do the same thing is another.”
Their breakthrough — if years of hard work and research can be called that — is the ability not just to make a metasurface camera that produces decent images, but to do it without exotic components or manufacturing processes.
“We’re really using all standard semiconductor processes and materials here, the exact same equipment — but with lenses instead of electronics,” said Devlin. “We can already make a million lenses a day with our foundry partners.”
The thing at the bottom is the chip where the image processor and logic would be, but the meta-optic could also integrate with that. The top is a pinhole. Image Credits: Metalenz
The first challenge is more or less contained in the fact that incoming light, without lenses to bend and direct it, hits the metasurface in a much more chaotic way. Devlin’s own PhD work was concerned with taming this chaos.
“Light on a macro [i.e. conventional scale, not close-focusing] lens is controlled on the macro scale, you’re relying on the curvature to bend the light. There’s only so much you can do with it,” he explained. “But here you have features a thousand times smaller than a human hair, which gives us very fine control over the light that hits the lens.”
Those features, as you can see in this extreme close-up of the metasurface, are precisely tuned cylinders, “almost like little nano-scale Coke cans,” Devlin suggested. Like other metamaterials, these structures, far smaller than a visible or near-infrared light ray’s wavelength, manipulate the radiation by means that take a few years of study to understand.
The result is a camera with extremely small proportions and vastly less complexity than the compact camera stacks found in consumer and industrial devices. To be clear, Metalenz isn’t looking to replace the main camera on your iPhone — for conventional photography purposes the conventional lens and sensor are still the way to go. But there are other applications that play to the chip-style lens’s strengths.
Something like the FaceID assembly, for instance, presents an opportunity. “That module is a very complex one for the cell phone world — it’s almost like a Rube Goldberg machine,” said Devlin. Likewise the miniature lidar sensor.
At this scale, the priorities are different, and by subtracting the lens from the equation the amount of light that reaches the sensor is significantly increased. That means it can potentially be smaller in every dimension while performing better and drawing less power.

Image (of a very small test board) from a traditional camera, left, and metasurface camera, right. Beyond the vignetting it’s not really easy to tell what’s different, which is kind of the point. Image Credits: Metalenz
Lest you think this is still a lab-bound “wouldn’t it be nice if” type device, Metalenz is well on its way to commercial availability. The $10 million Series A they just raised was led by 3M Ventures, Applied Ventures LLC, Intel Capital, M Ventures and TDK Ventures, along with Tsingyuan Ventures and Braemar Energy Ventures — a lot of suppliers in there.
Unlike many other hardware startups, Metalenz isn’t starting with a short run of boutique demo devices but going big out of the gate.
“Because we’re using traditional fabrication techniques, it allows us to scale really quickly. We’re not building factories or foundries, we don’t have to raise hundreds of mils; we can use what’s already there,” said Devlin. “But it means we have to look at applications that are high volume. We need the units to be in that tens of millions range for our foundry partners to see it making sense.”
Although Devlin declined to get specific, he did say that their first partner is “active in 3D sensing” and that a consumer device, though not a phone, would be shipping with Metalenz cameras in early 2022 — and later in 2022 will see a phone-based solution shipping as well.
In other words, while Metalenz is indeed a startup just coming out of stealth and raising its A round… it already has shipments planned on the order of tens of millions. The $10 million isn’t a bridge to commercial viability but short-term cash to hire and cover upfront costs associated with such a serious endeavor. It’s doubtful anyone on that list of investors harbors any serious doubts on ROI.
The 3D sensing thing is Metalenz’s first major application, but the company is already working on others. The potential to reduce complex lab equipment to handheld electronics that can be fielded easily is one, and improving the benchtop versions of tools with more light-gathering ability or quicker operation is another.
Though a device you use may in a few years have a Metalenz component in it, it’s likely you won’t know — the phone manufacturer will probably take all the credit for the improved performance or slimmer form factor. Nevertheless, it may show up in teardowns and bills of material, at which point you’ll know this particular university spin-out has made it to the big leagues.
