TC
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Auto Added by WPeMatico
Since the start of the year, I’ve covered nine M&A deals already, the largest being Citrix buying Wrike for $2.25 billion. But not every deal involves a huge price tag. Today we are going to look at three smaller deals that show there is plenty of activity at the lower-end of the acquisition spectrum.
As companies look for ways to enhance their offerings, and bring in some talent at the same time, smaller acquisitions can provide a way to fill in the product road map without having to build everything in-house.
This gives acquiring companies additional functionality for a modest amount of cash. In smaller deals, we often don’t even get the dollar amount, although in one case today we did. If the deal isn’t large enough to have a material financial impact on a publicly traded company, they don’t have to share the price.
Let’s have a look at three such deals that came through in recent days.
For starters, Tenable, a network security company that went public in 2018, bought French Active Directory security startup Alsid for $98 million. Active Directory, Microsoft’s popular user management tool, is also a target of hackers. If they can get a user’s credentials, it’s an easy way to get on the network and Alsid is designed to prevent that.
Security companies tend to enhance the breadth of their offerings over time and Alsid gives Tenable another tool and broader coverage across their security platform. “We view the acquisition of Alsid as a natural extension into user access and permissioning. Once completed, this acquisition will be a strategic complement to our Cyber Exposure vision to help organizations understand and reduce cyber risk across the entire attack surface,” according to the investor FAQ on this acquisition.
Emmanuel Gras, CEO and co-founder, Alsid says he started the company to prevent this kind of attack. “We started Alsid to help organizations solve one of the biggest security challenges, an unprotected Active Directory, which is one of the most common ways for threat actors to move laterally across enterprise systems,” Gras said in a statement.
Alsid is based in Paris and was founded in 2014. It raised a modest amount, approximately $15,000, according to Crunchbase data.
Copper, a CRM tool built on top of the Google Workspace, announced it has purchased Sherlock, a customer experience platform. They did not share the purchase price.
The pandemic pushed many shoppers online and providing a more customized experience by understanding more about your customer can contribute to and drive more engagement and sales. With Sherlock, the company is getting a tool that can help Copper users understand their customers better.
“Sherlock is an innovative engagement analytics and scoring platform, and surfaces your prospects’ and customers’ intentions in a way that drives action for sales, account management and customer success professionals,” Copper CEO Dennis Fois wrote in a blog post announcing the deal.
He added, “Relationships are based on engagement, and with Sherlock we are going to create CRM that is focused on action and momentum.”
It’s clear that APIs have changed the way we think about software development, but they have also created a management problem of their own as they proliferate across large organizations. RapidAPI, an API management platform, announced today that it has acquired Paw.
With Paw, RapidAPI adds the ability to design your own APIs, essentially giving customers a one-stop shop for everything related to creating and managing the API environment inside a company. “The acquisition enables RapidAPI to extend its open API platform across the entire API development lifecycle, creating a connected experience for developers from API development to consumption, across multiple clouds and gateways,” the company explained in a statement.
RapidAPI was founded in 2015 and has raised over $67 million, according to Crunchbase data. Its most recent funding came last May, a $25 million round from Andreessen Horowitz, DNS Capital, Green Bay Ventures, M12 (Microsoft’s Venture Fund) and Grove.
Each of these purchases fills an important need for the acquiring company and expands the abilities of the existing platform to offer more functionality to customers without putting out a ton of cash to do it.
Powered by WPeMatico
Mobile analytics and market data company App Annie launched a new app today that CEO Ted Krantz said is built not for the analyst who’s “immersed in the data,” but rather the executive who needs “a much more elevated, top-down view.”
The biggest new piece of the company’s Pulse app is something called the App Annie Performance Score, which Krantz compares to a FICO score for mobile apps. The idea is to take an app’s user acquisition, engagement, monetization and sentiment and boil them down into a single score that benchmarks how the app is performing relative to the competition.
Krantz said that eventually, the performance store could become more customizable for each customer, so that “you can tailor it to the metrics that matter to you.” The app also highlights any shifts in key app metrics and identifies potential causes, and it includes a newsfeed showing what’s happening to the apps and markets that a user follows.
