Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Duda announced Wednesday that it acquired Canada-based Snipcart, a startup that enables businesses to add a shopping cart to their websites.
The acquisition is Palo Alto-based Duda’s first deal, and follows the website development platform’s $50 million Series D round in June that brings its total funding to $100 million to date. Duda co-founder and CEO Itai Sadan declined to comment on the acquisition amount.
Duda, which works with digital agencies and SaaS companies, has approximately 1 million published paying sites, and the acquisition was driven by the company seeing a boost in e-commerce websites as a result of the global pandemic, he told TechCrunch.
This was not just about a technology acquisition for Duda, but also a talented team, Sadan said. The entire Snipcart team of 12 is staying on, including CEO Francois Lanthier Nadeau; the companies will be fully integrated by 2022 and the first collaborative versions will come out.
When he met the Snipcart team, Sadan thought they were “super experienced and held the same values.”
“We share many of the same types of customers, many of which are API-first,” he added. “If our customers need more headless commerce, they can build their own front end using Snipcart. Their customers will benefit from us growing the team — we plan to double it in the next year and roll out more features at a faster pace.”
The global retail e-commerce market is estimated to grow by 50% to $6.3 trillion by 2024, according to Statista. Duda itself has experienced a year over year increase of 265% in e-commerce sites being built on its platform, which Sadan said was what made Snipcart an attractive acquisition to further accelerate and manage its growth that includes over 17,000 customers.
Together, the companies will offer new capabilities, like payment and membership tools inside of the Duda platform. Many of Duda’s customers come with inventory and don’t want to manage it on another e-commerce platform, so Snipcart will be that component for taking their inventory and making it shoppable on the web.
“Everyone is thinking about how to introduce transactions into their websites and web experiences, and that is what we were looking for in an e-commerce platform,” Sadan said.
Powered by WPeMatico
Itamar Jobani was a software developer working for a medical company and “hated that time of the month” when he had to use the company’s chosen reimbursement tool.
“It was full of friction and as part of the company’s wellness team, I felt an urge to take care of the employee experience and find a better tool,” Jobani told TechCrunch. “I looked for something, but didn’t find it, so I tried to build it myself.”
What resulted was PayEm, an Israeli company he founded with Omer Rimoch in 2019 to be a spend and procurement platform for high-growth and multinational organizations. Today, it announced $27 million in funding that includes $7 million in seed funding, led by Pitango First and NFX, with participation by LocalGlobe and Fresh Fund, as well as $20 million in Series A funding led by Glilot+.
The company’s technology automates the reimbursement, procurement, accounts payable and credit card workflows to manage all of the requests and invoices, while also creating bills and sending payments to over 200 territories in 130 currencies.
It gives company finance teams a real-time look at what items employees are asking for funds to buy, and what is actually being spent. For example, teams can submit a request and go through an approval flow that can be customized with purchasing codes tied to a description of the transaction. At the same time, all transactions are continuously reconciled versus having to spend hours at the end of the month going through paperwork.
“Organizations are running in a more democratized way with teams buying things on behalf of the organization,” Jobani said. “We built a platform to cater to those needs, so it’s like a disbursement platform instead of a finance team always being in charge.”
The global B2B payments market is valued at $120 trillion annually and is expected to reach $200 trillion by 2028, according to payment industry newsletter Nilson Report. PayEm is among many B2B payments startups attracting venture capital — for example, last month, Nium announced a $200 million in Series D funding at a $1 billion valuation. Paystand raised $50 million in Series C funding to make B2B payments cashless, while Dwolla raised $21 million for its API that allows companies to build and facilitate fast payments.
Meanwhile, PayEm itself saw accelerated growth in the second quarter of 2021, including increasing its transaction volume by four times over the previous quarter and generating millions of dollars in revenue. It now boasts a list of hundreds of customers like Fiverr, JFrog and Next Insurance. It also launched new features like the ability to create corporate cards.
The company, which also has an office in New York, has 40 employees currently, and the new funds will enable the company to triple its headcount, focusing on hiring in the United States, and to bring additional features and payment capabilities to market.
“Each person can have a budget and a time frame for making the purchase, while accounting still feels in control,” Jobani added. “Everyone now has the full context and the right budget line item.”