Powered by WPeMatico
We talk a lot these days about the future of work and the proliferation of new and better tools for distributed workforces, but companies focused on developing fleet management software — even if they have not really been viewed as “tech startups” — have been working on this problem for many years already. Today, one of the older players in the field is announcing its first significant round of investment, a sign both of how investors are taking more notice of these B2B players, and how the companies themselves are seeing a new opportunity for growth.
BigChange, a U.K. startup that builds fleet management software to help track and direct jobs to those on the go whose “offices” tend to be vehicles, has closed a round of £75 million ($102 million at today’s rates). U.S. investor Great Hill Partners led the round.
The company has built a business by tapping into the advances of technology to build apps for field service engineers and those back at the mothership who run operations and help manage their jobs, workers who in the past might have used phone calls, paperwork and lots of extra round trips between offices and sites in order to run things.
“I founded BigChange to revolutionise mobile workforce management and bring it into the 21st century. Our platform eliminates paperwork, dramatically cuts carbon, creates efficiency, promotes safer driving and means that engineers are spending less time on the roads or filling out forms and more time completing jobs,” said founder and CEO Martin Port in a statement. “We are incredibly excited to partner with Great Hill and leverage their successful track-record scaling vertical and enterprise software companies both in the U.K. and overseas.”
BigChange said that Great Hill’s stake values the company at £100 million (or $136 million). One report points to part of that funding being a secondary transaction, with Port pocketing £48 million of that. The company has been around since 2012 and appears to be profitable. It has raised very little in funding (around $2 million) before this, at one point trying to raise an angel round but cancelling the process before it completed, according to filings tracked by PitchBook.
As the technology industry continues to become essentially a part of every other industry in the world, this deal is notable as a sign of how its boundaries are expanding and getting more blurred.
BigChange is not a London startup, nor from the Cambridge or Oxford areas, nor from Bristol or anywhere in the south. It’s from the north, specifically Leeds — a city that has an impressive number of startups in it even if these have not had anything like the funding or attention that startups in cities and areas in the South have attracted. (One eye-catching exception is the online store Pharmacy2U: the Leeds startup has been backed by Atomico, BGF and others: given the interest of companies like Amazon to grow in this space, it’s likely one to watch.)
One of the big themes in technology right now is how a lot of the action is getting decentralised — a result of many of us now working remotely to stave off the spread of COVID-19, many people using that situation to reconsider whether they need to be living in any specific place at all, and subsequently choosing to relocate from expensive regions like the Bay Area to other places for better quality of life.
There are of course other cities, like Manchester, Edinburg, Cardiff and more in the U.K., with technology ecosystems (just as there have been across many cities in the U.S. for years). But when one of these, this time out of Leeds, attracts a significant funding round, it points to the potential of something similar playing out in the U.K., too, with not just talent but more money going into regions beyond the usual suspects.
The other part of the decentralisation story here focuses on what BigChange is actually building.
Here, it’s one of the many companies that have dived into the area of building apps and larger pieces of software aimed not at “knowledge workers” but those who do not sit at desks, are on the move and tend to work with their hands. For those who are on the road, it has apps to better manage their jobs and routes (which it calls JourneyWatch). For those back in the dispatch part of the operations, it has an app to track them better and use the software to balance the jobs and gain further analytics from the work (sold as JobWatch). These work on ruggedised devices and lean on SaaS architecture for distribution, and there are some 50,000 people across some 1,500 organizations using its apps today, with those customers located around the world, but with a large proportion of them in the U.K. itself.
BigChange is not the only company targeting workers in the field. We covered a significant funding round for another one of them out of North America, Jobber, which builds software for service professionals, just last month. Others tapping into the opportunity of bringing tech to a wider audience beyond knowledge workers include Hover (technology and a wider set of tools for home repair people to source materials, make pricing and work estimates, and run the administration of their businesses) and GoSite (a platform to help all kinds of SMBs — the key factor being that many of them are coming online for the first time — build out and run their businesses). Others in this specific area include Klipboard, Azuga, ServiceTitan, ServiceMax and more.