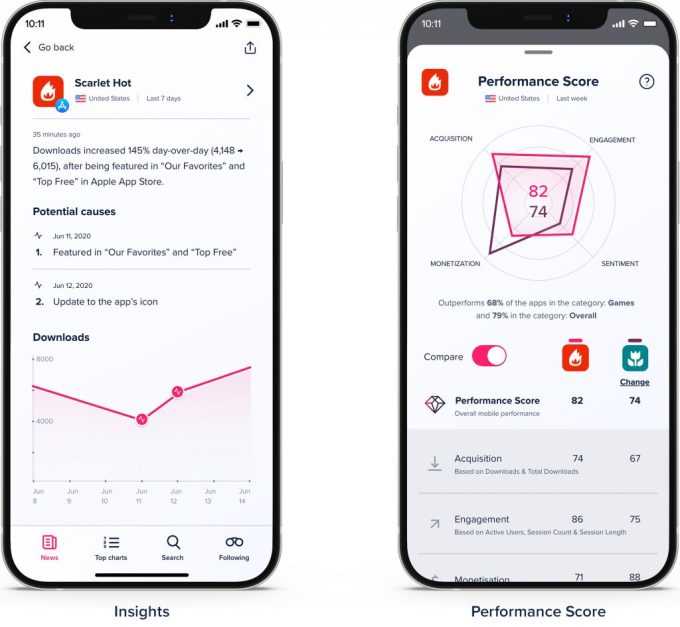
Image Credits: App Annie
The goal, Krantz added, is to provide executives with a quick overview of the data they need without requiring them to dig through it or wait for a report — especially as “mobile is becoming such an imperative.” It’s the team’s “aspiration” to create an app that executives check every day, though he’s not necessarily expecting that to happen initially.
The Pulse app is based on App Annie’s market-level data, so Krantz said it shouldn’t be affected by Apple’s upcoming privacy changes. At the same time, he acknowledged that the company’s broader goals of bringing together first-party and third-party data are starting too look “a little tricky.”
App Annie Pulse is currently available on iOS, with the company planning to launch an Android version in the second quarter of this year. And while the full features of Pulse are only available to paying App Annie customers, Krantz said there are also plans for “revamping the free side of the equation and make that a little more meaty.”
Powered by WPeMatico
The founders of Accord, an early-stage startup focused on bringing order to B2B sales, are not your typical engineer founders. Instead, the two brothers, Ross and Ryan Rich, worked as sales reps seeing the problems unique to this kind of sale firsthand.
In November 2019, they decided to leave the comfort of their high-paying jobs at Google and Stripe to launch Accord and build what they believe is a missing platform for B2B sales, one that takes into account the needs of both the sales person and the buyer.
Today the company is launching with a $6 million seed round from former employer Stripe and Y Combinator. It should be noted that the founders applied to YC after leaving their jobs and impressed the incubator with their insight and industry experience, even though they didn’t really have a product yet. In fact, they literally drew their original idea on a piece of paper.
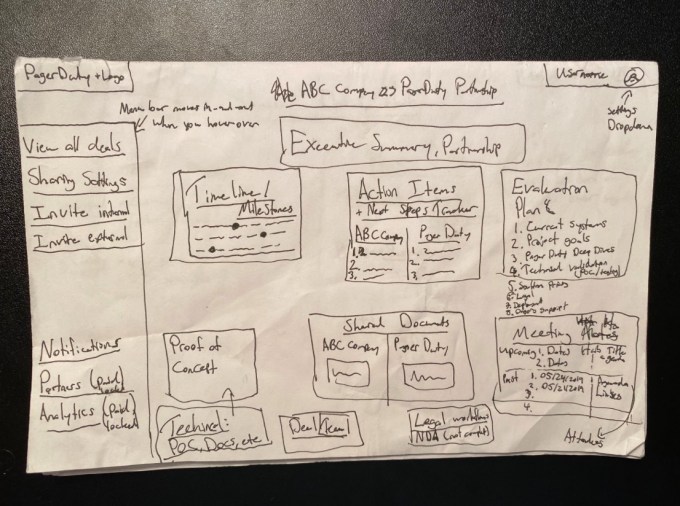
The original prototype was just a drawing of their idea. Image Credits: Accord
Recognizing they had the sales skills, but lacked programming chops, they quickly brought in a third partner, Wayne Pan, to bring their idea to life. Today, they have an actual working program with paying customers. They’ve created a kind of online hub for B2B salespeople and buyers to interact.
As co-founder Ross Rich points out, these kinds of sales are very different from the consumer variety, often involving as many as 14 people on average on the buyer side. With so many people involved in the decision-making process, it can become unwieldy pretty quickly.