Powered by WPeMatico
In the customer service industry, your accent dictates many aspects of your job. It shouldn’t be the case that there’s a “better” or “worse” accent, but in today’s global economy (though who knows about tomorrow’s) it’s valuable to sound American or British. While many undergo accent neutralization training, Sanas is a startup with another approach (and a $5.5M seed round): using speech recognition and synthesis to change the speaker’s accent in near real time.
The company has trained a machine learning algorithm to quickly and locally (that is, without using the cloud) recognize a person’s speech on one end and, on the other, output the same words with an accent chosen from a list or automatically detected from the other person’s speech.
It slots right into the OS’s sound stack so it works out of the box with pretty much any audio or video calling tool. Right now the company is operating a pilot program with thousands of people in locations from the USA and UK to the Philippines, India, Latin America, and others. Accents supported will include American, Spanish, British, Indian, Filipino and Australian by the end of the year.
To tell the truth, the idea of Sanas kind of bothered me at first. It felt like a concession to bigoted people who consider their accent superior and think others below them. Tech will fix it… by accommodating the bigots. Great!
But while I still have a little bit of that feeling, I can see there’s more to it than this. Fundamentally speaking, it is easier to understand someone when they speak in an accent similar to your own. But customer service and tech support is a huge industry and one primarily performed by people outside the countries where the customers are. This basic disconnect can be remedied in a way that puts the onus of responsibility on the entry-level worker, or one that puts it on technology. Either way the difficulty of making oneself understood remains and must be addressed — an automated system just lets it be done more easily and allows more people to do their job.
It’s not magic — as you can tell in this clip, the character and cadence of the person’s voice is only partly retained and the result is considerably more artificial sounding:
But the technology is improving and like any speech engine, the more it’s used, the better it gets. And for someone not used to the original speaker’s accent, the American-accented version may very well be more easily understood. For the person in the support role, this likely means better outcomes for their calls — everyone wins. Sanas told me that the pilots are just starting so there are no numbers available from this deployment yet, but testing has suggested a considerable reduction of error rates and increase in call efficiency.
It’s good enough at any rate to attract a $5.5M seed round, with participation from Human Capital, General Catalyst, Quiet Capital, and DN Capital.
“Sanas is striving to make communication easy and free from friction, so people can speak confidently and understand each other, wherever they are and whoever they are trying to communicate with,” CEO Maxim Serebryakov said in the press release announcing the funding. It’s hard to disagree with that mission.
While the cultural and ethical questions of accents and power differentials are unlikely to ever go away, Sanas is trying something new that may be a powerful tool for the many people who must communicate professionally and find their speech patterns are an obstacle to that. It’s an approach worth exploring and discussing even if in a perfect world we would simply understand one another better.
Powered by WPeMatico
On the heels of Heroes announcing a $200 million raise earlier today, to double down on buying and scaling third-party Amazon Marketplace sellers, another startup out of London aiming to do the same is announcing some significant funding of its own. Olsam, a roll-up play that is buying up both consumer and B2B merchants selling on Amazon by way of Amazon’s FBA fulfillment program, has closed $165 million — a combination of equity and debt that it will be using to fuel its M&A strategy, as well as continue building out its tech platform and to hire more talent.
Apeiron Investment Group — an investment firm started by German entrepreneur Christian Angermayer — led the Series A equity round, with Elevat3 Capital (another Angermayer firm that has a strategic partnership with Founders Fund and Peter Thiel) also participating. North Wall Capital was behind the debt portion of the deal. We have asked and Olsam is only disclosing the full amount raised, not the amount that was raised in equity versus debt. Valuation is also not being disclosed.
Being an Amazon roll-up startup from London that happens to be announcing a fundraise today is not the only thing that Olsam has in common with Heroes. Like Heroes, Olsam is also founded by brothers.
Sam Horbye previously spent years working at Amazon, including building and managing the company’s business marketplace (the B2B version of the consumer marketplace); while co-founder Ollie Horbye had years of experience in strategic consulting and financial services.
Between them, they also built and sold previous marketplace businesses, and they believe that this collective experience gives Olsam — a portmanteau of their names, “Ollie” and “Sam” — a leg up when it comes to building relationships with merchants; identifying quality products (versus the vast seas of search results that often feel like they are selling the same inexpensive junk as each other); and understanding merchants’ challenges and opportunities, and building relationships with Amazon and understanding how the merchant ecosystem fits into the e-commerce giant’s wider strategy.