You might recognise the name Great Hill Partners as the PE firm that has taken majority stakes in a range of media companies like Gizmodo, Ziff Davis (way back when) and Storyblocks, and backed companies like The RealReal and Wayfair. In this case, the company was attracted by how BigChange was being adopted by a very wide range of industries that fall under “field service” as part of their workload.
“Unlike niche players that focus on smaller customers and specific sub-verticals, Martin and his accomplished team have built a flexible, all-in-one platform for field service professionals and operators,” said Drew Loucks, a partner at Great Hill Partners, in a statement. “BigChange’s technology is differentiated not only by its ability to serve commercial and residential clients of nearly any scale or vertical, but also by its award-winning product development and customer service capabilities.”
Powered by WPeMatico
There is so much data sitting inside companies these days, but getting data to the people who need it most remains a daunting challenge. Polytomic, a graduate of the Y Combinator Winter 2020 cohort set out to solve that problem, and today the startup announced a $2.4 million seed.
Caffeinated Capital led the round with help from Bow Capital and a number of individual investors including the founders of PlanGrid, Tracy Young and Ralph Gootee, the company where Polytomic founders CEO Ghalib Suleiman and CTO Nathan Yergler both previously worked.
“We synch internal data to business systems. You can imagine your sales team living in Salesforce and would like to see who’s using your product from your customer data that lives in other internal databases. We have a no-code web app that moves internal data to the business systems of the office,” Suleiman told me.
Data lives in silos across every company, and Polytomic lets you build the connectors by dragging and dropping components in the Polytomic interface. This new data then shows up as additional fields in the target application. So you might have a usage percentage field added to Salesforce automatically if you were connecting to customer usage data.
The company actually sells the product to business operations teams, who would be charged with setting up a catalogue or menu of data sources that live in Polytomic. This is usually handled by someone like a business analyst who can configure the different sources. Once that’s done, anyone can build connectors to these data sources by selecting them from the menu and then choosing where to deliver the data.
The founders came up with the idea for the company because when they were at PlanGrid, they faced a problem getting data to the people who needed it in the company. The problem became more pronounced as the company grew and they had ever more data and more employees who needed access to it.
They left PlanGrid in 2018 and launched Polytomic a year later to begin attacking the problem. The two founders joined YC as a way to learn to refine the product, and were still working on it on Demo Day, delivering their presentation off the record because they weren’t quite done with it yet.
They released the first iteration of the product last September and report some progress getting customers and gaining revenue. Early customers include Brex, ShipBob, Sourcegraph and Vanta.
The company has no additional employees beyond the two founders as of yet, but with the seed funding in the bank, they plan to begin hiring a few people this year.
Powered by WPeMatico
Time is critical for healthcare providers, especially in the middle of the pandemic. Singapore-based Bot MD helps save time with an AI-based chatbot that lets doctors look up important information from their smartphones, instead of needing to call a hospital operator or access its intranet. The startup announced today it has raised a $5 million Series A led by Monk’s Hill Venture.
Other backers include SeaX, XA Network and SG Innovate, and angel investors Yoh-Chie Lu, Jean-Luc Butel and Steve Blank. Bot MD was also part of Y Combinator’s summer 2018 batch.
The funding will be used to expand in the Asia-Pacific region, including Indonesia, the Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia, and to add new features in response to demand from hospitals and healthcare organizations during COVID-19. Bot MD’s AI assistant currently supports English, with plans to release Bahasa Indonesian and Spanish later this year. It is currently used by about 13,000 doctors at organizations including Changi General Hospital, National University Health System, National University Cancer Institute of Singapore, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore General Hospital, Parkway Radiology and the National Kidney Transplant Institute.
