Recent Funding
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
What do you call the grey area between a Series A and a Series B? In 2020, when the money is taken on opportunistically, you call it a Series A-1 extension, according to Teampay. Even if the new capital was raised at a new, higher valuation.
At least that’s what Teampay CEO Andrew Hoag has done with his company’s new $5 million investment, adding it onto its September, 2019-era Series A. TechCrunch covered that round, and the company’s $4 million seed round in 2018, keeping tabs on the corporate spend-management company as it grows.
Indeed, Teampay has posted big growth since its Series A was announced, pushing its annual recurring revenue (ARR) up by 320% and its total spend managed up by 800%. The first number implies that it has managed to monetize well as its usage, the second number, has spiked.
Teampay, Hoag said in an interview, wants to help companies control their bank accounts. This has gotten harder in 2020, as companies went from having an office with many employees to many employees in home offices. The rising complexity of running companies in the aftermath of COVID-19 and its economic disruptions has been a boon for the startup, with Teampay seeing its sales cycle cut in half, the CEO said, and bigger companies coming to its door, looking for help.
The startup targets the midmarket with its spend software, helping companies control what Hoag views as a business process problem, not merely an ability-to-spend issue. Teampay doesn’t want to reinvent the corporate card, but instead provide a set of tools to help companies manage their outflows, no matter what format they take (ACH, virtual cards, etc.).
So unlike Divvy, say, or Brex, Teampay generates most of its income from software fees instead of interchange revenues, though the company did tell TechCrunch that it has room to derive more revenues from spend over time. On the topic of competition, Teampay has lots in various forms. Brex and Ramp and Divvy and Airbase, not to mention old-guard products like Concur and Expensify, are in the market.
But with a fresh $5 million led by Fin Venture Capital and participated in by prior investors like Crosscut, and Tribe, and the ubiquitous Precursor, Teampay has new ammunition with which to go hunting.
With this raise, Teampay has now raised $21 million in known equity financing to date. I asked Hoag why the new round is not simply called a Series B. He said that the letter-series round demarcations have lost some of their specificity in 2020 (true), undercutting the main thrust of my quibble, and that this round was too small to be called a Series B (also true).
Instead, he said, Teampay pulled forward a bit of its future Series B on the back of big growth, presumably to help the company do more today in anticipation of its later, more traditionally sized next round.
TechCrunch has covered aggressive extension rounds in recent months, putting Teampay in good company with firms that are doing well, leading to their taking on more capital to go even faster. Let’s see how much further it can amp its ARR before its real Series B.
Powered by WPeMatico
U.K.-based Fertifa has bagged a £1 million (~$1.3 million) seed to plug into a fertility-focused workplace benefits platform. Passion Capital is investing in the round, along with some unnamed strategic angel investors.
The August 2019-founded startup sells bespoke reproductive health and fertility packages to U.K. employers to offer as workplace benefits to their staff — drawing on the use of technologies like telehealth to expand access to fertility support and cater to rising demand for reproductive health services.
Challenges conceiving can affect around one in seven couples, per the U.K.’s National Health Service (NHS).
In recent years fertility startups have been getting more investor attention as VC firms cotton on to growing market. Employers have also responded, with tech industry workplaces among those offering fertility “perks” to staff. Although the access-to-services issue can be more acute in the U.S. — given substantial costs involved in obtaining treatments like IVF.
In the U.K. the picture is a little different, given that the country’s taxpayer-funded NHS does fund some fertility treatments — meaning IVF can be free for couples to access. Although how much support couples get can depend on where in the country they live, with some NHS trusts funding more rounds of IVF than others. There can also be access restrictions based on factors such as a woman’s age and the length of time trying to conceive.
This means U.K. couples can run out of free fertility support before they’ve been able to conceive — pushing them toward paying for private treatment. Hence Fertifa spotting an opportunity for a workplace benefits model around reproductive health services.
It signed up its first employers this spring and summer, and says it now has a portfolio of corporate clients with an employee pool from a few hundreds to >10,000 — although it isn’t breaking out customer numbers. Rather, it says its services are available to around 700,000 U.K. employees at this point.