Olsam is also taking a slightly different approach when it comes to target companies, by focusing not just on the usual consumer play, but also on merchants selling to businesses. B2B selling is currently one of the fastest-growing segments in Amazon’s Marketplace, and it is also one of the more overlooked by consumers. “It’s flying under the radar,” Ollie said.
“The B2B opportunity is very exciting,” Sam added. “A growing number of merchants are selling office supplies or more random products to the B2B customer.”
Estimates vary when it comes to how many merchants there are selling on Amazon’s Marketplace globally, ranging anywhere from 6 million to nearly 10 million. Altogether those merchants generated $300 million in sales (gross merchandise value), and it’s growing by 50% each year at the moment.
And consolidating sellers — in order to achieve better economies of scale around supply chains, marketing tools and analytics, and more — is also big business. Olsam estimates that some $7 billion has been spent cumulatively on acquiring these businesses, and there are more out there: Olsam estimates there are some 3,000 businesses in the U.K. alone making more than $1 million each in sales on Amazon’s platform.
(And to be clear, there are a number of other roll-up startups beyond Heroes also eyeing up that opportunity. Raising hundreds of millions of dollars in aggregate, others that have made moves this year include Suma Brands [$150 million], Elevate Brands [$250 million], Perch [$775 million], factory14 [$200 million], Thrasio [currently probably the biggest of them all in terms of reach and money raised and ambitions], Heyday, The Razor Group, Branded, SellerX, Berlin Brands Group [X2], Benitago, Latin America’s Valoreo and Rainforest and Una Brands out of Asia.)
“The senior team behind Olsam is what makes this business truly unique,” said Angermayer in a statement. “Having all been successful in building and selling their own brands within the market and having worked for Amazon in their marketplace team – their understanding of this space is exceptional.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Even as hundreds of millions of people in India have a bank account, only a tiny fraction of this population invests in any financial instrument.
Fewer than 30 million people invest in mutual funds or stocks, for instance. In recent years, a handful of startups have made it easier for users — especially the millennials — to invest, but the figure has largely remained stagnant.
Now, an Indian startup believes that it has found the solution to tackle this challenge — and is already seeing good early traction.
Nishchay AG, former director of mobility startup Bounce, and Misbah Ashraf, co-founder of Marsplay (sold to Foxy), founded Jar earlier this year.
The startup’s eponymous six-month-old Android app enables users to start their savings journey for as little as 1 Indian rupee.
Users on Jar can invest in multiple ways and get started within seconds. The app works with Paytm (PhonePe support is in the works) to set up a recurring payment. (The startup is the first to use UPI 2.0’s recurring payment support.) They can set up any amount between 1 Indian rupee to 500 for daily investments.
The Jar app can also glean users’ text messages and save a tiny amount based on each monetary transaction they do. So, for instance, if a user has spent 31 rupees in a transaction, the Jar app rounds that up to the nearest tenth figure (40, in this case) and saves nine rupees. Users can also manually open the app and spend any amount they wish to invest.
Once users have saved some money in Jar, the app then invests that into digital gold.
The startup is using gold investment because people in the South Asian market already have an immense trust in this asset class.
India has a unique fascination for gold. From rural farmers to urban working class, nearly everyone stashes the yellow metal and flaunts jewelry at weddings.
Indian households are estimated to have a stash of over 25,000 tons of the precious metal whose value today is about half of the country’s nominal GDP. Such is the demand for gold in India that the South Asian nation is also one of the world’s largest importers of this precious metal.
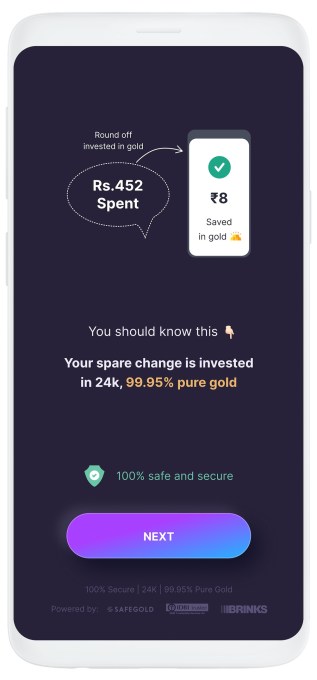
Jar’s Android app (Image Credits: Jar)
“When you’re thinking about bringing the next 500 million people to institutional savings and investments, the onus is on us to educate them on the efficacies of the other instruments that are in the market,” said Nishchay.