Co-founder and chief executive officer Dorothea Koh told TechCrunch that Bot MD integrates hospital information usually stored in multiple systems and makes it easier to access.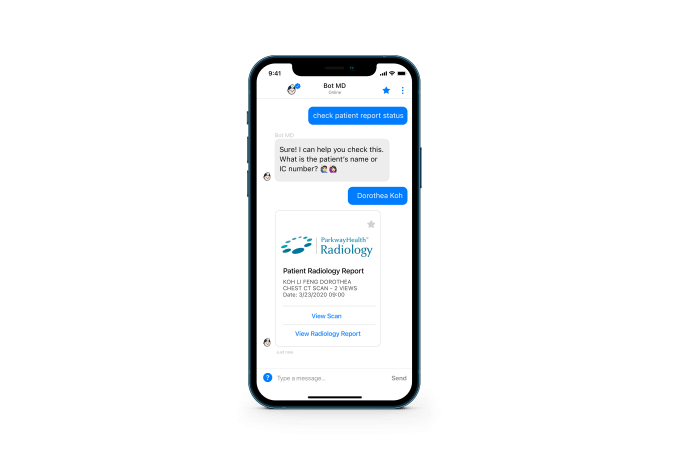
Image Credits: Bot MDWithout Bot MD, doctors may need to dial a hospital operator to find which staffers are on call and get their contact information. If they want drug information, that means another call to the pharmacy. If they need to see updated guidelines and clinical protocols, that often entails finding a computer that is connected to the hospital’s intranet.
“A lot of what Bot MD does is to integrate the content that they need into a single interface that is searchable 24/7,” said Koh.
For example, during COVID-19, Bot MD introduced a new feature that takes healthcare providers to a form pre-filled with their information when they type “record temperature” into the chatbot. Many were accessing their organization’s intranet twice a day to log their temperature and Koh said being able to use the form through Bot MD has significantly improved compliance.
The time it takes to onboard Bot MD varies depending on the information systems and amount of content it needs to integrate, but Koh said its proprietary natural language processing chat engine makes training its AI relatively quick. For example, Changi General Hospital, a recent client, was onboarded in less than 10 days.
Bot MD plans to add new clinical apps to its platform, including ones for electronic medical records (EMR), billing and scheduling integrations, clinical alerts and chronic disease monitoring.
Powered by WPeMatico
When you want to buy a refrigerator or a television, you can walk to the nearby electronics store or visit an e-commerce website like Amazon. But where do you go when you’re looking for parts of a crane, a door or chassis of different machines?
For several businesses globally, the answer to that question is increasingly Zetwerk, a Bangalore-based startup.
The three-year-old startup runs a business-to-business marketplace for manufacturing items that connects OEMs (original equipment manufacturers) and EPC (engineering procurement construction) customers with manufacturing small-businesses and enterprises.
All the products it sells today are custom-made. “Nobody has a stock of such inventories. You get the order, you find manufacturers and workshops that make them,” explained Amrit Acharya, co-founder and chief executive of Zetwerk, in an interview with TechCrunch.
Its customers — there are over 250 of them, up from 100 a year ago — operate across two-dozen industries (including process plants, oil & gas, steel, aerospace, medical devices, apparel and luxury goods) in the infrastructure space, and approach Zetwerk with digital designs they wish to be translated into physical products.
Customers aren’t alone in seeing value in Zetwerk. On Wednesday, the Indian startup said it has raised $120 million in a Series D financing round led by existing investors Greenoaks Capital and Lightspeed Venture Partners. Existing investors Sequoia Capital and Kae Capital also participated in the Series D round.
The new round, which brings Zetwerk’s to-date raise to $193 million, gives the firm a post-money valuation of somewhere between $600 million to $700 million, a person familiar with the matter told TechCrunch. (A quick side note: Zetwerk announced a $21 million Series C round last year, but ended up raising $31 million in that round.)
Zetwerk was co-founded by Acharya, Srinath Ramakkrushnan, Rahul Sharma and Vishal Chaudhary. Long before Acharya and Ramakkrushnan joined forces to tackle this space, they had been contemplating this idea.
Both of them studied at IIT Madras, went to the same exchange program in Singapore, and were colleagues at Kolkata-headquartered conglomerate ITC. While working there, they realized that part of a product manager’s job at the firm was dealing with gazillions of suppliers and the manufacturing items they offered.
The process was archaic: There were no databases, and people couldn’t track shipments.
The early version of Zetwerk, which was a database of suppliers, was a direct response to this. But after listening to requests from customers, the startup saw a bigger opportunity and transformed itself into a full-fledged marketplace with integrations with third-party vendors. Once a firm has placed an order, Zetwerk allows them to keep tabs on the progress of manufacturing and then the shipping. There are also quality checks in place.