“We provide within the application shared next steps and milestones to align on and that the buyer can track asynchronously, a resource hub to avoid sorting through those hundreds of emails and threads for a single document or presentation and stakeholder management to make sure the right people are looped in at the right time,” Rich explained.
Accord also integrates with the company CRM like Salesforce to make sure all of that juicy data is being tracked properly in the sales database. At the same time, Rich says the startup wants this platform to be a place for human interaction. Instead of an automated email or text, this provides a place where humans can actually interact with one another, and he believes that human element is important to help reduce the complexity inherent in these kinds of deals.
With $6 million in runway and a stint at Y Combinator under their belts, the founders are ready to make a more concerted go-to-market push. They are currently at nine people, mostly engineers aside from the two sales-focused founders. He figures to be bringing in some new employees this year, but doesn’t really have a sense of how many they will bring on just yet, saying that is something that they will figure out in the coming months.
As they do that, they are already thinking about being inclusive with several women on the engineering team, recognizing if they don’t start diversity early, it will be more difficult later on. “[Hiring a diverse group early] only compounds when you get to nine or 10 people and then when you’re talking to someone and they are wondering, ‘Do I trust this team and is that a culture where I want to work?’ He says if you want to build a diverse and inclusive workplace, you have to start making that investment early.
It’s early days for this team, but they are building a product to help B2B sales teams work more closely and effectively with customers, and with their background and understanding of the space, they seem well-positioned to succeed.
Powered by WPeMatico
SLAs, SLOs, SLIs. If there’s one thing everybody in the business of managing software development loves, it’s acronyms. And while everyone probably knows what a Service Level Agreement (SLA) is, Service Level Objectives (SLOs) and Service Level Indicators (SLIs) may not be quite as well known. The idea, though, is straightforward, with SLOs being the overall goals a team must hit to meet the promises of its SLA agreements, and SLIs being the actual measurements that back up those other two numbers. With the advent of DevOps, these ideas, which are typically part of a company’s overall Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) efforts, are becoming more mainstream, but putting them into practice isn’t always straightforward.
Nobl9 aims to provide enterprises with the tools they need to build SLO-centric operations and the right feedback loops inside an organization to help it hit its SLOs without making too many trade-offs between the cost of engineering, feature development and reliability.
The company today announced that it has raised a $21 million Series B round led by its Series A investors Battery Ventures and CRV. In addition, Series A investors Bonfire Ventures and Resolute Ventures also participated, together with new investors Harmony Partners and Sorenson Ventures.
Before starting Nobl9, co-founders Marcin Kurc (CEO) and Brian Singer (CPO) spent time together at Orbitera, where Singer was the co-founder and COO and Kurc the CEO, and then at Google Cloud, after it acquired Orbitera in 2016. In the process, the team got to work with and appreciate Google’s site reliability engineering frameworks.
As they started looking into what to do next, that experience led them to look into productizing these ideas. “We came to this conclusion that if you’re going into Kubernetes, into service-based applications and modern architectures, there’s really no better way to run that than SRE,” Kurc told me. “And when we started looking at this, naturally SRE is a complete framework, there are processes. We started looking at elements of SRE and we agreed that SLO — service level objectives — is really the foundational part. You can’t do SRE without SLOs.”
As Singer noted, in order to adopt SLOs, businesses have to know how to turn the data they have about the reliability of their services, which could be measured in uptime or latency, for example, into the right objectives. That’s complicated by the fact that this data could live in a variety of databases and logs, but the real question is how to define the right SLOs for any given organization based on this data.
“When you go into the conversation with an organization about what their goals are with respect to reliability and how they start to think about understanding if there’s risks to that, they very quickly get bogged down in how are we going to get this data or that data and instrument this or instrument that,” Singer said. “What we’ve done is we’ve built a platform that essentially takes that as the problem that we’re solving. So no matter where the data lives and in what format it lives, we want to be able to reduce it to very simply an error budget and an objective that can be tracked and measured and reported on.”
The company’s platform launched into general availability last week, after a beta that started last year. Early customers include Brex and Adobe.
As Kurc told me, the team actually thinks of this new funding round as a Series A round, but because its $7.5 million Series A was pretty sizable, they decided to call it a Series A instead of a seed round. “It’s hard to define it. If you define it based on a revenue milestone, we’re pre-revenue, we just launched the GA product,” Singer told me. “But I think just in terms of the maturity of the product and the company, I would put us at the [Series] B.”