“We want to give them the instrument they trust the most, which is gold,” he said. The startup plans to eventually offer several more investment opportunities, he said.
The founders met several years ago when they were exploring if MarsPlay and Bounce could have any synergies. They stayed in touch and, last year during one of their many conversations, realized that neither of them knew much about investments.
“That’s when the dots started to connect,” said Misbah, drawing stories from his childhood. “I come from a small town in Bihar called Bihar Sharif. During my childhood days, I saw my family deeply troubled with debt because of poor financial decisions and no savings,” he said.
“We both understand what a typical middle class family goes through. Someone who comes from this background never had any means in the past but their aspirations are never-ending. So when you start earning, you immediately start to spend it all,” said Nishchay.
“The market needs products that will help them get started,” he said.
That idea, which is similar to Acorn and Stash’s play in the U.S. market, is beginning to make inroads. The app has already amassed about half a million downloads, the founders said. Investors have taken notice, too.
On Wednesday, Jar announced it has raised $4.5 million from a clutch of high-profile investors, including Arkam Ventures, Tribe Capital, WEH Ventures, and angels including Kunal Shah (founder of CRED), Shaan Puri (formerly with Twitch), Ali Moiz (founder of Stonks), Howard Lindzon (founder of Social Leverage), Vivekananda Hallekere (co-founder of Bounce), Alvin Tse (of Xiaomi) and Kunal Khattar (managing partner at AdvantEdge).
“Over 400 million Indians are about to embrace digital financial services for the first time in their lives. Jar has built an app that is poised to help them — with several intuitive ways including gamification — start their investment journey. We love the speed at which the team has been executing and how fast they are growing each week,” said Arjun Sethi, co-founder of Tribe Capital, in a statement.
Transactions and AUM on the Jar app are surging 350% each month, said Nishchay. The startup plans to broaden its product offerings in the coming days, he said.
Powered by WPeMatico
Heroes, one of the new wave of startups aiming to build big e-commerce businesses by buying up smaller third-party merchants on Amazon’s Marketplace, has raised another big round of funding to double down on that strategy. The London startup has picked up $200 million, money that it will mainly be using to snap up more merchants. Existing brands in its portfolio cover categories like babies, pets, sports, personal health and home and garden categories — some of them, like PremiumCare dog chews, the Onco baby car mirror, gardening tool brand Davaon and wooden foot massager roller Theraflow, category best-sellers — and the plan is to continue building up all of these verticals.
Crayhill Capital Management, a fund based out of New York, is providing the funding, and Riccardo Bruni — who co-founded the company with twin brother Alessio and third brother Giancarlo — said that the bulk of it will be going toward making acquisitions, and is therefore coming in the form of debt.
Raising debt rather than equity at this point is pretty standard for companies like Heroes. Heroes itself is pretty young: it launched less than a year ago, in November 2020, with $65 million in funding, a round comprised of both equity and debt. Other investors in the startup include 360 Capital, Fuel Ventures and Upper 90.
Heroes is playing in what is rapidly becoming a very crowded field. Not only are there tens of thousands of businesses leveraging Amazon’s extensive fulfillment network to sell goods on the e-commerce giant’s marketplace, but some days it seems we are also rapidly approaching a state of nearly as many startups launching to consolidate these third-party sellers.
Many a roll-up play follows a similar playbook, which goes like this: Amazon provides the marketplace to sell goods to consumers, and the infrastructure to fulfill those orders, by way of Fulfillment By Amazon and its Prime service. Meanwhile, the roll-up business — in this case Heroes — buys up a number of the stronger companies leveraging FBA and the marketplace. Then, by consolidating them into a single tech platform that they have built, Heroes creates better economies of scale around better and more efficient supply chains, sharper machine learning and marketing and data analytics technology, and new growth strategies.
What is notable about Heroes, though — apart from the fact that it’s the first roll-up player to come out of the U.K., and continues to be one of the bigger players in Europe — is that it doesn’t believe that the technology plays as important a role as having a solid relationship with the companies it’s targeting, key given that now the top marketplace sellers are likely being feted by a number of companies as acquisition targets.