“At Fertifa we want to make fertility services more widely accessible to people,” says founder and CEO Tony Chen. “Some levels of fertility services can be provided by the NHS but every single NHS trust is different with eligibility, requirements and resources, and so unfortunately it can too often be reduced to a “postcode lottery”.
“We believe that everyone should have easy access to information, resources, education and services relating to fertility — and that working with workplaces is one way to start. With our efforts and partnerships we hope to normalise the conversations about fertility at work, just as other forms of health are openly discussed and provided for.”
Passion Capital partner Eileen Burbidge — who is joining Fertifa’s board (along with Passion’s Malin Posern) — has been public about her own use of IVF and takes a very personal interest in the fertility space.
“The unfortunate fact is that over recent years, even though success rates have increased and of course more and more patients are exploring the benefits of IVF, NHS funding has been declining and the number of patients using the NHS for their first cycle has also been decreasing,” she tells TechCrunch.
“This doesn’t take away from the fact that it’s brilliant what we get from the NHS here in the U.K., but there’s clearly a lot more which can be done to further increase accessibility and affordability — given less and less funding for the NHS in the face of increasing demand of both the NHS and private routes.”
Fertifa says its model is to provide direct care and support to employees — rather than being a broker or acting as part of a referral system. So it has two in-house clinicians at this stage (out of a team of 10-15 people). Although it also says it “partners” with clinicians and clinics across the U.K. So it’s not doing everything in-house.
It offers what it bills as a “full range” of fertility and gynaecology services — from assisted reproductive technology such as IVF, IUI and more; fertility planning such as egg, sperm and embryo freezing to donor-assisted and third-party reproduction such as donor eggs and sperm; as well as surrogacy and adoption.
Its doctors, nurses and “fertility advocates” are there to provide a one-to-one care service to support patients throughout the process.
“We use technology in a number of ways and are ambitious about how it will help us to maintain an advantage over others in the sector and provide the best customer experience,” says Chen, noting it has developed “a full end-to-end” app for patients to guide them through the various stages of their fertility journey.
“On the employer side we have a full employer portal as well which provides educational resources, support options and access to services for HR/People teams to use and share with their workforces. Additionally, we use telehealth to enable more efficient, convenient (particularly in the age of COVID-19 restrictions) and immediate consultations with clinicians and nurses. Finally, we are refining our machine learning algorithms to help drive more informed decision making for patients and clinicians alike.”
It’s not currently applying AI but says that over time its in-house medical experts will use artificial intelligence to aid decision-making — with the aim of reducing clinic visits, enhancing the patient experience and yielding better clinical pregnancy rates.
Chen points to the U.K.’s Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority having already made its data publicly available on more than 100,000 couples and their treatment and outcomes — suggesting such data-sets will underpin the development of new predictive models for fertility.
“With additional insight and data sources [we] could more accurately predict probability of success for a patient — or the best type of treatment for them,” he adds.
While Fertifa’s current focus is U.K. expansion — targeting workplaces of all sizes and scale — it’s also got its eye on scaling overseas down the line. Although it will of course face more competition at that point, with the likes of Y Combinator backed Carrot already offering global fertility benefits packages for employers.
“Fertility and reproductive health is important to people all over the world,” says Chen. “Globally one in four women experience a miscarriage, every LGBT+ individual requires support to become a parent, and everyone needs to be increasingly empowered to take control of their reproductive health through fertility preservation treatment.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Workplace SaaS tools for teams have seen rocket ship growth in the past several years, and that adoption has given rise to a host of software tools geared toward improving individual productivity. Many of the startups behind these tools see building a cult following among individual users as the best way to set themselves up for later enterprise-wide success.
Raycast is a developer-focused productivity tool that aims to be the quickest way to get common tasks done. Today, it’s launching into public beta and sharing with TechCrunch that the team has raised new funding from Accel months after graduating from Y Combinator.