Zetwerk website
Zetwerk operates in such a unique space today — Shailesh Lakhani, managing director at Sequoia India, says the startup has defined a new category of marketplace — that by and large it’s not competing with any other firm in India — or South Asia. (The startup competes with domain project consultants in the offline world.)
The opportunity in India itself is gigantic. According to industry reports, manufacturing today accounts for 14% of India’s GDP. Vaibhav Agarwal, a partner at Lightspeed, estimates that the market is as large as $40 billion to $60 billion in India and global trade-tailwinds that creates opportunity to serve international demand.
As more and more companies expand or shift their manufacturing to India — in part due to import duties imposed by India and geo-political tension with China, the global hub for manufacturing — this opportunity has only grown bigger in recent years.
“India has a lot of depth in manufacturing, but much of it has not been tapped well,” said Acharya.
Zetwerk — which grew 3X last year and reported revenue of $43.9 million in the financial year that ended in March, a 20X growth from the year prior — plans to deploy the new capital to expand to more areas of categories, and broaden its technology stack. Consumer goods (which covers items such as mixer grinders and TVs) is an area Zetwerk expanded to last year, and said it accounts for 15% of the revenue it generated in the last six months.
Currently 25 of its customers are in the U.S., Canada, Europe and other international markets. Acharya said the startup plans to open offices overseas this year as it scouts for more international customers.
“We are excited to partner with Zetwerk on the next leg of their journey, as they expand their value proposition globally. Zetwerk’s operating system for manufacturing has digitized multiple supply chains end-to-end, ensuring on-time delivery and high quality standards. This has led to rapid growth in India and internationally, with the potential to quickly become one of the most important manufacturing platforms globally,” said Neil Shah, partner at Greenoaks Capital, in a statement.
Powered by WPeMatico
Landed, a startup aiming to improve the hiring process for hourly employers and job applicants, is officially launching its mobile app today. It’s also announcing that it has raised $1.4 million in seed funding.
Founder and CEO Vivian Wang said that the app works by asking applicants to fill out a profile with information like work experience and shift availability, as well as recording videos that answer basic common interview questions. It then uses artificial intelligence to analyze those responses across 50 traits such as communication skills and body language, then matches them up with job listings from employers.
Landed has been in beta testing since March of last year — yes, right as COVID-19 was hitting the United States. Wang acknowledged that this was bad news for some of the startup’s potential customers, but she said businesses like grocery stores and fast food restaurants needed the product more than ever.
“That’s why we continuously grew through 2020,” she said.
After all, Landed allowed those businesses to continue hiring without having to conduct large group interviews in person. Even beyond health concerns, she said managers struggle with rapid turnover in these positions (something Wang saw herself during her time on the corporate team at Gap, Inc.) and with a hiring process that’s usually “only a small part of their job.” So Landed saves time and automates a large part of the product.

Landed CEO Vivian Wang. Image Credits: Landed
Meanwhile, Wang said job applicants benefit because they can find jobs more easily and quickly, often within a week of creating a profile. She also argued that Landed can improve on existing diversity and inclusion efforts by allowing managers to see a broader pool of candidates, and because its AI matching isn’t subject to the same unconscious biases that employers might have.
Of course, bias can also be inadvertently built into AI, but when I raised this issue, Wang pointed to Landed’s partnerships with local nonprofits to bring in underrepresented candidates, and she added, “AI can be scary when there are no human checks in place. We partner directly with our employers to ensure the matches that we’re sending them are the right matches, and there are calibration periods.”
Landed is free for job applicants, while it charges a monthly fee to employers, with customers already including Wendy’s, Chick-fil-A and Grocery Outlet franchisees. In fact, Grocery Outlet Ventura owner Eric Sawyer said that by using the app, he’s gone from hiring one person for every 10 interviews to hiring one person for every three interviews.
“My time spent on scheduling and performing interviews has been cut in half by utilizing the Landed app for most of my communications,” he said in a statement.