“The tech is very important,” said Alessio in an interview. “It helps us build robust processes that tie all the systems together across multiple brands and marketplaces. But what we have is very different from a SaaS business. We are not building an app, and tech is not the core of what we do. From the acquisitions side, we believe that human interactions ultimately win. We don’t think tech can replace a strong acquisition process.”

Image Credits: Heroes
Heroes’ three founder-brothers (two of them, Riccardo and Alessio, pictured above) have worked across a number of investment, finance and operational roles (the CVs include Merrill Lynch, EQT Ventures, Perella Weinberg Partners, Lazada, Nomura and Liberty Global) and they say there have been strong signs so far of its strategy working: of the brands that it has acquired since launching in November, they claim business (sales) has grown five-fold.
Collectively, the roll-up startups are raising hundreds of millions of dollars to fuel these efforts. Other recent hopefuls that have announced funding this year include Suma Brands ($150 million); Elevate Brands ($250 million); Perch ($775 million); factory14 ($200 million); Thrasio (currently probably the biggest of them all in terms of reach and money raised and ambitions), Heyday, The Razor Group, Branded, SellerX, Berlin Brands Group (X2), Benitago, Latin America’s Valoreo and Rainforest and Una Brands out of Asia.
The picture that is emerging across many of these operations is that many of these companies, Heroes included, do not try to make their particular approaches particularly more distinctive than those of their competitors, simply because — with nearly 10 million third-party sellers today on Amazon globally — the opportunity is likely big enough for all of them, and more, not least because of current market dynamics.
“It’s no secret that we were inspired by Thrasio and others,” Riccardo said. “Combined with COVID-19, there has been a massive acceleration of e-commerce across the continent.” It was that, plus the realization that the three brothers had the right e-commerce, fundraising and investment skills between them, that made them see what was a ‘perfect storm’ to tackle the opportunity, he continued. “So that is why we jumped into it.”
In the case of Heroes, while the majority of the funding will be used for acquisitions, it’s also planning to double headcount from its current 70 employees before the end of this year with a focus on operational experts to help run their acquired businesses.
Powered by WPeMatico
Founded in 2012, Whoop is far from a household name in the world of fitness trackers. But over the years, the company has attracted its share of converts. It hasn’t had any issue attracting venture capital over the years, either. Last time we checked in on the Boston-based company was in late-2019, when it raised $55 million. Now it’s back with a massive $200 million raise.
The Series F round brings Whoop’s total funding to nearly $405 million — a pretty massive investment for a company of its size. The round, led by SoftBank’s Vision Fund 2, puts the valuation at a jaw-dropping $3.6 billion valuation.
Additional investors include IVP, Cavu Venture Partners, Thursday Ventures, GP Bullhound, Accomplice, NextView Ventures and Animal Capital. They join a long list of former backers, including the National Football League Players Association, Jack Dorsey and a number of professional athletes.
The company’s targeting of athletes marks a strong contrast with leading consumer wearables like the Apple Watch and Fitbit. In fact, the company has a specific offering for sports teams, as well as solutions for businesses, healthcare and government/defense.
Whoop’s name made the rounds recently when Fitbit announced a “Daily Readiness Score” for the Charge 5, which many likened to the company’s more advanced analytics.
The company cites “rapid growth” in its membership offering over the past year as a motivation behind seeking additional funding. That was likely driven, in part, by the decision in 2019 to make the $500 wearable free, while focusing on a subscription service that starts at $18 a month for an 18-month membership (the shorter the membership, the more the monthly fee).
Whoop is eying international expansion beyond the U.S. and using the massive influx of cash on R&D for its hardware, software and analytics solutions. Money will also go toward expanding headcount, which is currently in excess of 500 (with nearly half of those employees having joined in the past year).
“We are thrilled to deepen our partnership with SoftBank as we grow internationally,” founder and CEO Will Ahmed said in a release. “While we have experienced amazing growth in the past year, the potential of our technology and the vast market for health monitoring remains largely untapped.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Apna, a 21-month-old startup that is helping millions of blue- and gray-collar workers in India upskill themselves, find communities and land jobs, is inching closer to becoming the fastest tech firm in the world’s second-largest internet market to become a unicorn.