The company has closed a $2.7 million seed round led by Accel, with participation from YC, Jeff Morris Jr.’s Chapter One fund, as well as angel investors Charlie Cheever, Calvin French-Owen and Manik Gupta .
The desktop software takes a note from peers like Superhuman and Command E, allowing users to quickly pull up and modify data with keyboard shortcuts. Users can easily create and re-modify issues in Jira, merge pull requests in GitHub and find documents. The software is very much a developer-focused version of Apple’s Spotlight search that aims to help software engineers navigate with a single tool all the parts of their job that aren’t development work.
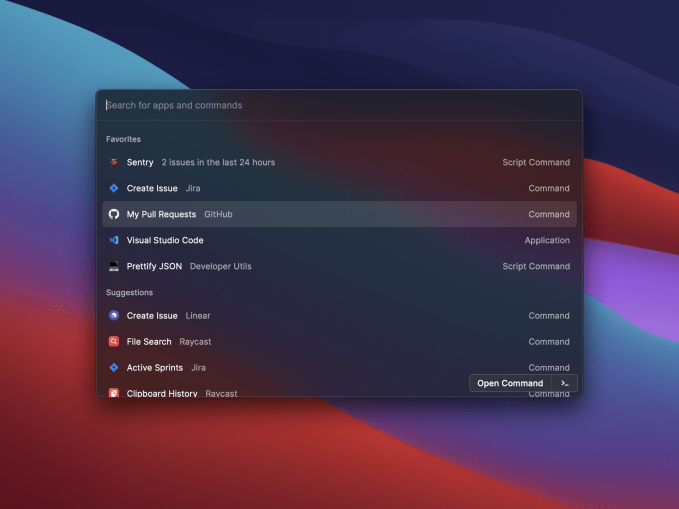
Image via Raycast.
Like plenty of workplace tools startups, one of the keys for Raycast is building out a network of extensions that can encompass a user’s workflow. For now, the software supports integrations from Asana, Jira, Zoom, Linear, G Suite, Calendar, GitHub and Reminders, alongside core functionality that can help manage system settings and a calculator that can handle complex math problems. As the startup launches out of public beta, they’re looking to double down on extensions and are rolling out a developer program for early access to their API.
The Mac-only software is free while in public beta, but the company does plan on charging a monthly subscription for the service eventually, though they aren’t quite ready to talk about pricing yet.
Raycast’s team is interested in appealing to individual users for now, but might eventually expand to becoming a teams-level enterprise product that could help onboard new employees faster by quickly orienting them with their office’s software suite, but that’s all a bit down the road, the team says.
“We’re staying focused on single-player mode for a while,” CEO Thomas Paul Mann tells TechCrunch.
Powered by WPeMatico
Despite e-commerce firms Amazon and Walmart and others pouring billions of dollars into India, offline retail still commands more than 95% of all sales in the world’s second largest internet market.
The giants have acknowledged the strong hold neighborhood stores (mom and pop shops) have in the country, and in recent quarters scrambled for ways to work with them. Mukesh Ambani, India’s richest man, has made the dynamics more interesting in the past year as he works to help these neighborhood stores sell online.
But the market opportunity is still too large, and there are many aspects of the old retail business that could use some tech. That’s the bet WareIQ, a Bangalore-headquartered, Y Combinator-backed startup is making. And it has just raised a $1.65 million seed financing round from YC, FundersClub, Pioneer Fund, Soma Capital, Emles Venture Advisors and founders of Flexport.
The one-year-old startup operates a platform to leverage the warehouses across the country. It has built a management system for these warehouses, most of which largely engage in offline business-to-business commerce and have had little to no prior e-commerce exposure.
“We connect these warehouses across India to our platform and utilize their infrastructure for e-commerce order processing,” said Harsh Vaidya, co-founder and chief executive of WareIQ, in an interview with TechCrunch. The company offers this as a service to retail businesses.
Who are these businesses? Third-party sellers (some of whom sell to Amazon and Flipkart and use WareIQ to speed up their delivery), e-commerce firms, social commerce platforms, as well as neighborhood stores and social media influencers.