The team told me that it closed the round at the end of last November, and while it considered pitching new VCs, its existing investors were already interested in putting more money into the company and since its previous round had been oversubscribed, they decided to add to this new round some of the investors that didn’t make the cut for the Series A.
The company plans to use the new funding to advance its roadmap and expand its team, especially across sales, marketing and customer success.
Powered by WPeMatico
Managing IoT devices in a large organization can be a messy proposition, especially when many of them aren’t even managed directly by IT and often involve integrating with a number of third-party systems. SecuriThings wants to help with a platform of services to bring that all under control, and today the startup announced a $14 million Series A.
Aleph led the round with participation from existing investor Firstime VC and a number of unnamed angels. The company has raised a total of $17 million, according to Crunchbase data.
Roy Dagan, company CEO and co-founder, says that he sees organizations with many different connected devices running on a network, and it’s difficult to manage. “We enable organizations to manage IoT devices securely at scale in a consolidated and cost-efficient manner,” Dagan told me.
This could include devices like security cameras, along with access control systems and building management systems involving thousands — or in some instances, tens of thousands — of devices. “The technology we build, we integrate with management systems, and then we deploy our capabilities which are focused on the edge devices. So that’s how we also find the devices, and then we have these different capabilities running on the edge devices or fetching information from the edge devices,” Dagan explained.
Image Credits: SecuriThings
The company has formed partnerships with a number of key device manufacturers, including Microsoft, Convergint Technologies and Johnson Controls, among others. They work with a range of industries including airports, casinos and large corporate campuses.
Aaron Rosenson, general partner at lead investor Aleph, says the company is solving a big problem managing the myriad devices inside large organizations. “Until SecuriThings came along, there were these massive enterprise software categories of automation, orchestration and observability just waiting to be built for IoT,” Rosenson said in a statement. He says that SecuiThings is pulling that all together for its customers.
The company was founded in 2016 originally with the idea of being an IoT security company, and while they still are involved in securing these devices, their ability to communicate with them gives IT much greater visibility and insight and the ability to update and manage them.
Today, the company has 30 employees, and with the new investment it will be doubling that number by the end of the year. While Dagan didn’t cite specific customer numbers, he did say they have dozens of customers with deal sizes of between five and seven figures.
Powered by WPeMatico
Meet Powder, a French startup that helps you share video clips of your favorite games, follow people with the same interests and interact with them. The company has raised a $14 million Series A round led by Serena.
Powder wants to build the video infrastructure for social gaming. While many communities of gamers already share content on Twitch, Discord and Reddit, there isn’t a dominant mobile app focused on gaming.
You could call it an Instagram or Snapchat for gamers, but the startup has built specific tools that make it similar and yet different from those mainstream social platforms.
Powder can capture video content from any platform. You can record with your console and access your footage by connecting your account with Powder. You can capture videos on your PC using the company’s desktop app. You can also capture videos of mobile games.
The company tries to identify the most relevant events in your favorite game — it can be when you score a goal on Rocket League, when you are the last person standing in Fortnite, etc.
You can then trim your video, add filters, music and stickers and share a video with your followers. Other users can share reactions, add comments and send messages.
Image Credits: Powder
Overall, the company has raised $18 million and is pretty transparent about its funding story. In August 2018, the company raised a $400,000 pre-seed round with Kima Ventures and the co-founders of Zenly, Antoine Martin and Alexis Bonillo. In March 2019, General Catalyst, Slow Ventures, Dream Machine, SV Angel, Brian Pokorny, Florian Kahn and Guillaume Luccisano invested $1.5 million.
Around May 2020, the company had to raise a $1.3 million seed extension with Alven Capital, Seraam Invest, Farmers, Maxime Demeure, Jean-Nicolas Vernin and some existing investors. Bpifrance and CNC also put some money in the company. And now, Serena is leading the $14 million Series A round with General Catalyst, Slow Ventures, Alven Capital, Bpifrance’s Digital Venture fund, Secocha Ventures, Turner Novak and Kevin Hartz also participating in today’s round.
As you can see, it’s been a long and winding road. That’s because Powder didn’t come up with its social app for gamers overnight. The company tried many different consumer apps. It would iterate on an idea for a few weeks and then kill the concept if it didn’t pan out. With Powder, the company seems to have found a great distribution mechanism to attract more downloads, leading to more users.