The new funding was led by Javelin Venture Partners, with participation from Y Combinator, Palm Drive Capital and various angel investors. Wang said this will allow Landed to continue expanding — the service is currently available in seven metro areas (Northern California; Southern California; Virginia Beach/Chesapeake, Virginia; Phoenix/Scottsdale, Arizona; Atlanta, Georgia; Reno, Nevada and Dallas-Ft. Worth, Texas), with a goal of tripling that number by the end of the year.
Wang added that eventually, she wants to provide other services to job applicants, such as loans (at a lower rate than payday lenders) and job training, turning Landed into a “lifestyle stability platform” that combines job stability, financial stability and educational “upskilling” for blue-collar workers.
Powered by WPeMatico
The growth of remote working and managing workforces that are distributed well beyond the confines of a centralized physical office — or even a single country — have put a spotlight on the human resources technology that organizations use to help manage those people. Today, one of the HR startups that’s been seeing a surge of growth is announcing a round of funding to double down on its business.
Oyster, a startup and platform that helps companies through the process of hiring, onboarding and then providing contractors and full-time employees in the area of “knowledge work” with HR services like payroll, benefits and salary management, has closed a Series A round of $20 million.
The company is already working in 100 countries, and CEO and Tony Jamous (who co-founded the company with Jack Mardack) said in an interview that the plan is to expand that list of markets, and also bring in new services, particularly to address the opportunity in emerging markets to hire more people.
Currently, Oyster does not cover candidate sourcing or any of the interviewing and evaluation process: those could be areas where it might build its own tech or partner to provide them as part of its one-stop shop. It has dabbled in virtual job fairs, as a pointer to one potential product that it might explore.
“There are 1.5 billion knowledge workers coming into the workforce in the next 10 years, mostly from emerging economies, while in developed economies there are some 90 million jobs unfilled,” Jamous said. “There are super powers you can gain from being globally distributed, but it poses a major challenge around HR and payroll.”
Emergence Capital, the B2B VC that has backed the likes of Zoom, Salesforce, Bill.com and our former sister site Crunchbase, is leading the funding. The Slack Fund (Slack’s strategic investment vehicle) and London firm Connect Ventures (which has previously backed the company at seed stage) are also participating. The investment will accelerate Oyster’s rapid growth, and support its mission of enabling people to work from anywhere.
Oyster’s valuation is not being disclosed. The startup has raised about $24 million to date.
One of the great ironies of the global health pandemic is that while our worlds have become much smaller — travel and even local activities have been drastically curtailed, and many of us spend day in, day out at home — the employment opportunity and scope of how organizations are expected to operate has become significantly bigger.
Public health-enforced remote working has led to companies de-coupling workers from offices, and that has opened the door to seeking out and working with the best talent, regardless of location.
This predicament may have become more acute in the last year, but it’s been one that has been gradually coming into focus for years, helped by trends in cloud computing and globalization. Jamous said that the idea for Oyster that came to him was something he’s been thinking about for years, but became more apparent when he was still at his previous startup, Nexmo — the cloud communications provider that was acquired by Vonage for $230 million in in 2016.
At Nexmo we wanted to be a great local employer. We were headquartered in two countries but wanted to have people everywhere,” he said. “We spent millions building employment infrastructure to do that, becoming knowledgeable about local laws in France, Korea and more countries.” He realized quickly that this was a highly inefficient way to work. “We weren’t ready for the complexity and diversity of issues that would come up.”
After he moved on from Nexmo and did some angel investing (he backs other distributed work juggernauts like Hopin, among others), he decided that he would try to tackle the workforce challenge as the focus of his next venture.
That was in mid-2019, pre-pandemic. It turned out that the timing was spot on, with every organization looking in the next year at ways to address their own distributed workforce challenges.
The emerging market focus, meanwhile, also has a direct link to Jamous himself: He left his home country of Lebanon to study in France when he was 17, and has essentially lived abroad since then. But as with many people who move from developed into emerging markets, he knew that the base of technical talent in his home country was something that was worth tapping and nurturing to help residents and the countries themselves improve their lots in life; and he thought he could use tech to help there, too.
Related to that wider social mission, Oyster has a pending application to become a B-Corporation.