Any online store, for instance, can send its products to WareIQ, which has integrations with several popular e-commerce platforms and marketplaces. It works with courier partners to move items from one warehouse to another to offer the fastest delivery, explained Vaidya.
The infrastructure stitched together by WareIQ also enables an online seller to set up their own store and engage with customers directly, thereby saving fees they would have paid to Amazon and other established e-commerce players.
“The sellers were not able do this on their own before because it required them to talk directly to warehousing companies that maintain their own rigid contracts, and high-security deposits, and they still needed to work with multiple technology providers to complete the tech-stack,” he said. WareIQ also offers these sellers last-mile delivery, cash collection and fraud detection among several other services.
“In a way, we are building an open-source Amazon fulfilment service, where any seller can send their goods to any of our warehouses and we fulfil their Amazon orders, Myntra orders, Flipkart orders or their own website orders. We also comply with the standard of these individual marketplaces, so our sellers get a Prime tag on Amazon,” he said.
WareIQ is free for anyone to sign up with any charge and it takes a cut by the volume of orders it processes. The startup today works with more than 40 fulfilment centres and plans to deploy the fresh capital to expand its network to tier 2 and tier 3 cities, he said. It’s also hiring for a number of tech roles.
Powered by WPeMatico
If you miss hanging out with your co-workers but don’t want to spend a single second more on Zoom, the latest product from Donut might be the answer.
The startup is launching its new Watercooler product today while also announcing that it has raised $12 million in total funding, led by Accel and with participation from Bloomberg Beta, FirstMark, Slack Fund and various angel investors.
Co-founder and CEO Dan Manian told me that this is actually money that the startup raised before the pandemic, across multiple rounds. It just didn’t announce the fundraising until now.
The startup’s vision, Manian said, is “to create human connection between people at work.” Its first product, Intros, connects via Slack teammates who didn’t already know each other, often with the goal of setting up quick coffee meetings (originally in-person and now virtual).
Donut says it has facilitated 4 million connections across 12,000 companies (including The New York Times, Toyota and InVision), with 1 million of those connections made since the beginning of the pandemic.
However, Manian said customers have been asking Donut to facilitate more frequent interactions, especially since most people aren’t going to have these coffee meetings every day. At the same time, people face the dueling issues of isolation and Zoom fatigue, where “the antidote to one thing makes the other pain worse.” And he suggested that one of the hardest things to recreate while so many of us are working remotely are “all the little microinteractions that you have while you’re working.”
That’s where Watercooler comes in — as the name suggests, it’s designed to replicate the feeling of hanging out at the office watercooler, having brief, low-key conversations. Like Intros, it integrates with Slack, creating a new channel where Watercooler will post fun, conversation-starting questions like “‘What’s your favorite form of potato?” or “What’s one thing you’ve learned in your career that you wish you knew sooner?”
Talking about these topics shouldn’t take much time, but Manian argued that brief conversations are important: “Those things add up to friendship over time, they’re what actually transform you from co-worker to friend.” And those friendships are important for employers too, because they help with team cohesion and retention.
I fully endorse the idea of a Slack watercooler — in fact, the TechCrunch editorial team has a very active “watercooler” channel and I’m always happy to waste time there. My big question was: Why do companies need to purchase a product for this?
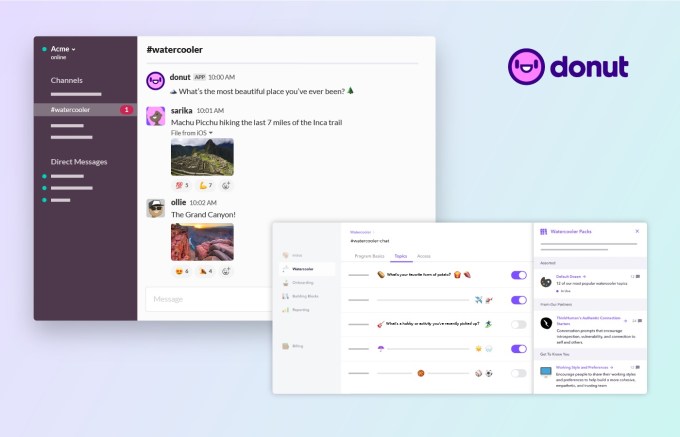
Donut Watercooler. Image Credits: Donut
Manian said that there were “a bunch of our early adopters” who had tried doing this manually, but it was always in the “past tense”: “It got too hard to come up with the questions, or it took real work coming up with them, whoever was doing it already had a it full time job.”