“The idea behind Powder started in December 2019. We had already worked on several projects and none of them really took off. We thought we would create a community first and then a product,” co-founder and CEO Stanislas Coppin told me. He previously co-founded Mindie, a music video app.
Powder started as a Discord server with tens of thousands of members. The team then developed an app that would appeal to that community, the “metaverse camera” as Coppin says. Overall, 1.5 million people have downloaded the iOS app since its launch.
There are three other co-founders: Barthélémy Kiss, Yannis Mangematin and Christian Navelot. There are 18 employees and the company just launched on Android.
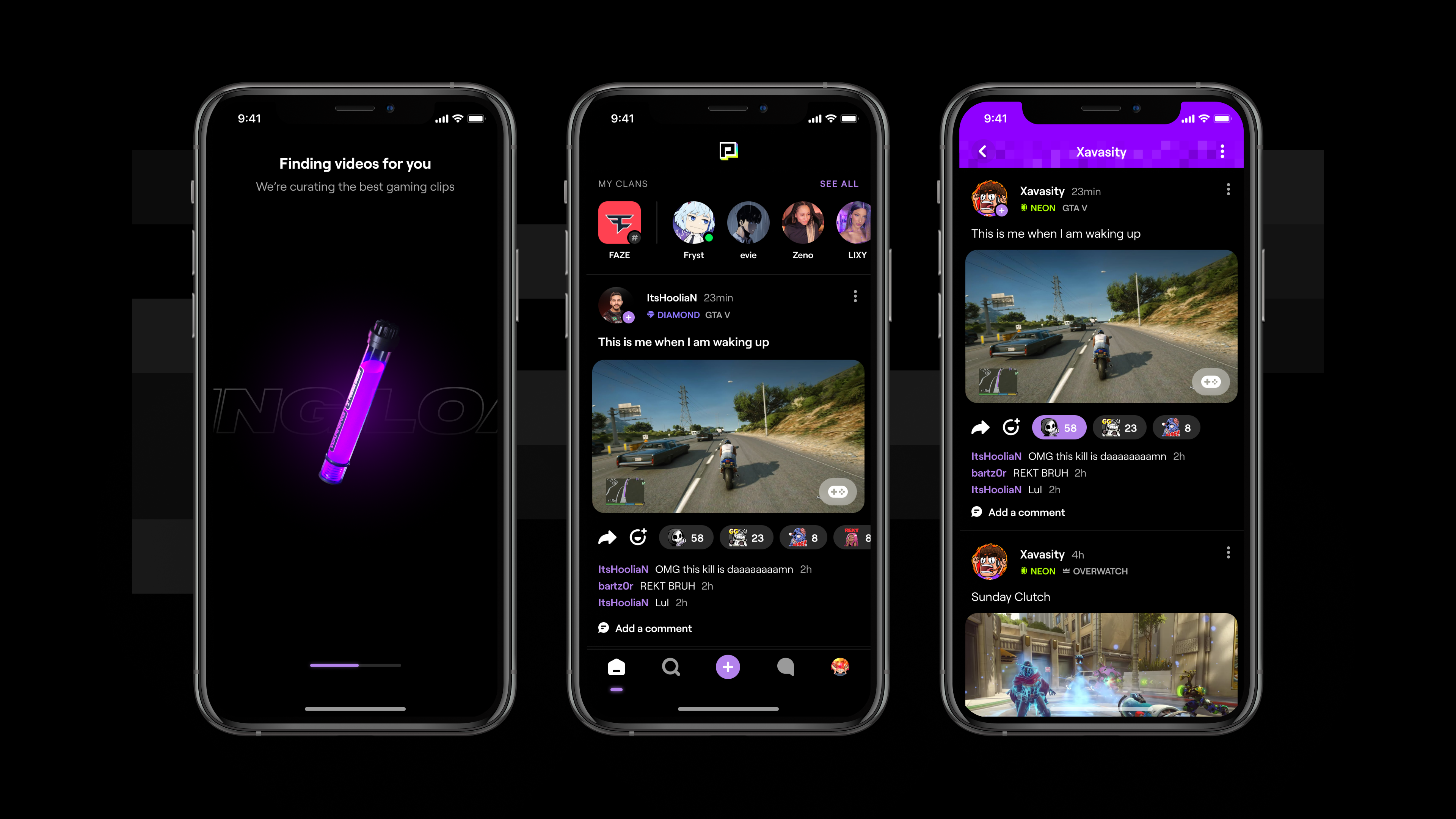
Image Credits: Powder
Powered by WPeMatico
In a large win for the Korean startup ecosystem, dating powerhouse Match Group announced this afternoon that it would buy social networking company Hyperconnect for a combined cash and stock deal valued at $1.73 billion.