Jamous is not the only one that has founded an HR company based on his personal experience: Turing’s founders have cited their own backgrounds growing up in India and working with people remotely from there as part of their own impetus for building Turing; and Remote’s founder hails from Europe but built GitLab (where he had been head of product) based on a similar premise of tapping into the talent he knew existed all around the world.
And indeed, Oyster is not alone in tackling this opportunity. The list of HR startups looking to be the ADPs of the world of distributed work include Deel, Remote, Hibob, Papaya Global, Personio, Factorial, Lattice, Turing and Rippling. And these are just some of the HR startups that have raised money in the last year; there are many, many more.
The attraction of Oyster seems to come in the simplicity of how the services are provided — you have options for contractors and full-timers, and full, larger staff deployments in other countries. You have options to add benefits for employees if you choose. And you have some tools to work out how hires fit into your bigger budgets, and also to guide you on remuneration in each local market. Pricing ranges from $29 per person, per month for contractors, to $399 for working with full employees, to other packages for larger deployments.
Oyster works with local partners to provide some aspects of these services, but it has built the technology to make the process seamless for the customer. As with other services, it essentially handles the employment and payroll as a local provider on behalf of its customers, but can do so under contract terms that reconcile both a company’s own policies and those of the local jurisdictions (which can differ widely between each other in areas like vacation time, redundancy terms, maternity leave and more).
“It has a few well-funded competitors, but that’s usually a good signal,” said Jason Green, the Emergence partner who led its investment. “But you want to bet on the horse that will lead the race, and that comes down to execution. Here, we are betting on a team that’s done it before, an entrepreneur experienced in building a company and selling it. Tony’s made money and knows how to build a business. But more than that, he’s mission driven and that will matter in the space, and to employees.”
Powered by WPeMatico
In a creator-economy world, if you’re only as good as your last YouTube video, then your next YouTube video had better be bigger and louder than the last.
Vibely, a new startup co-founded by Asana alumni Teri Yu and Theresa Lee, wants to turn the constant, and often exhausting, beast of content creation on its head. The startup has created a premium, creator-controlled community platform that allows fans to gather and be monetized in new ways, beyond what is possible on YouTube or TikTok.
The core of Vibely, and what the co-founders hope will keep users coming back, is the ability to let any creator make a challenge for their fans to enjoy. For example, a creator whose brand evokes thoughtfulness could ask fans to sketch out their personal growth goals or take action around a new year’s resolution everyday. Or a fitness influencer could motivate fans to work out for a sprint of days.
“Most people in the creator economy are thinking about how to immediately monetize and get that instant gratification of like money here,” Yu said, which is why creators sell merchandise or hop on Cameo. “We’re focusing on long-term strategic communities.” Yu describes her startup’s shift as a mindset change, from a linear relationship between creators and fans to a multi-directional relationship between fans, superfans, new fans and creators.
Image Credits: Vibely
Vibely’s pitch is two-fold. For fans, the platform gives them a chance to chat with other fans from around the world. It also lets fans participate in community challenges and have a place to plan virtual hangouts over shared love for makeup or dance. The startup helps creators simultaneously, by giving them a one-stop shop to announce plans, do call to actions and create an ambassador program. It lets the “creator scale their time and have a multi-directional relationship with the community under or beneath them.”
Notably, Vibely is trying to be different from Patreon or OnlyFans, which is basically paywalled content for fans. Vibely doesn’t need creators to post more content, it just needs them to pop into a premium community and interact with fans in a meaningful way.
The startup is formalizing a sporadic daily occurrence: When a creator posts content, their comment sections in YouTube, Instagram and TikTok light up with fans discussing every detail you can imagine, from a suggestive hair flip to if that background poster has a hidden message. Creators often pop in to respond to a spicy thread or a random compliment, which incentivizes fans to keep swarming the content section.
The startup has spent little on customer acquisition cost and relied heavily on word of mouth. In December, Vibely launched a part-in-person, part-virtual creator house to pair top TikTok creators with their followers, generating some buzz. In 2020, Vibely had more than 600 communities with 392,000 messages sent and 37,000 challenges completed. Creators include Lavendaire, with 1.3 million YouTube subscribers and Rowena Tsai, who has 520,000 subscribers.