With Watercooler, on the other hand, the company can choose from pre-selected topics and questions, set the frequency with which those questions are posted and then everything happens automatically.
Manian also noted that different organizations will focus on different types of questions. There are no divisive political questions included, but while some teams will stick to easy questions about things like potatoes and breakfast foods, others will get into more substantive topics like the ways that people prefer to receive feedback.
And yes, Manian thinks companies will still need these tools after the pandemic is over.
“Work has fundamentally changed,” he said. “I don’t think we’ll put remote work back in the bottle. I think it’s here to stay.”
At the same time, he described the past few months as “training wheels” for a hybrid model, where some team members go back to the office while others continue working remotely. In his view, teams will face an even bigger challenge then: To keep their remote members feeling like they’re connected and in-the-loop.
Powered by WPeMatico
Code is the lifeblood of the modern world, yet the tooling for some programming environments can be remarkably spartan. While developers have long had access to graphical programming environments (IDEs) and performance profilers and debuggers, advanced products to analyze and improve lines of code have been harder to find.
These days, the most typical tool in the kit is a linter, which scans through code pointing out flaws that might cause issues. For instance, there might be too many spaces on a line, or a particular line might have a well-known ambiguity that could cause bugs that are hard to diagnose and would best be avoided.
What if we could expand the power of linters to do a lot more though? What if programmers had an assistant that could analyze their code and actively point out new security issues, erroneous code, style problems and bad logic?
Static code analysis is a whole interesting branch of computer science, and some of those ideas have trickled into the real-world with tools like semgrep, which was developed at Facebook to add more robust code-checking tools to its developer workflow. Semgrep is an open-source project, and it’s being commercialized through r2c, a startup that wants to bring the power of this tool to the developer masses.
The whole project has found enough traction among developers that Satish Dharmaraj at Redpoint and Jim Goetz at Sequoia teamed up to pour $13 million into the company for its Series A round, and also backed the company in an earlier, unannounced seed round.
The company was founded by three MIT grads — CEO Isaac Evans and Drew Dennison were roommates in college, and they joined up with head of product Luke O’Malley. Across their various experiences, they have worked at Palantir, the intelligence community, and Fortune 500 companies, and when Evans and Dennison were EIRs at Redpoint, they explored ideas based on what they had seen in their wide-ranging coding experiences.

The r2c team, which I assume only writes bug-free code. Image by r2c.
“Facebook, Apple, and Amazon are so far ahead when it comes to what they do at the code level to bake security [into their products compared to] other companies, it’s really not even funny,” Evans explained. The big tech companies have massively scaled their coding infrastructure to ensure uniform coding standards, but few others have access to the talent or technology to be on an equal playing field. Through r2c and semgrep, the founders want to close the gap.
With r2c’s technology, developers can scan their codebases on-demand or enforce a regular code check through their continuous integration platform. The company provides its own template rulesets (“rule packs”) to check for issues like security holes, complicated errors and other potential bugs, and developers and companies can add their own custom rulesets to enforce their own standards. Currently, r2c supports eight programming languages, including JavaScript and Python, and a variety of frameworks, and it is actively working on more compatibility.
One unique focus for r2c has been getting developers onboard with the model. The core technology remains open-sourced. Evans said that “if you actually want something that’s going to get broad developer adoption, it has to be predominantly open source so that developers can actually mess with it and hack on it and see whether or not it’s valuable without having to worry about some kind of super restrictive license.”