Tiger Global is in advanced stages of talks to lead a $100 million round in Apna, according to four sources familiar with the matter. The proposed terms value the startup at over $1 billion, the sources said.
The round hasn’t closed yet, so terms of the deal may change, some of the sources cautioned.
If the round materializes, Apna will become the youngest Indian startup to attain the much-coveted unicorn status. The startup, which launched its app in December 2019, was valued at $570 million in its Series B financing round in June this year. It will also be the third financing round Apna would have secured in a span of less than seven months.
Tiger Global, an existing investor in Apna, didn’t respond to a request for comment earlier this month. Apna founder and chief executive Nirmit Parikh, an Apple alum, declined to comment on Tuesday.
Indian cities are home to hundreds of millions of low-skilled workers who hail from villages in search of work. Many of them have lost their jobs amid the coronavirus pandemic that has slowed several economic activities in the world’s second-largest internet market.
Apna, whose name is inspired from a 2019 Bollywood song, is building a scalable networking infrastructure so that these workers can connect to the right employers and secure jobs. On its eponymous Android app, users also upskill themselves, review their interview skills and become eligible for more jobs.
As of June this year, Apna had amassed over 10 million users and was facilitating more than 15 million job interviews each month. All jobs listed on the Apna platform are verified by the startup and free of cost for the candidates.
The startup has also partnered with some of India’s leading public and private organizations and is providing support to the Ministry of Minority Affairs of India, National Skill Development Corporation and UNICEF YuWaah to provide better skilling and job opportunities to candidates.
The investment talks further illustrate Tiger Global’s growing interest in India. The New York-headquartered firm has made several high-profile investments in India this year, including in BharatPe, Gupshup, DealShare, Classplus, Urban Company, CoinSwitch Kuber and Groww.
More than two dozen Indian startups have become a unicorn this year, up from 11 last year, as several high-profile investors, including Tiger Global, SoftBank and Falcon Edge, have increased the pace of their investments in the world’s second most populous nation.
Apna also counts Insight Partners, Lightspeed and Sequoia Capital among its existing investors.
Powered by WPeMatico
Software billing startup Octane announced Tuesday that it raised $2 million on a post-money valuation of $10 million to advance its pay-as-you-go billing software.
Akash Khanolkar and his co-founders met a decade ago at Carnegie Mellon University and since then went off in different directions. In Khanolkar’s case, he ran a cloud consulting business and saw how fast companies like Datadog and Snowflake were coming to market and dealing with Amazon Web Services.
He found that the commonality in all of those fast-growing companies was billing software using a pay-as-you-go business model versus the traditional flat-rate plans, Khanolkar told TechCrunch.
However, he explained that monitoring consumption means that billing becomes complicated: companies now have to track how customers are using the software per second in order to bill correctly each month.
Seeing the shift toward consumption-based billing, the co-founders came back together in June 2020 to create Octane, a metered billing system that helps vendors create a plan, monitor usage and charge in a similar way to Snowflake and AWS, Khanolkar said.
“We are API-driven, and you as a vendor will send us usage data, and on our end, we store it and then do real-time aggregations so at the end of the month, you can accordingly bill customers,” Khanolkar said. “We have seen contention between engineering and product. Engineers are there to create core plans, so we built a no-code experience for product teams to be able to create new price plans and then perform changes, like adding coupons.”
Within the global cloud billing market, which is expected to reach $6.5 billion by 2025, there are a set of Octane competitors, like Chargebee and Zuora, that Khanolkar said are tackling the subscription management side and succeeding in the past several years. Now there is a usage and consumption-based world coming and a whole new set of software businesses, like Octane, coming in to succeed there.
The new round of funding was led by Basis Set Ventures and included Dropbox co-founder Arash Ferdowsi, Github CTO Jason Warner, Fortress CTO Assunta Gaglione, Scale AI CRO Chetan Chaudhary, former Twilio executive Evan Cummack, Esteban Reyes, Abstraction Capital and Script Capital.
“With the rise of product-led growth and usage-based pricing models, usage-based billing is a critical and foundational piece of infrastructure that has been simply missing,” said Chang Xu, partner at Basis Set Ventures, via email. “At the same time, it’s something that every department cares about as it’s your revenue. Many later-stage companies we talk to that have built this in-house talk about the ongoing maintenance costs and wishes that there is a vendor they can outsource it to.”