Yu says that there is one day where Kim Kardashian might have a community on the platform, but the main “bread and butter” of Vibely is searching for creators who represent a true interest, value or belief system. This can be a book influencer or a religious creator, for example.
“[Creators] are controlling their own destiny,” Yu said. “On Instagram or Facebook, you might create content but the algorithm decides at the end of the day whether or not your audience sees it. With Vibely, they have 100% control since this is their community.” The startup is planning to make money through membership dues and in-app mechanics like social currencies and rewards.
Vibely’s moonshot goal is to be a more positive, and supportive, Discord, a platform used by gamer communities across the world. So far, Yu says that less than .1% of Vibely users have been flagged by other users, although notably would not share total user numbers. There is also an ambassador program that appoints a user to oversee a community, as well as a global community manager on the team.
“The ceiling of where [Discord] can support is really only going to be gamers,” she said. “But creators want to protect their brand right now and make sure people have a positive experience,” so they are looking for another place to set up.
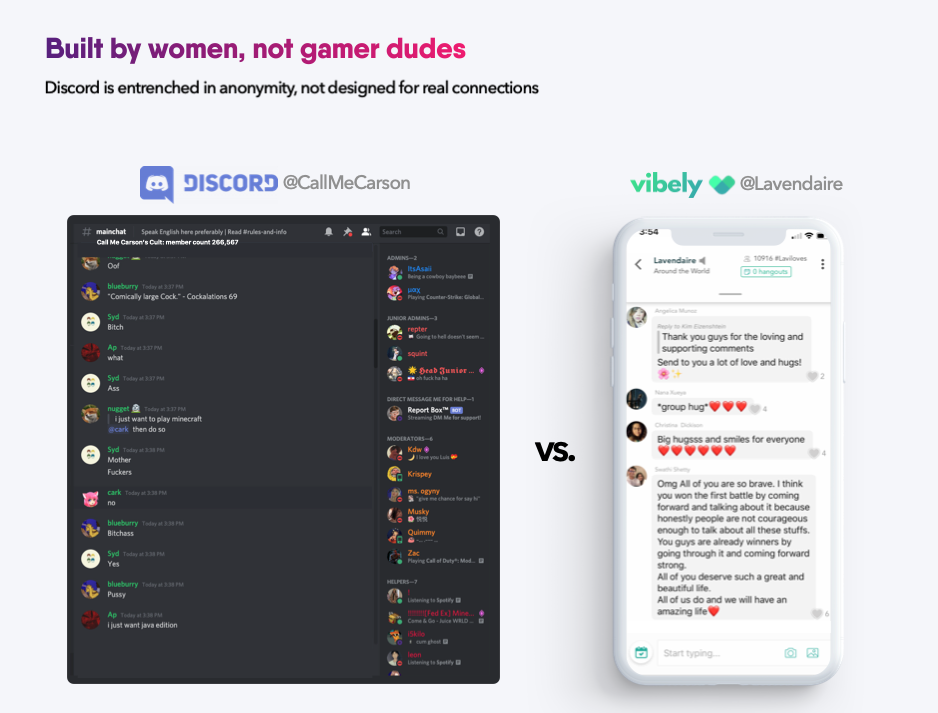
Image Credits: Vibely
While moderation is apparently going well so far, Vibely will most certainly encounter problems as more and more users join its platform. In the world of challenges, craze and hype led by fanatics could potentially become harmful if someone takes it too far. While Vibely aims to be a judgement-free zone for people to connect around the world, scale has a uniquely pessimistic way of forking that from time to time. Some consumer apps have responded to this truth by aggressively hiring on-staff moderators, but that too can become grueling work.
To hit the ground running, Vibely announced today that it has raised $2 million in seed financing from backers including Steve Chen, the co-founder of YouTube; Justin Rosenstein, the co-founder of Asana and co-creator of Netflix’s “Social Dilemma” documentary; Scott Heiferman, the co-founder of Meetup; Turner Novak, formerly an investor at Gelt, and more.
Powered by WPeMatico