Beyond its model, the key has been getting developers to actually use the tool. No one likes bugs, and no developer wants to find more bugs that they have to fix. With semgrep and r2c though, developers can get much more immediate and comprehensive feedback — helping them fix tricky errors before they move on and forget the context of what they were engineering.
“I think one of the coolest things for us is that none of the existing tools in the space have ever been adopted by developers, but for us, it’s about 50/50 developer teams who are getting excited about it versus security teams getting excited about it,” Evans said. Developers hate finding more bugs, but they also hate writing them in the first place. Evans notes that the company’s key metric is the number of bugs found that are actually fixed by developers, indicating that they are offering “good, actionable results” through the product. One area that r2c has explored is actively patching obvious bugs, saving developers time.
Breaches, errors and downtime are a bedrock of software, but it doesn’t have to be that way. With more than a dozen employees and a hefty pool of capital, r2c hopes to improve the reliability of all the experiences we enjoy — and save developers time in the process.
Powered by WPeMatico
AppFollow, an app management startup, has raised a $5 million Series A round led by Barcelona’s Nauta Capital, alongside existing investors Vendep Capital and RTP Global participating.
The Helsinki-headquartered company says it benefitted during the pandemic and even in April 2020 as the desire for automation and apps exploded. It says it now has 70,000 clients on its platform globally, including McDonald’s, Disney, Expedia, PicsArt, Flo, Jam City and Discord.
CEO Anatoly Sharifulin said in a statement: “AppFollow helps teams understand sentiment, both for your users and competitor’s, figure out how your potential customers search for apps and use this knowledge to make your app more visible and, of course, follow on your KPIs like downloads and revenues to be sure that all is under control.”
Eugene Kruglov of Nauta Capital said: “We are extremely delighted to partner with Nauta Capital on this round. And having both of current investors and as well some of our customers to participate in the round proves that we are on the right direction to become the market standard for effective app management.”
The company, which employs 65 people across nine countries, all working remotely, will use the investment to strengthen its presence in the U.S. and Europe, hire VP-level executives in sales and marketing, and diversify their platform.
Powered by WPeMatico
Outrider, a startup aiming to bring its autonomous technology to the nerve center of the supply chain, has raised $65 million in funding just eight months after coming out of stealth. The Series B round was led by Koch Disruptive Technologies and brings its total funding raised to $118 million.
Other existing investors increased their investments, including NEA, 8VC and Prologis Ventures, according to the company. New investors included Henry Crown and Company and Evolv Ventures.
The company’s aim to automate distribution yards doesn’t get the same kind of attention as the more public-facing robotaxis that other companies are pursuing. But it could be as impactful and potentially lucrative to the company that pulls it off. Distribution yards are where goods make the transition from long-haul trucks to warehouses, and eventually the consumer. These hubs of economic activity rely on humans to make repetitive, manual tasks using diesel-powered yard trucks. There are some 400,000 distribution yards located in the United States, a number that provides an idea of the potential size of the opportunity.
The Golden, Colorado startup previously known as Azevtec developed a three-part system that includes an autonomous electric yard truck, software to manage the operations and site infrastructure. The total system automates the manual aspect of yard operations, including moving trailers around the yard as well as to and from loading docks. The system can also hitch and unhitch trailers, connect and disconnect trailer brake lines and monitor trailer locations.
Outrider touts the dual benefits of its electric and autonomous system. The company notes that its electric yard trucks are ideal for autonomy due to their reduced maintenance, lower operating costs and reliable clean power. Andrew Smith, the company’s founder and CEO, says disruptions caused by COVID-19 has highlighted the need for this kind of automated distribution yard technology.
Outrider, which now employs 110 employees, has completed “multiple” pilot programs, including one with Georgia-Pacific, and expanded its customer base since coming out of stealth in February.