We are super impressed with the Octane team with their dedication to building a best-in-class and robust usage-based billing solution. They’ve validated this opportunity by talking to lots of engineering teams so they can solve for all the edge cases, which is important in something as mission critical as billing. We are convinced that Octane will become an inevitable part of the tech infrastructure.”
The new funding will go primarily toward hiring engineers, as well as product, marketing and sales staff. Octane currently has seven employees, and Khanolkar expects to be around 10 by the end of the year.
The company is working with a large range of companies, primarily focused on infrastructure and the depth gauge industries. Octane is also seeing some unique use cases emerge, like a construction company using the usage meter to track the hours an employee works and companies in electric charging using the meter for those purposes.
“We didn’t envision construction guys using it, but in theory, it could be used by any company that tracks time — even legal,” Khanolkar added.
He declined to speak about the company’s revenue, but did say it now had two to three years of runway.
Up next, the company plans to roll out new features like price experimentation based on usage to help customers better make decisions on how to price their software, another problem Khanolkar sees happening. It will build ways that customers can try different plans against usage data to validate which one works the best.
“We are still in the early innings of consumption-based models, but we see more end users opting to go with an enterprise that wants to let them try out the software and then pay as they go,” he added.
Powered by WPeMatico
Walnut raised $15 million in Series A funding, led by Eight Roads Ventures, to continue developing its sales experience platform.
Founders Yoav Vilner and Danni Friedland started the company in July 2020. Vilner told TechCrunch that while at a previous company, he was building a category called technology marketing in Israel. He realized that company sales people often ran into problems when it was time to demonstrate their product — the product would break, or they would have to ask another department to open something or add a feature, none of which happened instantaneously, Vilner added.
He and Friedland’s answer to that problem is a no-code platform for teams to create customized product demonstrations quickly, be able to integrate them into their sales and marketing processes and then generate insights from the demos.
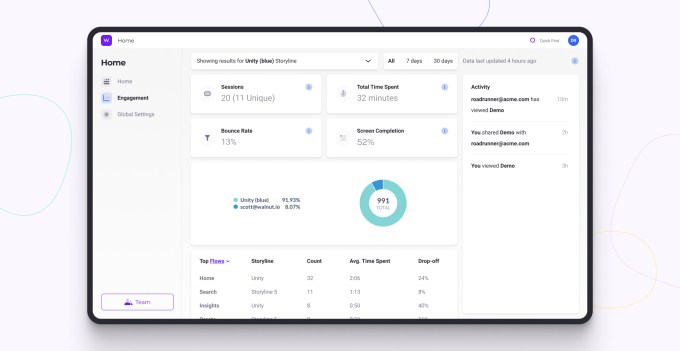
Walnut engagement example. Image Credits: Walnut
“We let the sales and marketing teams replicate the SaaS product in our cloud environment, which is disconnected from the back end,” Vilner explained. “They can create a storyline to fit their customer and the demonstration, and then following the demo, sales leaders can get insight on what was good or bad. It encourages the sharing of knowledge and what story worked best for which kind of company.”
The company’s latest round gives it $21 million raised to date, and follows a $6 million seed round that included NFX, A Capital, Liquid2 Ventures and Graph Ventures, Vilner said.
Walnut serves over 60 business-to-business clients, including Adobe, NetApp, Varonis and People AI. In addition to Tel Aviv, the company has offices in New York and London.
Vilner intends to use the new funding to grow the team across the U.S, Europe and Israel and continue developing its technology and platform, including tools to embed demos into a website for product-led growth. He also expects to double the team of 25 over the next year.
Eyal Rabinovich, an investor at Eight Roads Ventures, said his brother is a Walnut customer, and the company fits with one of the firm’s theses around broad vertically integrated brands in SaaS and deep technology.
Rabinovich was tracking the sales enablement space for a while and said many companies claim to provide something unique, but it is usually workflow and processes. In Walnut’s case, it is solving something at the core of sales.
“They make everything measurable, and the ‘holy grail’ is conversion, and even just 1% conversion could mean millions of dollars,” he added. “Every company we spoke to wanted to use this product. Customers were telling us they closed the sales cycle within two weeks.”
Powered by WPeMatico