Hyperconnect, which is projected to have $200 million in revenue in 2020 (up 50% from 2019) according to the company, offers two apps — Azar and Hakuna Live — which allow users to connect to each other across language barriers. The two are complementary, with Azar focused on one-to-one video chats and Hakuna Live focused on the online live broadcast market. In their press statement, the companies noted that 75% of Hyperconnect’s revenue originates in Asia.
It’s the largest acquisition to date by Match Group, which also owns the popular dating apps Tinder and Hinge, along with many other assorted properties.
One theme of the acquisition and Hyperconnect’s story is technology. The company built what it describes as “the first mobile version” of WebRTC, a now well-developed standard that is designed to offer resilient peer-to-peer connections between users without relying on a company to serve as a middleman server.
For instance, a video chat between two participants would be transmitted directly between the two of them using WebRTC, without the video being broadcast through Hyperconnect’s servers. That’s designed to improve reliability by removing latency while also reducing the cost of bandwidth for the service to Hyperconnect. WebRTC is now a well-deployed open-source standard, with companies such as Google using it in products like Google Meet.
In addition to its innovative work on WebRTC, Hyperconnect built infrastructure to support two users who speak and text in different languages to interact with each other directly through its apps using real-time translation. In a marketing post on Google Cloud, Hyperconnect is a marquee customer of the cloud service’s speech, real-time translation and messaging APIs.
In the companies’ joint press statement, both sides emphasized R&D and engineering as key wins for the deal. That begs the question then what Match Group is looking to build with its massive new purchase? While the group has largely confined itself to dating, live broadcast and other media verticals may well be in its sights once it acquires the technology from Hyperconnect.
The deal is expected to close in 2021 Q2.
Powered by WPeMatico
When Amazon announced last week that founder and CEO Jeff Bezos planned to step back from overseeing operations and shift into an executive chairman role, it also revealed that AWS CEO Andy Jassy, head of the company’s profitable cloud division, would replace him.
As Bessemer partner Byron Deeter pointed out on Twitter, Jassy’s promotion was similar to Satya Nadella’s ascent at Microsoft: in 2014, he moved from executive VP in charge of Azure to the chief exec’s office. Similarly, Arvind Krishna, who was promoted to replace Ginni Rometti as IBM CEO last year, also was formerly head of the company’s cloud business.
Could Nadella’s successful rise serve as a blueprint for Amazon as it makes a similar transition? While there are major differences in the missions of these companies, it’s inevitable that we will compare these two executives based on their former jobs. It’s true that they have an awful lot in common, but there are some stark differences, too.
For starters, Jassy is taking over for someone who founded one of the world’s biggest corporations. Nadella replaced Steve Ballmer, who had taken over for the company’s face, Bill Gates. Holger Mueller, an analyst at Constellation Research, says this notable difference could have a huge impact for Jassy with his founder boss still looking over his shoulder.
“There’s a lot of similarity in the two situations, but Satya was a little removed from the founder Gates. Bezos will always hover and be there, whereas Gates (and Ballmer) had retired for good. [ … ] It was clear [they] would not be coming back. [ … ] For Jassy, the owner could [conceivably] come back anytime,” Mueller said.
But Andrew Bartels, an analyst at Forrester Research, says it’s not a coincidence that both leaders were plucked from the cloud divisions of their respective companies, even if it was seven years apart.
“In both cases, these hyperscale business units of Microsoft and Amazon were the fastest-growing and best-performing units of the companies. [ … ] In both cases, cloud infrastructure was seen as a platform on top of which and around which other cloud offerings could be developed,” Bartels said. The companies both believe that the leaders of these two growth engines were best suited to lead the company into the future.
Powered by WPeMatico
“We intend to build the Standard Oil of renewable energy,” said James McGinniss, the co-founder and chief executive of David Energy, in a statement announcing the company’s new $19 million seed round of debt and equity funding.
McGinniss’ company is aiming to boost renewable energy adoption and slash energy usage in the built environment by creating a service that operates on both sides of the energy marketplace.