Powered by WPeMatico
Robust.AI today announced that it has raised a $15 million Series A, led by Jazz Venture Partners. Existing partners Playground Global, Liquid2, Fontinalis, Jaan Tallinn and Mark Leslie also participated in the round, which brings the Bay Area-based robotics AI startup’s funding up to $22.5 million.
Founded mid-2019, the company counts Rodney Brooks among its C-level executives. The iRobot co-founder serves as the startup’s CTO, following the unexpected closure of the promising (but financially untenable) Rethink, which gave the world the Baxter and Sawyer robots. (Fellow iRobot co-founder Helen Greiner also notably landed at a new venture in recent months). CEO Gary Marcus, meanwhile, is also the co-founder of Geometric Intelligence, which was acquired by Uber, back in 2016.
At the core of Robust.AI are plans to build “the world’s first industrial-grade cognitive engine for robots,” essentially providing collaborative robots sufficient problem-solving capacity to effectively work alongside humans.
The company is still quite new, but many robotics and automation investments have seemingly been fast-tracked by a pandemic that has hamstrung much of the human workforce. Robust’s stated mission is to overhaul the software stack that runs many of these machines, in order to to make them function better in often complex environments.
“Finding market fit is as important in robots and AI systems as any other product,” Brooks said in a statement. “We are building something we believe most robotics companies will find irresistible, taking solutions from single-purpose tools that today function in defined environments, to highly useful systems that can work within our world and all its intricacies.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Seattle-based Pulumi, one of the newer startups in the ”infrastructure-as-code” space, today announced that it has raised a $37.5 million Series B funding round led by NEA. Previous investors Madrona Venture Group and Tola Capital also participated in this round, which brings the total investment in the company to $57.5 million.
The new investment follows the launch of Pulumi 2.0, which got the company closer to its vision of becoming what the team calls a “cloud engineering platform” and impressive growth over the last year, with a 10x growth in adoption in the last 12 months.
“We started with infrastructure as code, because we felt like that was a foundational piece that gave us the programming model, along with the cloud resource model,” Pulumi co-founder and CEO Joe Duffy told me. “That was an important place to start. With [Pulumi] 2.0, we launched support for testing, for policy as code — so that you could actually apply governance and compliance as part of your infrastructure management — and really helping more of the team work together.”
Indeed, after starting with a focus on infrastructure teams, Pulumi is now looking to expand across teams.
“The infrastructure team is becoming the nucleus that pulls the whole team together. We’re actually calling this cloud engineering,” Duffy explained. “What we’re calling cloud engineering is developers using the cloud in a first-class way, infrastructure teams helping them do that and increasingly pulling in security engineers to make sure that governance is part of the story as well. The 2.0 release was our first time exploring those adjacencies and trying to paint a path to realizing the full Pulumi vision.”
Infrastructure as code isn’t necessarily new, of course. The promise of Pulumi is that it isn’t hobbled by any legacy products but that the team designed it as a cloud-native product from the ground up. That’s something NEA’s Aaron Jacobson, who will join the company’s board, also stressed.
“If you think about how fast the cloud has evolved just in 10 years, Pulumi is built in a place of multi-cloud, of Kubernetes, of serverless, Jacobson said. “And much of the original infrastructure-as-code constructs didn’t even have those in mind. Since Pulumi is newer to market and has come after all those constructs, it just has better integration, it’s just a more delightful experience to developers.”
NEA’s Scott Sandell is actually taking this a bit further. “Venture capitalists are in the business of pattern recognition,” he said. “And the pattern that I recognized actually goes all the way back to when I was a product manager in the windows group. And I saw that developers don’t want to have to deal with complexity — they want to have the complexity managed for them.” That, he argues, is what Pulumi does for developers — and it surely helped both Duffy and his co-founder and Pulumi executive chairman Eric Rudder, who left successful careers at Microsoft to build this company.
In addition to the new funding, Pulumi also today announced that it brought in a number of new executives, including industry veterans Jay Wampold as CMO, Lindsay Marolich as senior director of demand generation, Kevin Kotecki as VP of sales and Lee-Ming Zen as VP of engineering.
Powered by WPeMatico