The company combines energy management services for commercial buildings through the software it has developed with the ability to sell energy directly to customers in an effort to reduce the energy consumption and the attendant carbon footprint of the built environment.
The company’s software, Mycor, leverages building demand data and the assets that the building has at its disposal to shift user energy consumption to the times when renewable power is most available, and cheapest.
It’s a novel approach to an old idea of creating environmental benefits by reducing energy consumption. Using its technology, David Energy tracks both the market price of energy and the energy usage by the buildings it manages. The company sells energy to customers at a fixed price and then uses its windows into energy markets and energy demand to make money off the difference in power pricing.
That’s why the company needed to raise $15 million in a monthly revolving credit facility from Hartree Partners. So it could pay for the power its customers have bought upfront.

Image Credits: Getty Images
There are a number of tailwinds supporting the growth of a business like David Energy right now. Given the massive amounts of money that are being earmarked for energy conservation and energy efficiency upgrades, companies like David, which promise to manage energy consumption to reduce demand, are going to be huge beneficiaries.
“Looking at the macro shift and the attention being paid to things like battery storage and micro grids we do feel like we’re launching this at the perfect time,” said McGinniss. “We’re offering [customers] market rates and then rebating the savings back to them. They’re getting the software with a market energy supply contract and they are getting the savings back. Bringing that whole bundled package together really brings it all together.”
In addition to the credit facility, the company also raised $4.1 million in venture financing from investors led by Equal Ventures and including Operator Partners, Box Group, Greycroft, Sandeep Jain and Xuan Yong of RigUp, returning angel investor Kiran Bhatraju of Arcadia and Jason Jacobs’ recently launched My Climate Journey Collective, an early-stage climate tech fund.
“Renewable energy generators are fundamentally different in their variable, distributed, and digitally-native nature compared to their fossil fuel predecessors while customer loads like heating and driving are shifting to electricity consumption from gas. The sands of market power are shifting and incumbents are poorly-positioned to adapt to evolving customer needs, so there’s a massive opportunity for us to capitalize.”
Founded by McGinniss, Brian Maxwell and Ahmed Salman, David Energy raised $1.5 million in pre-seed financing back in March 2020.
As the company expands, its relationship with Hartree, an energy and commodities trading desk, will become even more important. As the startup noted, Hartree is the gateway that David needs to transact with energy markets. The trader provides a balance sheet for working capital to purchase energy on behalf of David’s customers.
“Renewables are causing fundamental shifts in energy markets, and new models and tools need to emerge,” said Dinkar Bhatia, co-head of North American Power at Hartree Partners. “James and the team have identified a significant opportunity in the market and have the right strategy to execute. Hartree is excited to be a commodity partner with David Energy on the launch of the new smart retail platform and is looking forward to helping make DE Supply the premier retailer in the market,” said McGinniss.
David now has retail electricity licenses in New York, New Jersey and Massachusetts and is looking to expand around the country.
“David Energy stands to reinvent the way that hundreds of billions of dollars a year in energy are consumed,” said Equal Ventures investor Rick Zullo. “Business model creativity and finding ways to change user behavior with new models is just as important if not more important than the technology innovation itself.”
Zullo said his firm pitched David Energy on leading the round after years of looking for a commercial renewable energy startup. The core insight was finding a service that could appeal not to the new construction that already is working with top-of-the-line energy management systems, but with the millions of square feet that aren’t adopting the latest and greatest energy management systems.
“Finding something that will go and bring this to the mass market was something we had been on the hunt for really since the inception of Equal Ventures,” said Zullo.
The innovation that made David attractive was the business model. “There is a landscape of hundreds of dead companies,” Zullo said. “What they did was find a way to subsidize the service. They give away at low or no cost and move that in with line items. The partnership with Partree gives them the opportunity to be the cheapest and also the best for you and the highest margin regional energy provider in the market.”
Powered by WPeMatico
Four years ago when Zach Jones went to do due diligence on C-Zero, a startup out of Santa Barbara, California commercializing a new approach to producing hydrogen, for the small family office he was working for, he had no idea he’d wind up as the company’s chief executive officer.
Or that the company would wind up raising money from Breakthrough Energy Ventures, the billionaire-backed investment vehicle focused on financing companies developing technologies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and some of the world’s largest industrial and oil and gas companies.
At the time, Jones was working for Beryllium Capital, a small investment office out of South Dakota, and had identified a potential investment opportunity in C-Zero, a company commercializing a new way of making hydrogen developed by Eric McFarland, a professor at UCSB.
There was only one problem — McFarland had the research, but didn’t know how to run a company. That’s when Jones stepped in. His firm didn’t make the investment, but when the former Economist science writer took over, the company was able to nab a seed round from PG&E and SoCal Gas, California’s two massive utilities.
The reason for their investments is the same reason Breakthrough Energy Ventures became interested in the young company. Even with renewable energy production coming on line at a breakneck pace, much of the world will still be using fossil fuels for the foreseeable future, and the greenhouse gas emissions from that fossil fuel production needs to go to zero.
C-Zero is developing a technology that converts natural gas to hydrogen, a much cleaner source of fuel, and solid carbon as the only waste stream for use in electrical generation, process heating and the production of commodity chemicals like hydrogen and ammonia.
“Our CTO talks about running a coal mine in reverse,” Jones said.

Night image of an industrial manufacturing plant. Image Credits: Getty Images
The company’s technology is a form of methane pyrolysis, which uses a proprietary chemical catalyst to separate the hydrogen gas from other particles, leaving behind that solid carbon waste. The process, which is neither waste free (there’s that solid carbon) nor renewable (the feedstock is natural gas), is cleaner than current low-cost methods of hydrogen production and far cheaper than the more renewable ways of making hydrogen.
Making renewable hydrogen requires making electricity to send a charge through water to split the liquid into hydrogen and oxygen. And it takes far more energy to pull a hydrogen atom off of an oxygen atom than it does to split that hydrogen from a carbon atom.
“The reason that hydrogen is interesting is that it is a great supplement to intermittent renewables,” said Jones. “It’s really about energy storage… when you look at long duration storage on a daily and seasonal basis… it becomes exorbitantly expensive. Having a chemical fuel is going to be critical part of decarbonizing everything.”
Jones describes the technology as “pre-combustion carbon capture,” and thinks that it could be critical to unlocking the benefits of hydrogen for a range of industrial applications including heavy vehicle fueling, utility power generation and industrial power for manufacturing.
He’s not alone.
“Over $100 billion of commodity hydrogen is produced annually,” said Carmichael Roberts, Breakthrough Energy Ventures, the new lead investor in C-Zero’s $11.5 million funding. “Unfortunately, the overwhelming majority of that production comes from a process called steam methane reforming, which also produces large quantities of CO2. Finding low-cost, low-emission methods of hydrogen production — such as the one C-Zero has created — will be critical to unlocking the molecule’s potential to decarbonize major segments of the agricultural, chemical, manufacturing and transportation sectors.”
Joining the Bill Gates-backed Breakthrough Energy Ventures in the new round is Eni Next (the investment arm of the Italian oil and gas and power company), Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and the hydrogen technology-focused venture firm AP Ventures.
Mitsubishi Heavy Industries already has an application for C-Zero’s technology. The company is in the process of re-powering an existing coal plant to run on a combination of natural gas and hydrogen by 2025. It’s possible that C-Zero’s technology could help get there.
Beyond the lower-cost methods used in manufacturing hydrogen, C-Zero may be one of the first companies that could qualify for new tax credits on carbon sequestration established by the IRS in the U.S. earlier this year. Those credits would give qualifying companies $20 per ton of sequestered solid carbon — the exact waste product from C-Zero’s process.
Even as C-Zero begins commercializing its technology it faces some stiff competition from some of the largest chemical companies in the world.
The German chemicals giant BASF has been developing its own flavor of methane pyrolysis for nearly a decade and has begun building test facilities to scale up production of its own clean hydrogen.
Two other big European corporations are also joining the hydrogen production game as the French chemicals company Air Liquide announced a joint venture with Siemens Energy to work on hydrogen production.
Jones acknowledges that the company’s technology is only a stopgap solution… for now. In the future, as the world moves to renewable natural gas production from waste, he envisions the potential of a potentially circular hydrogen economy.
“In 100 years will this technology be around? If it is it’ll be because we’re using renewable natural gas,” Jones said. There are a lot of steps that need to be traveled to get there, but Jones is confident in the near-term success of the project.
“There’s always going to be a need for a very energy dense fuel. Liquid hydrogen is the most energy dense thing that’s out there outside of something that’s nuclear in nature,” he said. “I think that hydrogen is here to stay. At the end of the day the lowest cost of energy that has the lowest cost for avoided CO2 is what’s going to win.”
Powered by WPeMatico